Superpage - Images
Superpage Topics
ABO incompatible HSCT
Adsorption studies
ASFA guidelines overview
Biological product deviation
Blood donor testing
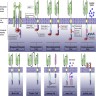
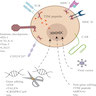
CAR T cell therapy
CAR T cell therapy
Cellular therapy reactions
Cold stored platelets
Coombs test / DAT
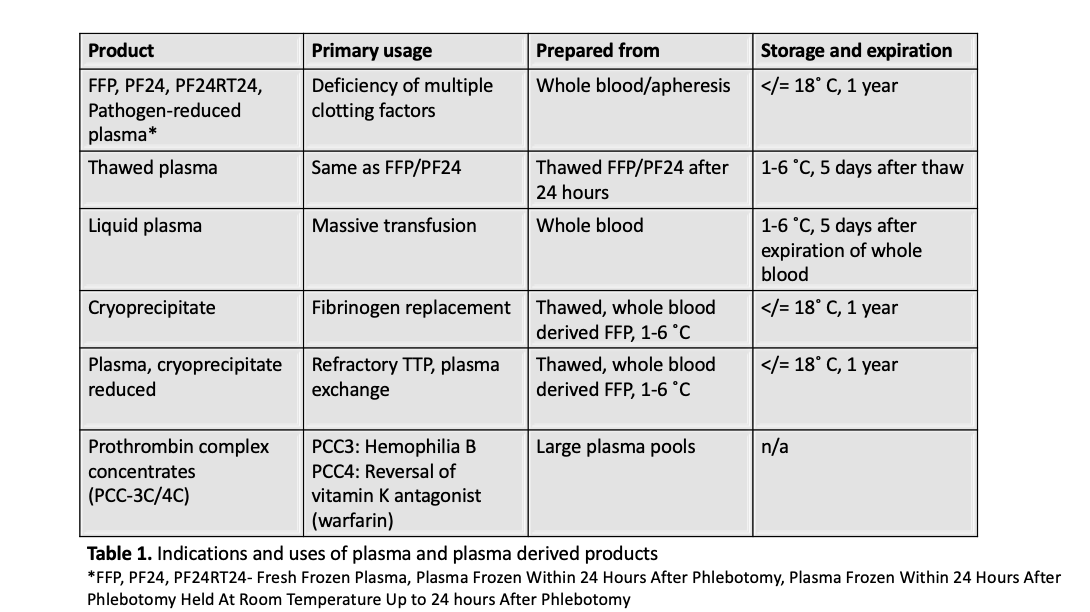
Cryoprecipitate use
Granulocyte use
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn
Hemovigilance
Irradiation
Lookbacks
Massive transfusion
Patient blood management
Plateletpheresis
Pretransfusion testing
Rh immune globulin
Sickle cell disease
Transfusion related acute lung injury
Washing & volume reductionABO incompatible HSCT
Diagrams / tables
Major / minor / bidirectional incompatibility
| O | A | B | AB | ||
| O | Compatible | Major | Major | Major | |
| A | Minor | Compatible | Bidirectional | Major | |
| B | Minor | Bidirectional | Compatible | Major | |
| AB | Minor | Minor | Minor | Compatible | |
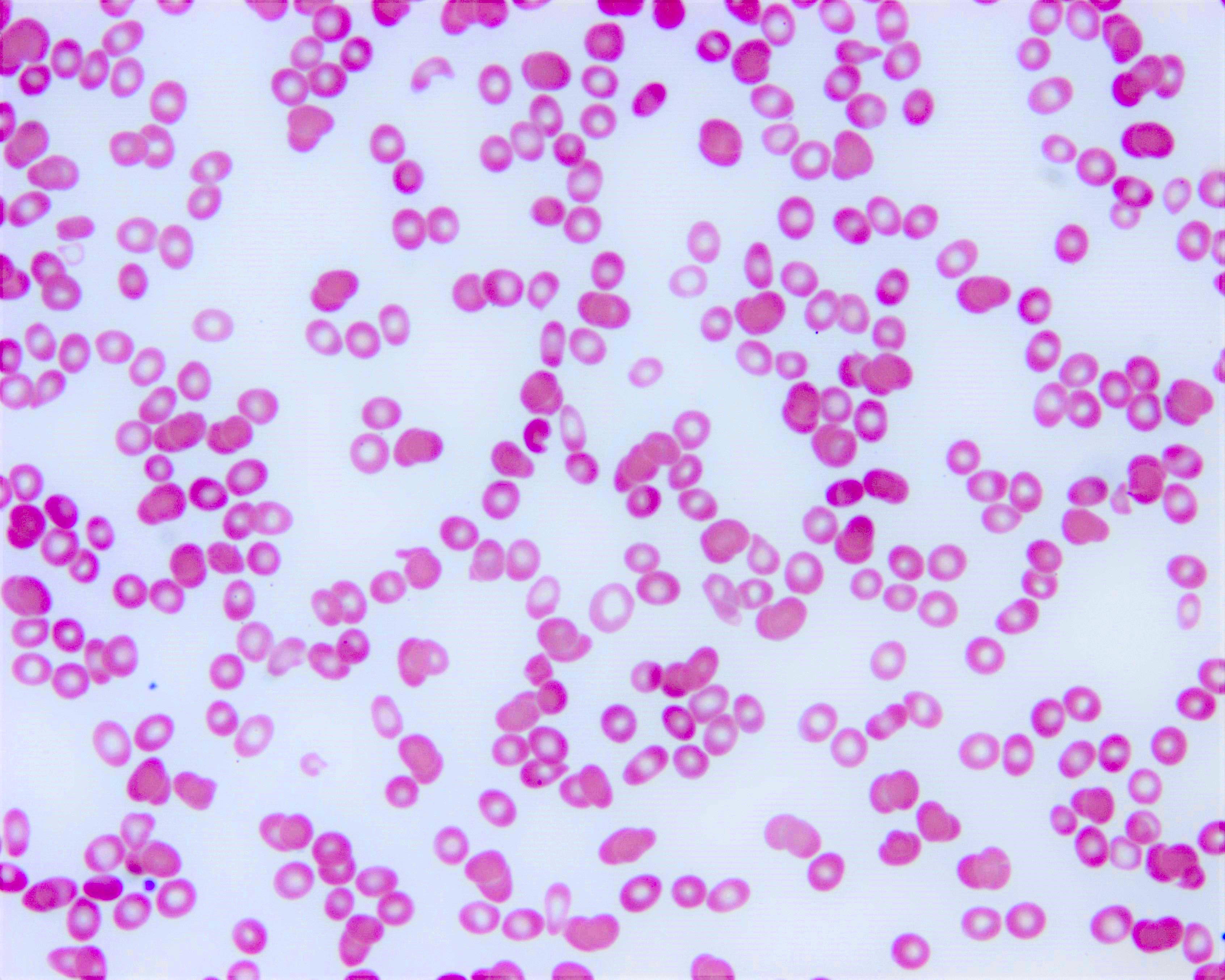
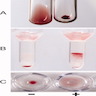
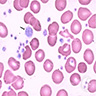
Adsorption studies
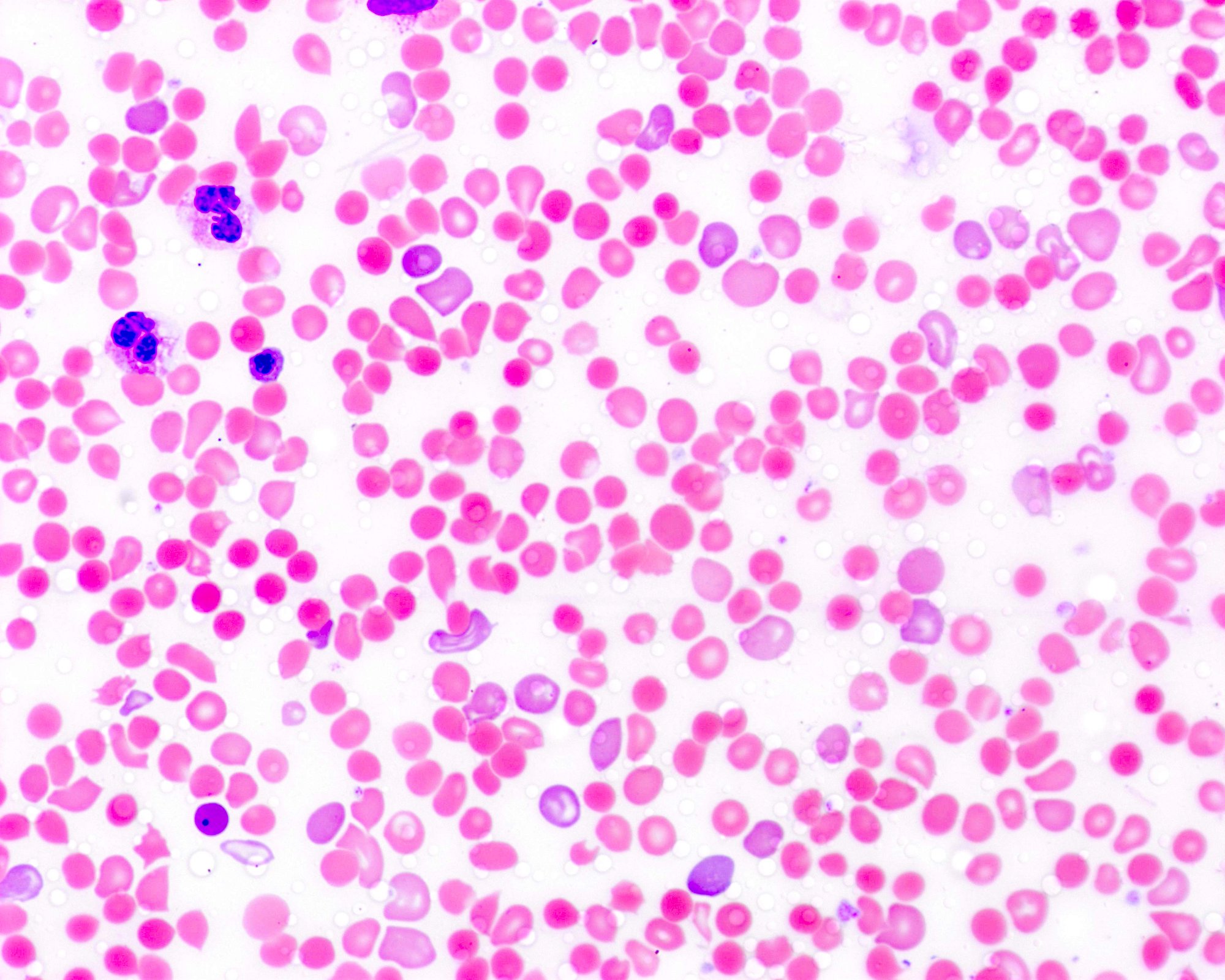
Peripheral smear images
ASFA guidelines overview
Diagrams / tables
Category definitions for therapeutic apheresis
| Category | Description |
| I | Apheresis is accepted as first line therapy, either as a primary standalone treatment or in conjunction with treatment modalities |
| II | Apheresis is accepted as second line treatment, either standalone or in conjunction with other treatment modalities |
| III | Apheresis decision should be individualized; the optimum role of apheresis is not established |
| IV | Disorders for which apheresis is ineffective or harmful based on the published data |
Grading recommendations and evidence for therapeutic apheresis
| Description | Methodological quality of supporting evidence | Implications | |
| Grade 1A | Strong recommendation, high quality evidence | Randomized controlled trials without important limitations or overwhelming evidence from observational studies | Strong recommendation; can apply to most patients in most circumstances without reservation |
| Grade 1B | Strong recommendation, moderate quality evidence | Randomized controlled trials with important limitations (inconsistent results, methodological flaws, indirect or imprecise) or exceptionally strong evidence from observational studies | Strong recommendation; can apply to most patients in most circumstances without reservation |
| Grade 1C | Strong recommendation, low quality or very low quality evidence | Observational studies or case series | Strong recommendation but may change when higher quality evidence becomes available |
| Grade 2A | Weak recommendation, high quality evidence | Randomized controlled trials without important limitations or overwhelming evidence from observational studies | Weak recommendation; best action may differ depending on circumstances or patients' or societal values |
| Grade 2B | Weak recommendation, moderate quality evidence | Randomized controlled trials with important limitations (inconsistent results, methodological flaws, indirect or imprecise) or exceptionally strong evidence from observational studies | Weak recommendation; best action may differ depending on circumstances or patients' or societal values |
| Grade 2C | Weak recommendation, low quality or very low quality evidence | Observational studies or case series | Very weak recommendation; other alternatives may be equally reasonable |
- Reference: Curr Opin Hematol 2019;26:461
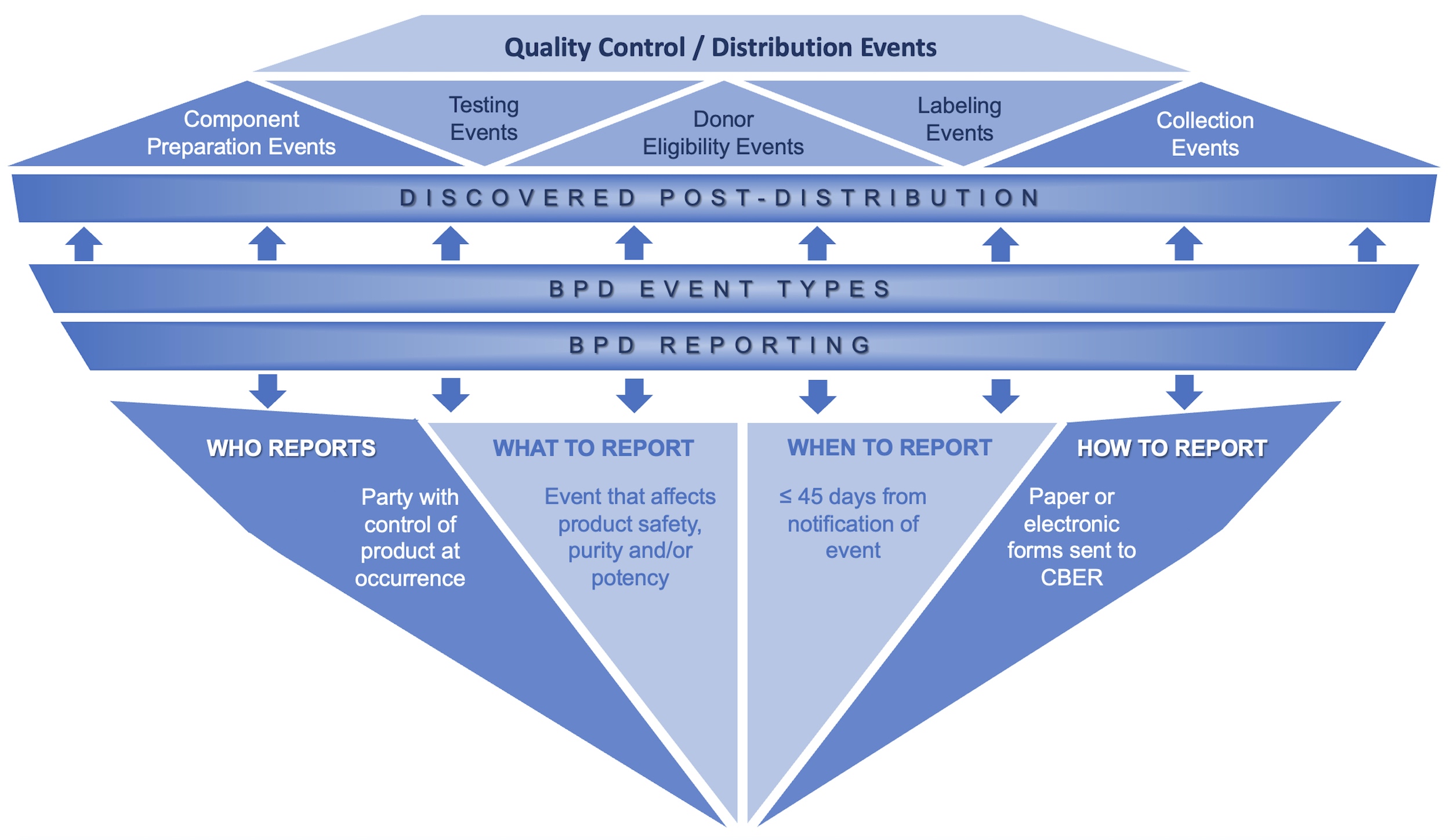
Biological product deviation
Diagrams / tables
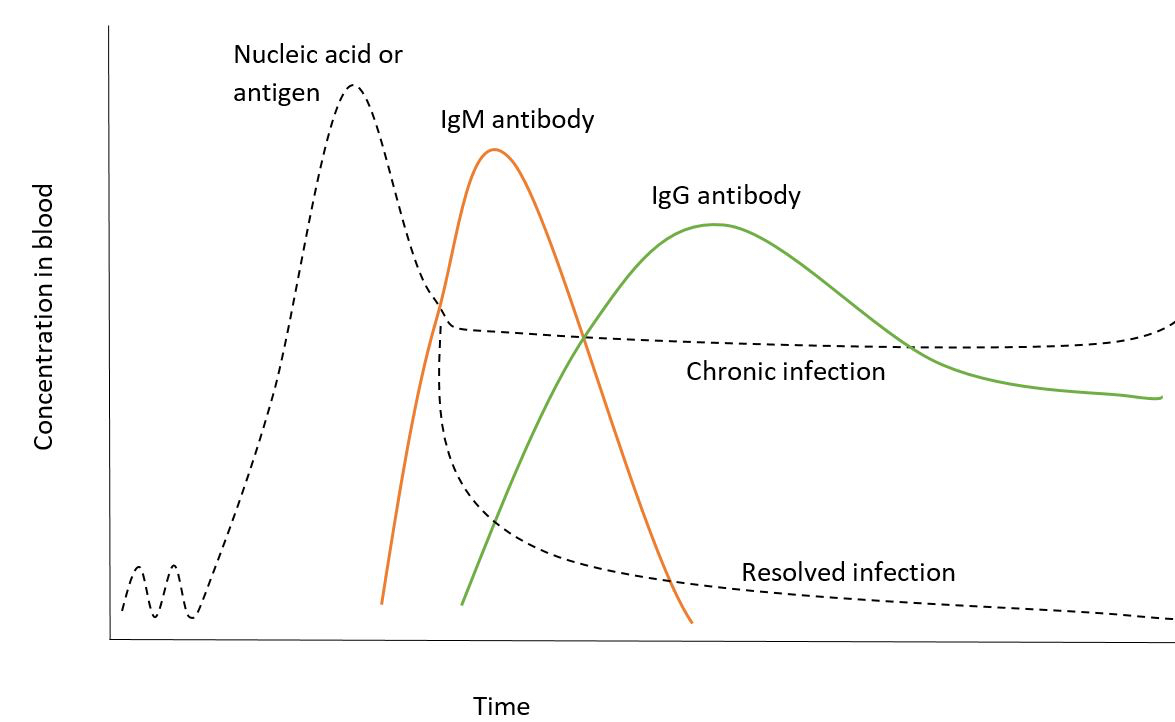
Blood donor testing
Diagrams / tables
CAR T cell therapy
CAR T cell therapy
Diagrams / tables
Cellular therapy reactions
Diagrams / tables
Table 1: Infusion toxicity by etiology
| DMSO | Cytokines | RBC / hemoglobin | Plasma | Volume | Citrate | |
| Nausea / emesis | X | |||||
| Fever / chills | X | X | X | |||
| Cough | X | X | ||||
| Flushing | X | X | ||||
| Shortness of breath, hypoxia | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Hypotension | X | X | X | |||
| Hypertension | X | X | X | |||
| Bradycardia | X | X | ||||
| Arrythmia | X | X | X | X | ||
| Neurologic | X | X | X | |||
| Gastrointestinal pain | X | X | X |
Cold stored platelets
Diagrams / tables
Coombs test / DAT
Cryoprecipitate use
Diagrams / tables
Granulocyte use
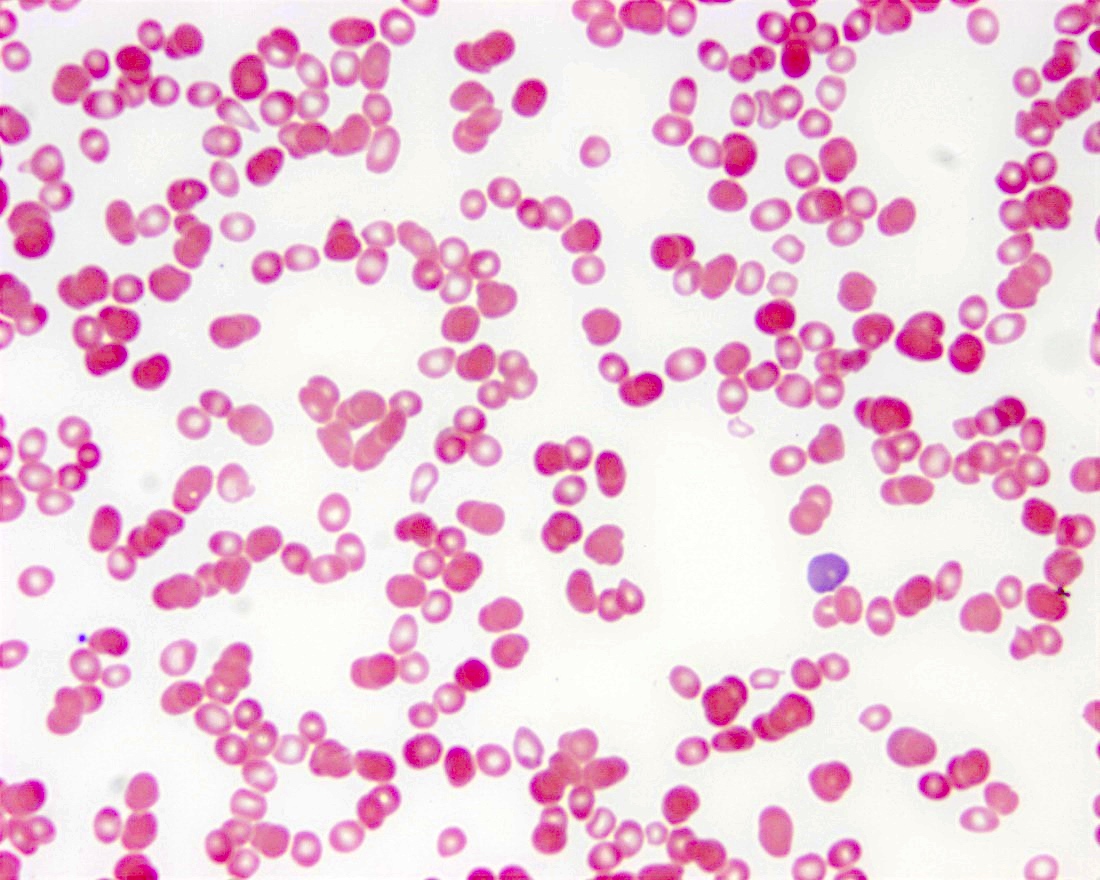
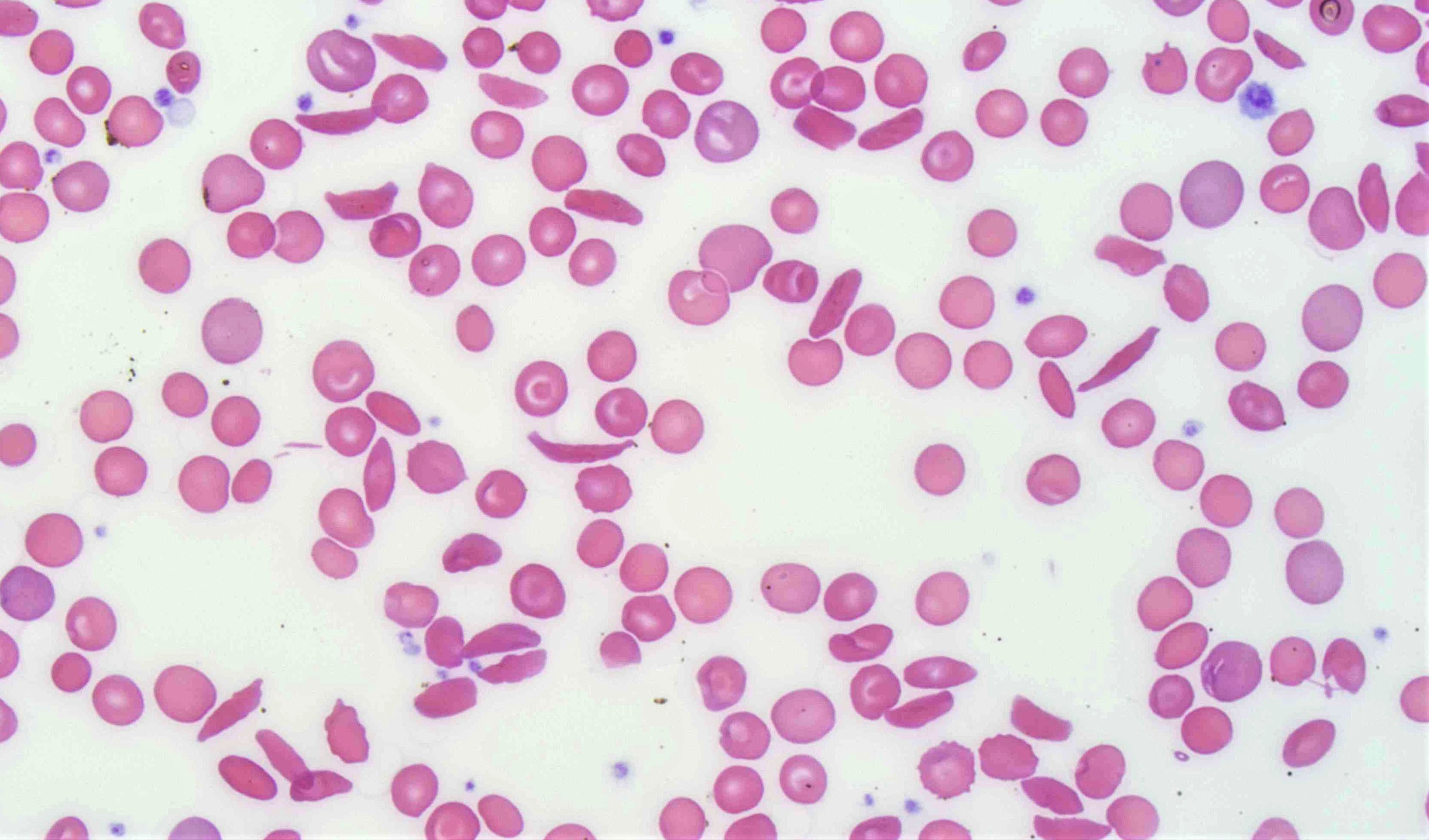
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn
Peripheral smear images
Hemovigilance
Diagrams / tables
NHSN hemovigilance module adverse reaction codes, severity codes and imputability
| Case definition | Severity | Imputability |
| Definitive: the adverse reaction fulfills all of the case definition criteria | Nonsevere: medical intervention (e.g., symptomatic treatment) is required but there is minimal risk of permanent damage to the transfusion recipient | Definite: there is conclusive evidence that the reaction can be attributed to the transfusion |
| Probable: the adverse reaction meets some of the clinical signs and symptoms or radiologic, laboratory evidence or available information but does not meet all definitive case definition criteria | Severe: inpatient hospitalization or prolonged hospitalization is directly attributable to the transfusion reaction, persistent or significant disability or incapacity of the patient as a result of the reaction or a medical or surgical intervention is necessary to preclude permanent damage or impairment of a body function | Probable: there are other potential causes present that could explain the recipient's symptoms but transfusion is the most likely cause of the reaction |
| Possible: the reported clinical signs or symptoms, radiologic or laboratory evidence and available information are not sufficient to meet definitive or probable case definition criteria | Life threatening: major intervention was required after the transfusion reaction (e.g., vasopressors, intubation, transfer to intensive care) to prevent death | Possible: there are other potential causes that are most likely; however, transfusion cannot be ruled out |
| Death: the recipient died as a result of the transfusion reaction | Doubtful: there is evidence clearing in favor of a cause other than the transfusion but transfusion cannot be excluded | |
| Not determined: the severity of the adverse reaction is unknown or not stated | Ruled out: there is conclusive evidence beyond reasonable doubt of a cause other than the transfusion | |
| Not determined: the relationship between the reaction and transfusion is unknown or not stated |
Table modified from: Transfusion 2015;55:703
Irradiation
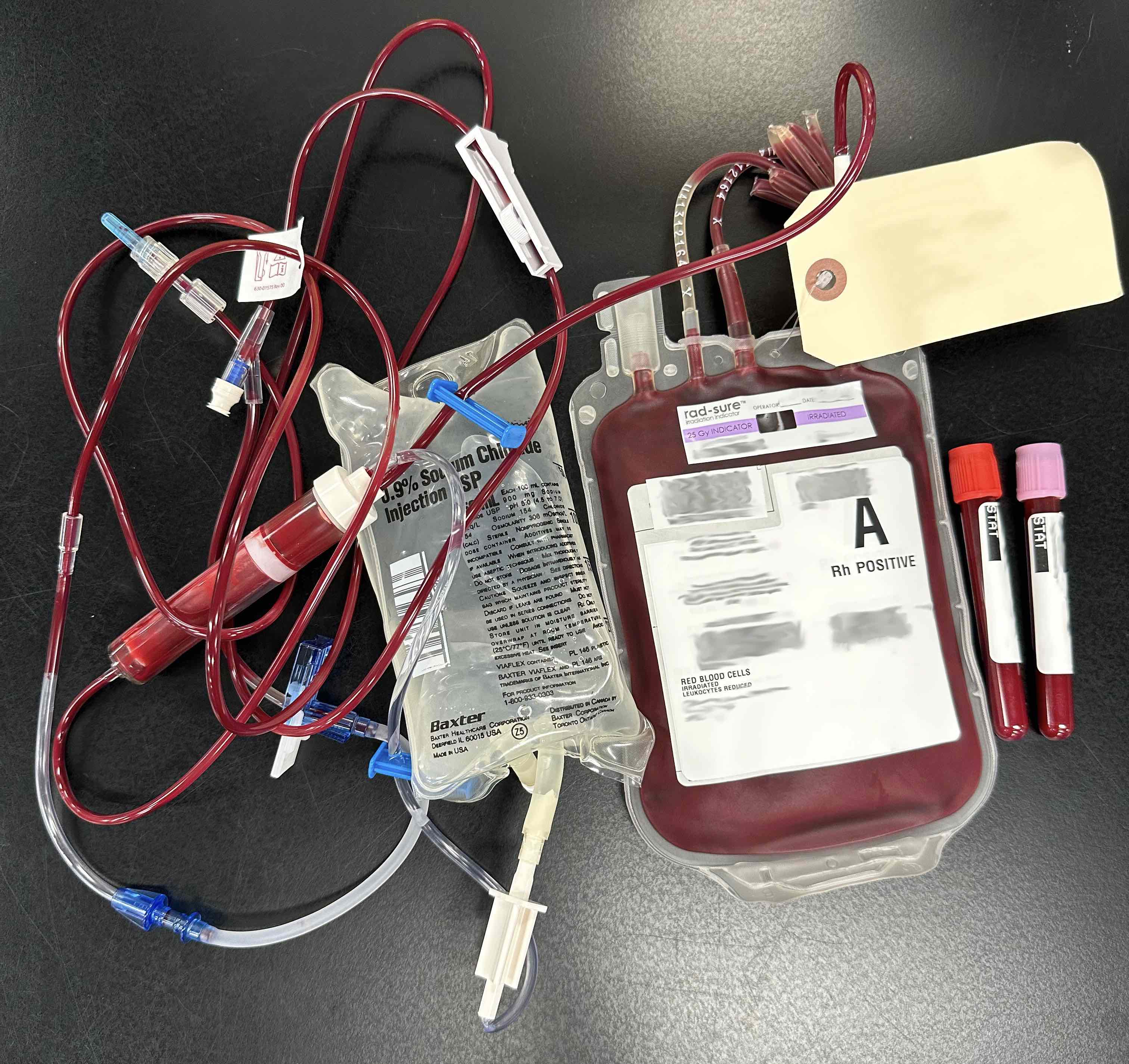
Clinical images
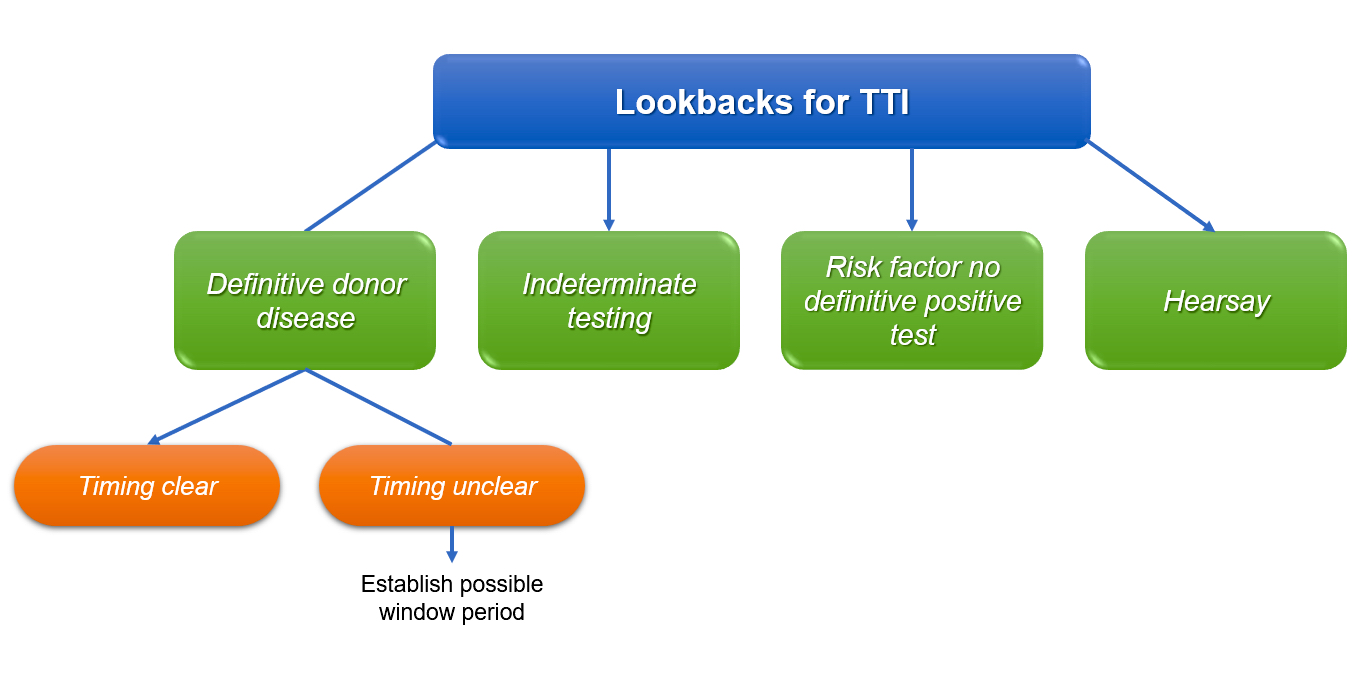
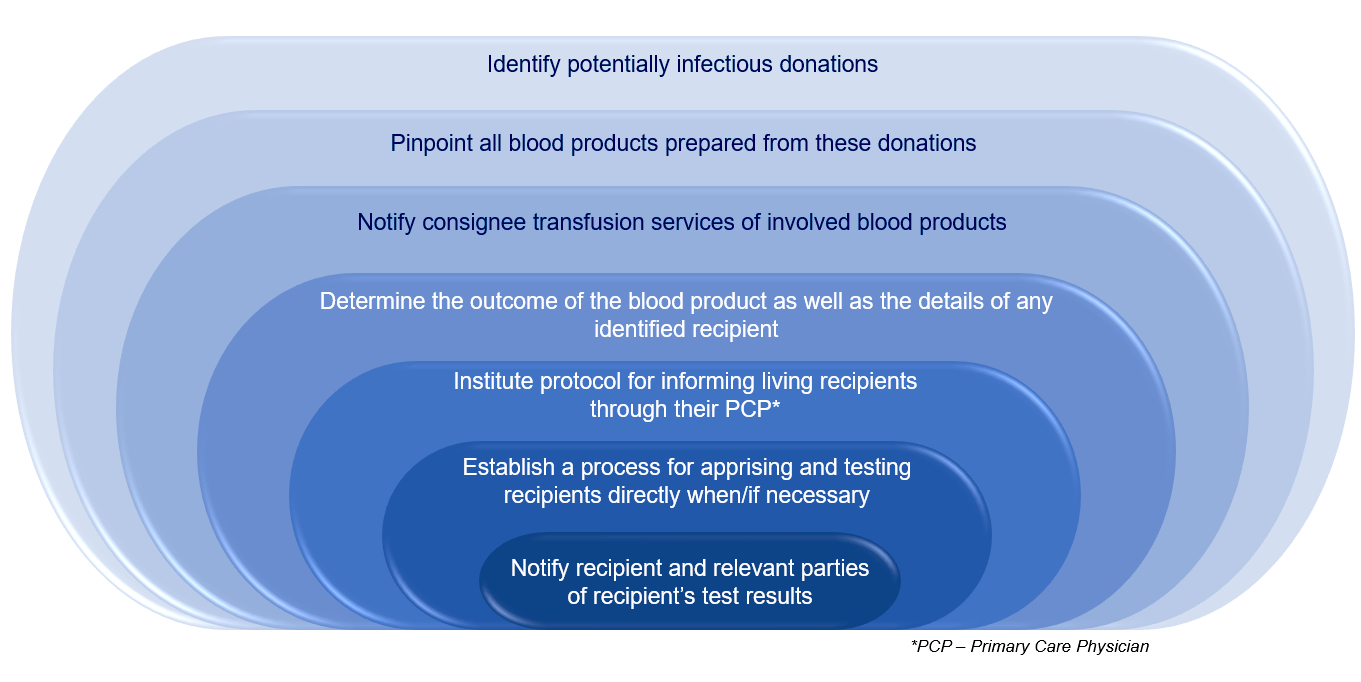
Lookbacks
Diagrams / tables
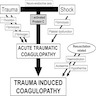
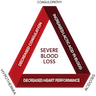
Massive transfusion
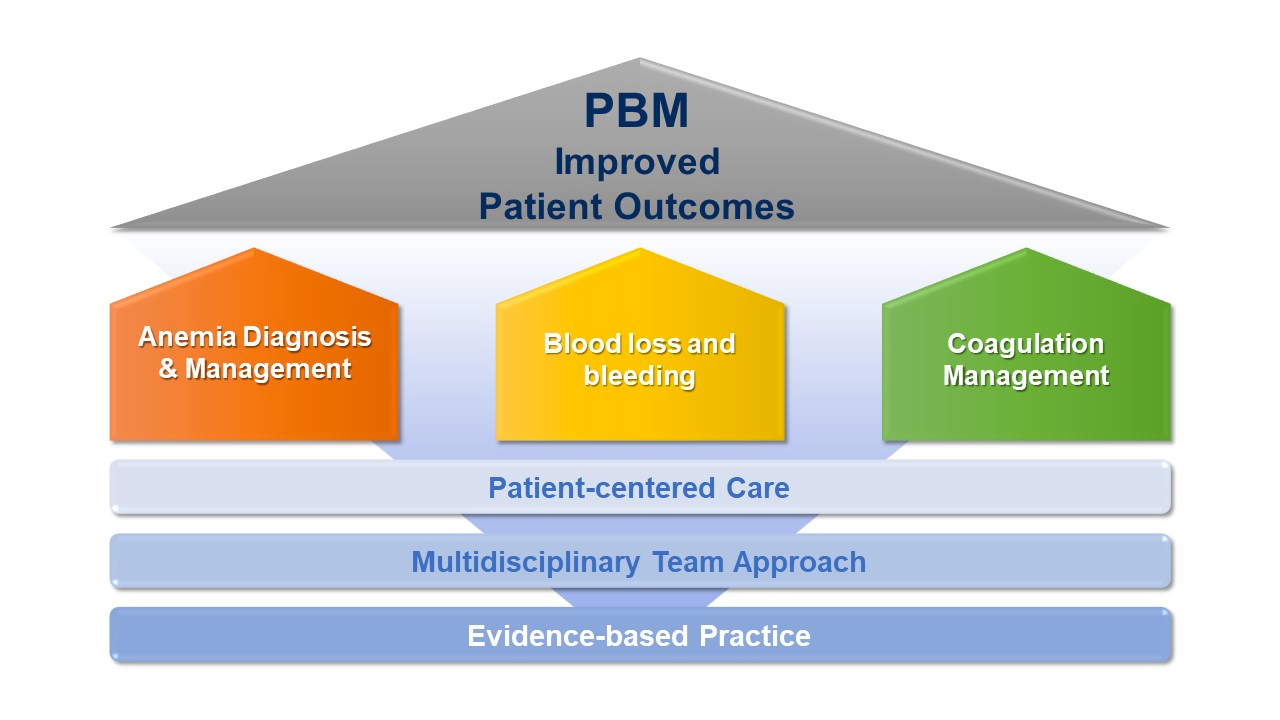
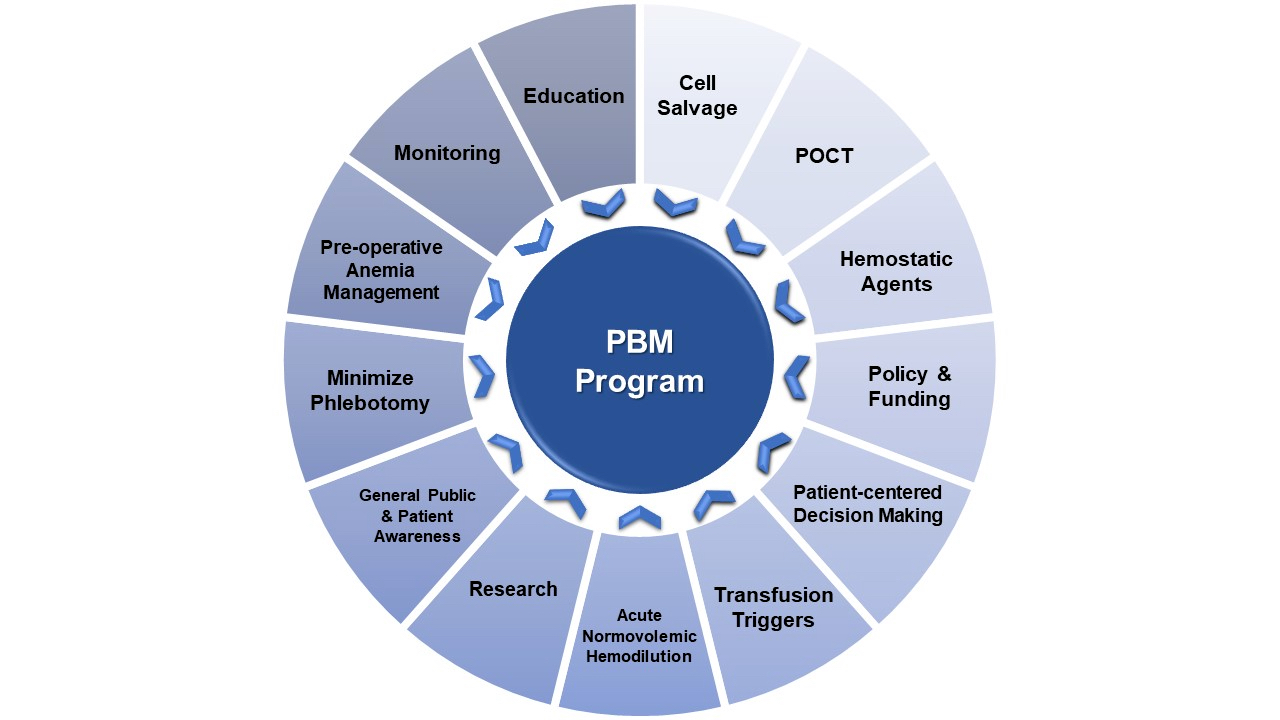
Patient blood management
Plateletpheresis
Pretransfusion testing
Rh immune globulin
Sickle cell disease
Transfusion related acute lung injury
Washing & volume reduction
Recent Transfusion medicine Pathology books
Find related Pathology books: hematopathology, lab medicine, other, transfusion, management