Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Basal cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/anusbasalcell.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Very rare tumor of perianal skin, representing 0.2% of anorectal tumors and less than 0.5% of all basal cell carcinomas at all sites (Am J Dermatopathol 1996;18:371, Rev Gastroenterol Mex 2013;78:52)
- Nodular subtype most common in this location
Essential features
- Rare perianal malignancy identical to basal cell carcinoma of skin
Sites
- Perianal skin (not anus proper)
Pathophysiology
- Appears to behave similarly to basal cell carcinoma at other locations
Clinical features
- Usually 1 - 2 cm but can be 10 cm or larger; recurrence uncommon (Br J Surg 1981;68:856)
- Patients may also have basal cell carcinomas elsewhere (Dis Colon Rectum 1999;42:1200)
Diagnosis
- Biopsy
Case reports
- 69 year old man with perianal basal cell carcinoma (Indian J Dermatol 2010;55:178)
- 88 year old woman with polypoid basal cell carcinoma on the perianal region (J Dermatol 2004;31:51)
Treatment
- Wide local excision with negative margins
Gross description
- Indurated, ulcerated lesion with irregular borders
Microscopic (histologic) description
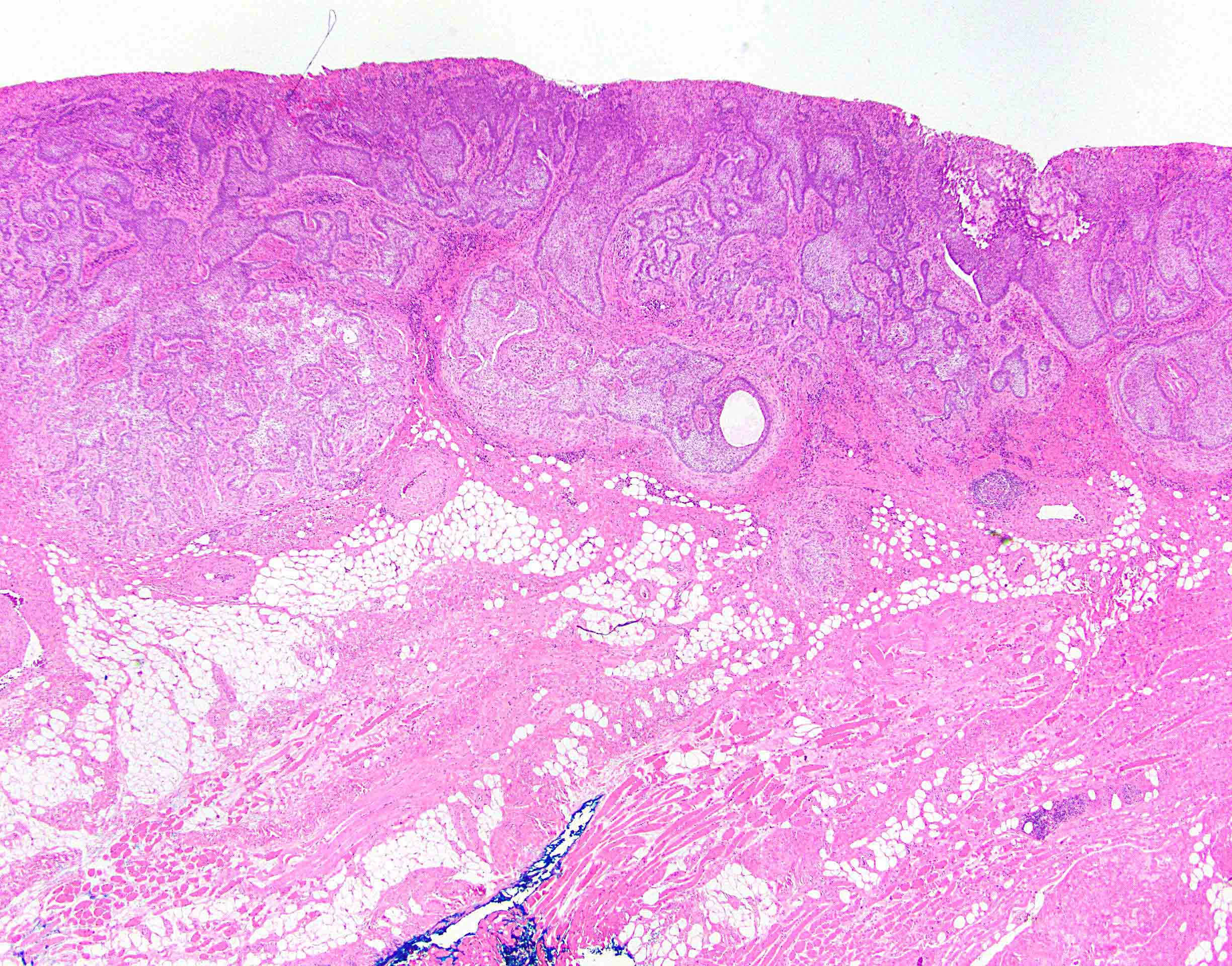
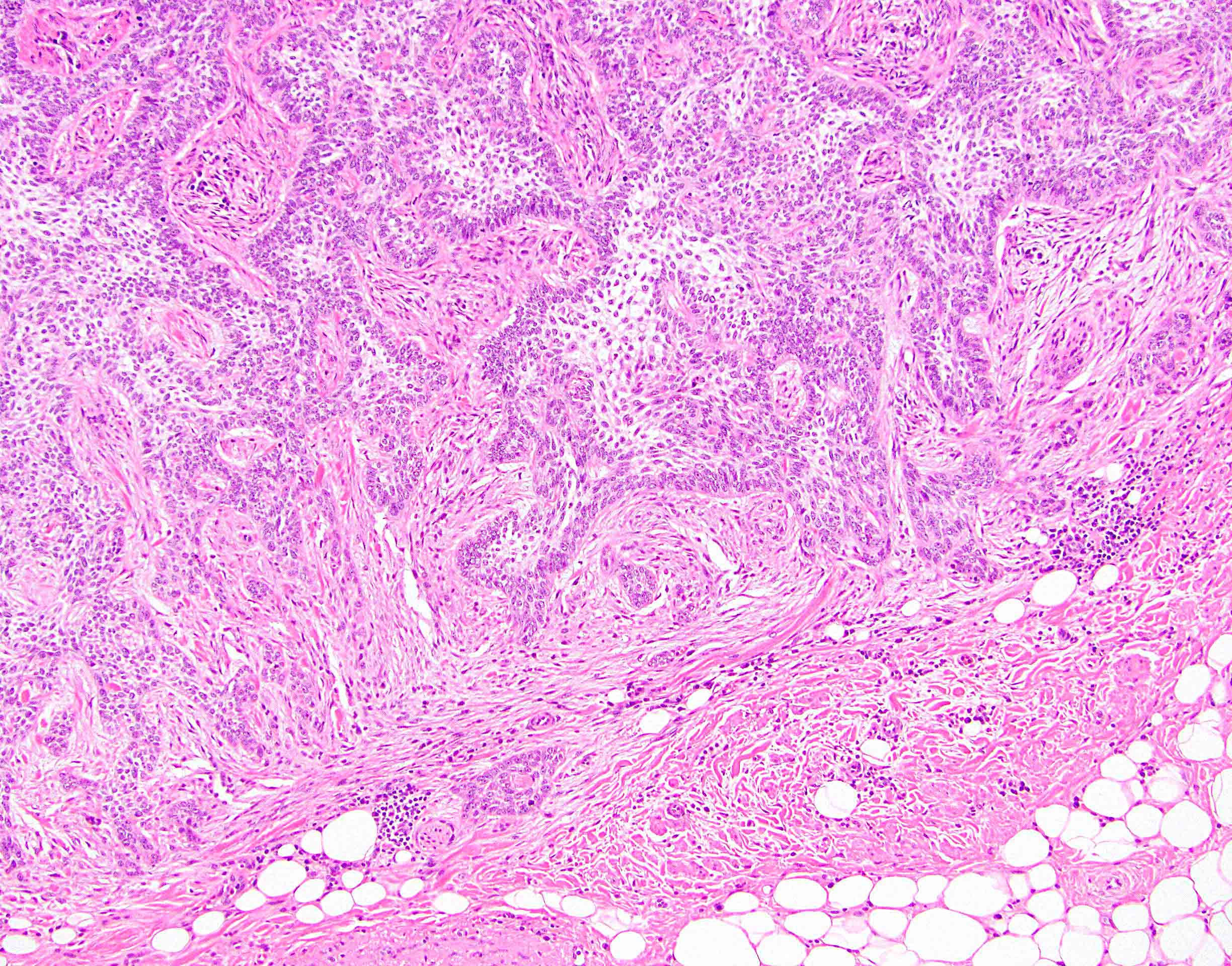
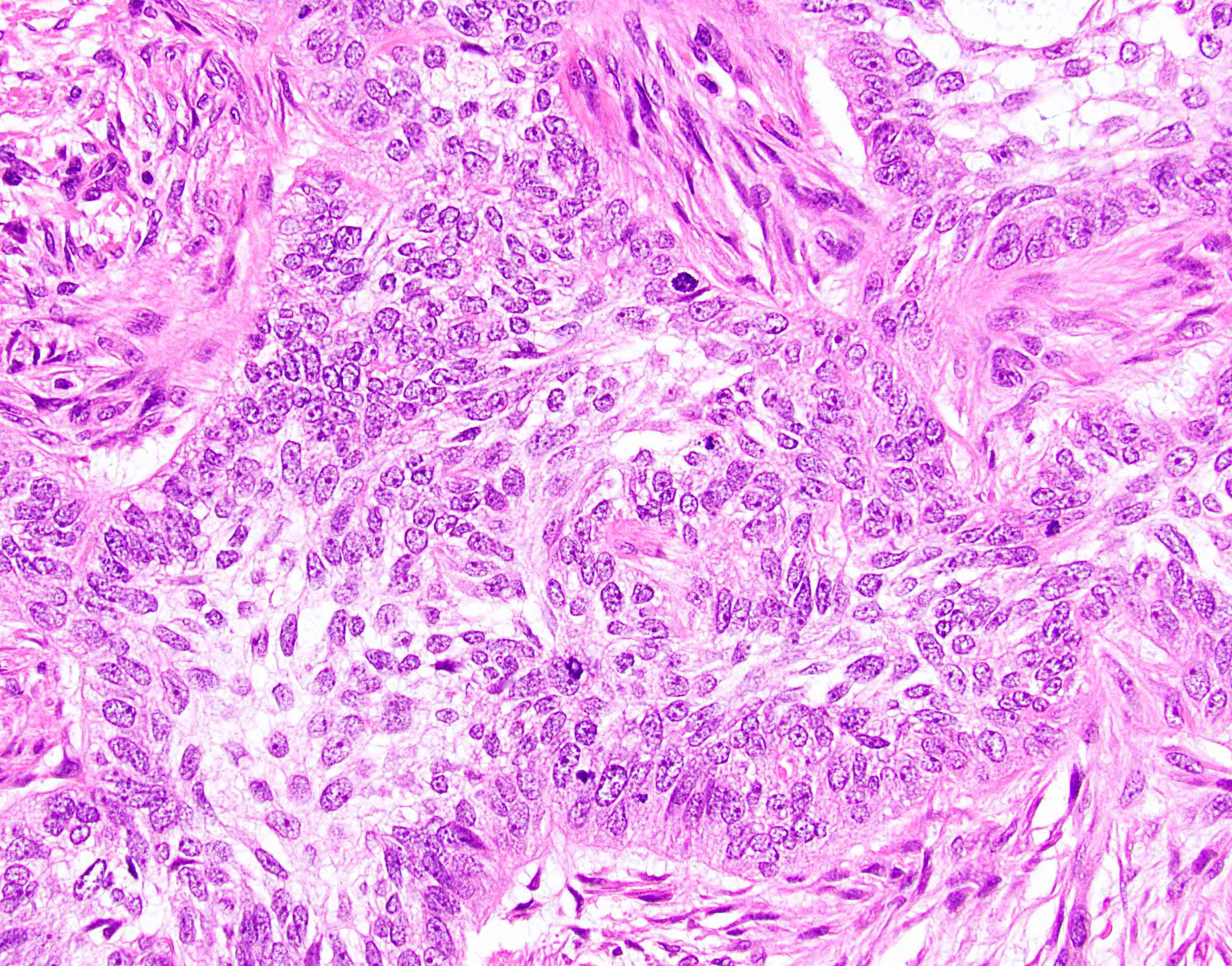
- Resembles basal cell carcinoma at other sites (see Skin nonmelanocytic chapter)
- Retraction artifact helps distinguish from basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Flow cytometry description
- Lower S phase fraction than anal basaloid squamous cell carcinomas (Am J Dermatopathol 1996;18:371)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, perianal, resection:
- Basal cell carcinoma (1.6 cm), completely excised
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous cell carcinoma of anal canal, basaloid type:
- Much more common
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. It histologically resembles basal cell carcinoma at other sites
Comment Here
Reference: Basal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Basal cell carcinoma