Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Fibroepithelial polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderfibroepithelialpolyp.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
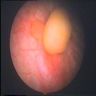
- Exophytic intraluminal mass of vascular connective tissue and variable inflammatory cells covered by normal urothelium
Epidemiology
- Rare; usually reported in children
- In adults, male predominance, median age 44 years, range 17-70 years
Sites
- Usually near verumontanum or bladder neck
- More common in proximal ureter than bladder
Etiology
- Nonneoplastic
Clinical features
- May be incidental / asymptomatic
Case reports
- Boys ages 2 and 5 years (Pediatr Surg Int 2008;24:613)
- 3 year old boy with 15 cm polyp (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2003;6:179)
- 14 year old boy (Arch Ital Urol Androl 2005;77:118)
Treatment
- Transurethral resection; don’t recur
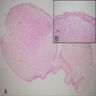
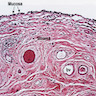
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Urothelial or rarely columnar epithelial lining
- Either (a) polypoid mass with cloverleaf-like projections and florid cystitis cystica et glandularis of nonintestinal type in stalk, (b) papillary tumor composed of numerous small, rounded fibrovascular cores containing dense fibrous tissue, or (c) polypoid lesion with secondary tall, finger-like projections (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:460)
- Broader stalks than papilloma; no prominent edema or inflammation
- May have degenerative stromal atypia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:241)
Differential diagnosis
- Florid cystitis cystica et. glandularis: not polypoid, no cloverleaf pattern
- Inverted papilloma: anastomosing nests and cords growing downward
- Polypoid or papillary cystitis: edematous, lacks prominent fibrous connective tissue in lamina propria, inflammatory infiltrate, often large areas of bladder involved
- Urothelial papilloma: more papillary and less polypoid, narrower fibrous stalks, delicate loose fibroconnective tissue