Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Alghamdi M, Sarungbam S. With trophoblastic differentiation. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladdertrophoblasticdiff.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Urothelial carcinoma with focal or diffuse trophoblastic / syncytiotrophoblastic morphology or beta hCG immunoreactivity
Essential features
- Carries a worse prognosis compared to conventional urothelial carcinoma
- Multinucleated giant cells admixed with urothelial carcinoma is the most commonly encountered pattern
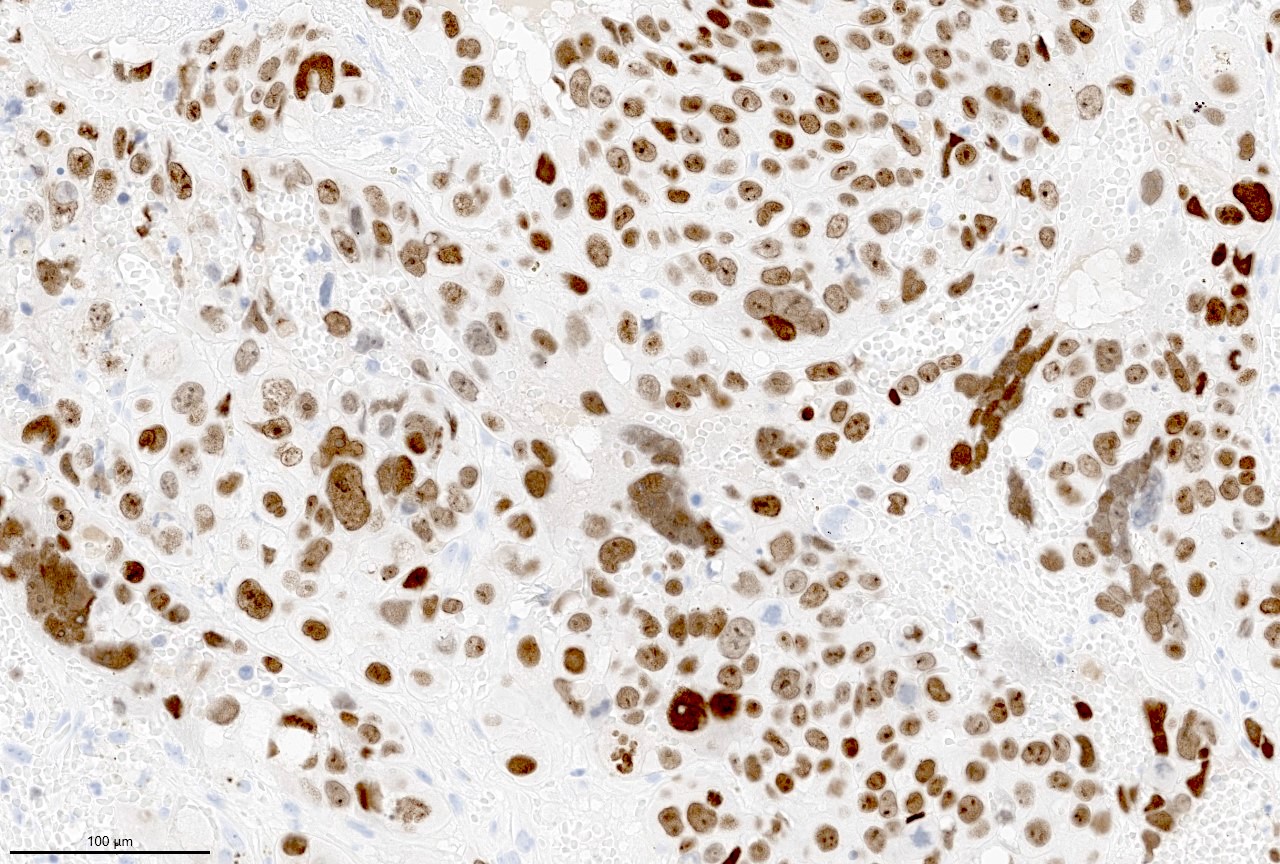
- Beta hCG immunohistochemical stain highlights cells with trophoblastic differentiation
- Reporting the presence of this element is recommended
Terminology
- Urothelial carcinoma with choriocarcinomatous differentiation
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 0.7 - 18.9% of urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder and 2.1 - 18.2% in the upper urinary tract (Urol Oncol 2021;39:732.e17, Virchows Arch 2020;477:111)
- Mean age: 63 years (range: 43 - 89 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1322)
- M:F = 2.6:1 - 4.3:1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1322)
Sites
- Can be seen along the entire urothelial tract, including urinary bladder, prostatic urethra and upper urothelial tract (Urol Oncol 2021;39:732.e17)
Pathophysiology
- Some reports consider it as metaplastic / retrodifferentiation from urothelial to trophoblastic differentiation (Acta Cytol 1992;36:176)
Etiology
- Similar risk factors to conventional urothelial carcinoma (Eur Urol 2013;63:234)
Clinical features
- Gross hematuria
- Hormonal manifestations due to beta hCG (e.g. gynecomastia) have been reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1322)
Diagnosis
- Transurethral resection for bladder tumors
- Cystoscopic biopsy
Laboratory
- Serum beta hCG can be elevated (Br J Urol 1986;58:143)
- Elevation of serum beta hCG is not uncommon in high grade invasive urothelial carcinoma even without obvious trophoblastic differentiation (J Urol 1986;136:403)
Prognostic factors
- Has been associated with higher stage and grade (Cancer 1993;71:1835, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1322)
- Nonfocal expression of beta hCG has been associated with more aggressive disease, nonpapillary, multifocal, larger size (> 3 cm) and muscle invasive disease with nodal metastasis (Urol Oncol 2021;39:732.e17)
- Due to association with aggressive behavior, reporting the presence of this element is recommended (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1244)
Case reports
- 39 year old man with gross hematuria (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2020;18:e190)
- 48 year old man with left sided flank pain and gross hematuria (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2017;15:e73)
- 77 year old man presented with gross hematuria (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2017;15:188)
- 78 year old man presented with asymptomatic gross hematuria for 6 months (IJU Case Rep 2020;3:76)
Treatment
- Depending on the stage of the disease, modalities include transurethral resection, intravesical therapies, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or cystectomy
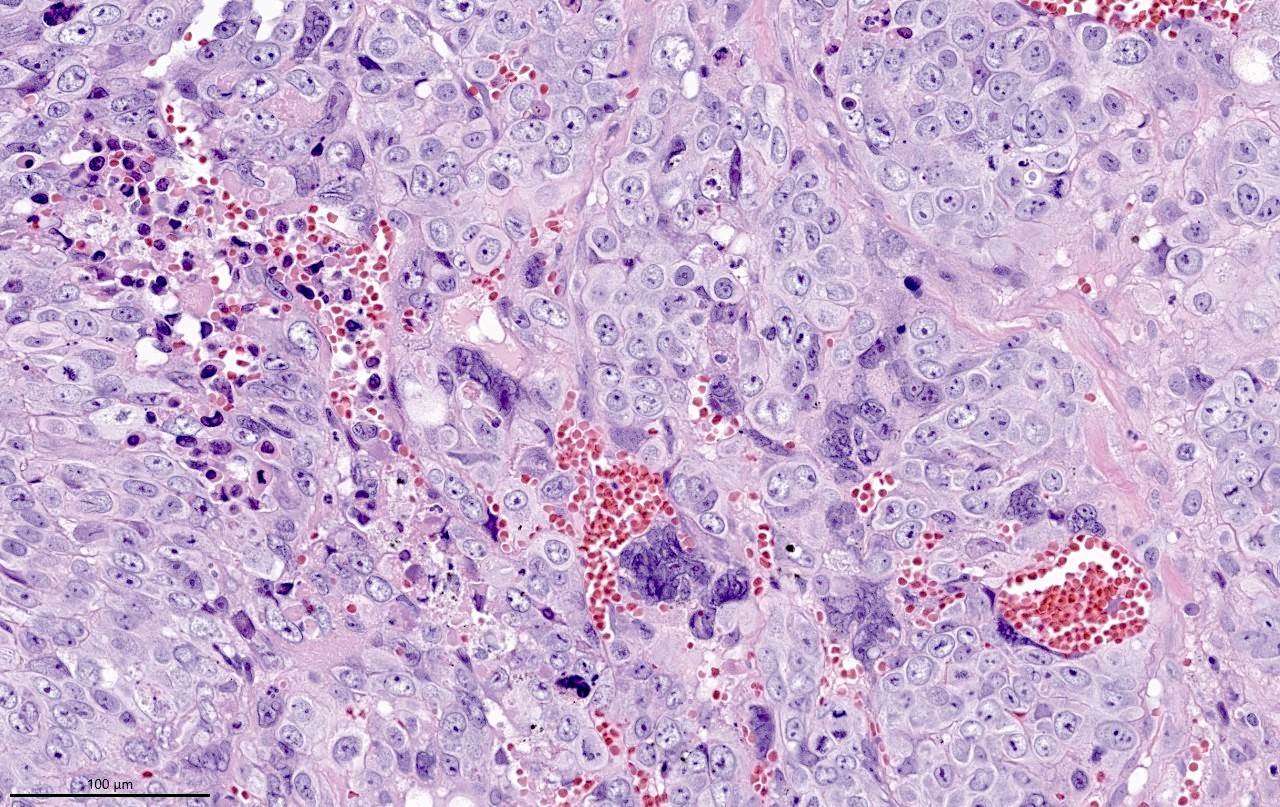
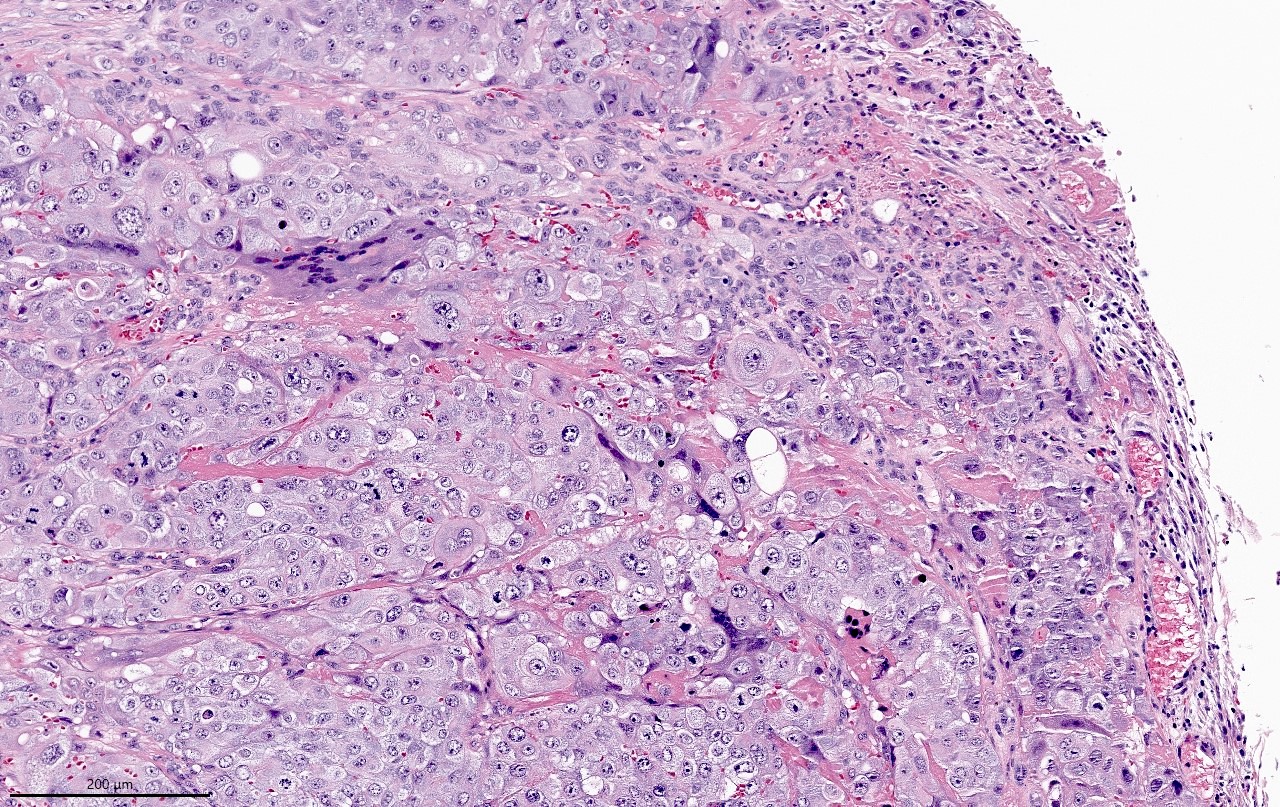
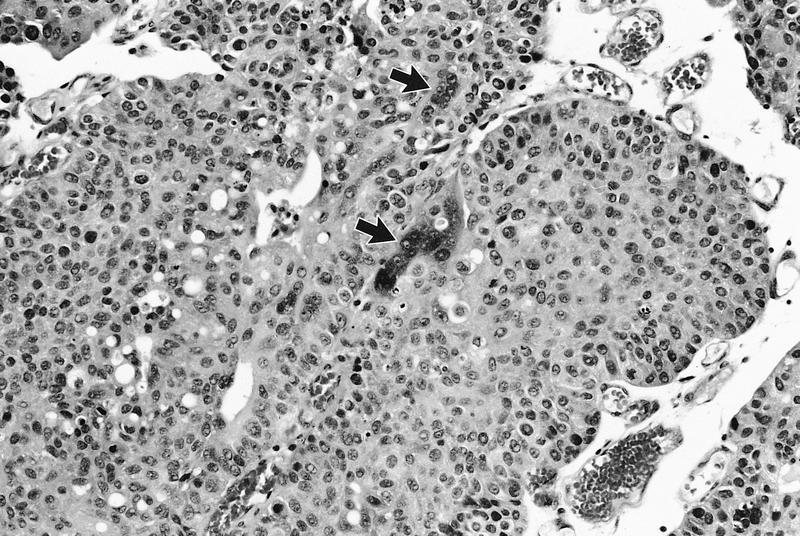
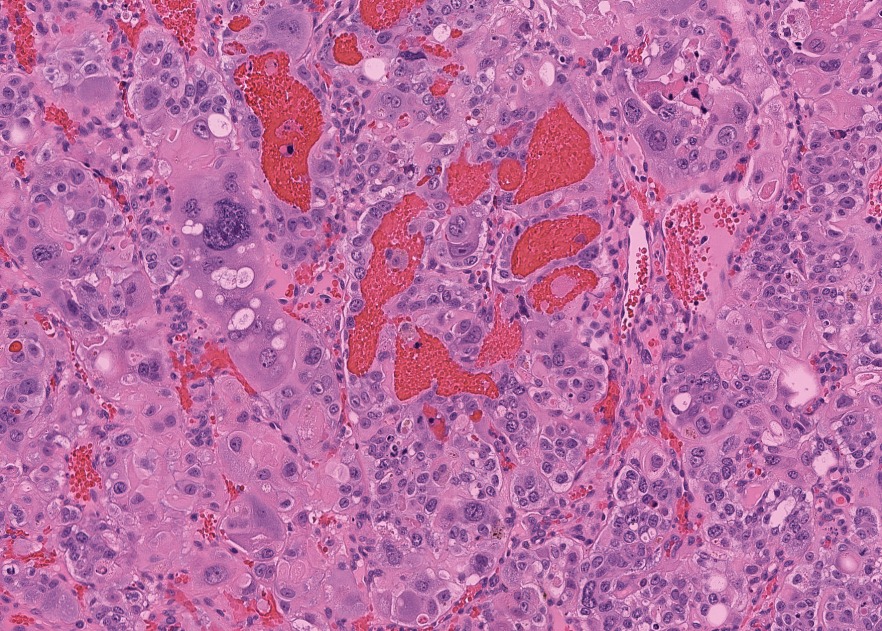
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Wide spectrum of trophoblastic differentiation, ranging from scattered isolated cells with trophoblastic differentiation to pure choriocarcinoma
- Often admixed with conventional urothelial carcinoma or other variants / subtypes
- When present as scattered isolated cells, they can be in the form of cytotrophoblasts (usually indistinguishable from high grade urothelial carcinoma or syncytiotrophoblast (recognizable by their multinucleated giant cells)
- Resembles choriocarcinoma in other organs
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Mixture of mononuclear and multinucleated giant cells with marginal indistinct vacuole-like cytoplasmic inclusions, which stains positively for human placental lactogen (HPL) (Cytopathology 2013;24:405)
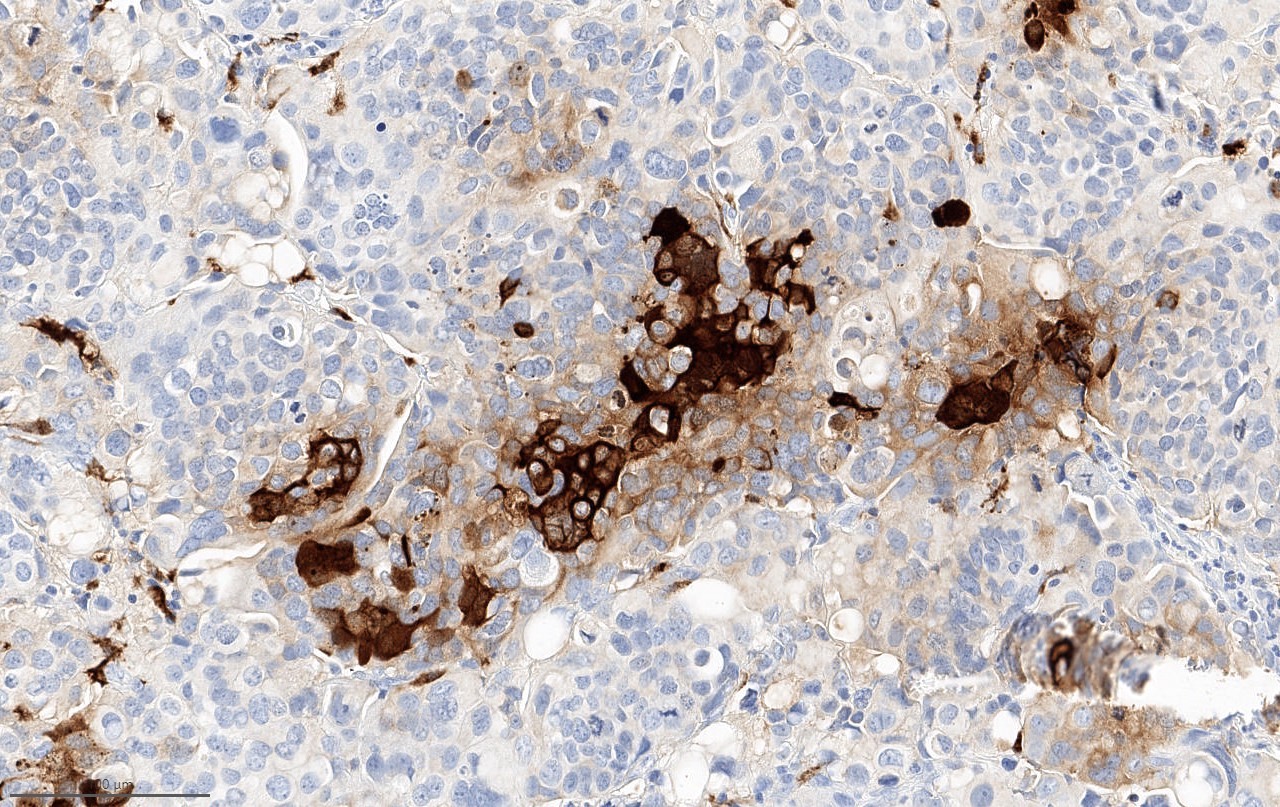
Positive stains
- Beta hCG: syncytiotrophoblasts and intermediate trophoblasts
- GATA3 and HSD3B1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1322)
- SALL4: ~50% (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1322)
- Placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) and human placental lactogen (HPL) (Int Urol Nephrol 2004;36:529, Cancer 1989;63:2497)
- CK7, CK8 and CK19 (Hum Pathol 2002;33:1234)
- AE1 / AE3 stains all trophoblastic cells
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Losses of chromosomes 10, 11p12-p14 and 13q22-qter and gains of chromosomes 1q and 12p12-p13
- High level amplification at 12q14-q21 (Hum Pathol 2002;33:1234)
Sample pathology report
- Bladder, tumor, transurethral resection:
- Invasive urothelial carcinoma, high grade, with trophoblastic differentiation (5%), invasive to lamina propria (see comment)
- Comment: Muscularis propria is identified and is non-involved. Immunohistochemical studies reveal that a subset of tumor cells are positive for beta hCG and GATA3 supporting the presence of trophoblastic differentiation.
Differential diagnosis
- Urothelial carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells:
- Urothelial carcinoma with pleomorphic giant cells:
- Giant cells are highly pleomorphic and can be uni or multinucleated
- Giant cells are negative for beta hCG
Board review style question #1
Which immunohistochemical stain is useful to confirm the trophoblastic differentiation on a bladder biopsy with multinucleated giant cells?
- Beta hCG
- CD68
- CK7
- OCT4
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2