Table of Contents
Definition / general | Diagrams / tables | Structure | Microenvironment | Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) | Hematopoietic regulatory factors | Hematopoietic lineages | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Additional referencesCite this page: Luca DC. General. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonemarrownormalbonemarrow.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- 3 - 6% of total body weight
- Major organ for hematopoiesis at birth; also primary and secondary lymphoid organ
- Hematopoiesis sites change from axial and radial skeleton in newborns to flat bones of central skeleton by mid teens
- Pluripotent stem cells develop into myeloid blasts (myeloblasts, monoblasts, erythroblasts and megakaryoblasts) or lymphoblasts
- Cells are in storage pools for 5 - 7 days, then to blood and then to tissues
- Estimated daily production rates to maintain homeostasis in adults: 50 - 100 x 109 neutrophils, 150 - 200 x 109 platelets and 150 - 200 x 109 erythrocytes
- Cellularity of 90 - 100% in the first years of life, then adult proportions of ~50% reached over a widely variable time interval
- High M:E ratio during the first 3 days of life, progressive decrease by the third week and adult level (3 - 4:1) at 1.5 - 3 years of age
- Lymphocytes predominate in the first 1.5 - 3 years; relatively numerous eosinophils in the first 3 months
- Iron stores are usually absent during the first year of life (exception - first month can have occasional iron stores), then increase progressively and reach adult levels by 5 - 6 years of life
Diagrams / tables
Structure
- Highly organized meshwork of thin walled capillary - venous sinuses surrounded by extracellular matrix, encased by cortical bone and traversed by trabecular bone (J Clin Pathol 1992;45:645)
- Nutrient (medullary) artery ramifies through marrow space to supply medullary cavity; its arterioles branch into capillaries that are continuous with thin walled sinusoids (capillary - venous sinuses)
- Capillary - venous sinus (CVS, basic bone marrow structural unit): inner endothelial cells and outer adventitial reticular cells (phagocytic, can become lipocytes; also synthesize collagen, laminin, fibronectin and proteoglycans)
- All newly formed mature hematopoietic cells are released into capillary - venous sinus, then pass into the blood: transcellularly (via cytoplasm) for erythrocytes and granulocytes, or via megakaryocyte pseudopod extension and fragmentation for platelets
- Capillary - venous sinus coalesce into venules, then veins, carrying newly formed mature hematopoietic cells to the systemic circulation
- No lymphatic channels
- Topographic distribution: myeloid - peritrabecular, erythroid - central, megakaryocytes associated with sinus walls and lymphocytes throughout (no lymphoid follicles in infancy)
Microenvironment
- Also known as "hematopoietic inductive environment"
- Formed by the adventitial (stromal) cells and their products (extracellular matrix proteins, cytokines, inhibitory factors and adhesion molecules)
- Provides support for hematopoietic stem cell renewal and produces factors responsible for osteogenesis
- Heterogeneous cell population: fixed fibroblasts, macrophages and adipose cells
- Extracellular matrix: collagen, fibronectin, laminin, thrombospondin and proteoglycans
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
- Cells with multilineage hematopoietic differentiation potential and sustained self renewal activity
- Detected by their ability to regenerate long term multilineage hematopoiesis in myeloablated recipients
- Very infrequent in the bone marrow: 0.01 - 0.05% of mononuclear cells
- Defined via functional rather than morphologic characteristics: ability to undergo self renewal and produce multilineage progeny
- Express CD34, various cytokine receptors / adhesion molecules / extracellular matrix protein receptors (SCF, bFGF, IL11 / 3 / 1 / 6, GM-CSF, etc.)
- Endothelial cells likely have major role in regulation of trafficking and homing of hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow
- Immunophenotype: CD34+, Thy1+, c-kit+, Rhodamine 123 low, Lin-, CD45RO+, CD38-, flt+ and adhesion molecules
- Spectrum of evolution / maturation: hematopoietic stem cells → progenitor cell with multilineage commitment → progenitor cell with single lineage commitment → blast cell → mature cell
- Developmental continuum: progressive loss of proliferative capacity and gradual acquisition of specific lineage characteristics
Hematopoietic regulatory factors
- Cytokines produced by T lymphocytes, the monocyte - macrophage lineage and other bone marrow stromal cells (either inducers or inhibitors)
- Stimulatory cytokines (inducers): stem cell factor (SCF), colony stimulating factors (CSFs) and various interleukins (IL)
- Inhibitory cytokines: tumor necrosis factor beta (TNF-β), transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α) and macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP-1α)
- Some factors may be pleiotropic (positive or negative effect): TGF-β
Hematopoietic lineages
- Myeloid - monocytic: predominant in the bone marrow, progeny includes neutrophils (most numerous), eosinophils, basophils, monocytes / macrophages, dendritic cells and mast cells
- Other: erythroid, megakaryocytic, lymphoid, natural killer and osteoclasts
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Bone marrow biopsy: arterioles, venules, capillaries, sinusoids, adipose tissue, connective tissue and hematopoietic cells; mitotically active cells are usually paratrabecular and perivascular
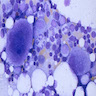
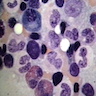
- Bone marrow aspirate: hematopoietic cells (myeloid, erythroid, megakaryocytic, lymphoid), plasma cells (rare in infants), osteoblasts (most common in infants), osteoclasts, occasional adipocytes, endothelial cells or capillaries
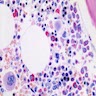
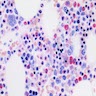
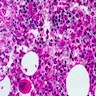
Microscopic (histologic) images
Additional references