Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Motanagh S, Muller K. Lactating adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastlactatingadenoma.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Well circumscribed mass, arising during or shortly after pregnancy, composed of cuboidal cells with actively secreting, closely packed glands
Essential features
- Most prevalent breast lesion in pregnant women and during postpartum period
- Must be distinguished from carcinoma, as breast cancer is the second most common malignancy during pregnancy
- Age range (19 - 34 years), female
- Benign, slow growing
- Unknown capability of malignant transformation
Terminology
- Adenomatous lactational hyperplasia, nodular lactational hyperplasia (not recommended by WHO)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 19 - 34 years, female, predominantly in third decade of life
- Most prevalent breast lesion in pregnant women (mostly third trimester) and during postpartum period (puerperium)
Sites
- Predominantly in breast, may develop in ectopic breast tissue along milk line extending from axilla to vulva (Radiol Case Rep 2017;12:215, Pan Afr Med J 2012;13:47)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown if de novo neoplasm or hyperplastic condition
- Some postulate may arise in a pre-existing adenoma (tubular adenoma, fibroadenoma) with superimposed lactational changes; however, lack of MED12 exon 2 mutations, frequently found in fibroadenomas, does not support this theory (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:11)
- Increase in serum estrogen, progesterone and prolactin
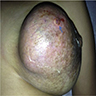
Clinical features
- Painless, soft, palpable, solid, mobile discrete mass
- May be bilateral and multifocal
- Infarction may lead to pain, tenderness and rapid enlargement
Diagnosis
- Imaging: ultrasound (first line modality given increased density of pregnant / lactating breast tissue), mammogram, MRI (J Am Coll Radiol 2018;15:S263, AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;200:3213)
- Invasive procedure: biopsy, fine needle aspiration
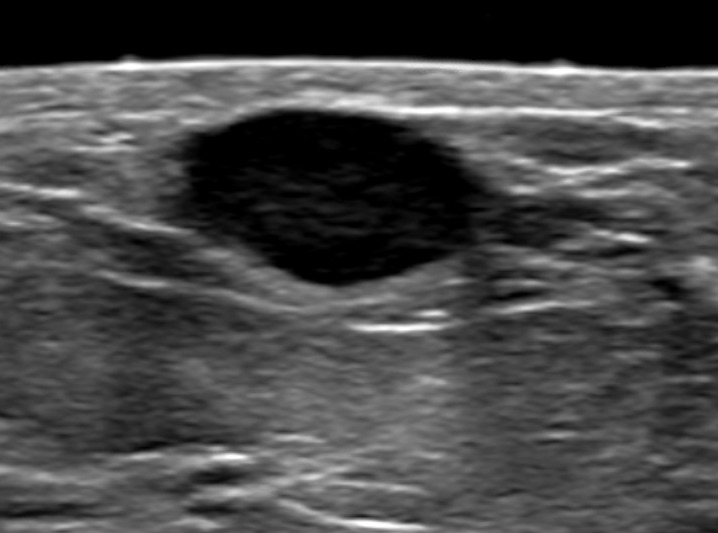
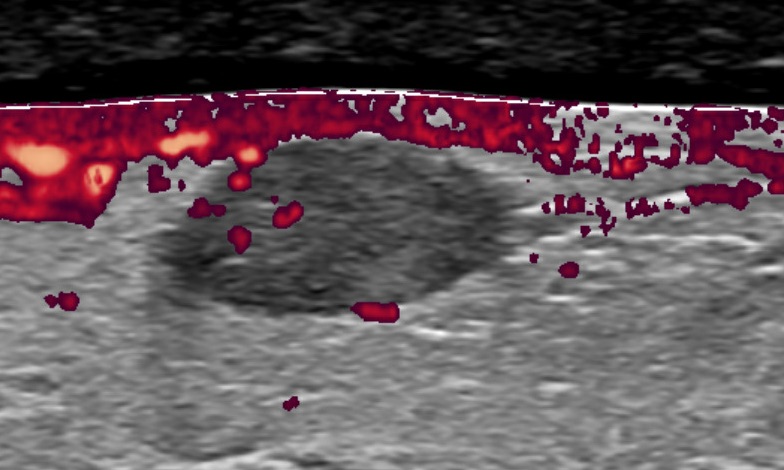
Radiology description
- Homogeneous, circumscribed, hypoechoic mass, with posterior acoustic enhancement and gentle lobulations (J Hum Lact 2016;32:559)
- May show hypervascularization (Breast Care (Basel) 2019;14:30)
- May appear hyperechoic or radiolucent due to milk fat
- Rarely shows irregular margins mimicking malignancy (Radiology 1998;206:271)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Slow growing, spontaneous regression
- No progression to cancer on follow up studies
- Unknown if capable of carcinogenesis or risk factor
- Coexistence of lactating adenoma with breast malignancy reported (Indian J Cancer 2015;52:585, J Clin Pathol 2005;58:87)
Case reports
- 21 year old woman with rapidly enlarging giant lactating adenoma (J Surg Case Rep 2010;2010:8)
- 22 year old woman with continuously enlarging lactating adenoma misdiagnosed as malignancy on imaging (Breast J 2019;25:1278)
- 25 year old lactating woman with co-occurrence of lactating adenoma and infiltrating ductal carcinoma (J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:ED14)
- 33 year old woman with aggressively enlarging lactating adenoma prompting multiple biopsies (Radiol Case Rep 2017;12:215)
- 35 year old woman with lactating adenoma 6 months postpartum and continued breast feeding within 24 hours post operation (J Hum Lact 2016;32:559)
Treatment
- Observation for slow growing
- Many spontaneously regress after termination of breastfeeding
- Enucleation in cases that warrant excision (enlarging, worrisome clinical or histologic features)
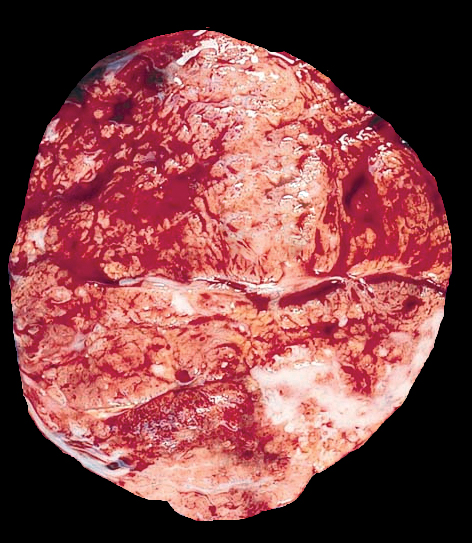
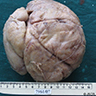
Gross description
- Lacks true capsule, well circumscribed, lobulated, solitary or multiple, firm / rubbery mass, gray-tan cut surface, may have necrosis / infarction (Radiol Case Rep 2017;12:215)
- Size: usually < 5 cm, rare reported cases of giant lactating adenomas up to 25 cm (J Surg Case Rep 2010;2010:8, AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;173:933)
Gross images
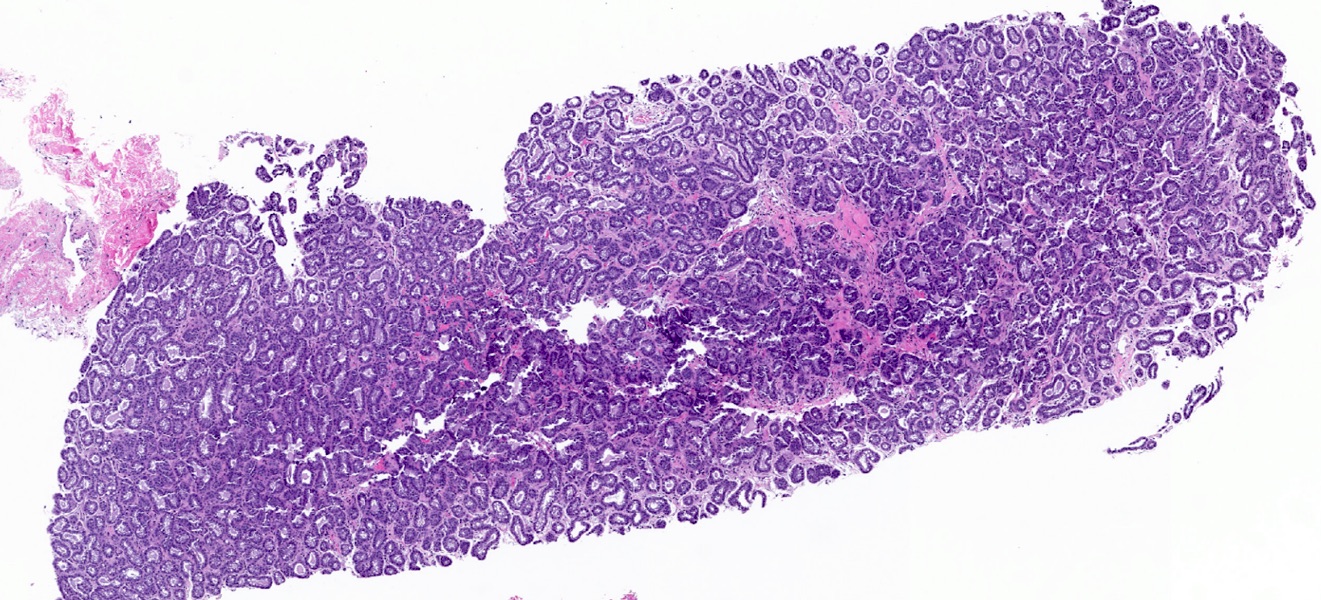
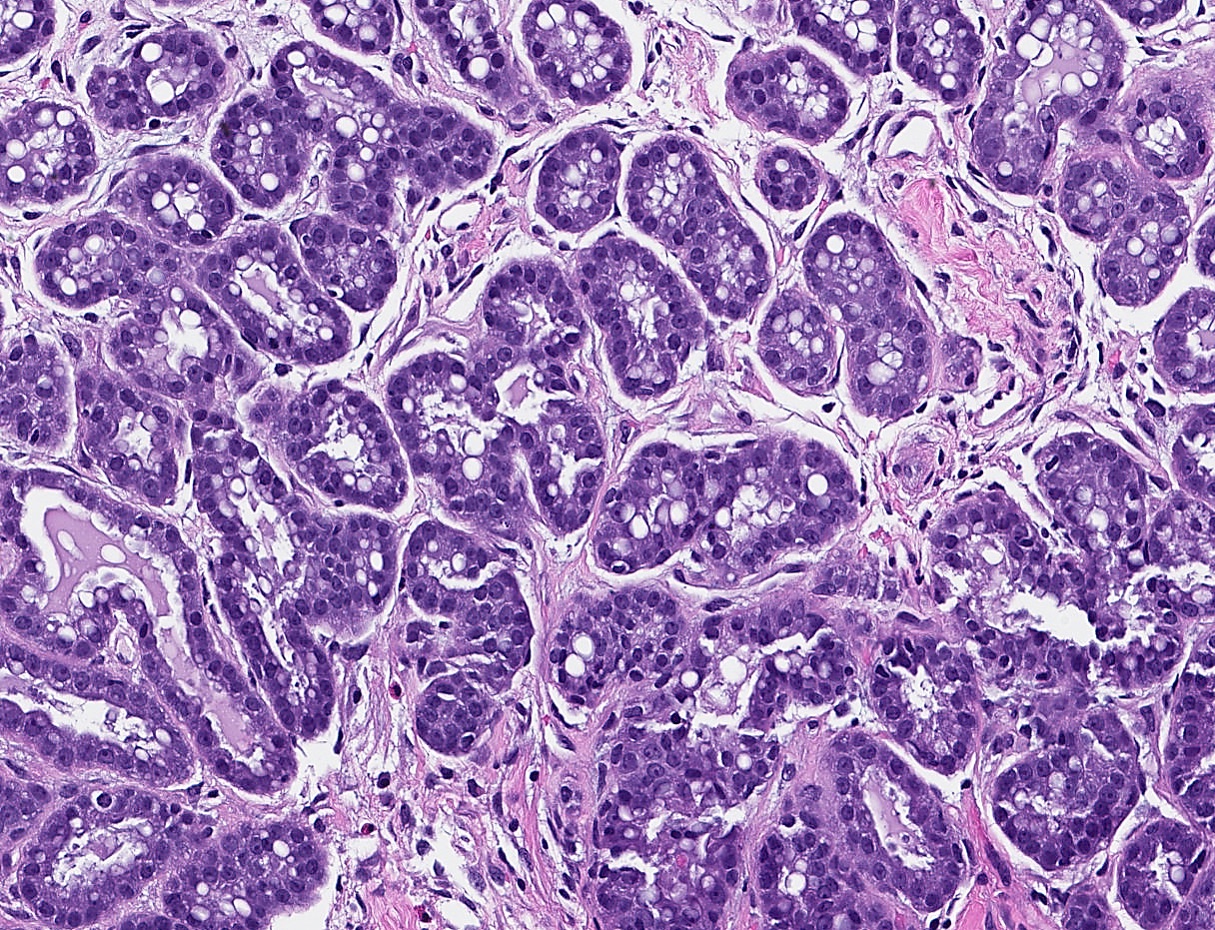
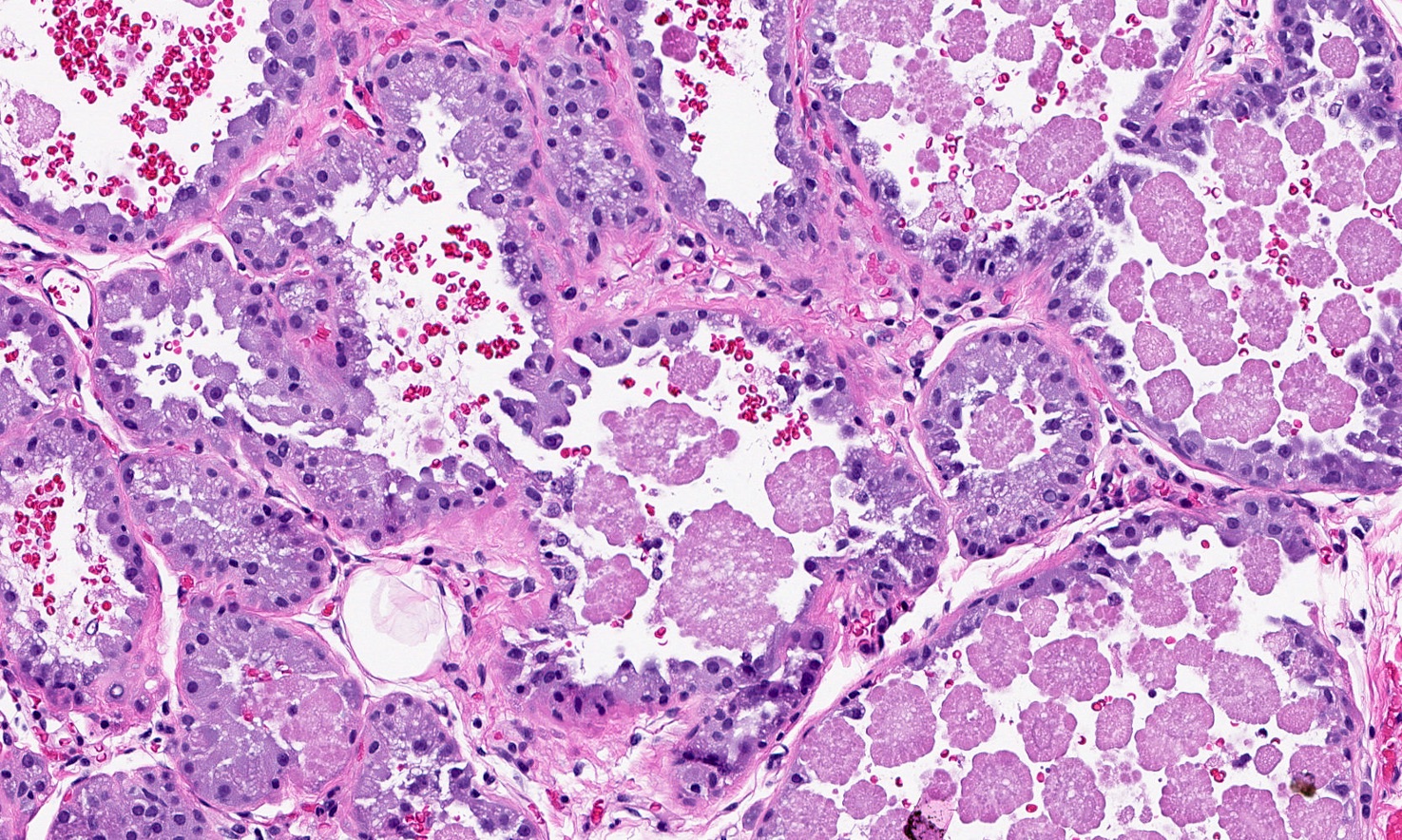
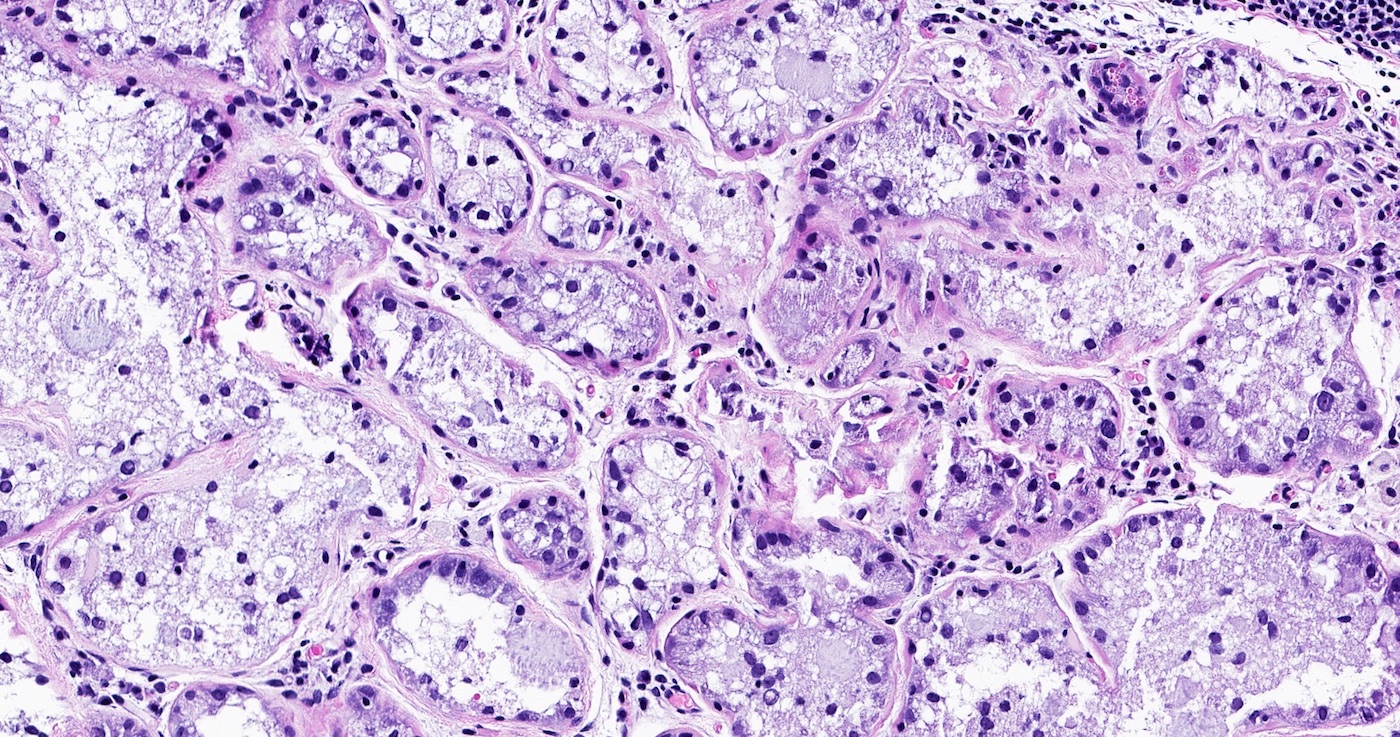
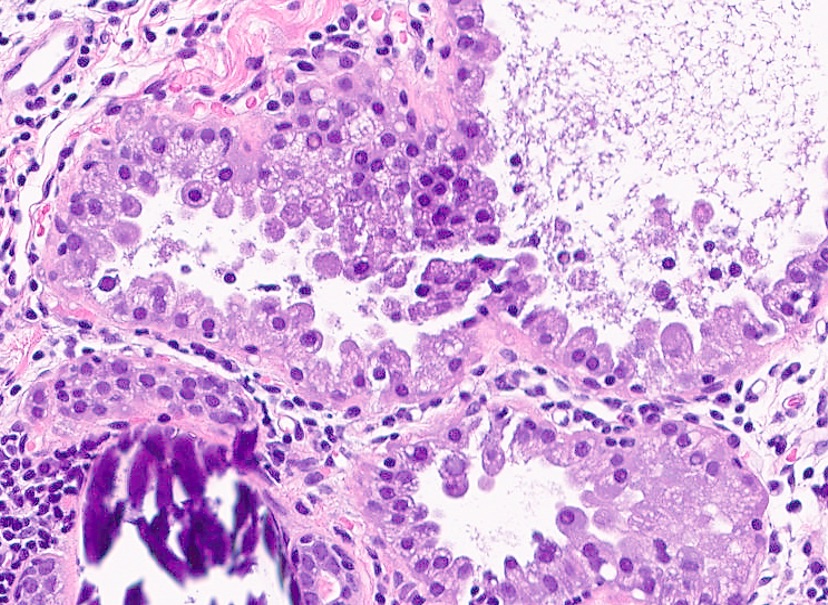
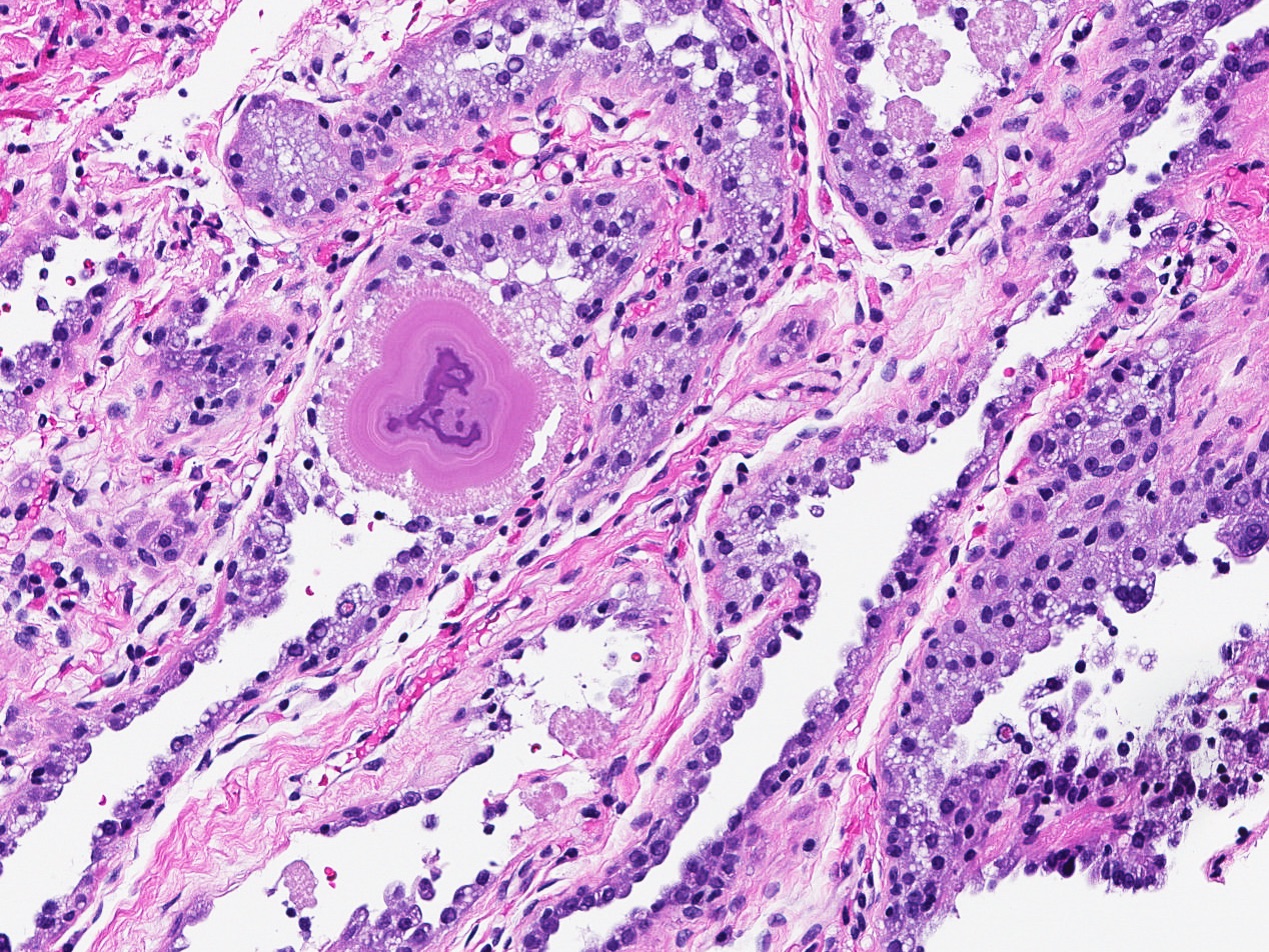
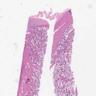
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed proliferation of hyperplastic closely packed lobules with both epithelial and myoepithelial cell layers separated by thin, delicate connective tissue
- Glands lined by actively secreting cuboidal or hobnail shaped cells with small round nuclei and granular to clear vacuolated cytoplasm
- Variably prominent small, pinpoint nucleoli may be seen but cells lack cytologic atypia
- Occasional mitoses may be seen
- Resembles pregnancy-like (pseudolactational) changes
- May resemble fibroadenoma or tubular adenoma with lactational change microscopically
Microscopic (histologic) images
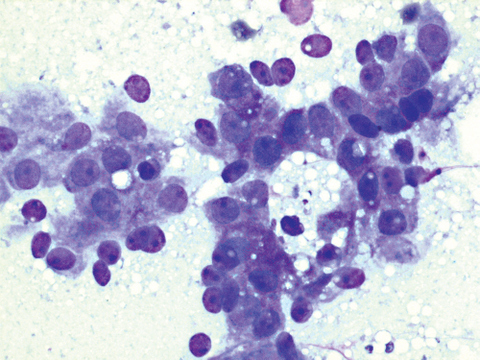
Cytology description
- Loose cohesive clusters of monomorphic cells or single cells
- Cells contain foamy to finely vacuolated cytoplasm, round uniform nuclei with fine chromatin and small nucleoli (J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:2417)
- Background of foamy material
Cytology images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 50 gene NGS panel showed no mutations in three lactating adenomas in one series, including MED12 exon 2 mutations (frequently seen in fibroadenomas) (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:11)
Sample pathology report
- Right breast mass, needle biopsy:
- Breast tissue with lactational change / lactating adenoma
- Microcalcifications associated with lactational change / lactating adenoma
Differential diagnosis
- Lobular hyperplasia (normal physiologic event in pregnancy):
- Not a well defined mass
- Delayed involution of lactation:
- Not a well defined mass
- Hyperplastic and involuting lobules
- Neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes in background
- More frequently associated with calcifications
- Fibroadenoma with secretory activity:
- Fibroepithelial architecture
- Prominent stroma
- Focal, not diffuse, proliferation of cells with secretory activity
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is correct for the entity pictured from this breast biopsy from a 27 year old pregnant woman?
- Frequently shows a prominent stromal component similar to fibroepithelial lesions
- Histologically composed of closely packed glands lined by actively secreting cuboidal or hobnail shaped cells
- Never develops in ectopic breast tissue along milk line
- The glands lack a myoepithelial cell layer
- Third most prevalent breast lesion in pregnant women
Board review style answer #1
B. Histologically composed of closely packed glands lined by actively secreting cuboidal or hobnail shaped cells
Comment Here
Reference: Lactating adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Lactating adenoma
Board review style question #2
What is the most common breast lesion in pregnant and lactating women?
- Adenomyoepithelioma
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia
- Fibroadenoma
- Invasive ductal carcinoma
- Lactating adenoma
Board review style answer #2