Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Li JJX, Tse GM. Phyllodes tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastphyllodesgeneral.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Biphasic fibroepithelial neoplasm with leaf-like epithelial (phyllodal) pattern and stromal proliferation
Essential features
- Biphasic fibroepithelial lesion characterized by leaf-like phyllodal epithelial pattern
- Graded and prognosticated by histologic changes of the stromal proliferation
- Epithelial component is benign in phyllodes tumor
Terminology
- Phyllodes tumor
- Cystosarcoma phyllodes (the use of this term is discouraged)
ICD coding
- Phyllodes tumor
- ICD-O: 9020/1 - Phyllodes tumor, NOS
- Benign phyllodes tumor
- Borderline phyllodes tumor
- Malignant phyllodes tumor
Epidemiology
- Incidence rate of 2.1 per 1 million women (Cancer 1993;71:3020)
- Constitutes 1% of breast tumors
- Benign phyllodes tumor most common (60 - 75%), followed by borderline (15 - 26%) and malignant (8 - 20%) tumors (WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board: Breast Tumours, 5th Edition, 2019)
- Average age 40 - 50 years (Cancer Med 2018;7:1030)
- Benign phyllodes tumor occurs at a younger age compared with borderline and malignant phyllodes tumors (J Clin Pathol 2012;65:69)
- Can occur rarely in pediatric age group and male
Sites
- Most commonly breast
- Reported to develop in ectopic breast tissue, including vulva (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:946)
Pathophysiology
- Biphasic lesion with epithelial stromal interaction involved in tumorigenesis (Cancer 1992;70:2115)
- Loss of epithelial interaction in stromal component believed to lead to malignant progression (Histopathology 2012;61:667)
- Areas resembling well differentiated liposarcoma in phyllodes tumor lack CDK4 and MDM2 expression / gene amplification as seen in primary well differentiated liposarcoma (Histopathology 2016;68:1040, Breast J 2016;22:282)
Etiology
- Currently unclear
- Increased incidence reported in Li-Fraumeni syndrome (Oncogene 2001;20:4621)
Clinical features
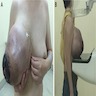
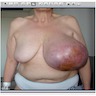
- Commonly presents with firm, asymptomatic, mobile breast mass
- Large tumor (up to 20 cm) can cause skin ulceration and pain (J Surg Case Rep 2015;2015:rjv162)
- Bloody nipple discharge uncommon and attributed to infarction and intraductal involvement (Histopathology 2007;50:666)
- Rare cases of hypoglycemia due to insulin-like growth factor II production (Breast J 2007;13:189)
Diagnosis
- Largely dependent on histologic diagnosis
- Imaging not accurate in diagnosis
- Ultrasound and mammography do not accurately differentiate phyllodes tumor from fibroadenoma (Br J Radiol 2014;87:20140239)
- Ultrasound unreliable in grading of phyllodes tumor (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2018;210:W173)
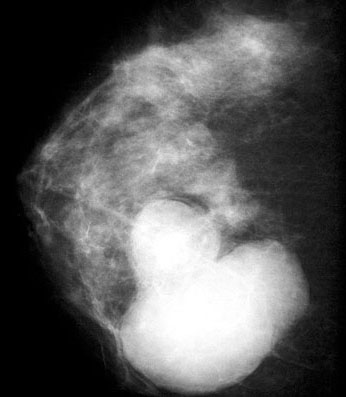
Radiology description
- Oval and lobulated lesions
- Hypoechoic on ultrasound
- Microcalcifications rare
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis correlates with histologic grade
- Benign phyllodes tumor
- Very low rate of local recurrence regardless of margin status (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013;141:353)
- Does not metastasize or cause mortality (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013;141:353)
- Recurrences may be benign but may also progress to borderline or malignant phylldoes tumors (Ann Surg Oncol 2019;26:2747)
- Borderline phyllodes tumor
- Behavior intermediate between benign and malignant phyllodes tumors (Histopathology 2016;68:5)
- Higher risk of local recurrence than benign phyllodes tumor
- Risk of metastasis present but very low
- Malignant phyllodes tumor
- 23 - 30% risk of local recurrence (Histopathology 2016;68:5)
- 9% risk of distant metastasis
- Sites include lung, pleura, bone, central nervous system, visceral organs and soft tissue
- Occurs within 10 years of diagnosis (Am Surg 2007;73:967)
- Presence of malignant heterologous elements, necrosis and tumor size correlated with metastasis (Virchows Arch 2018;472:615, Ann Surg Oncol 2019;26:2747)
- Axillary nodal involvement by metastatic disease uncommon
- Benign phyllodes tumor
- Positive margin status associated with local recurrence
- Tumor size is an independent risk factor for local recurrence (Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:2912)
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with painless breast mass (Case #255)
- 37 year old woman with multiple metastases including adrenal gland (Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2018;36:113)
- 44 year old woman with repeated local recurrence (Onco Targets Ther 2018;11:7787)
- 47 year old woman with malignant phyllodes tumor showing liposarcomatous differentiation (Radiol Case Rep 2019;14:531)
- 70 year old woman with benign phyllodes tumor and concomitant ductal carcinoma in situ (Am J Case Rep 2017;18:813)
Treatment
- Local excision with clear margins
- Narrow margins may be adequate for benign phyllodes tumor
- Exact extent of clearance under debate, currently no consensus as to adequate margin width, while 10 mm is generally considered acceptable (NCCN Guidelines: Breast Cancer - Phyllodes Tumor [Accessed 2 July 2020], Ann Surg Oncol 2019;26:2747)
- Axillary dissection not indicated
- Efficacy of radiotherapy unclear, may improve local control but not overall survival in borderline and malignant phyllodes tumor (Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:492)
- Efficacy of chemotherapy unclear
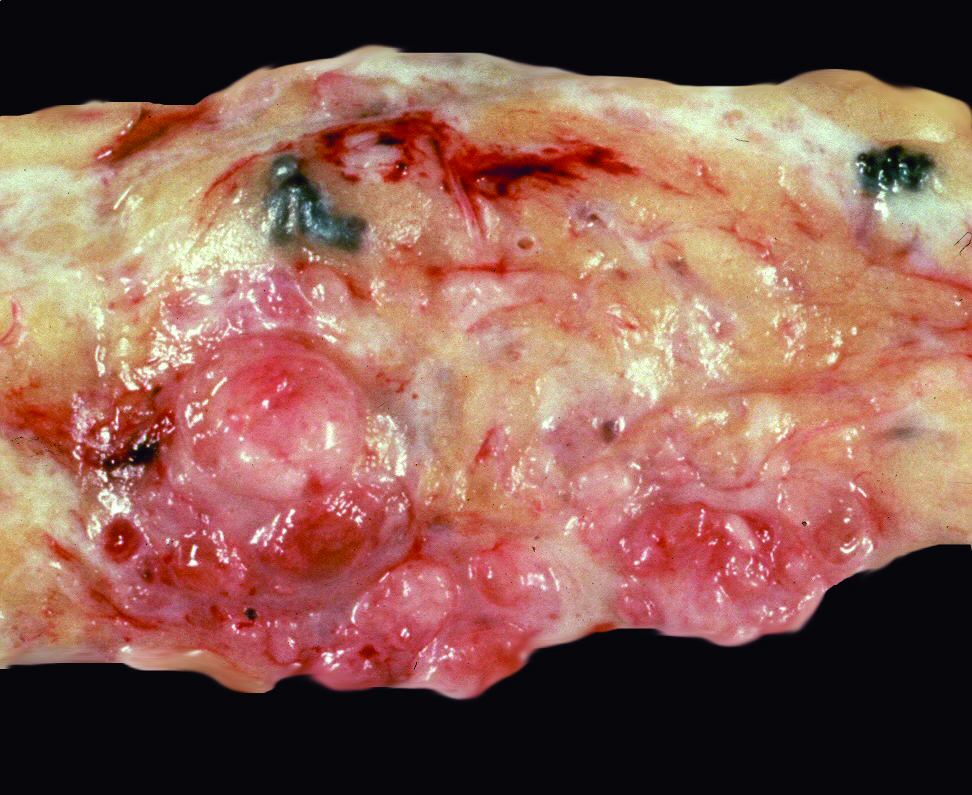
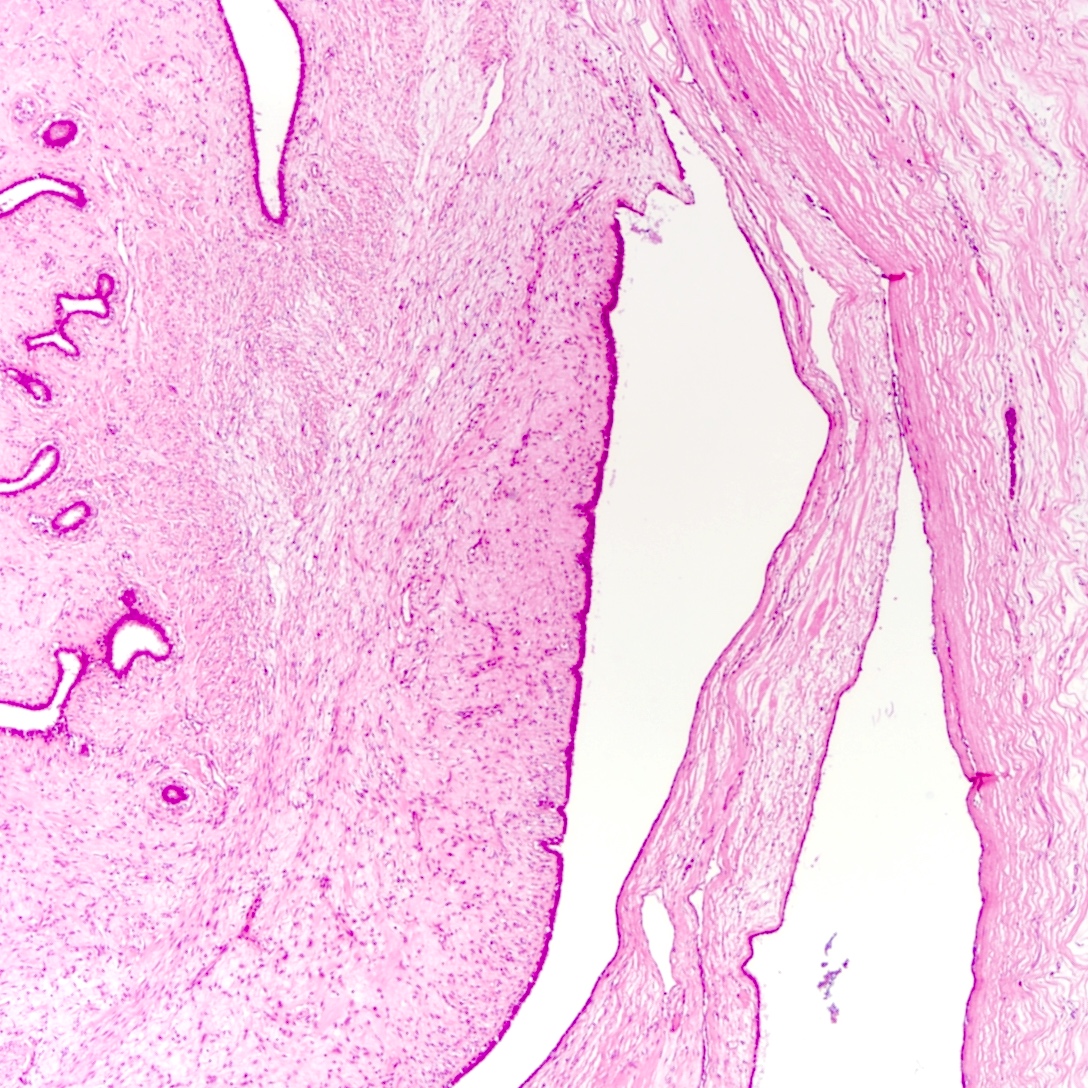
Gross description
- Rounded, shelled out borders
- Infiltrative in malignant and less commonly borderline phyllodes tumor
- Whorled, bosselated cut surface in a leaf-like pattern
- Skin ulceration, hemorrhage and cystic changes in large lesions (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;67:114)
- Ulceration and hemorrhage do not indicate malignant behavior per se
- Infarcted or very large benign phyllodes tumor can also show necrosis
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
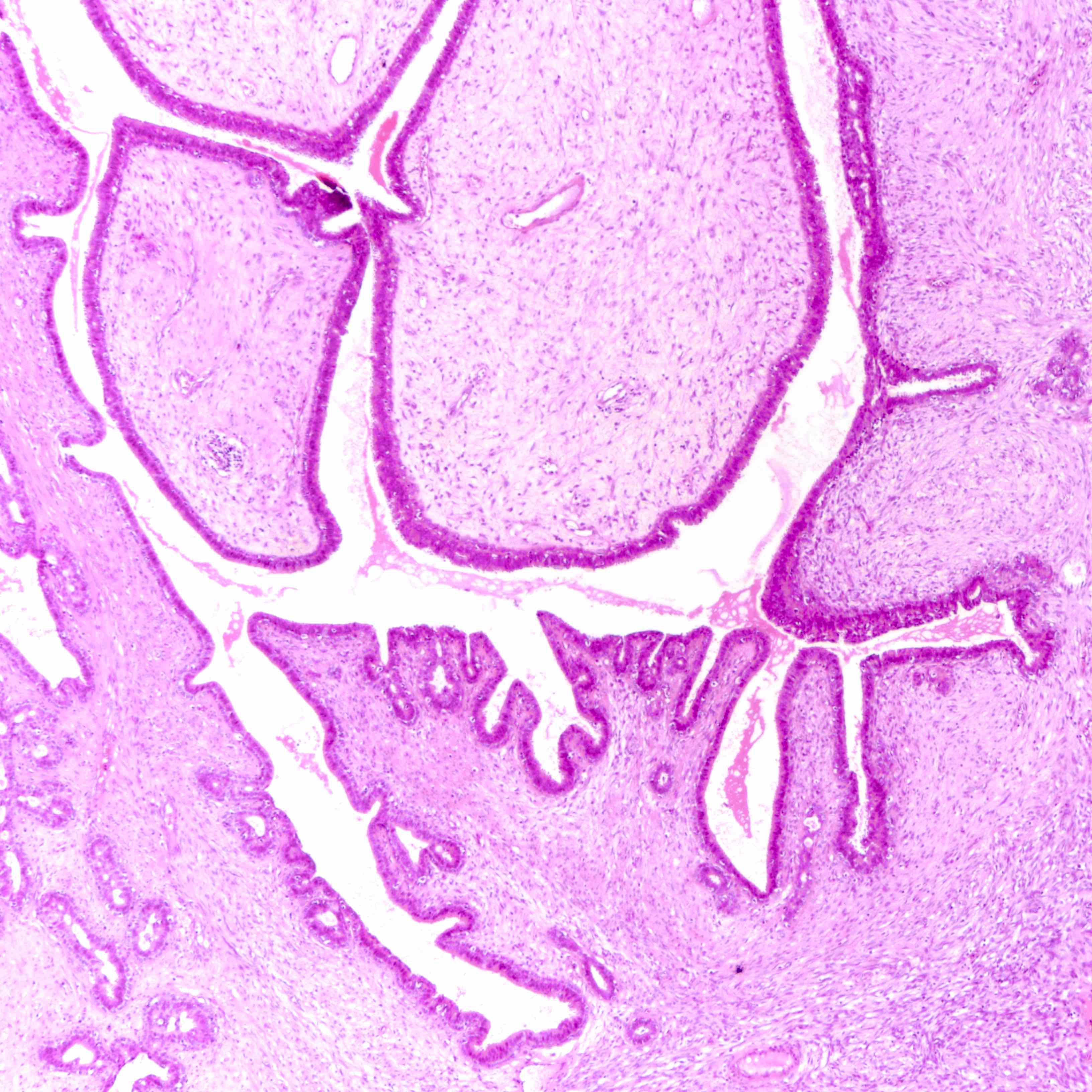
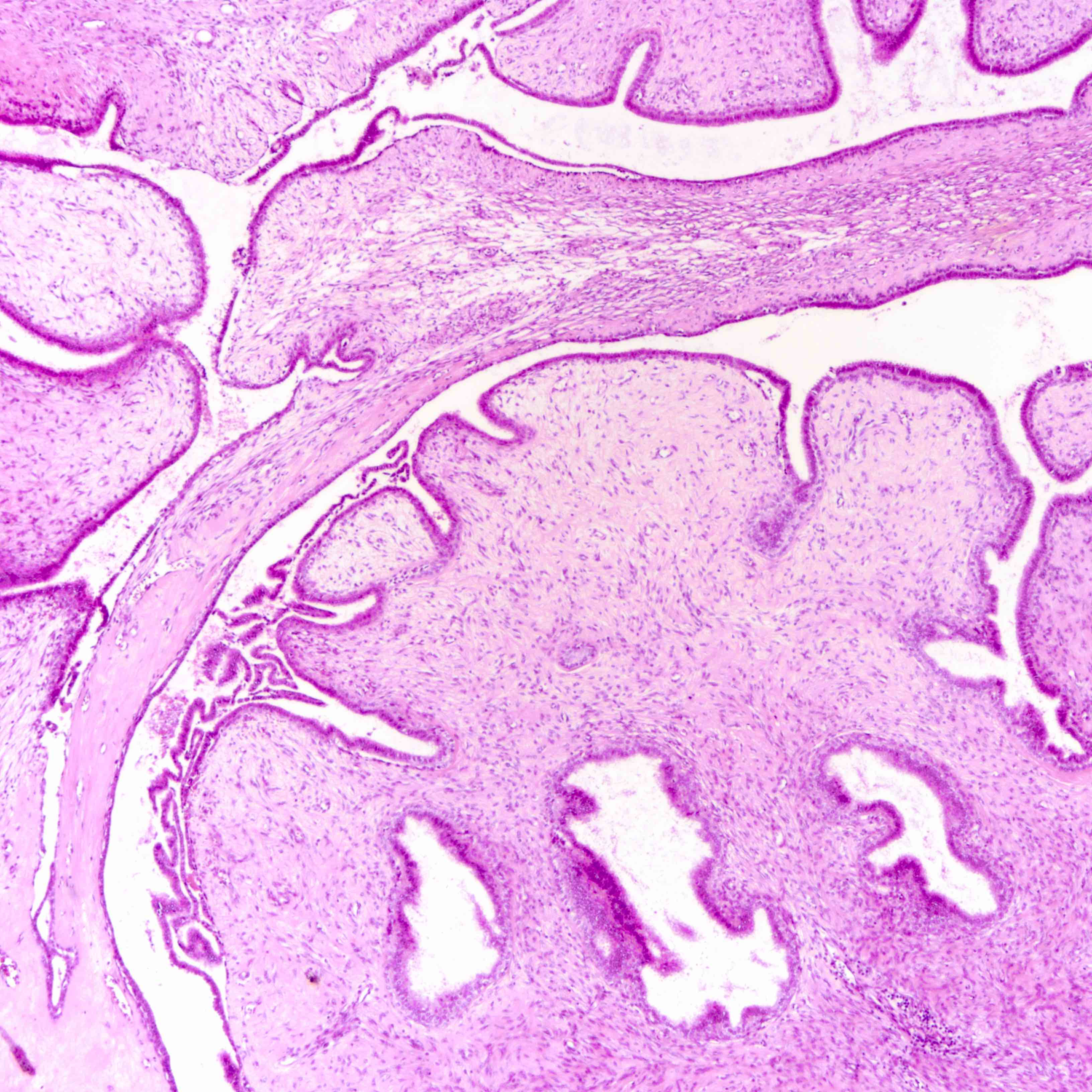
- Leaf-like (phyllodal) epithelial pattern formed by an exaggerated intracanalicular pattern
- Subepithelial condensation with increased stromal cellularity adjacent to epithelium
- Some regard tumors with predominant periductal stromal expansion (i.e., periductal stromal tumor) as a distinct subtype of phyllodes tumor
- Graded into benign, borderline and malignant histologic grades
Benign Borderline Malignant Stromal atypia Mild Moderate Marked Stromal cellularity Mildly increased, can be focal Moderately increased, can be focal Markedly and diffusely increased Stromal overgrowth* Absent Absent or very focal Present Mitotic count < 5/10 HPF or < 2.5/mm² 5 - 9/10 HPF or 2.5 - < 5/mm² ≥ 10/10 HPF or ≥ 5/mm² Tumor border Well defined Well defined or focally permeative Diffusely permeative Malignant heterologous elements Absent Absent Presence directly upgrades to malignant category** -
*Defined as absence of epithelial elements containing stroma only in 1 low power field
**Includes chondrosarcoma, liposarcoma (except well differentiated liposarcoma), osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, angiosarcoma and leiomyosarcoma
- Cystic degeneration, hemorrhage, stromal hyalinization and myxoid change reported
- Does not indicate malignancy (J Clin Diagn Res 2016;10:EC14)
- Multinucleated stromal giant cells occasionally seen (Pathology 2001;33:153)
- Can be found in phyllodes tumor of all histologic grades
- Epithelial elements usually bland
- Epithelium can be scarce in malignant phyllodes tumor with extensive stromal overgrowth
- Can show squamous metaplasia (Am J Clin Pathol 2005;123:529)
- Incidental involvement by in situ and invasive carcinomas (Clin Breast Cancer 2018;18:e421)
- Myoepithelial layer is preserved but can be attenuated
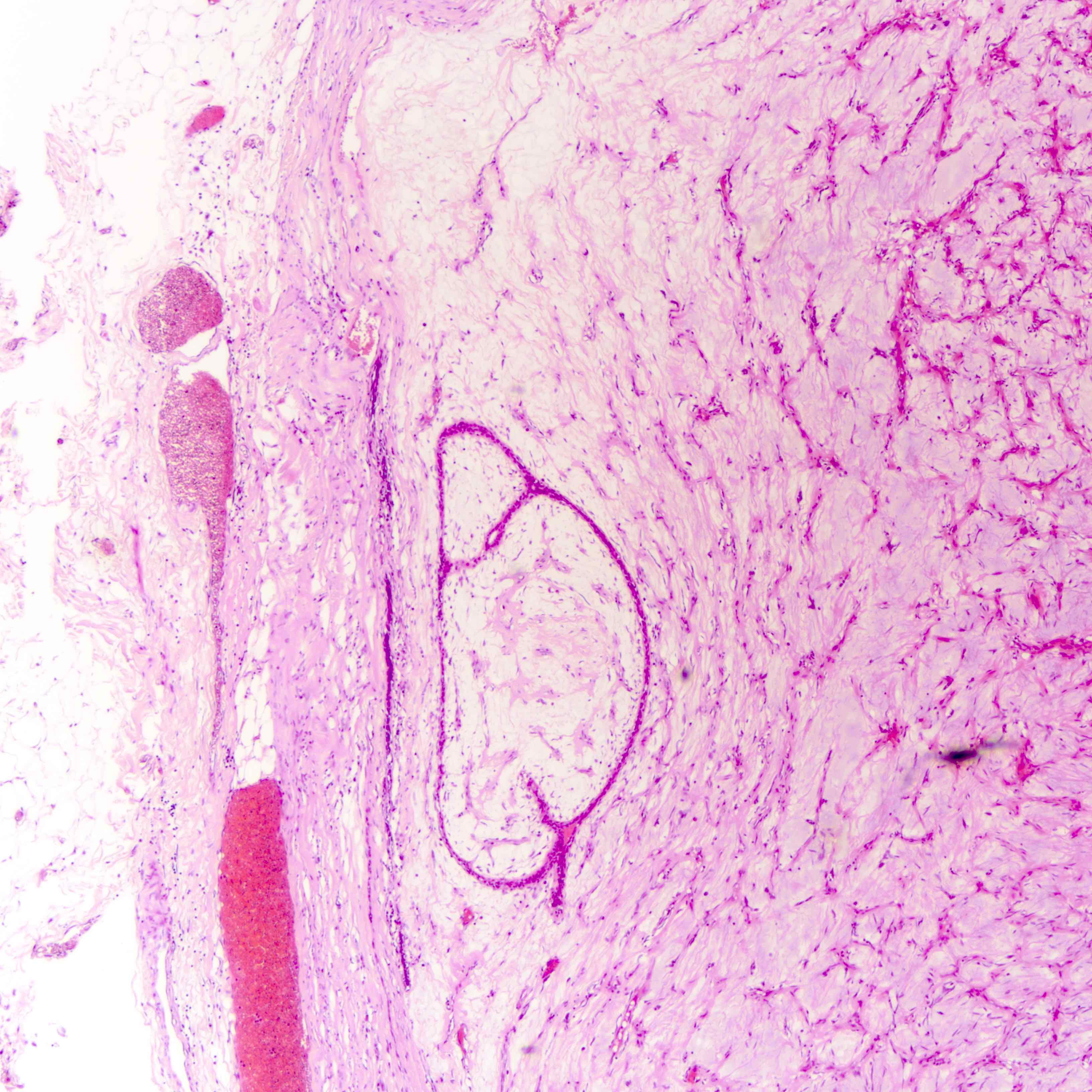
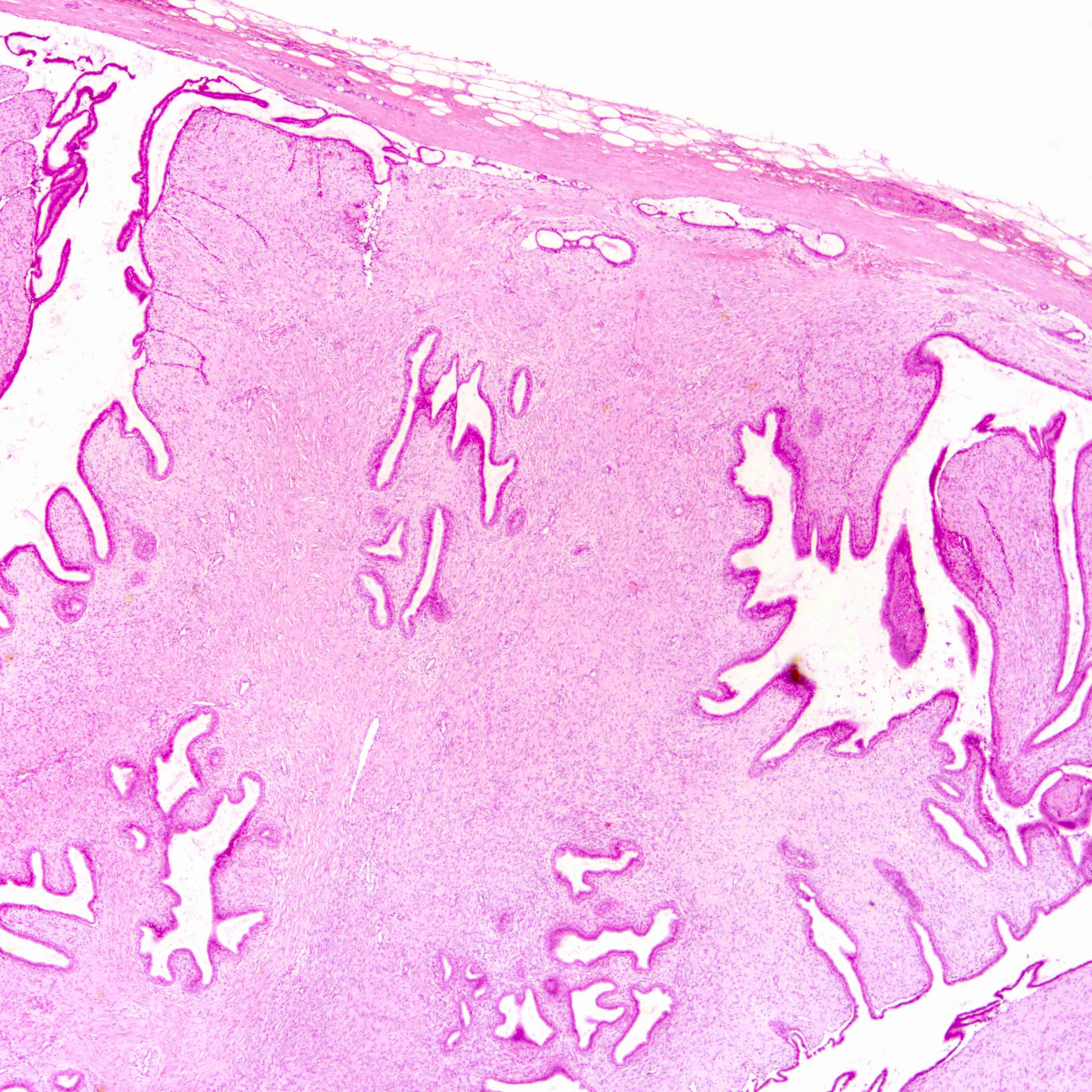
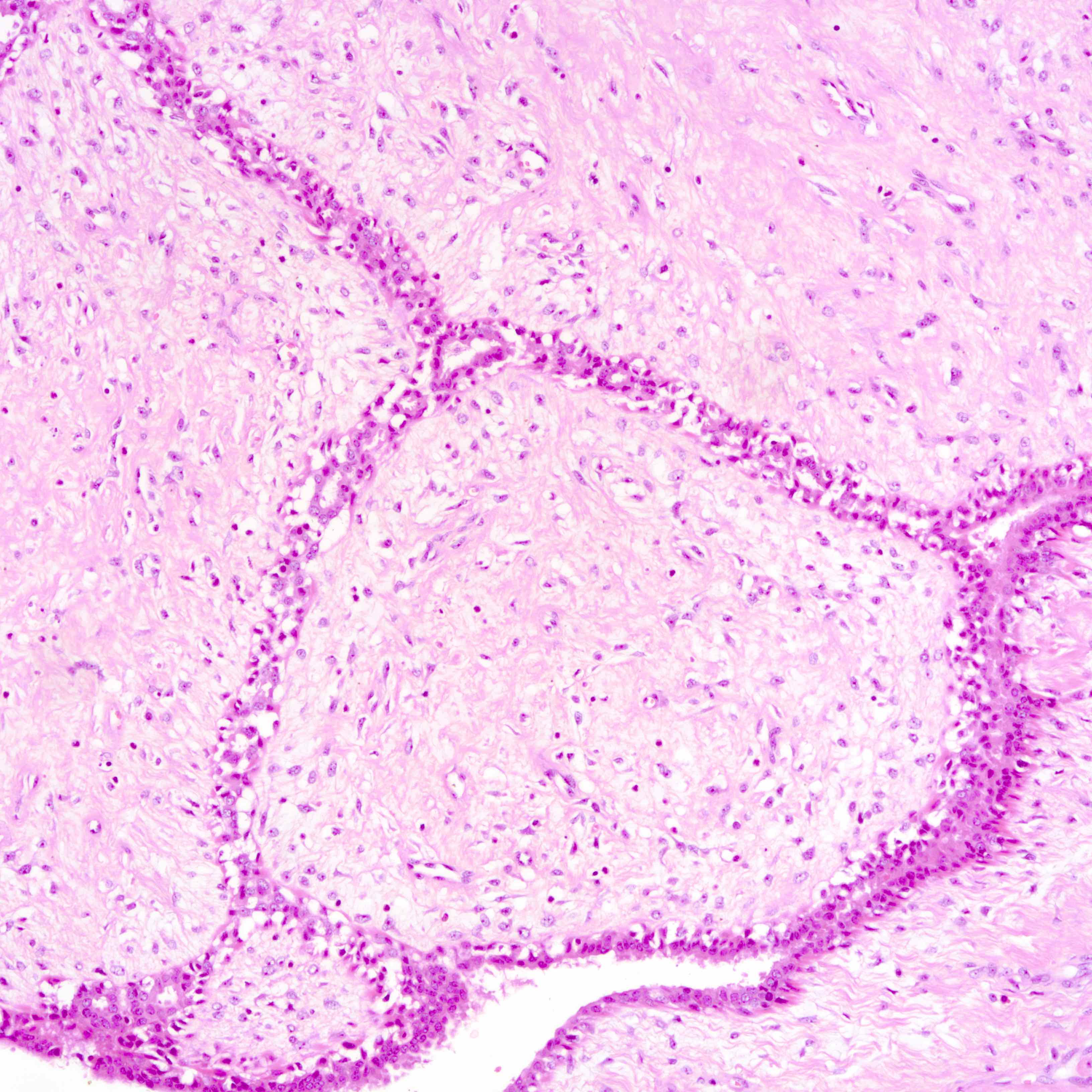
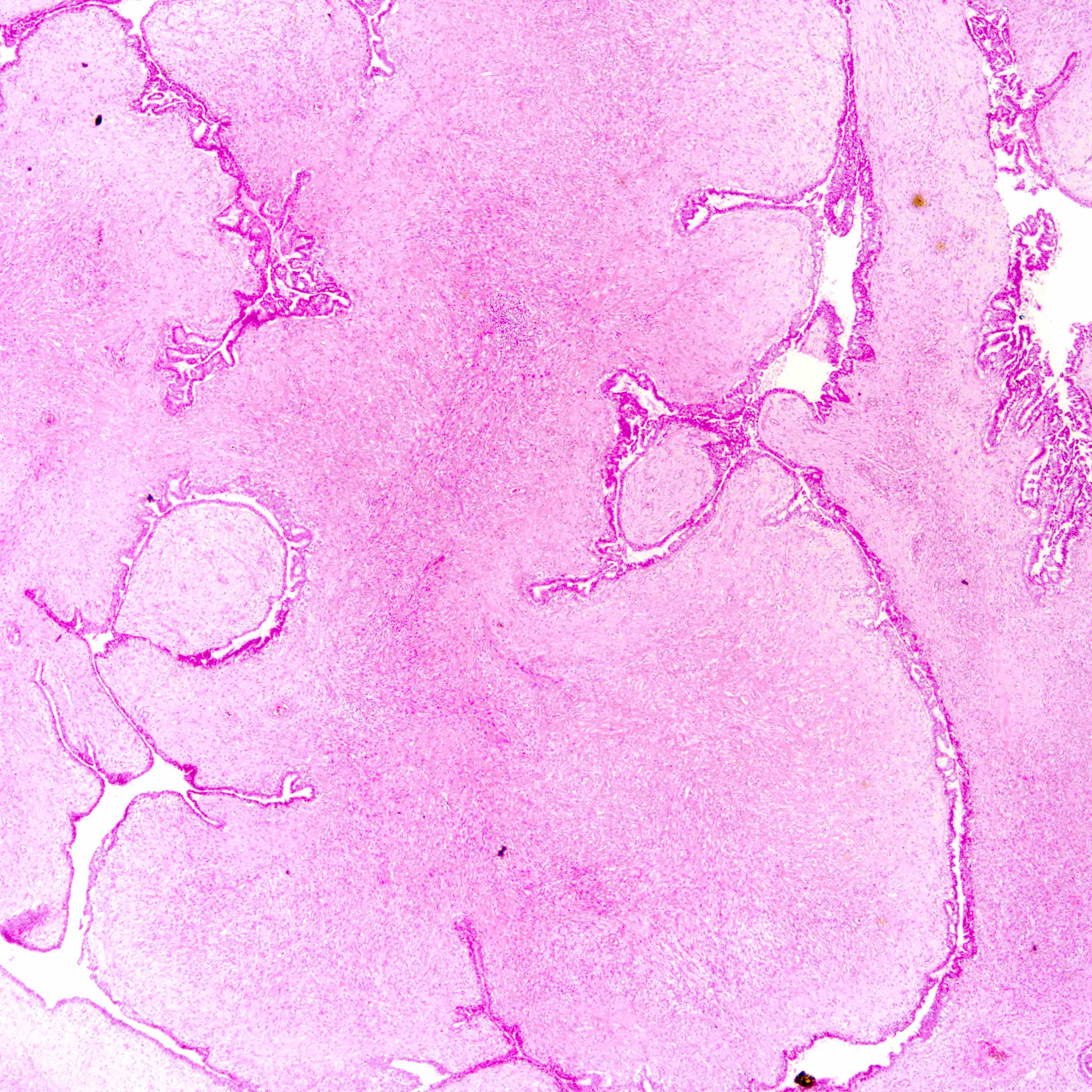
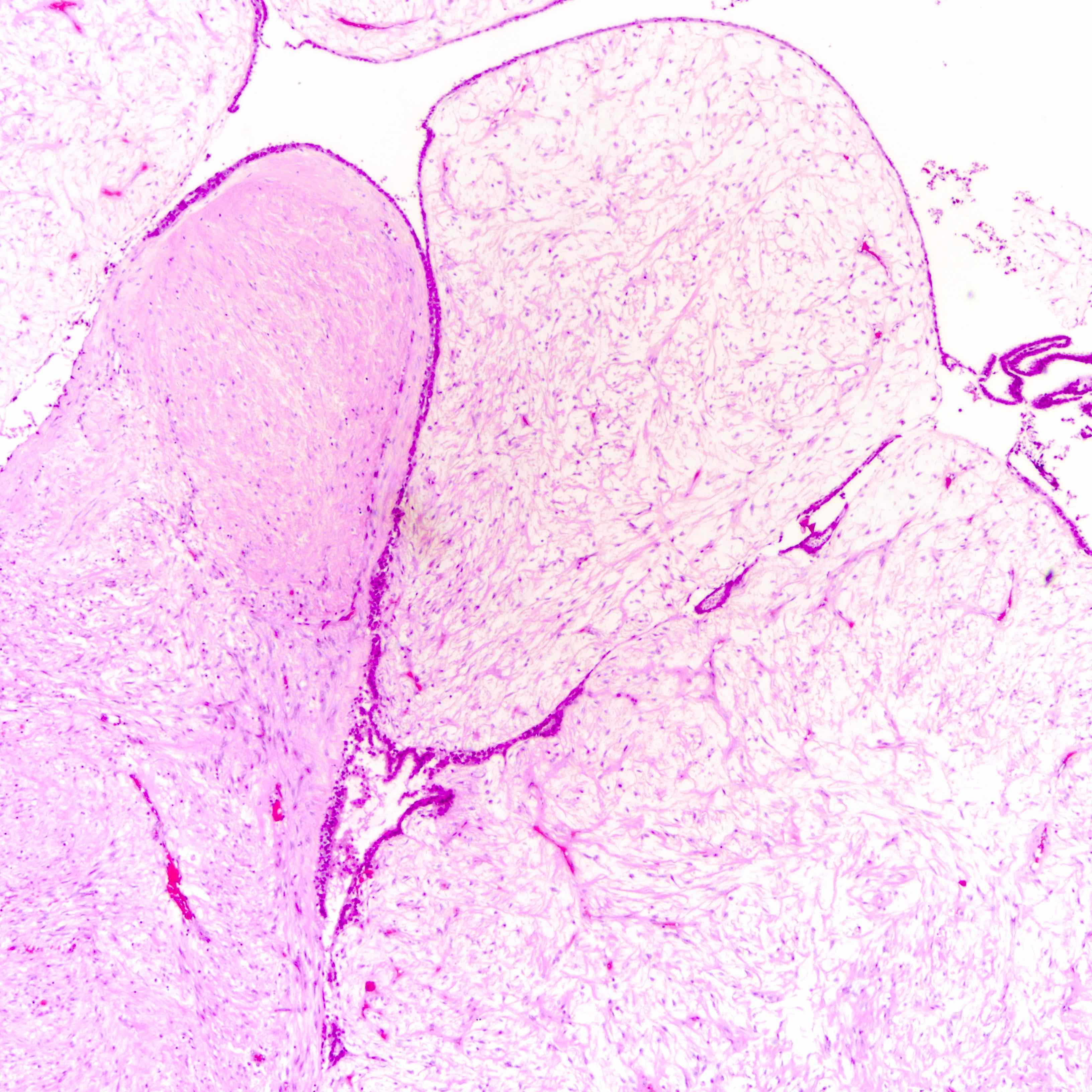
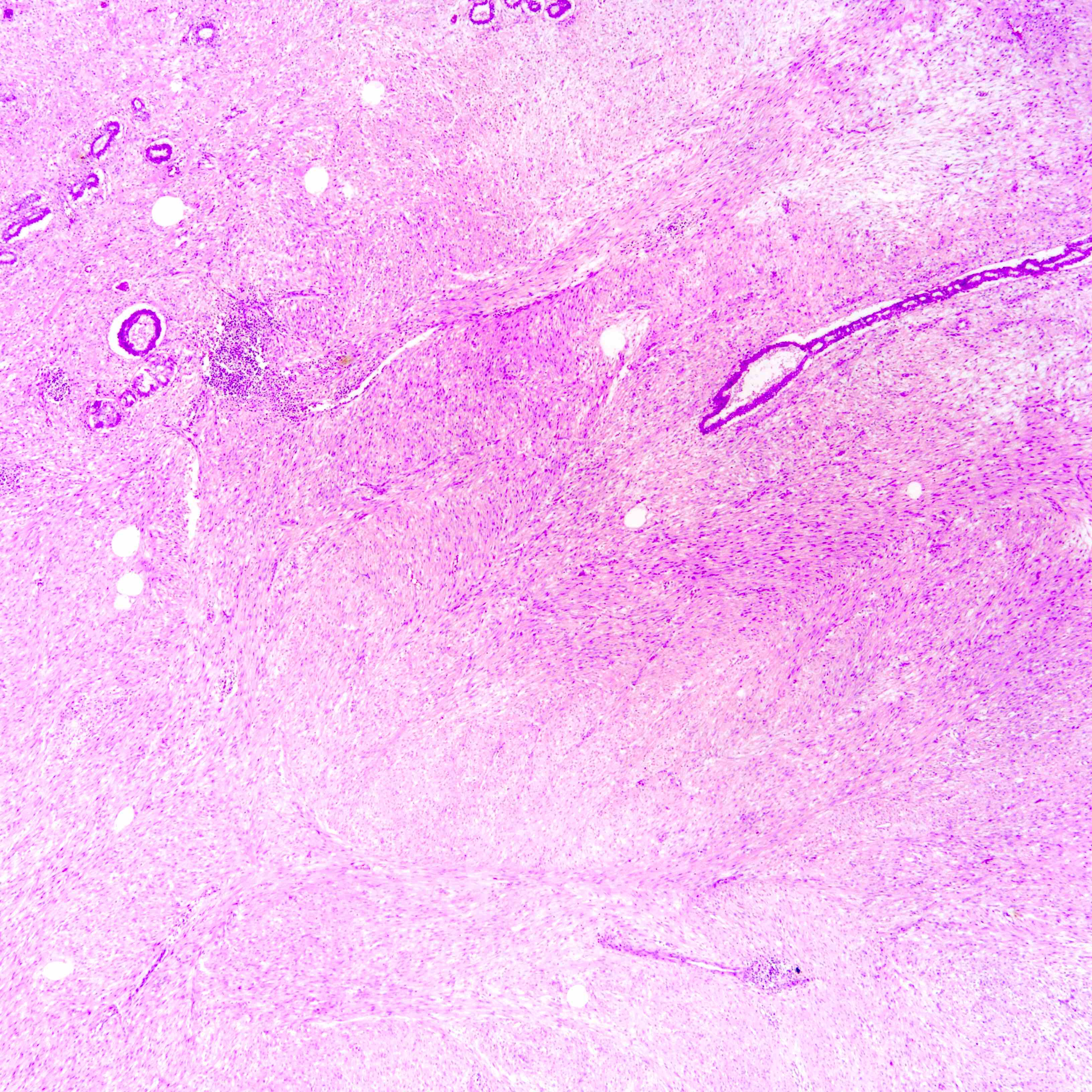
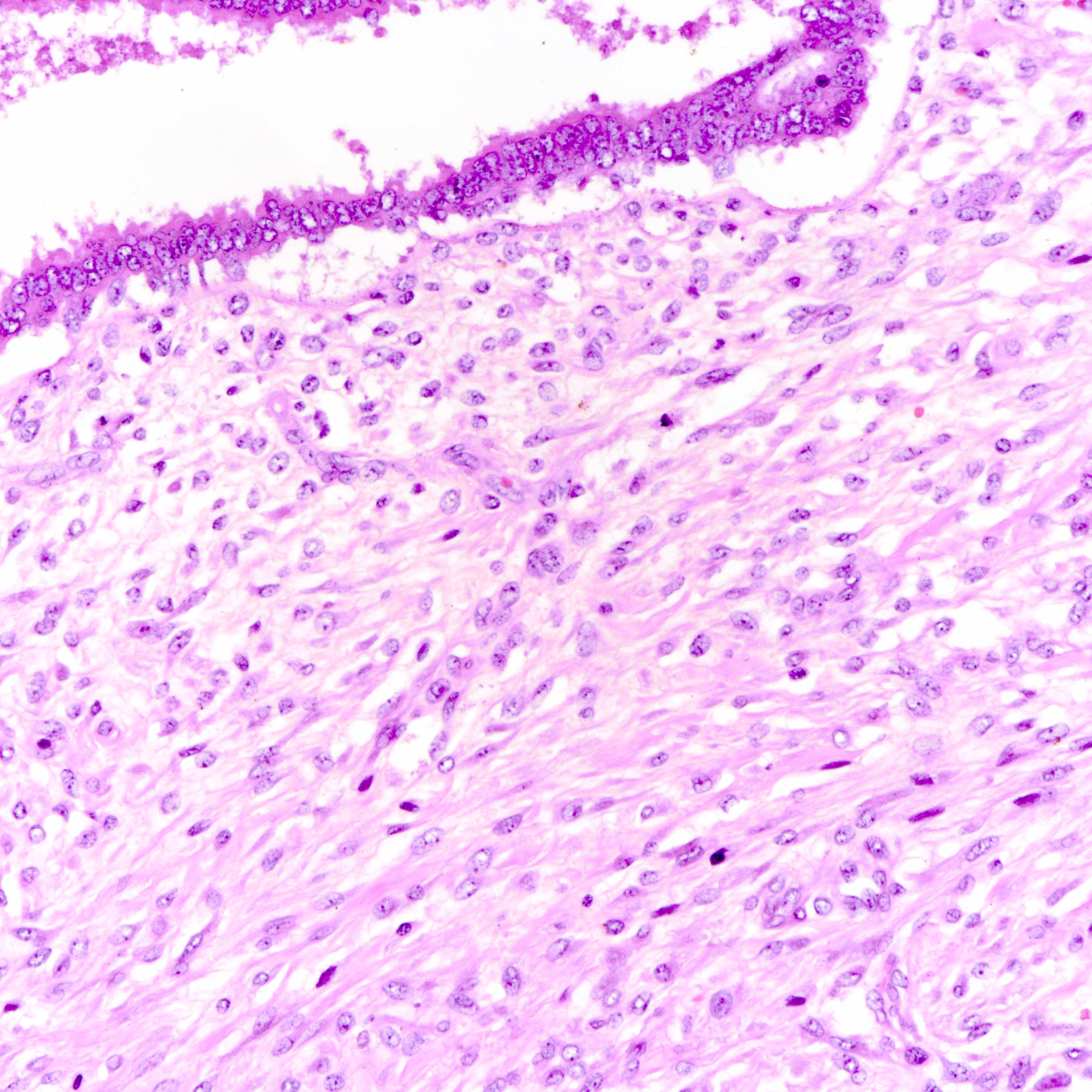
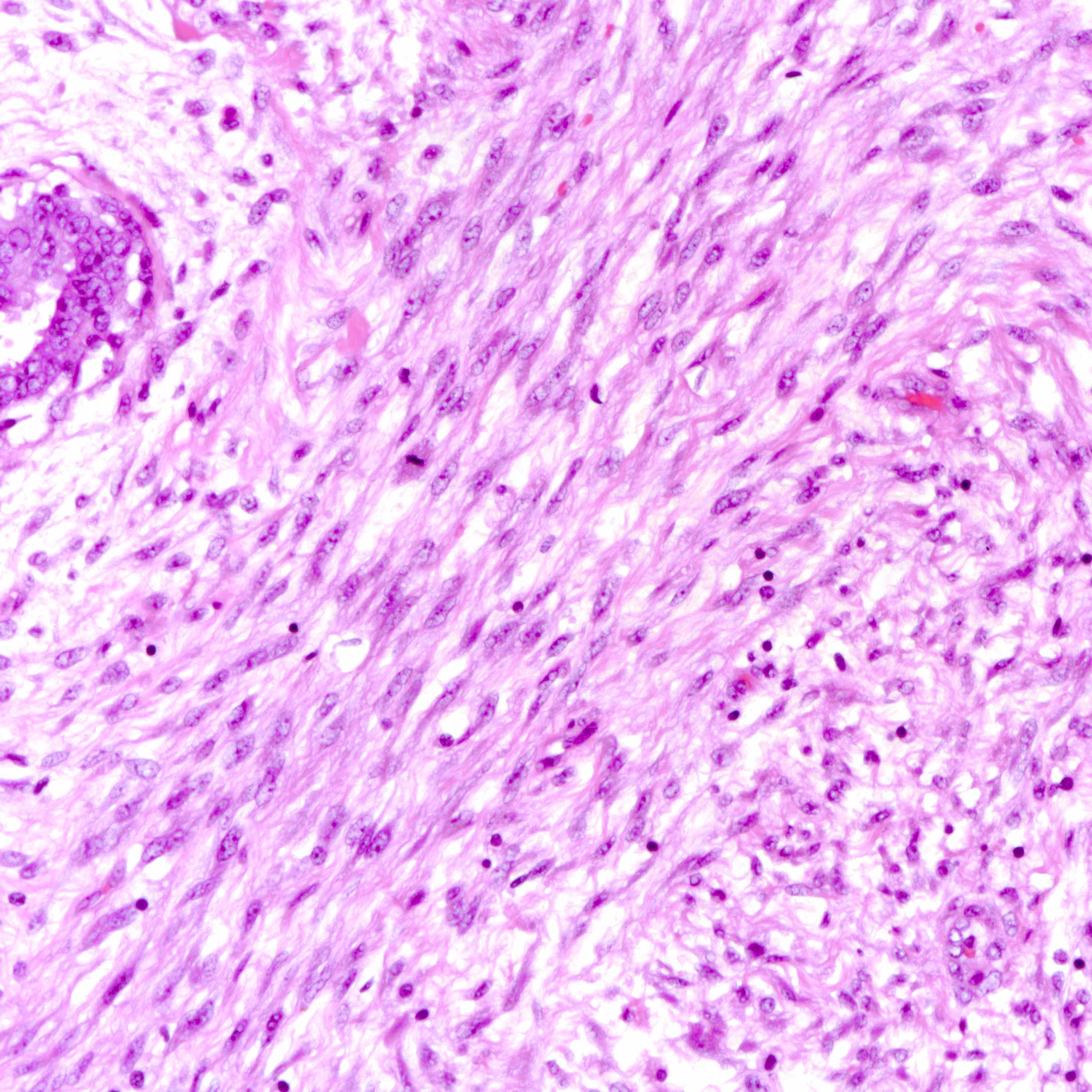
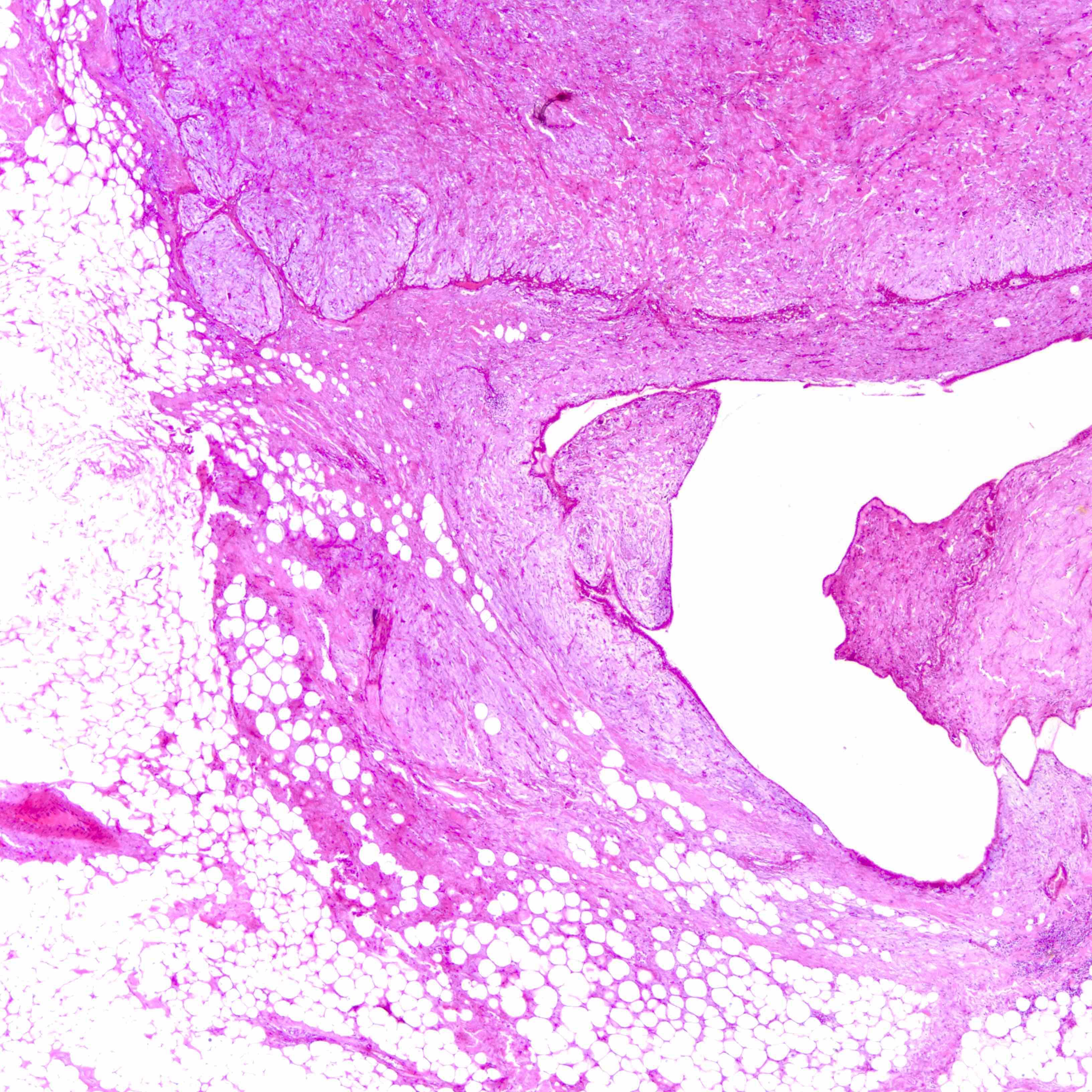
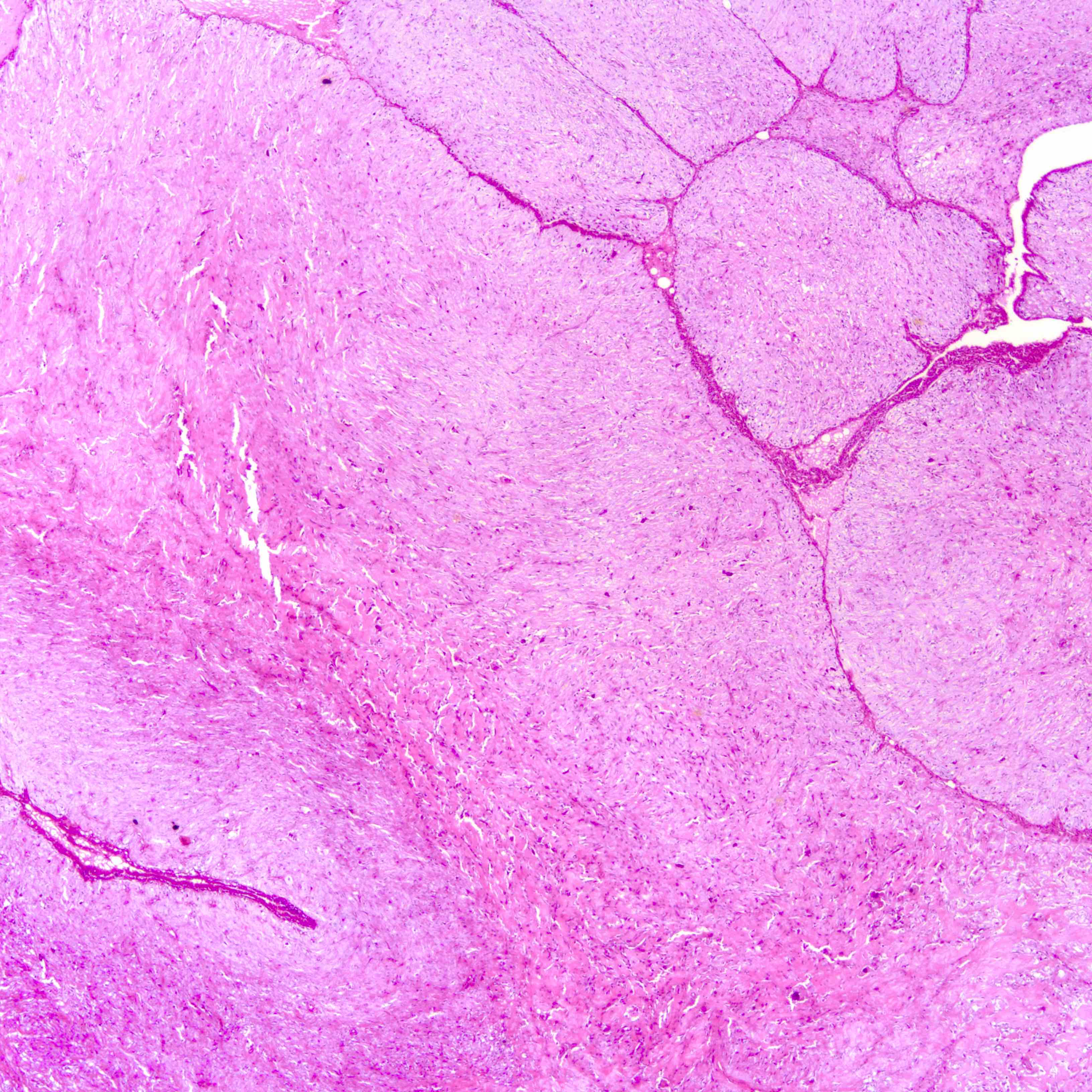
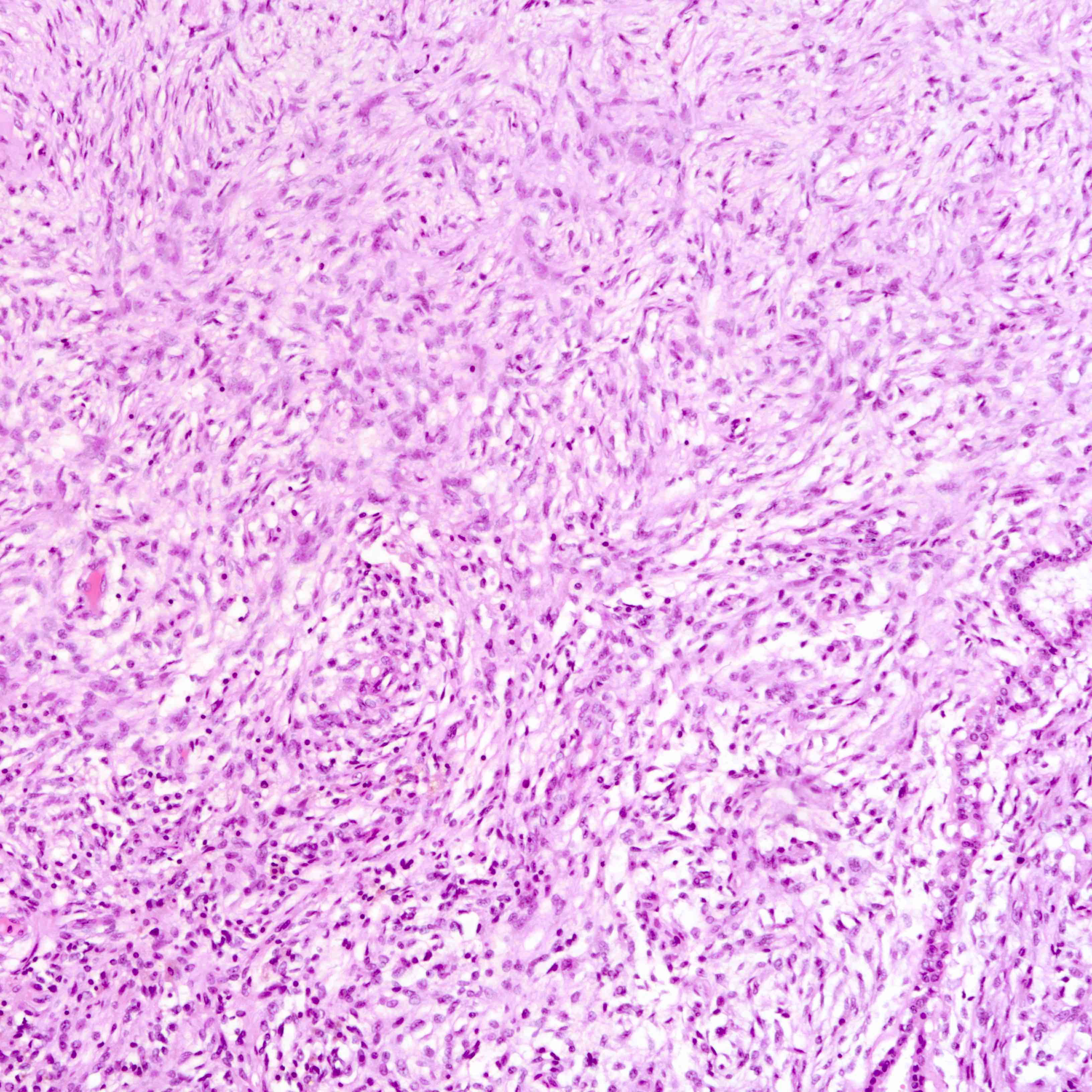
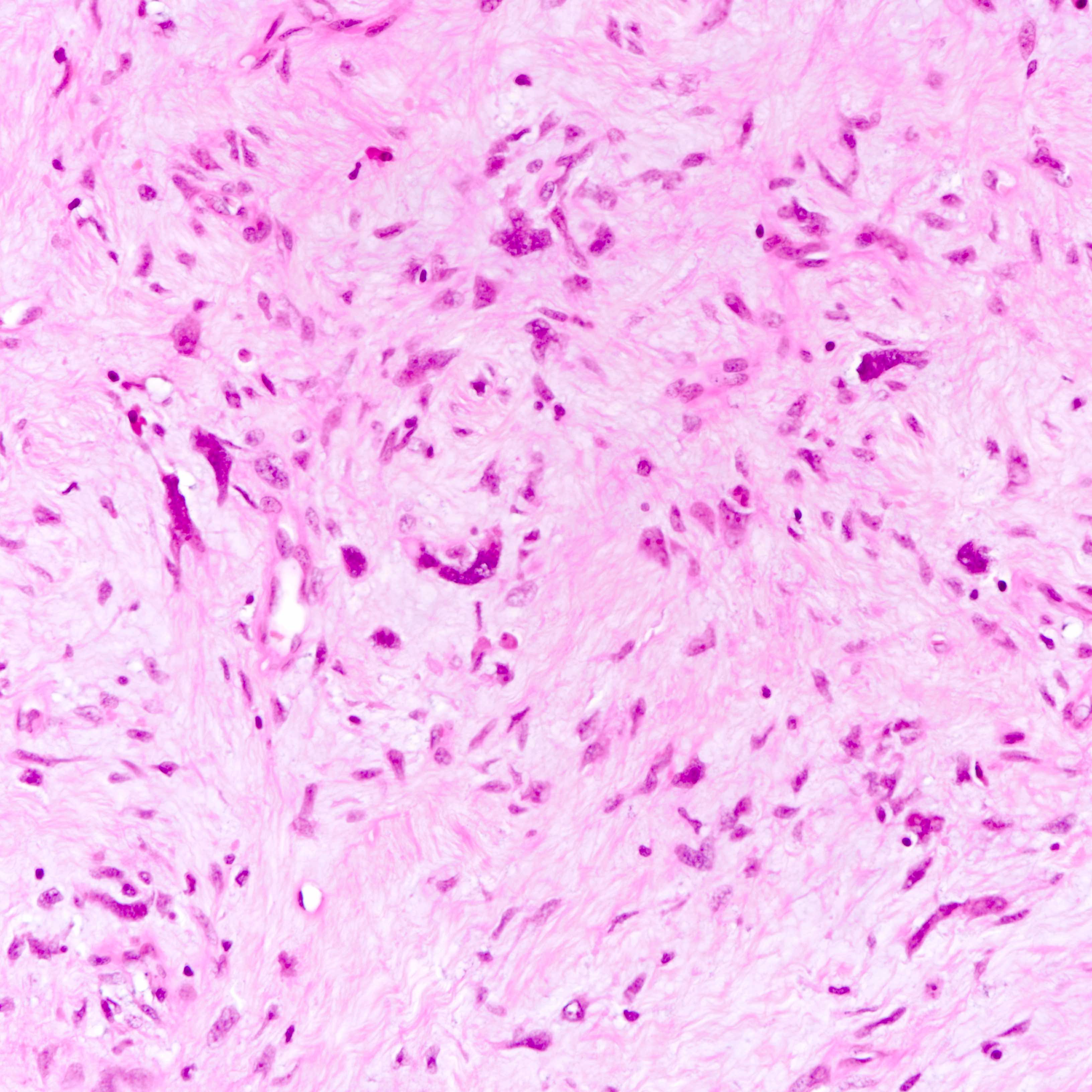
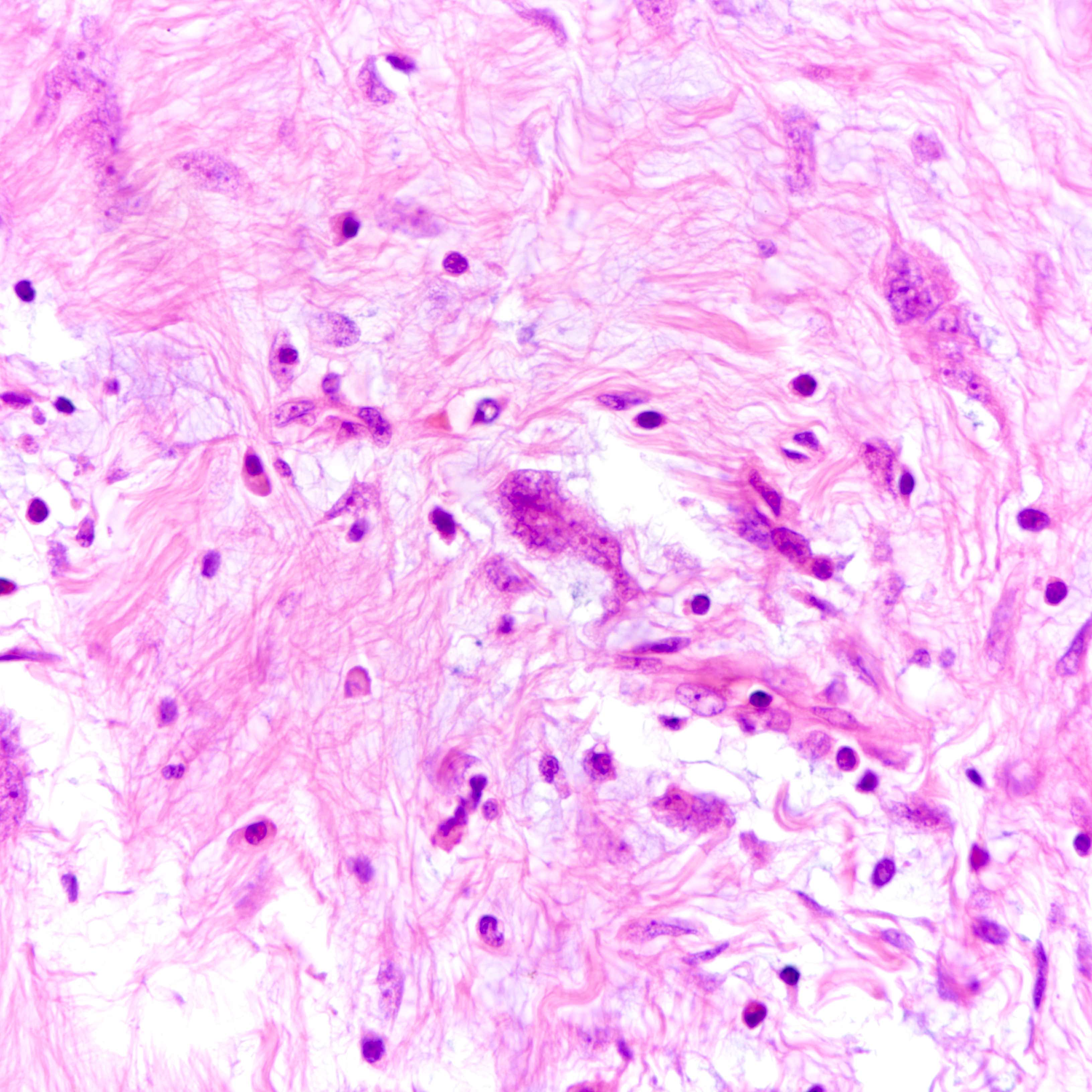
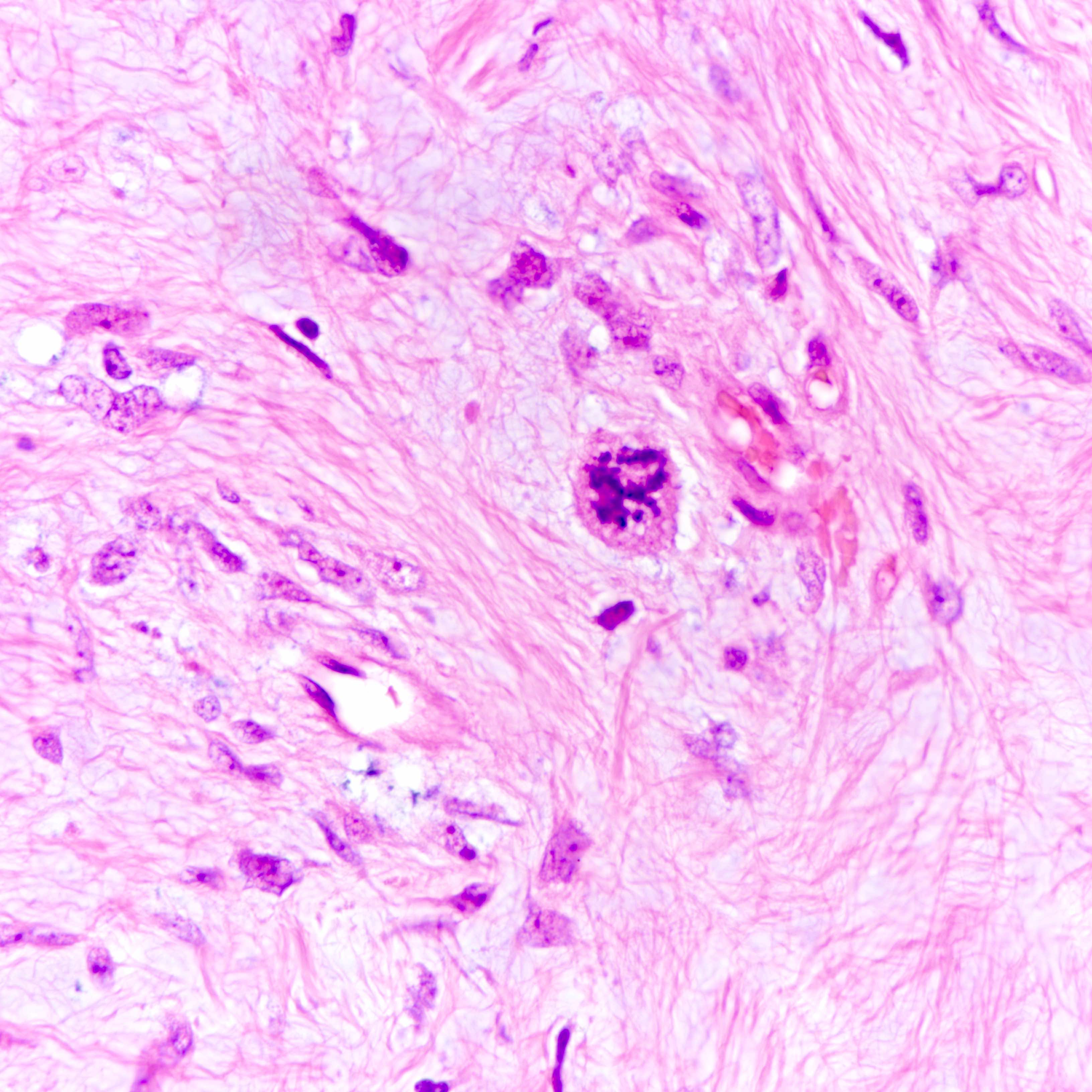
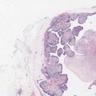
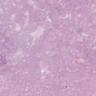
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Joshua J.X. Li, M.B.Ch.B. and Gary M. Tse, M.B.B.S.
Benign phyllodes tumor
Borderline phyllodes tumor
Malignant phyllodes tumor
Virtual slides
Cytology description
- Fibromyxoid stromal clumps
- Reduced epithelial stromal ratio compared with fibroadenomas
- Higher nuclear atypia and cellularity in phyllodes tumor of higher grades
- Large wavy and folded epithelial clusters
- Usually exhibits benign cytomorphology
- Occasionally, hyperplastic changes with enlarged and vesicular nuclei and small visible nucleoli may be seen
- Fibroblastic pavements
- Increased atypia in dispersed cells in phyllodes tumor of higher grades (Cancer Cytopathol 2010;118:33)
- Multinucleated tumor cells and marked stromal anaplasia reported in malignant phyllodes tumor (Cancer Cytopathol 2010;118:33)
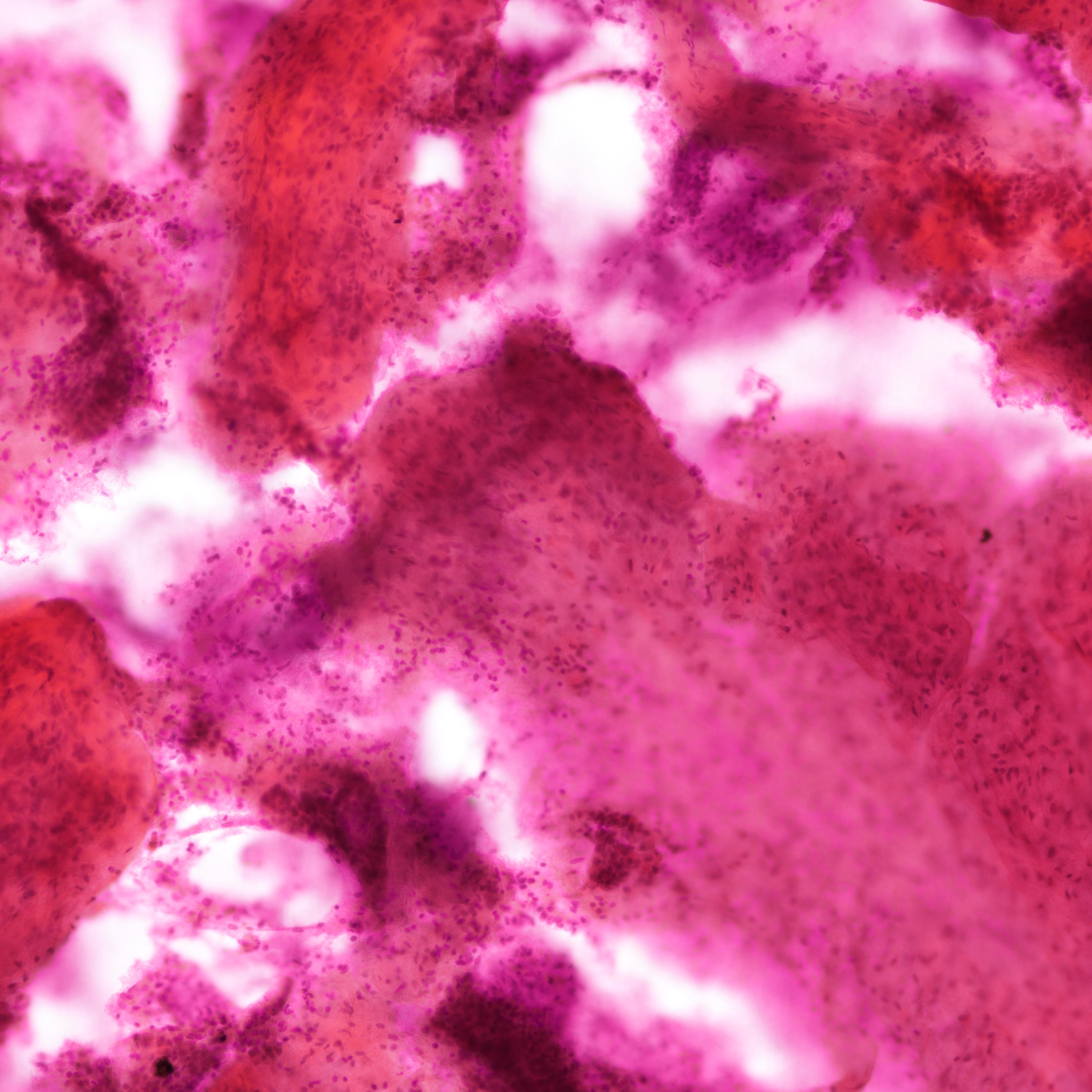
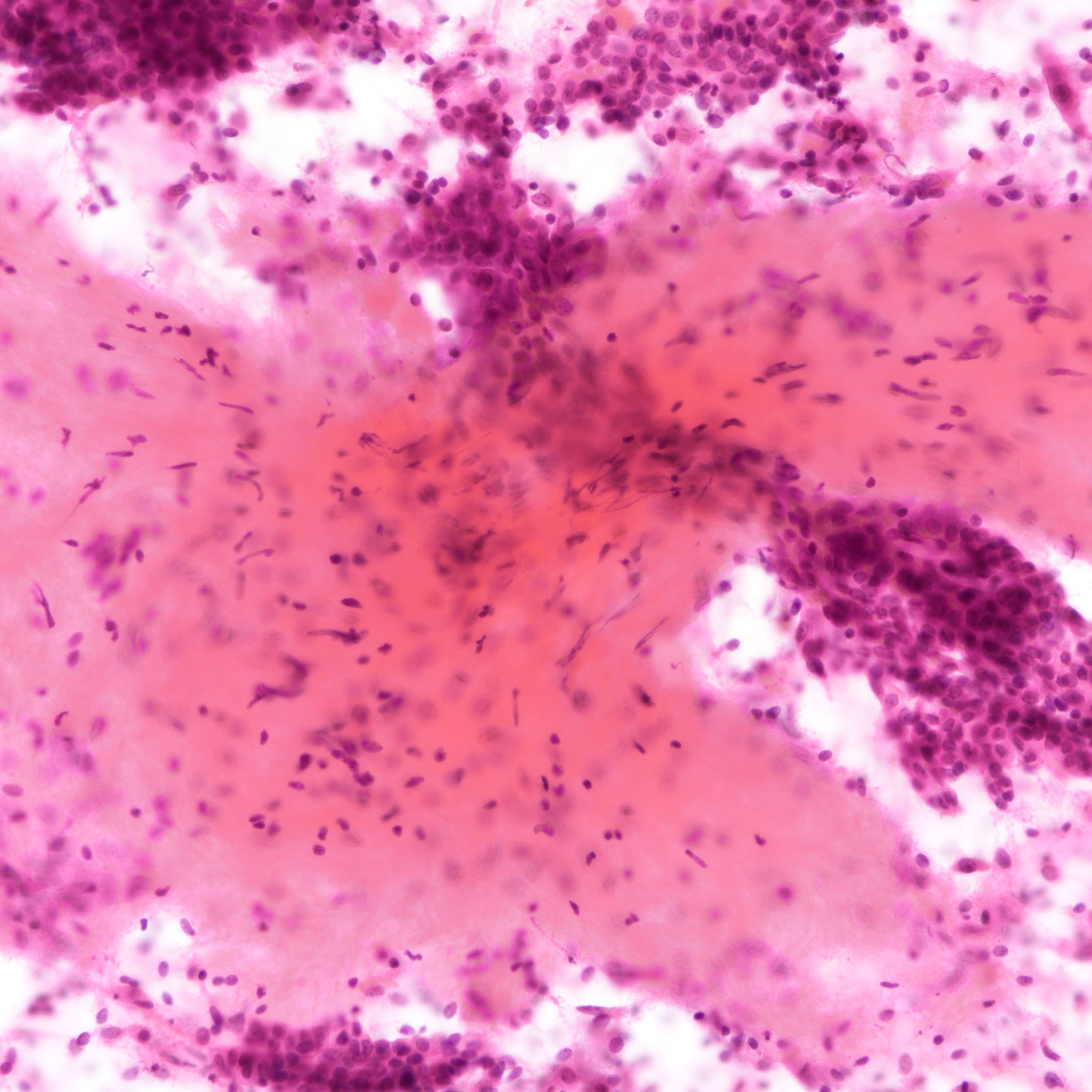
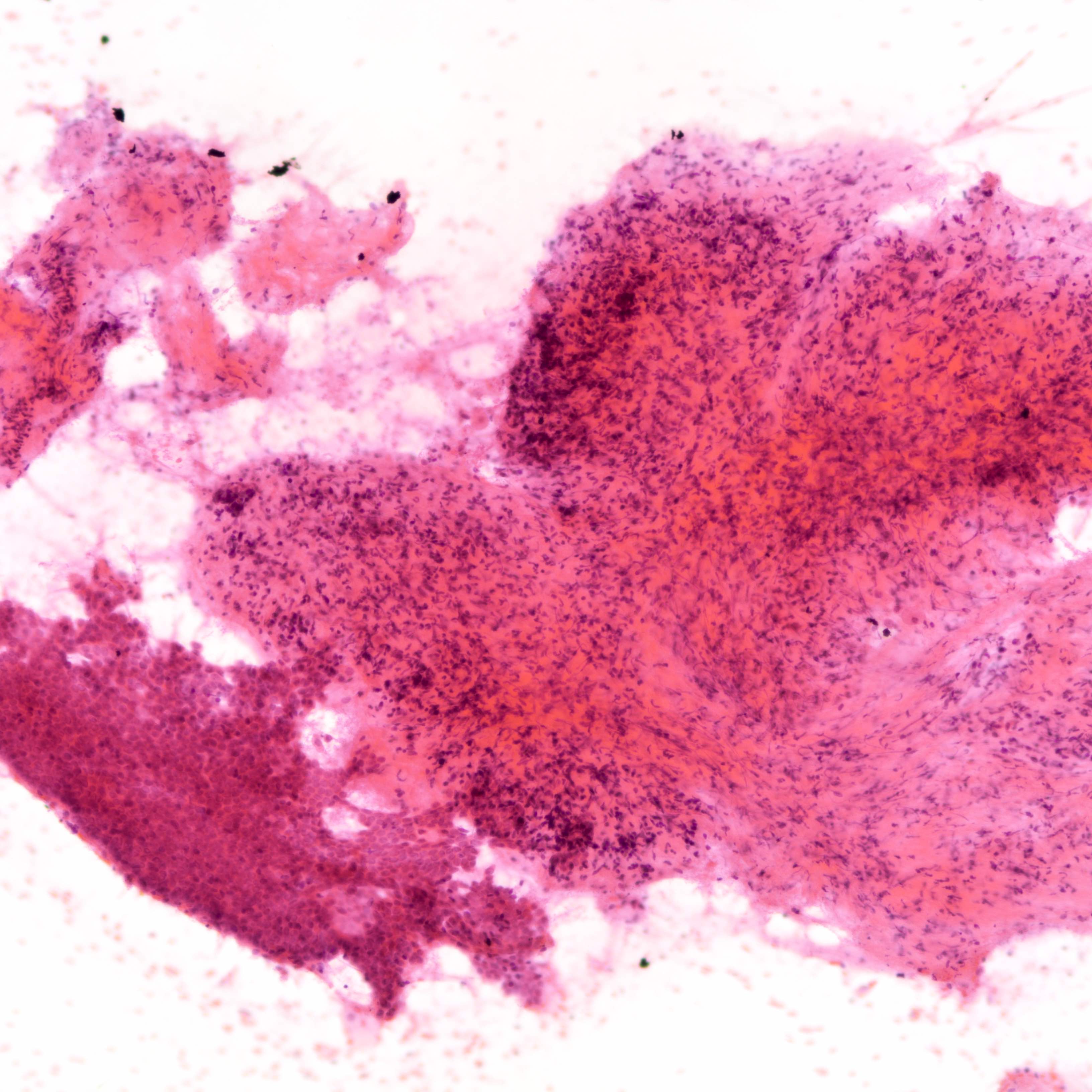
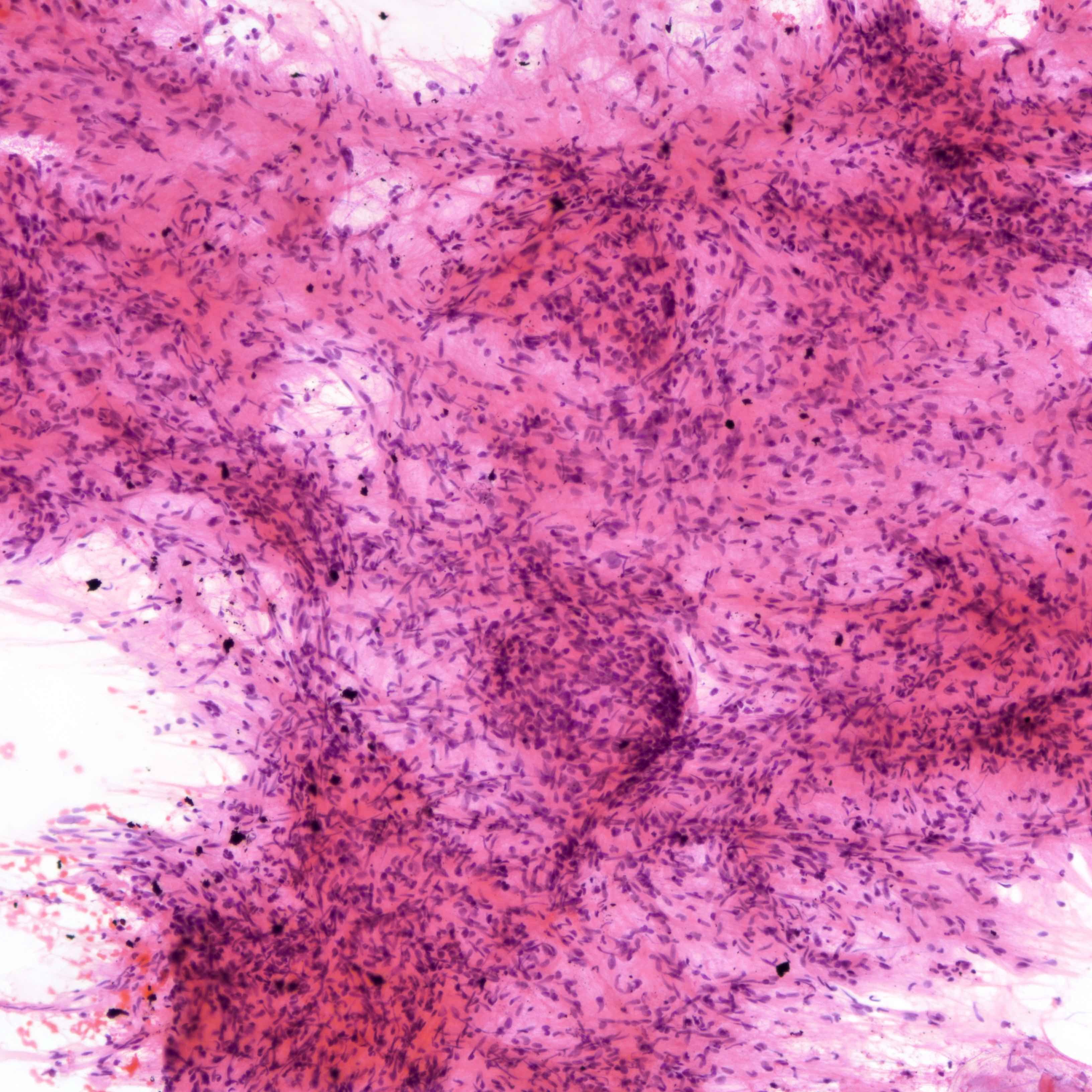
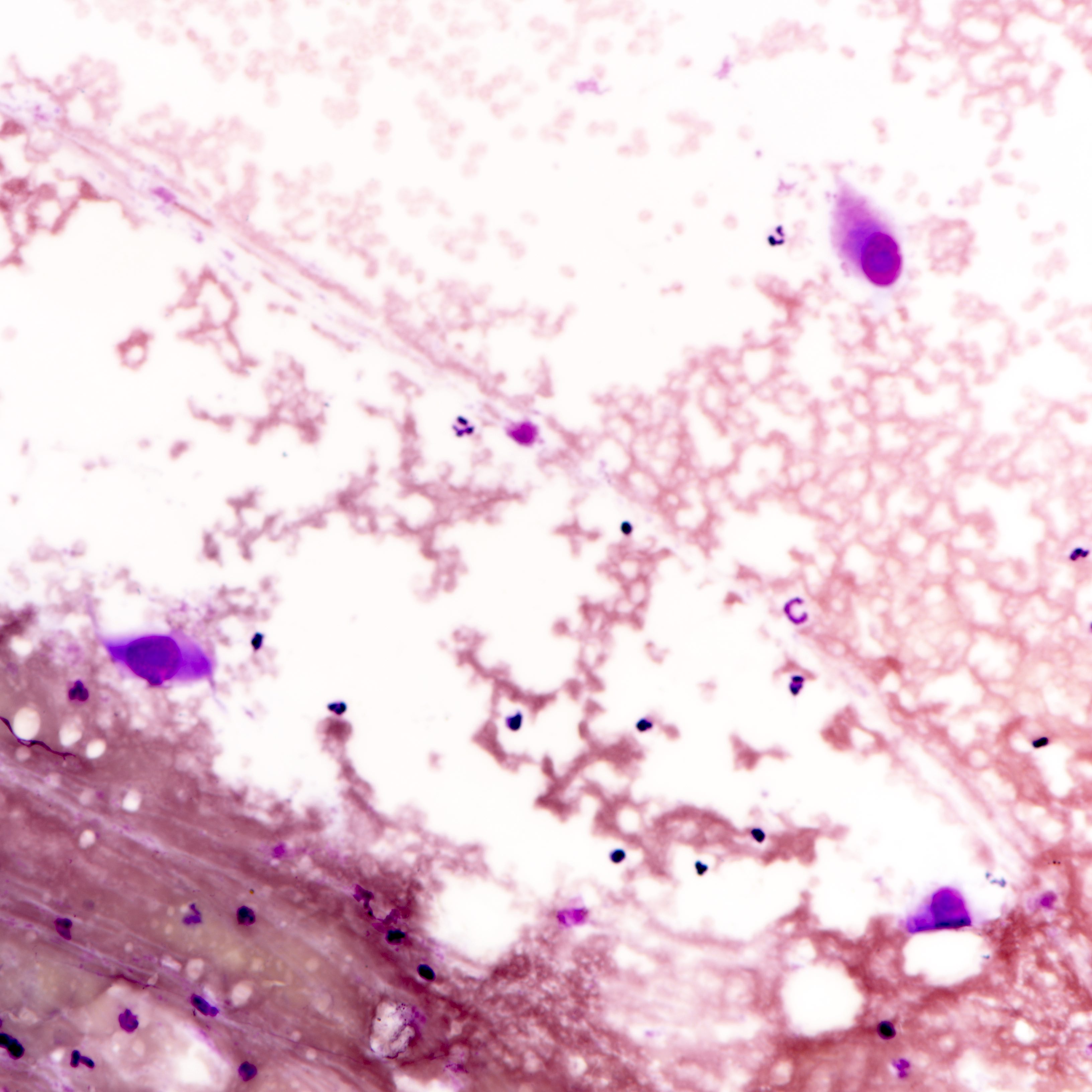
Cytology images
Contributed by Joshua J.X. Li, M.B.Ch.B. and Gary M. Tse, M.B.B.S.
Malignant phyllodes tumor
Positive stains
- Epithelial cells
- Cytokeratins, ER, PR, GCDFP-15
- Stromal cells
- Vimentin, CD34, BCL2, ER beta
- Increased KIT, p53 and Ki67 in phyllodes tumor of higher grade
- Cytokeratins, p63 (focal, can be confused with metaplastic carcinoma) (J Clin Pathol 2012;65:339, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1689)
Negative stains
- Stromal cells
- Cytokeratins, p40, p63 (except malignant phyllodes tumor)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Recurrent MED12 and RARA mutations in phyllodes tumors of all grades and fibroadenoma (Nat Genet 2015;47:1341)
- More frequent in benign phyllodes tumor
- Mutations in cancer driver genes (NF1, RB1, PIK3CA, EGFR, TP53 and ERBB4) exclusively seen in borderline and malignant phyllodes tumors (Nat Genet 2015;47:1341)
- TERT promoter mutation more common in borderline phyllodes tumor (Sci Rep 2018;8:3881)
- Chromosome abnormalities increase with grade (Mod Pathol 2007;20:435)
- Notably 1q gain and 13q loss
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, local excision:
- Benign phyllodes tumor
- Microscopic (optional): Sections show a stromal proliferation in a leaf-like pattern capped by benign ductal epithelium and intact intervening myoepithelial cell layer. The stromal proliferation is of low cellularity and the stromal cells show mild atypia. Stromal mitosis and stromal overgrowth are not prominent. The tumor is circumscribed. The tumor measures ____ in maximal dimension and is clear from (specify if < 1 cm ____) / involves the resection margins.
- Left breast, wide local excision:
- Borderline phyllodes tumor
- Microscopic (optional): Sections show a stromal proliferation featuring areas of leaf-like pattern and stromal expansion with moderate cellularity and stromal atypia. Scattered stromal mitotic figures are noted. The tumor is largely circumscribed with focally infiltrative borders. The tumor measures ____ in maximal dimension and is clear from (specify if < 1 cm ____) / involves the resection margins.
- Left breast, local excision:
- Malignant phyllodes tumor
- Microscopic (optional): Sections show a malignant spindle cell proliferation with diffusely increased cellularity, stromal overgrowth and marked stromal atypia. Stromal mitotic figures are frequent. The tumor shows infiltrative borders. The tumor measures ____ in maximal dimension and is clear from (specify if < 1 cm ____) / involves the resection margins.
Differential diagnosis
- Benign phyllodes tumor
- Fibroadenoma:
- Shows a combination of pericanalicular and intracanalicular epithelial patterns
- No phyllodal epithelial pattern
- Relatively uniform stromal cellularity, no subepithelial condensation
- Overlap in stromal cellularity and mitosis in cellular and juvenile fibroadenomas
- No significant stromal expansion
- Fibromatosis:
- Lacks epithelial component
- Spindle cells arranged in long sweeping fascicles
- CD34 negative (Histopathology 1994;25:469)
- Nuclear localization of beta catenin
- Fibroadenoma:
- Borderline / malignant phyllodes tumor
- Biphasic metaplastic carcinoma:
- Epithelial component often harbors in situ or invasive carcinomatous components
- Malignant heterologous element can be present
- Well differentiated liposarcoma (MDM2+) may histologically resemble heterologous liposarcomatous elements (MDM2-) in malignant phyllodes tumors but MDM2 staining is distinguishing
- Monophasic metaplastic carcinoma:
- Lacks epithelial components
- Malignant heterologous element can be present
- Cytokeratins, p63 positive
- Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma:
- Lacks marked atypia and stromal giant cells
- Cytokeratins, p63 positive
- Lacks nuclear beta catenin expression
- Primary or metastatic sarcomas:
- Very low incidence relative to malignant heterologous differentiation in phyllodes tumor and metaplastic carcinoma; correlate with clinical history
- Lacks epithelial component
- Immunohistochemistry not helpful in differentiation
- Biphasic metaplastic carcinoma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 36 year old woman presents with a self palpated breast mass. Imaging shows a rounded nodule; excision with narrow negative margins was performed. Stromal atypia and mitosis are absent. What is the most suitable follow up management for the patient?
- Adjuvant chemotherapy
- Hormonal therapy
- Local radiotherapy
- Lymph node dissection
- Observation
Board review style answer #1
E. Observation. Benign phyllodes tumor is not associated with mortality or metastasis; additional therapy is not indicated.
Comment Here
Reference: Phyllodes tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Phyllodes tumor
Board review style question #2
Which of the following features is diagnostic of malignant phyllodes tumor?
- Focus of infiltrative tumor border
- Involvement by low grade ductal carcinoma in situ
- Multinucleated stromal giant cells
- Small focus of osteosarcomatous differentiation
- Stromal overgrowth
Board review style answer #2
D. Small focus of osteosarcomatous differentiation. Borderline phyllodes tumor allows for, albeit a lesser degree compared to malignant phyllodes tumor, stromal overgrowth and an infiltrative tumor border. Multinucleated stromal giant cells can be seen in all grades of phyllodes tumor and does not impact histologic grading. The epithelial component of phyllodes tumor can show metaplasia, hyperplasia, in situ or invasive malignant changes, which may impact prognosis but does not affect histologic grading. Presence of malignant heterologous differentiation directly upgrades a phyllodes tumor into the malignant category.
Comment Here
Reference: Phyllodes tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Phyllodes tumor
Board review style question #3
Which of the following features can be seen in malignant phyllodes tumors but not metaplastic carcinomas?
- Bizarre anaplastic tumor cells
- Cytokeratin expression
- MED12 mutation
- p53 expression
- Rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation
Board review style answer #3
C. MED12 mutation. MED12 and RARA are frequent mutations in fibroepithelial lesions of the breast and are believed to be involved in the tumorigenesis of fibroepithelial lesions. MED12 and RARA mutations are absent in metaplastic carcinomas (Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:3859). p53 expression and TP53 mutation are detected in both malignant phyllodes tumor and metaplastic carcinomas. Aberrant cytokeratin expression, albeit patchy, can be seen in malignant phyllodes tumor. Bizarre tumor cells and malignant heterologous elements can be seen in both entities.
Comment Here
Reference: Phyllodes tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Phyllodes tumor