Table of Contents
Definition / general | Prognostic factors | Diagrams / tables | Uses by pathologists | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Additional referencesCite this page: Pernick N. CD95. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd95.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Also called Fas, Apo-1, TNF receptor superfamily member 6, TNFRSF6
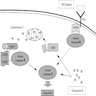
- Cell surface membrane receptor that activates apoptotic pathways when bound by Fas ligand (FasL, CD178)
- Extrinsic pathway: activation leads to assembly of a death inducing signaling complex (DISC) consisting of CD95, the Fas-associated death domain (FADD) adapter protein, the initiator caspase-8 (previously called FLICE or MACH) and cellular FLICE inhibitory protein (cFLIP), a regulatory protein that can block or promote autoproteolytic conversion of pro-caspase-8 to caspase-8 within the DISC; caspase 8 activates a cascade of caspases that ultimately activates caspase 3, which mediates apoptosis
- Intrinsic pathway: involves release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, which complexes with apoptosis inducing factor 1, procaspase 9 and ATP, leading to caspase 9 activation, which activates caspase 3
- Fas-FasL system mediates extra-thymic self-tolerance (FasL+ cells induce apoptosis in infiltrating Fas+ lymphocytes in testis, cornea), T cell mediated cytotoxicity, apoptosis during development, halting of immune response
- Defects in Fas-Fas ligand pathway (usually Fas but occasionally FasL germline mutations) cause autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, a rare childhood disorder associated with B cell lymphomas, classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma (Leuk Lymphoma 2004;45:423)
- CD95 downregulation may reduce CD4+ T cells in HIV (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:28)
- May be involved in clearance of benign ovarian epithelial inclusion cysts; derangement in pathway may cause ovarian surface epithelial carcinomas (Hum Pathol 2005;36:971)
- Polymorphisms in Fas or FasL: associated with increased risk of autoimmune hepatitis (Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100:1322), increased risk of type II diabetes (Genes Immun 2006;7:316); Fas -670 AG genotype is associated with increased risk of preterm premature rupture of membranes (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193:1132); Fas -670 AA genotype is associated with reduced liver graft survival (Tissue Antigens 2006;67:117); FAS -1377AA genotype is associated with increased risk of lung cancer (J Med Genet 2005;42:479)
Prognostic factors
- Reduced Fas expression is a poor prognostic factor for breast carcinoma (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:1360), colorectal carcinoma (Carcinogenesis 2006;27:1113), retinoblastoma (Ocul Immunol Inflamm 2003;11:107) and urothelial carcinoma (Br J Cancer 2005;93:544), but reduced Fas expression is a favorable prognostic factor in primary nodal diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Am J Hematol 2006;81:307) and subcutaneous panniculitis-like lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2004;121:408)
Uses by pathologists
- Prognostic factors (above)
Positive staining - normal
- Activated B cells, activated T cells (initially extra but nonfunctional Fas), resting T cells (low levels), numerous epithelium and connective tissue
Positive staining - disease
- Barrett’s esophagus (Hum Pathol 2002;33:686)
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (thyroid epithelial cells)
- Ovarian cystadenoma and serous borderline tumors
- Reed-Sternberg cells in classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:388)
Negative staining
- Invasive ovarian carcinoma
Additional references