Table of Contents
General | TSH receptor antibodies | Thyroperoxidase antibodies | Thyroglobulin antibodies | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Srichomkwun P. Thyroid autoantibodies. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/chemistrythyroglobulnab.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
General
- Antibody testing for evaluation of autoimmune thyroid disorders:
- TSH receptor antibodies (including thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin and thyrotropin binding inhibiting immunoglobulin)
- Thyroperoxidase antibody
- Thyroglobulin antibody
TSH receptor antibodies
Definition / general
Clinical features
Laboratory
Diagrams
Images hosted on other servers:
- TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) receptor antibodies (TRAbs) may have different effects on thyroid function
- Stimulating antibodies (TSAbs) cause hyperthyroidism
- Blocking antibodies (TBAbs) cause hypothyroidism
- Neutral TRAbs have no effect
Clinical features
- Clinical utility (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:2247):
- Confirm diagnosis of Graves disease (not routine use)
- Diagnosis of euthyroid Graves orbitopathy
- Predict remission before withdrawing antithyroid drug
- Pregnant women with previous Graves disease: determine risk of fetal / neonatal hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism (depends on functional type of TRAbs)
Laboratory
- Methodology:
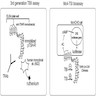
- 2 methods for measuring TRAbs (Endocr Pract 2020;26:97) (see diagram):
- Conventional immunoassay, binding assay or thyrotropin binding inhibiting immunoglobulins (TBII) assay:
- Advantage: international standardization, commercial automated immunoassays
- Disadvantage: does not differentiate the functional type of the antibodies
- Bioassay:
- Advantage: discriminates the functional type (TSAbs or TBAbs), preferred use in prediction of fetal / neonatal risk for hypothyroidism in pregnant women with active or treated autoimmune thyroid disease
- Disadvantage: more time consuming, requires experienced laboratory technician and available only in some centers
- Conventional immunoassay, binding assay or thyrotropin binding inhibiting immunoglobulins (TBII) assay:
- 2 methods for measuring TRAbs (Endocr Pract 2020;26:97) (see diagram):
- Third generation TBII assays have a sensitivity of over 97.2% and a specificity of over 98.3% for the diagnosis of Graves disease versus other causes of hyperthyroidism (Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2011;75:127)
- Reference range of TBII assay:
- Elecsys (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany): normal cutoff < 1.75 IU/L
Diagrams
Images hosted on other servers:
Thyroperoxidase antibodies
Definition / general
Clinical features
Laboratory
- Thyroperoxidase antibodies (TPOAbs) were formerly known as microsomal antibodies, which is still used in literature
- Almost all Hashimoto thyroiditis patients and nearly 75% of Graves disease patients have detectable TPOAbs (Horm Metab Res 2019;51:765)
- Moderately increased levels of TPOAbs may be found in 5 - 20% of the normal population and patients with nonthyroid autoimmune diseases, such as pernicious anemia, type I diabetes or other autoimmune disease (Front Immunol 2017;8:521)
Clinical features
- Clinical utility:
- Diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease
- Predict the likelihood of progression to permanent overt hypothyroidism in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (N Engl J Med 2017;376:2556)
- Predict risk of pregnancy loss in high risk patients and determine the need for thyroxine replacement therapy during pregnancy (Thyroid 2017;27:315)
Laboratory
- Methodology:
- Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA), chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) (Endocr J 2017;64:955)
- Reference range:
- Varies between different immunoassays due to TPO antigen preparations used to coat solid phase (Endocr J 2017;64:955)
- IMMULITE 2000 (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, NY, USA): normal cutoff < 35 IU/mL
Thyroglobulin antibodies
Definition / general
Clinical features
Laboratory
- Thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAbs) were formerly known as colloid antigen
- Marker of autoimmune thyroid disease (along with TPOAbs)
- TgAbs are detectable in 10% of the general population and 20% of thyroid cancer patients (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:5566, J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:1121)
- TgAbs are also detectable in nonthyroid autoimmune diseases, such as pernicious anemia, type I diabetes or other autoimmune diseases (Front Immunol 2017;8:521)
- TgAbs interfere with Tg measurement causing falsely low or undetectable Tg immunometric assay (IMA) values (Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;27:701)
Clinical features
- Clinical utility:
- Diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease (together with TPOAbs)
- Surrogate marker of differentiated thyroid cancer useful in postoperative follow up protocols (routine use with serum Tg levels) (Thyroid 2016;26:1)
Laboratory
- Methodology:
- Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay, chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (Endocr J 2017;64:955)
- Reference range:
- Varies between different immunoassays due to Tg antigen preparations used to coat solid phase (Endocr J 2017;64:955)
- IMMULITE 2000 (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, NY, USA): normal cutoff < 40 IU/mL
Board review style question #1
A 30 year old woman presented with bilateral proptosis. She denied a history of palpitation, perspiration or weight loss, clinically consistent with euthyroidism. Physical examination revealed mild exophthalmos and diffuse thyroid enlargement. Thyroid function test was normal. What is the best choice for the next laboratory test in this patient?
- IGF1 receptor antibodies
- Microsomal antibodies
- Thyroglobulin antibodies
- Thyroperoxidase antibodies
- TSH receptor antibodies
Board review style answer #1
E. TSH receptor antibodies. The patient presented with symptoms of euthyroid Graves orbitopathy, therefore TSH receptor antibodies should be performed to definitively diagnose this condition.
Comment Here
Reference: Thyroglobulin, TSH receptor and thyroperoxidase antibodies
Comment Here
Reference: Thyroglobulin, TSH receptor and thyroperoxidase antibodies