Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ahrendsen JT. Gangliocytoma & ganglioglioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorganglioncelltumor.html. Accessed May 9th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Uncommon, well differentiated, slow growing glioneuronal tumors composed predominantly of neoplastic mature ganglion-like cells (gangliocytoma) or a mixture of neoplastic ganglion-like cells and atypical glial cells (ganglioglioma)
Essential features
- Ganglioglioma and gangliocytoma are considered discreet tumor entities by the 2021 WHO classification of CNS tumors
- Neoplastic ganglion cells often display dysplastic / dysmorphic features
- Characterized by molecular alterations resulting in activation of the MAPK pathway (BRAF V600E is most common)
- Commonly associated with epilepsy
ICD coding
- ICD-O:
- ICD-11:
- 2A00.21 & XH5FJ3 - mixed neuronal - glial tumors & ganglioglioma, NOS
- 2A00.21 & XH6KA6 - mixed neuronal - glial tumors & gangliocytoma
Epidemiology
- Ganglioglioma:
- Incidence: 0.186 cases per 100,000 population worldwide (J Neurooncol 2017;131:525)
- ~2% of all primary intracranial tumors (Childs Nerv Syst 2016;32:1839, Cancer 2004;101:146)
- Predilection for children and young adults (majority are < 20 years old; median age is 12 years) but can occasionally be seen in older patients (N Engl J Med 2017;377:1648)
- Gangliocytoma:
- Generally similar to that of ganglioglioma
- Relative incidence in epilepsy related surgical resections is 1 - 3% (Brain Pathol 2012;22:350, N Engl J Med 2017;377:1648)
Sites
- Can occur throughout the CNS; temporal lobe is most common (~70%) (Acta Neuropathol 1994;88:166, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002;61:575)
Pathophysiology
- Ganglioglioma:
- Results from genetic alterations that lead to activation of the MAPK pathway and therefore cause increased cell proliferation
- Gangliocytoma:
- Data not available but likely closely resembles that of ganglioglioma
- References: Acta Neuropathol Commun 2020;8:30, Folia Neuropathol 2013;51:283
Etiology
- No known risk factors or environmental exposures for ganglioglioma or gangliocytoma
Clinical features
- Symptoms are related to the location of the tumor (N Engl J Med 2017;377:1648)
- Tumors in the cerebrum, especially temporal lobe, are associated with seizures / epilepsy (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002;61:575)
- Vast majority are sporadic; small proportion are associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008;67:240, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2018;6:47)
Diagnosis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain
- Stereotactic biopsy can be performed, especially in sites unamenable to surgical excision
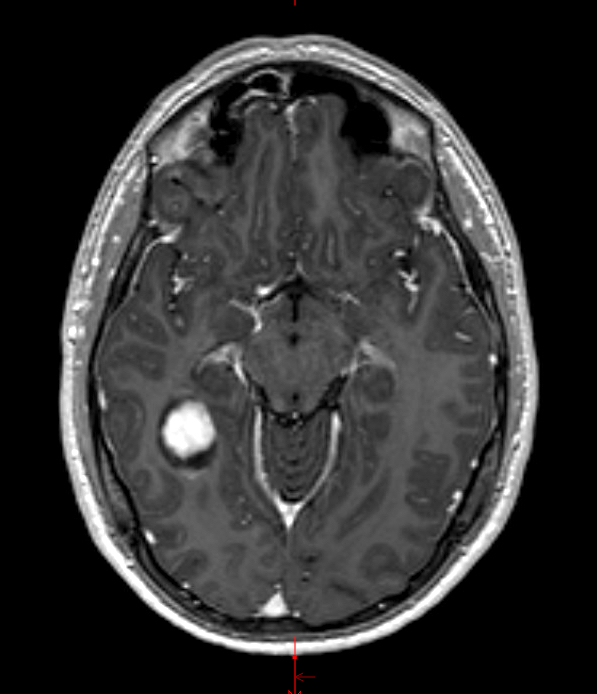
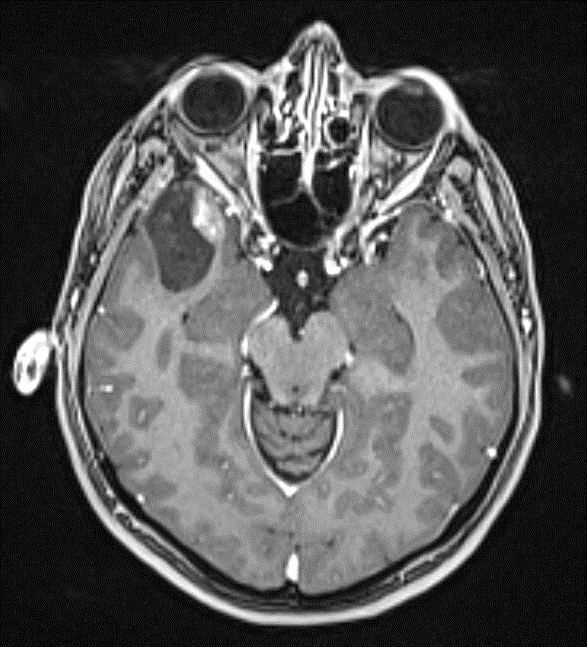
Radiology description
- Circumscribed, cystic mass with enhancing mural nodule
- Classically, well delineated, T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense cyst with enhancing mural nodule (Radiographics 2002;22:1177)
- Variable calcifications and enhancement
Prognostic factors
- Ganglioglioma:
- Low grade tumor with excellent overall prognosis (15 year overall survival is 83 - 94%) (J Neurosurg 2012;117:825)
- Complete surgical excision is best prognostic factor (Neuro Oncol 2014;16:409)
- Potential clinical benefit of RAF and MEK inhibitors is still under investigation (Neurology 2021;97:e673, Cancer Control 2021;28:10732748211040013)
- Although rare, the co-occurrence of BRAF V600E and CDKN2A / CDKN2B homozygous deletion or midline tumors with concurrent BRAF V600E and H3 K27M mutation seem to have worse outcomes (J Clin Oncol 2017;35:2934, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2018;6:47, Cancer Cell 2020;37:569, Brain Pathol 2018;28:103)
- See Microscopic (histologic) description for discussion about anaplastic ganglioglioma
- Gangliocytoma:
- Benign tumors with excellent long term survival
- Specific prognostic factors have not been identified
Case reports
- 3 year old boy with progressive quadriparesis, gait disturbance and sphincter deficit (Prague Med Rep 2018;119:122)
- 16 year old girl with worsening vision (Surg Neurol Int 2020;11:392)
- 22 year old man with spinal cord lesion resected 9 years prior (Front Oncol 2019;9:177)
- 43 year old woman with chronic headaches (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e11583)
Treatment
- Complete surgical resection, where possible (J Neurosurg 2012;117:825)
- Progressive, recurrent or refractory cases may benefit from RAF or MEK inhibitor treatment (J Clin Oncol 2013;31:e159, J Transl Med 2014;12:356)
Gross description
- Well demarcated, variably solid and cystic mass forming lesion
- Lacks areas of hemorrhage and necrosis
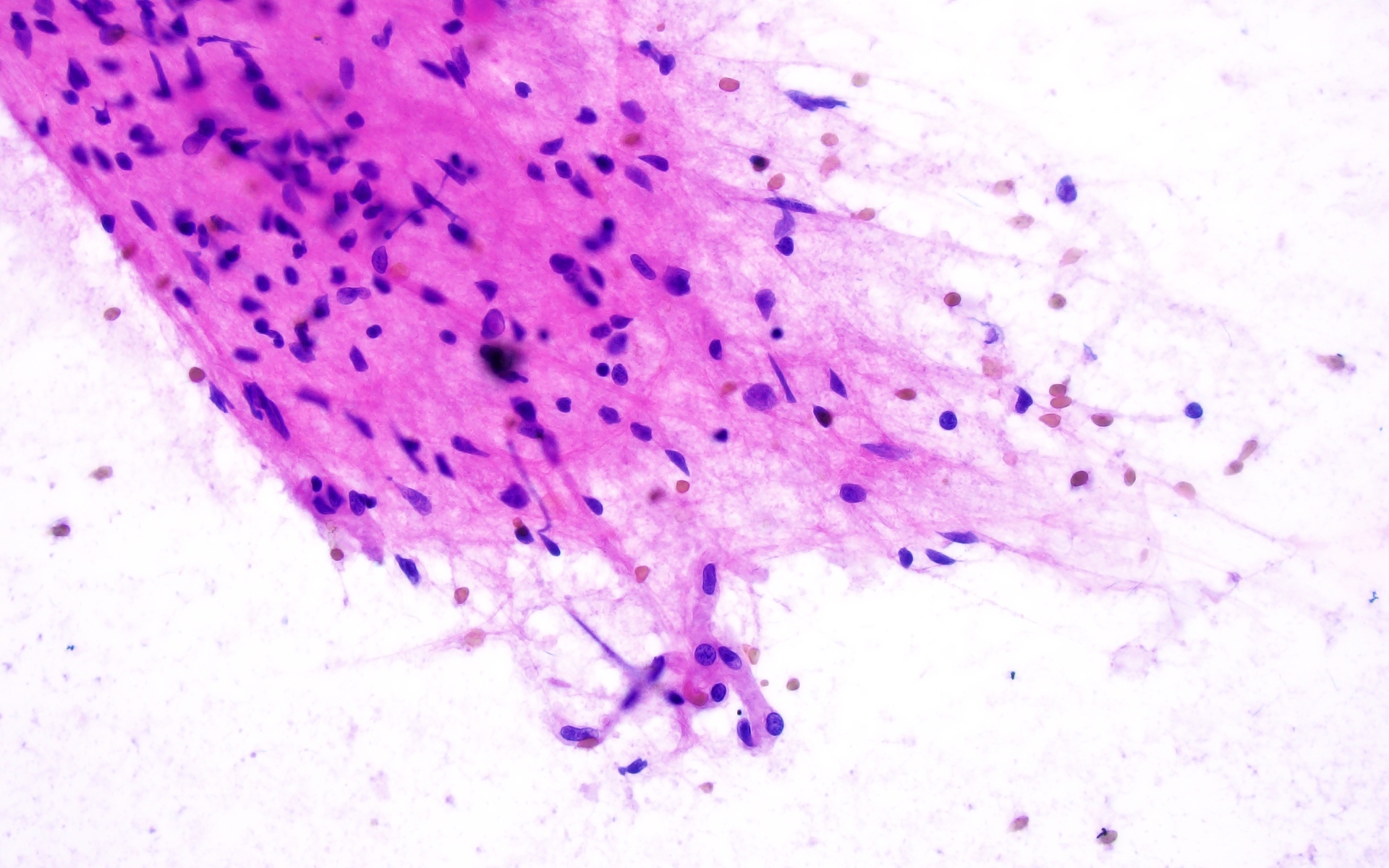
Frozen section description
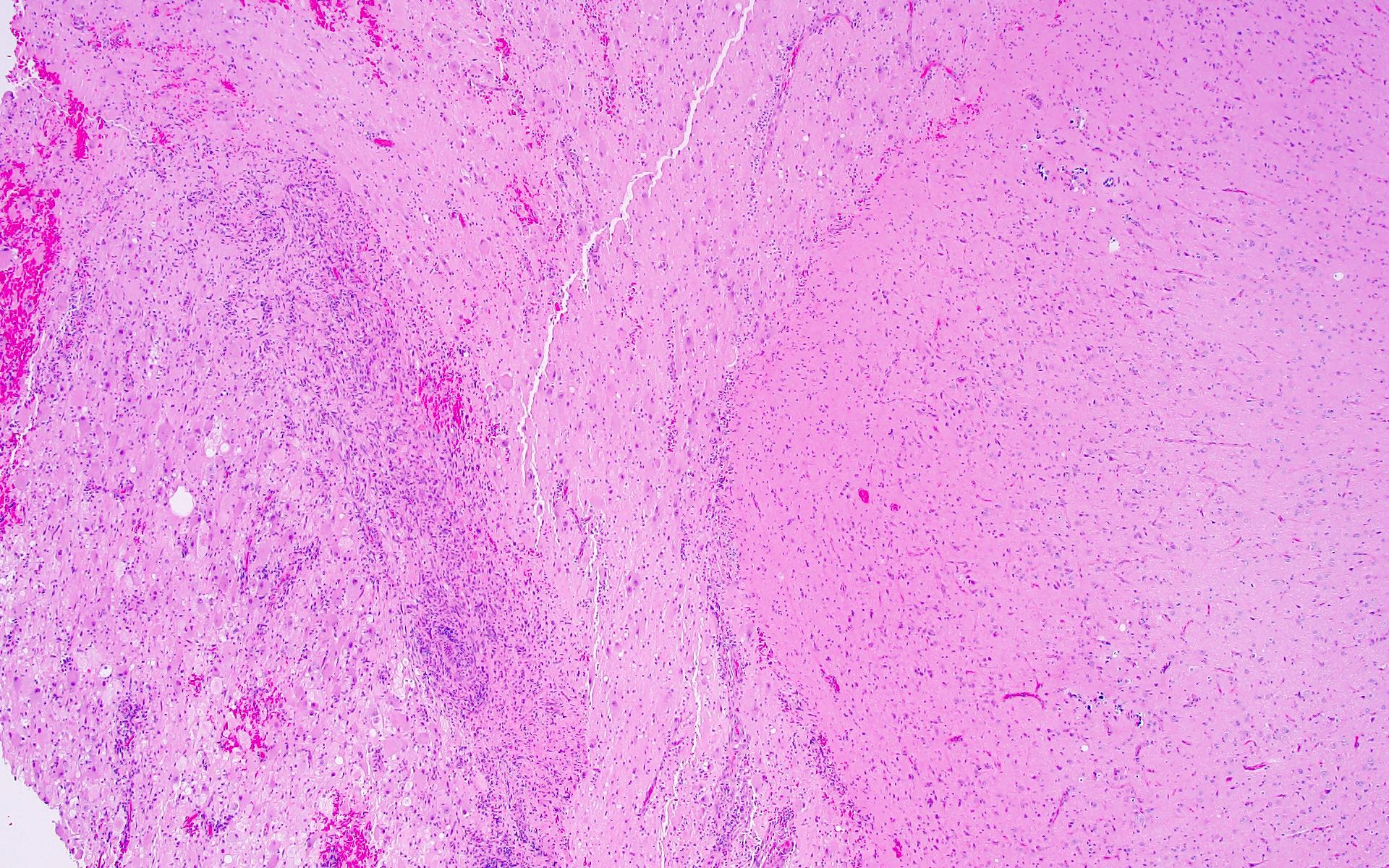
- Well demarcated mass but can show brain infiltration at the tumor edge
- Admixture of neuron-like cells and atypical glial cells (ganglioglioma) or predominantly neuron-like cells (gangliocytoma)
- Variable microcalcifications, perivascular lymphocytes, eosinophilic granular bodies
- Reference: Acta Cytol 2022;66:142
Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images
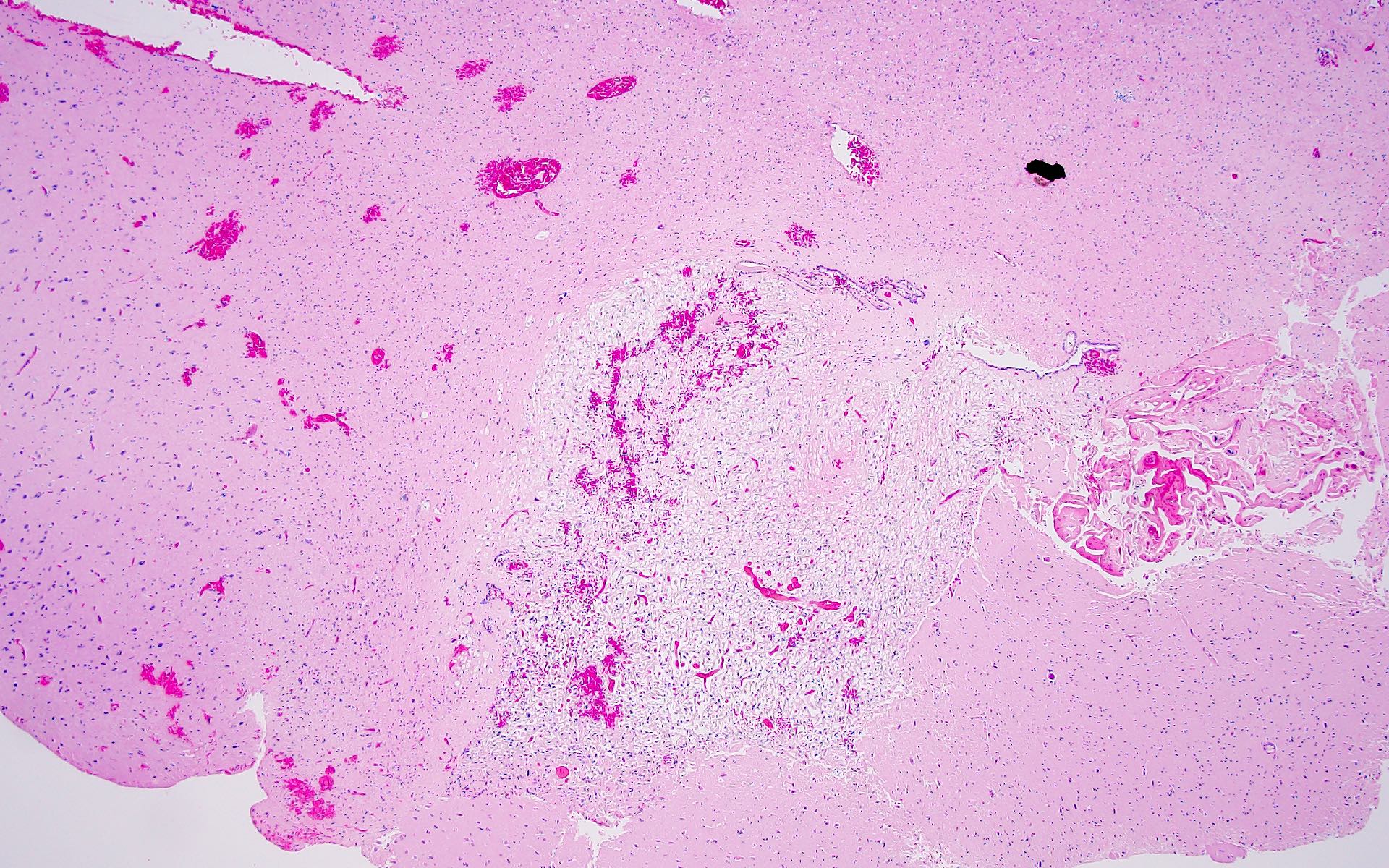
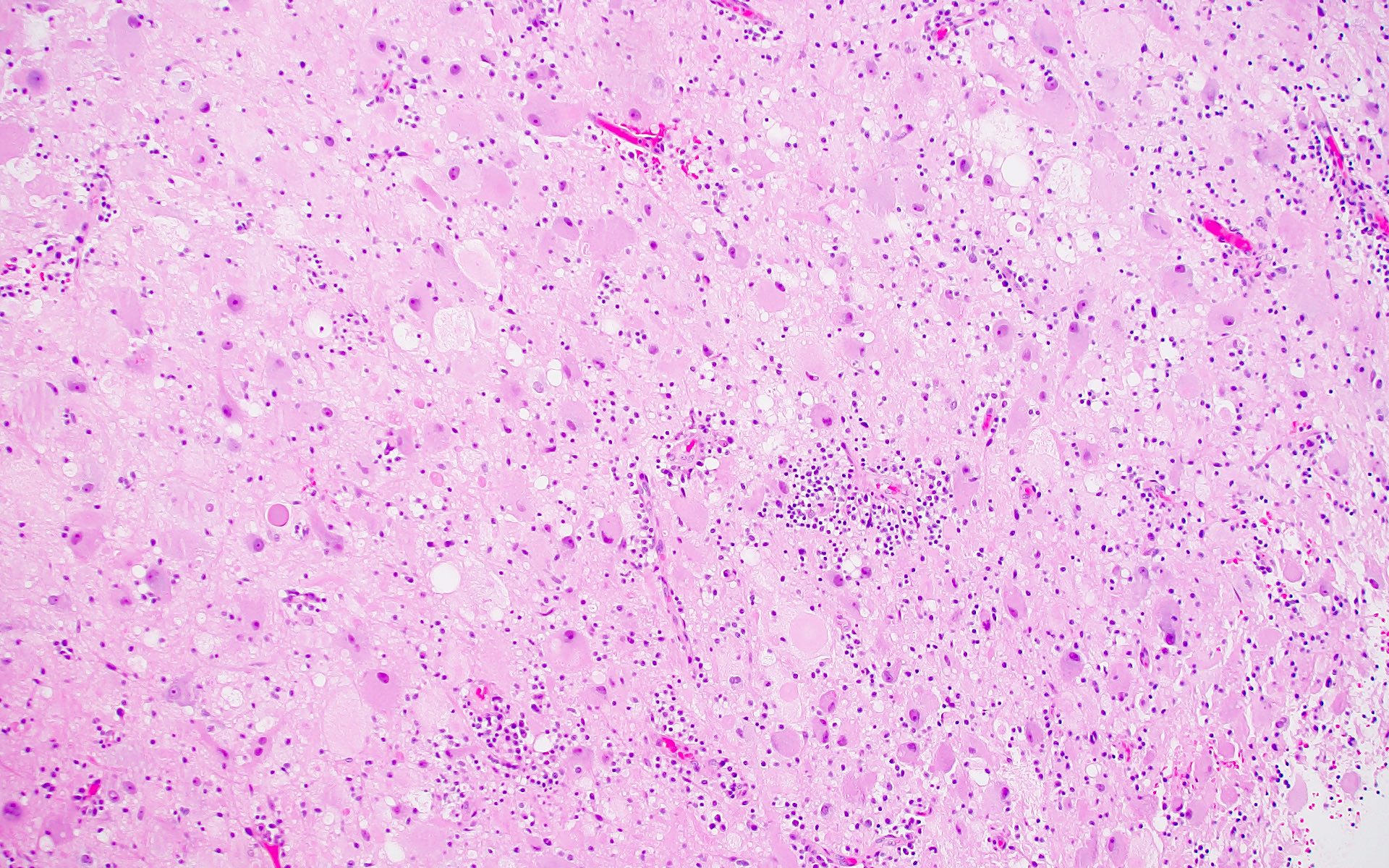
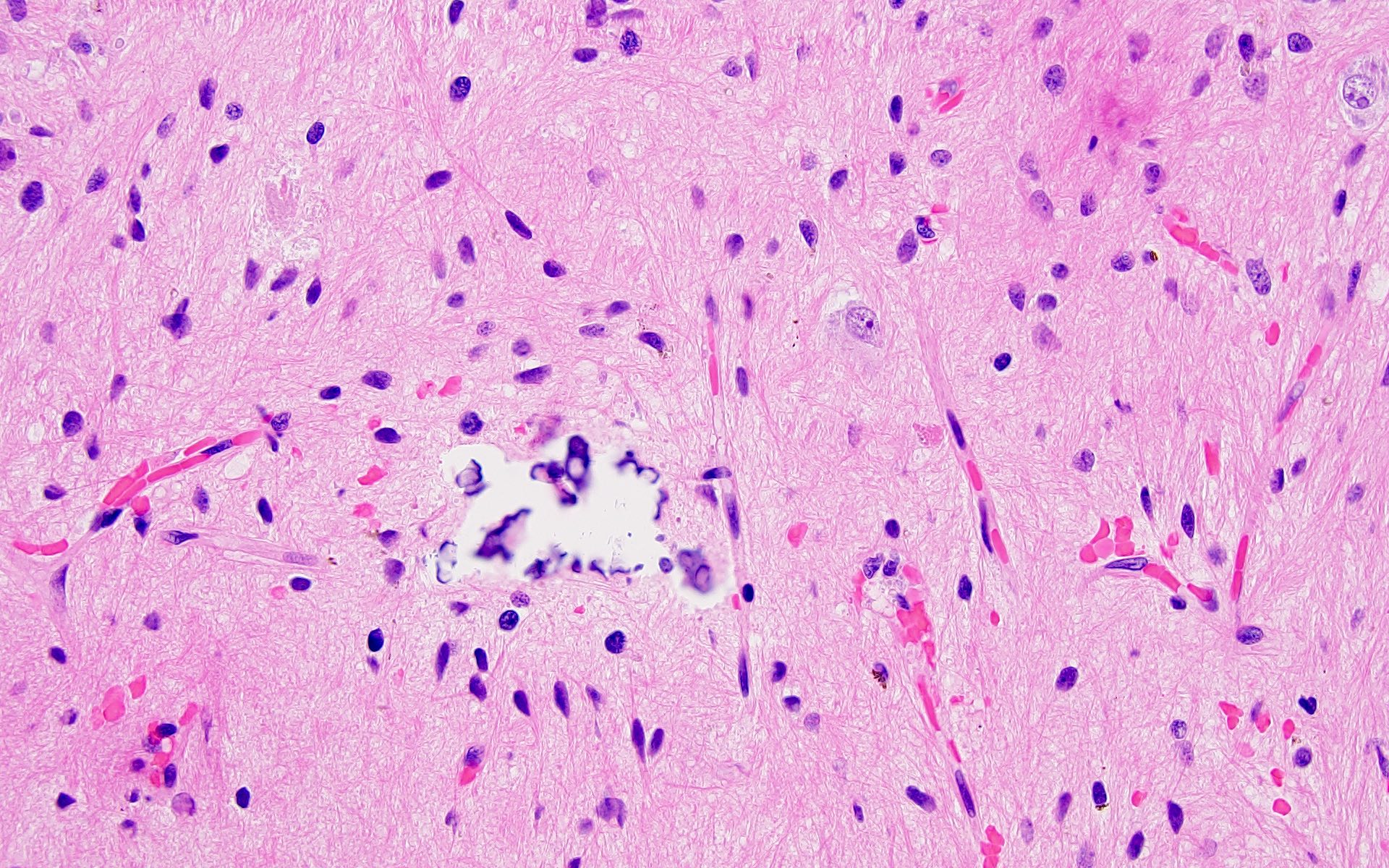
Microscopic (histologic) description
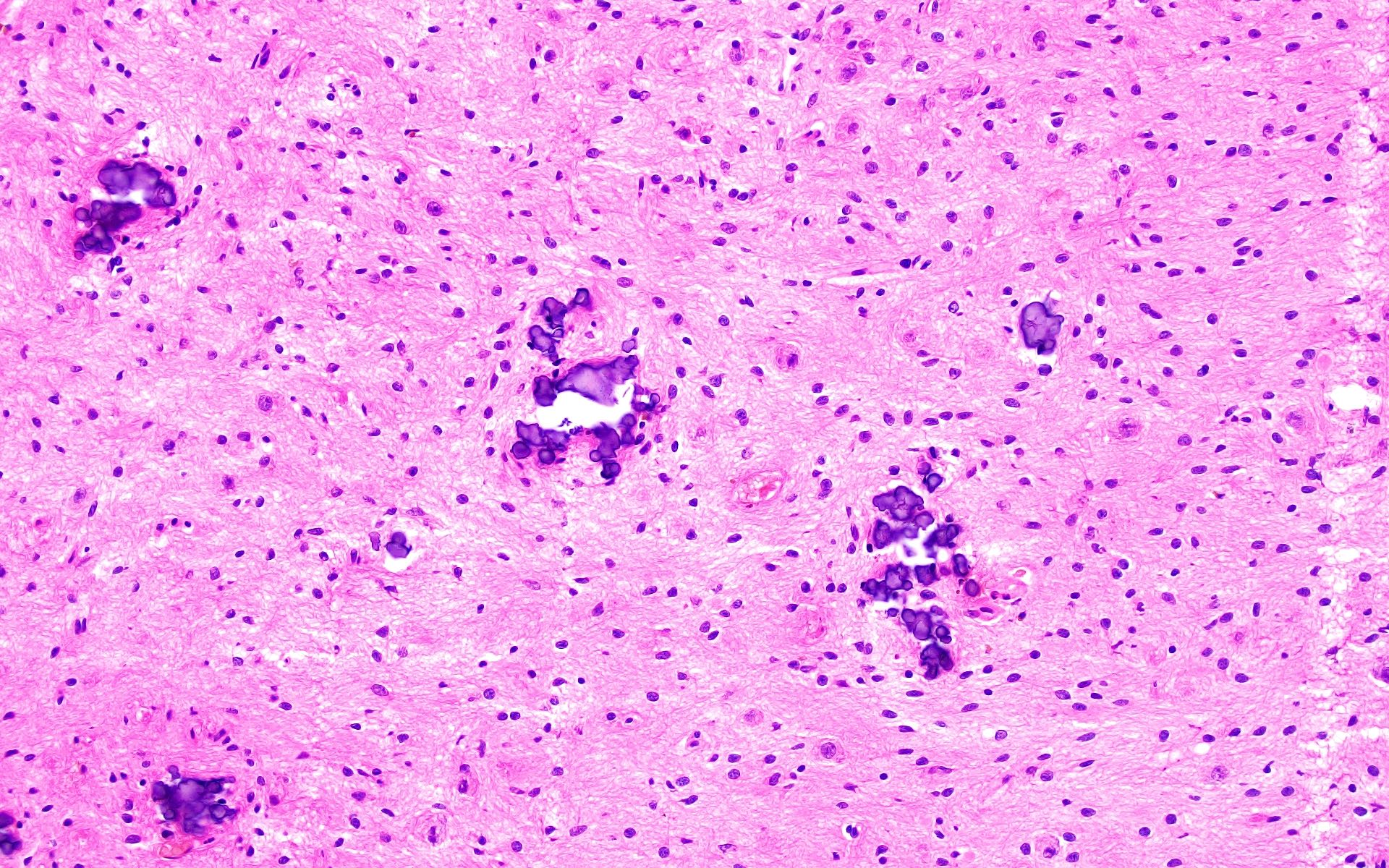
- Ganglioglioma:
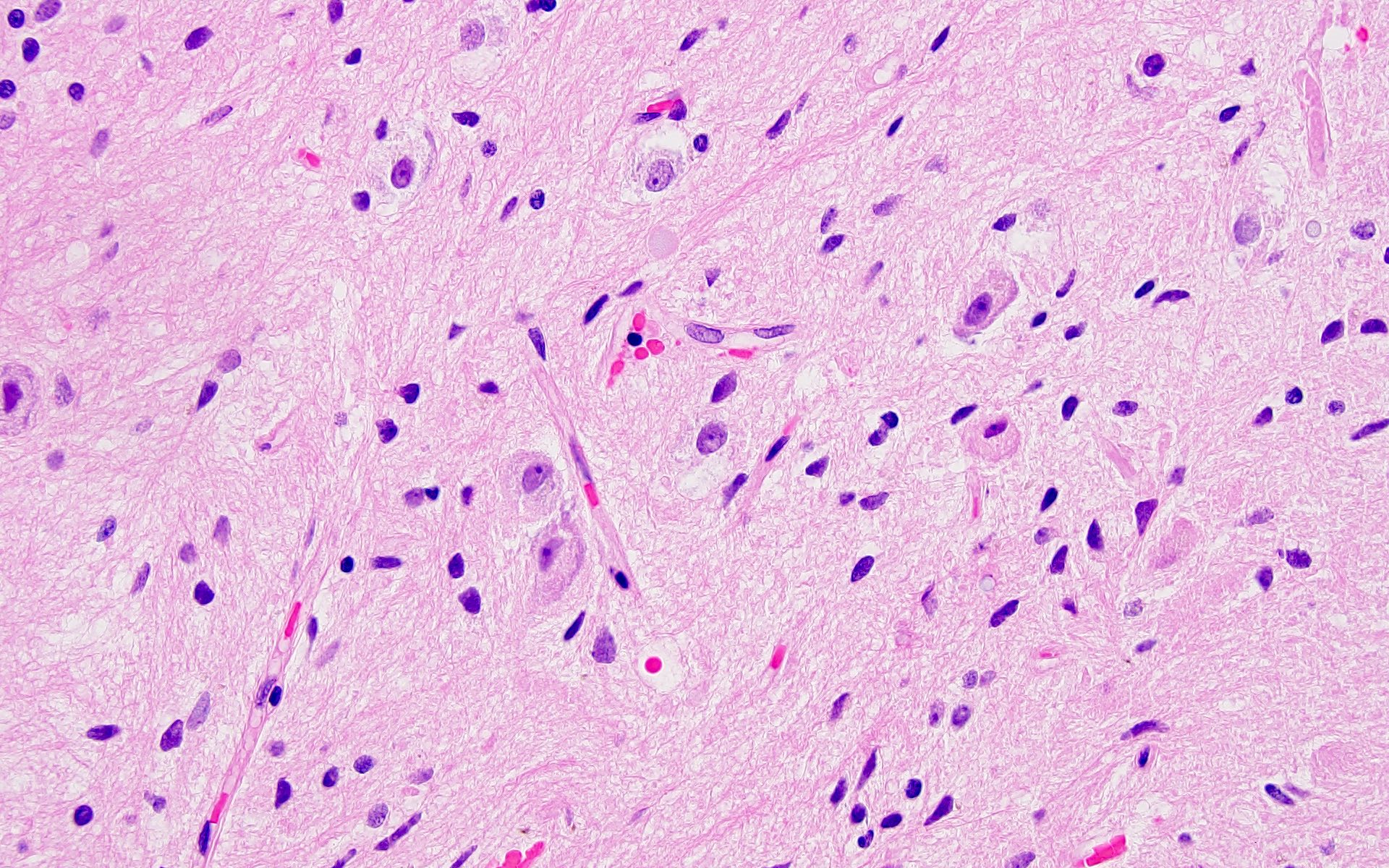
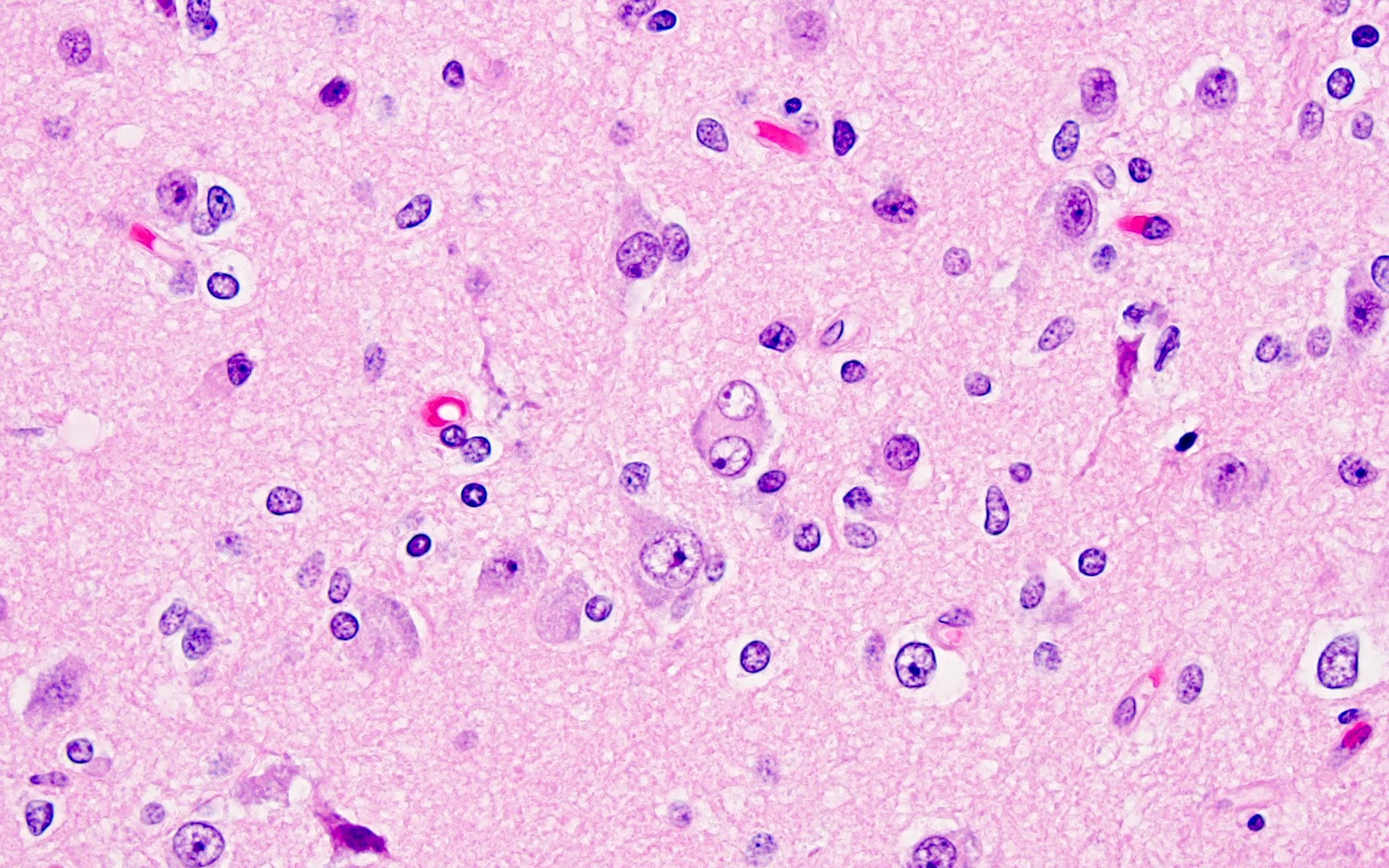
- Biphasic tumor with variable mixture of mature appearing ganglion-like cells and atypical glial cells
- Ganglion-like cells demonstrate dysmorphic features:
- Binucleation
- Neuron clustering (kissing neurons)
- Cytomegaly with ballooning cytoplasm
- Peripheral accumulation of Nissl substance
- Lack of organized cytoarchitecture (Acta Neuropathol 1994;88:166)
- Atypical glial cells are hyperchromatic, moderately enlarged and resemble those of fibrillary astrocytomas, pilocytic astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma (Hum Pathol 2016;49:107, Clin Interv Aging 2014;9:1981)
- Eosinophilic granular bodies more common than Rosenthal fibers (Acta Neuropathol 1994;88:166)
- Other common findings:
- Dystrophic calcifications
- Perivascular lymphoid infiltrates
- Prominent capillary network
- Low to absent mitotic activity (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002;61:575)
- Compact growth but microscopic infiltration can be seen along the tumor edge (Acta Neuropathol 2014;128:39, Nat Rev Neurol 2016;12:732)
- Rare cases with anaplastic features (anaplastic ganglioglioma) have been reported:
- Tumors with ganglioglioma-like histology and increased mitoses, microvascular proliferation, necrosis
- Many reported cases lack molecular analyses to exclude other high grade gliomas (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2016;75:971, Neuro Oncol 2017;19:678)
- Anaplastic ganglioglioma is a term that should be used with caution, especially if complete molecular characterization is not available (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2022;48:e12847)
- Gangliocytoma:
- Generally similar to that of ganglioglioma except lacking atypical neoplastic glial cells
- Composed almost entirely of large, dysmorphic ganglion cells (as described above), often arranged in irregular clusters
Microscopic (histologic) images
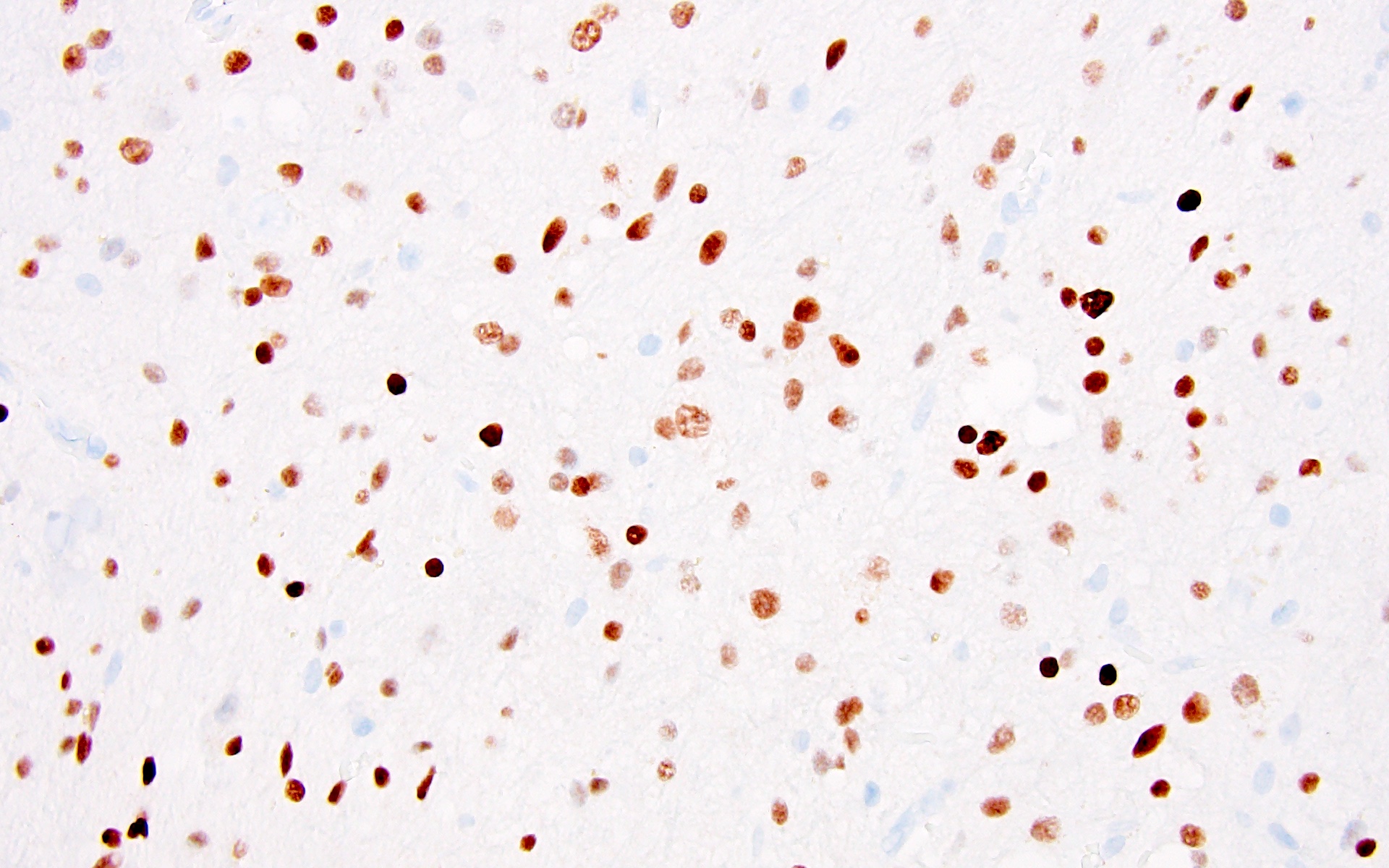
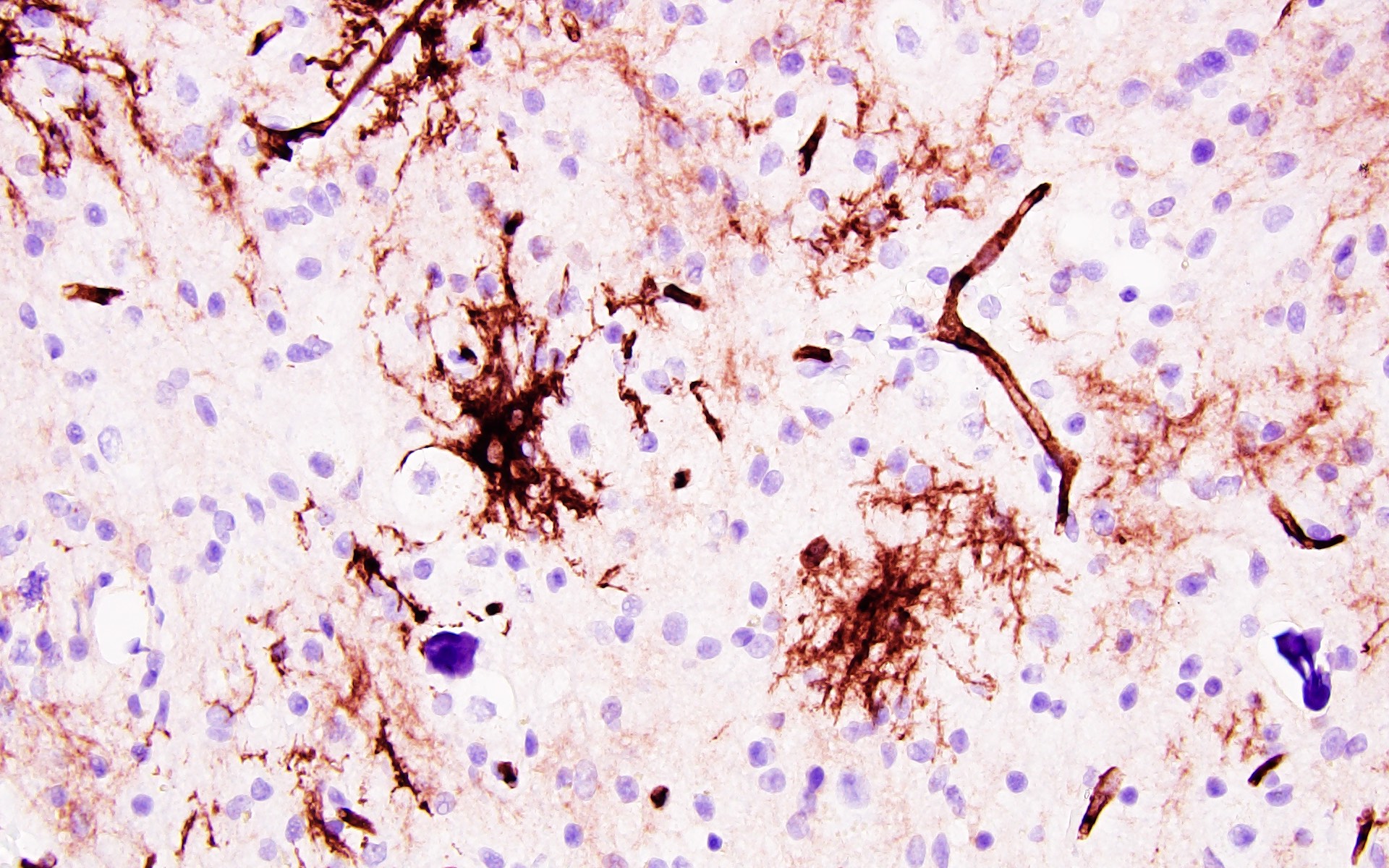
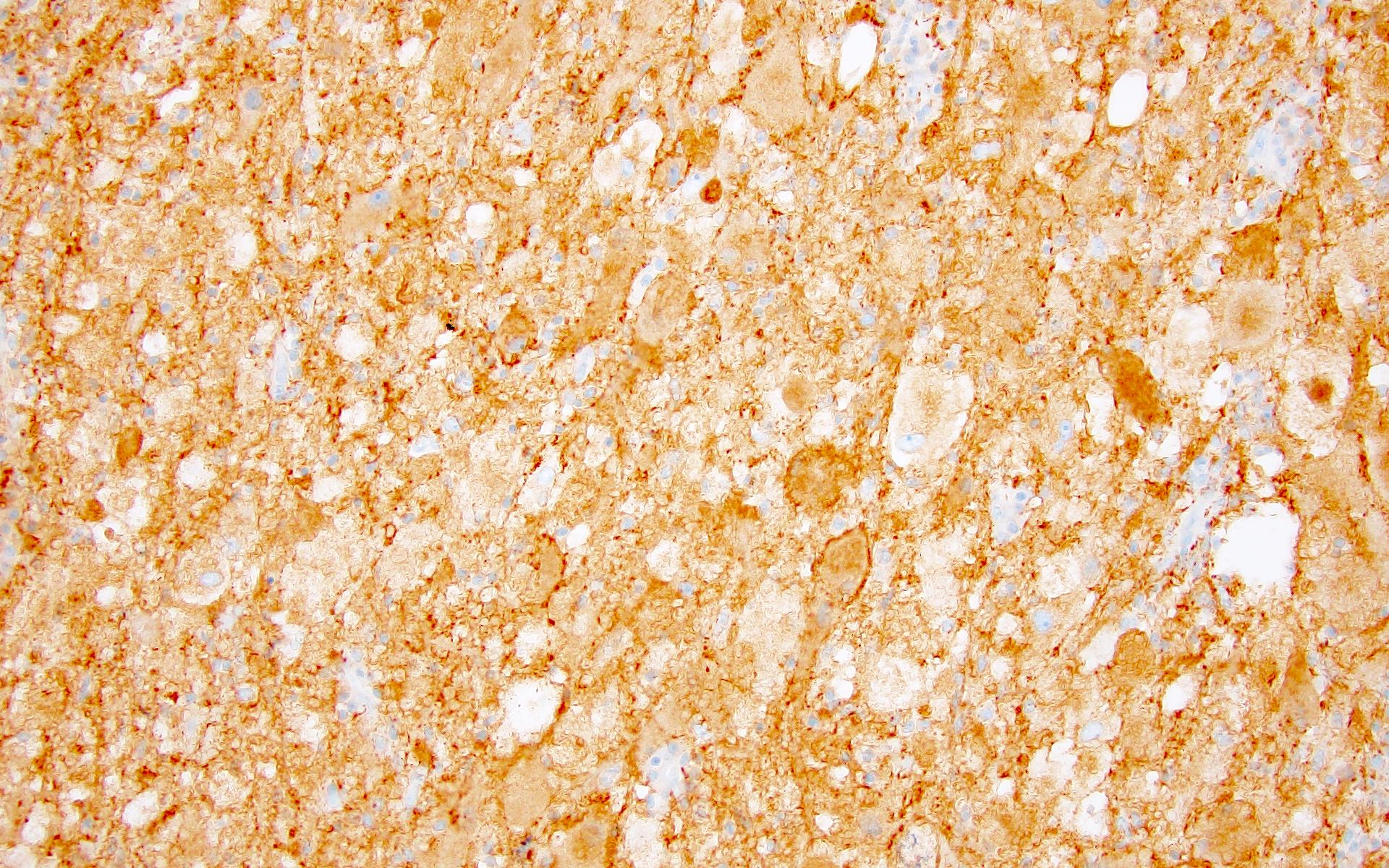
Positive stains
- Ganglion-like cells: MAP2, neurofilament, synaptophysin (neural markers)
- No reliable marker to distinguish nonneoplastic neurons from neoplastic ganglion-like cells
- Neoplastic glial cells: GFAP, Olig2 (Cancer 1997;79:989)
- CD34, either diffuse or patchy (arborescent pattern), within the tumor or adjacent cortex (Acta Neuropathol 1999;97:481)
- Ki67 low (< 5%) (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1995;54:513)
- BRAF V600E mutation specific antibody is available and generally positive in dysplastic ganglion-like cells (Acta Neuropathol 2013;125:891)
Negative stains
- Ganglion-like cells often lack NeuN immunoreactivity (which is positive in nonneoplastic neurons)
- Negative for IDH1 R132H staining
Electron microscopy description
- Not routinely used for clinical / diagnostic purposes
- Ultrastructural characteristics of ganglioglioma include:
- Ganglion-like cells with numerous dense core granules within the perikarya and cellular processes and abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (Cancer 1997;79:989)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Ganglioglioma:
- BRAF V600E is most common molecular alteration, seen in 10 - 60% of tumors (highest occurrence in cortical tumors, lowest in spinal cord tumors) (Acta Neuropathol 2011;121:397, Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:833, Hum Pathol 2016;49:107)
- Other alterations include other BRAF mutations, BRAF gene fusions (most commonly with KIAA1549), RAF1 gene fusions, KRAS activating mutations and NF1 inactivating mutations / deletions (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2018;6:47)
- BRAF V600E mutation can be detected by immunohistochemistry or gene sequencing (including droplet digital PCR, ddPCR) (Acta Neuropathol 2013;125:891)
- If negative for BRAF V600E, other MAPK activating alterations should be considered utilizing a large next generation sequencing panel or gene fusion panel (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2018;6:47)
- Ganglioglioma demonstrates a unique genome wide methylation pattern, which can be helpful in diagnostically challenging cases (Nature 2018;555:469)
- Gangliocytoma:
- No signature molecular profile published to date
Videos
Neuronal and glioneuronal tumors
by Dr. Fausto Rodriguez (PathCast)
Sample pathology report
- Brain mass, temporal lobe, resection:
- Ganglioglioma, BRAF V600E mutant, WHO grade 1
- Histologic classification: ganglioglioma
- WHO grade: 1
- Molecular information: BRAF V600E
Differential diagnosis
- Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD):
- Presence of MAPK activating alteration (such as BRAF V600E) can be helpful to exclude FCD
- If any genetic alterations are identified, FCD generally harbors alterations in the PI3K / AKT / mTOR pathway (Epilepsia 2011;52:158, Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2018;44:6)
- Dysplastic neurons typically retain NeuN immunoreactivity and shows poorly delineated cortical thickening, rather than a well circumscribed tumor mass
- Infiltrating low grade glioma:
- NeuN positive neurons with a neoplastic glial population are more in keeping with an infiltrating low grade glioma with entrapped neurons
- Will often see IDH1 / IDH2 mutations in low grade infiltrating gliomas
- Low grade infiltrating gliomas in children can have BRAF V600E mutations or MAPK alterations but will not show dysplastic ganglion cells
- Polymorphous low grade neuroepithelial tumor of youth (PLNTY):
- FGFR2 / FGFR3 gene fusions or BRAF V600E mutation
- Numerous calcifications and diffuse CD34 immunoreactivity (Acta Neuropathol 2017;133:417)
- At least focally infiltrative growth and oligodendroglial-like component
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNT):
- Multinodular growth
- Floating neurons in mucoid matrix
- Frequently FGFR1 alterations
- Typically lack of CD34 staining (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2019;45:95)
- Multinodular vacuolating neural tumor (MVNT):
- Multinodular growth typically without dysmorphic or binucleate neurons
- Lack of CD34 staining, Olig2 positive neuronal cells and prominent vacuolization (Acta Neuropathol 2018;135:485)
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA):
- Presence of xanthomatous cells, nuclear pleomorphism, reticulin rich network surrounding individual tumor cells and co-occurrence of both BRAF V600E and CDKN2A / CDKN2B homozygous deletion (Brain Pathol 2019;29:85)
- Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma (DIG):
- Usually occurs in infants and present with much larger tumors
- Histology demonstrates markedly desmoplastic stroma
- Hypothalamic hamartoma (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2018;21:324, Eur J Hum Genet 2015;23:92):
- Congenital lesion located along the floor of the hypothalamus
- Patients often present with gelastic seizures
- Pathognomonic lesion for Pallister-Hall syndrome (autosomal dominant, associated with mutations of GLI3)
- Dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma (Lhermitte-Duclos disease):
- Unique cerebellar lesion in patients with Cowden syndrome (PTEN hamartoma syndrome) (Hered Cancer Clin Pract 2010;8:6)
- Loss of PTEN, though MAPK alterations typically seen in ganglioglioma are absent
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 15 year old patient presents with chronic seizures that are refractory to medical management. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain reveals a cystic lesion with an area of solid enhancement located in the medial temporal lobe. Surgical resection was performed, revealing the histology shown above. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Ganglioglioma
- Glioblastoma
- Oligodendroglioma
- Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
Board review style answer #1
A. Ganglioglioma. This clinical scenario describes classic features of ganglioglioma: a young patient with refractory seizures who presents with a cystic mass with enhancing mural nodule and histology that demonstrates a biphasic tumor with admixed neoplastic glial cells and dysmorphic ganglion-like cells. Other common histologic findings include perivascular lymphocytes, calcifications and eosinophilic granular bodies. Glioblastoma (answer B) is a high grade, infiltrating neoplasm composed of markedly atypical glial cells with increased mitoses, necrosis and microvascular proliferation. Oligodendroglioma (answer C) generally occurs in adults with brain imaging that shows an infiltrative process and histologic examination that reveals tumor cells with perinuclear halos (fried egg appearance). Pilocytic astrocytoma (answer D) usually occurs in the cerebellum or optic pathway and is characterized by bipolar glial cells with hair-like (piloid) processes, Rosenthal fibers, eosinophilic granular bodies and degenerative atypia. Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (answer E) is a tumor found almost exclusively in patients with tuberous sclerosis; it is generally located near the ventricles and is composed of large, atypical, multinucleated astrocytes without a population of neoplastic ganglion-like cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Gangliocytoma & ganglioglioma
Comment Here
Reference: Gangliocytoma & ganglioglioma
Board review style question #2
A 10 year old patient with chronic epilepsy underwent surgical resection of a temporal lobe mass. The histology was compatible with ganglioglioma, WHO grade 1. What is the most likely molecular alteration present in this tumor?
- BRAF V600E mutation
- H3 K27M mutation
- IDH1 R132H mutation
- NF1 mutation
- NF2 mutation
Board review style answer #2
A. BRAF V600E mutation. This is the most common alteration observed in ganglioglioma. H3 K27M mutation (answer B) is a characteristic molecular alteration of diffusely infiltrating midline gliomas (such as diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma). IDH1 R132H (answer C) is the most common IDH mutation, which occurs in oligodendrogliomas and infiltrating astrocytomas. NF1 alterations (answer D) are commonly seen in pilocytic astrocytomas of the optic pathway (i.e., optic pathway glioma). NF2 mutations (answer E) are common in meningiomas and schwannomas
Comment Here
Reference: Gangliocytoma & ganglioglioma
Comment Here
Reference: Gangliocytoma & ganglioglioma