Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Feely M, Gonzalez RS. Juvenile polyposis syndrome. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorjuvenilepolyposissx.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
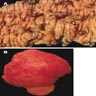
- Autosomal dominant syndrome leading to growth of numerous juvenile polyps, predominantly in the colon
Essential features
- Syndrome that encompasses 3 particular phenotypic groups, including juvenile polyposis of infancy, juvenile polyposis coli (colonic involvement only) and generalized juvenile polyposis
- Diagnostic criteria:
- 3 - 10 juvenile polyps, depending on criterion used
- Juvenile polyps throughout entire GI tract
- Any number of polyps in a patient with a family history of juvenile polyposis (Histopathology 1988;13:619)
- Associated risk of upper or lower GI malignancies is approximately 55% (Ann Surg Oncol 1998;5:751)
- Juvenile polyposis of infancy is a rare form that usually manifests before age 2, is not hereditable and is associated with a poor prognosis
Sites
- Polyps found throughout the GI tract, with the exception of the juvenile polyposis coli form, which is restricted to the colon
Pathophysiology
- SMAD4 mutations account for up to 20% of familial cases, while BMPR1A mutations are found in approximately 25% of cases (Am J Med Genet 2004;129C:44)
- Syndrome has incomplete penetrance and a large proportion of affected individuals have no family history (OMIM: Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome [Accessed 4 March 2021])
Clinical features
- If symptomatic, children typically present with painless rectal bleeding or prolapsing of polyps through rectum
Case reports
- 51 year old man with juvenile polyposis syndrome affecting the stomach (J Med Case Rep 2008;2:314)
Treatment
- Annual upper and lower endoscopic examinations with polypectomies
- Surgery reserved for diffuse polyposis not amenable to polypectomy or for associated malignancies
- Screening of family members recommended
Microscopic (histologic) description
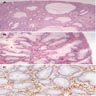
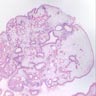
- Numerous cystic and dilated crypts or glands with inspissated mucin and occasional intraluminal neutrophils
- Lamina propria typically edematous with associated lymphocytes, plasma cells and occasional eosinophils and neutrophils
- Filiform, multilobated forms with increased glandular to stroma ratio may be encountered and have been variably termed nonclassic or atypical polyps
- May contain areas of conventional dysplasia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1996;120:1032)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Videos
Colonoscopy of juvenile polyposis
Sample pathology report
- Colon, total colectomy:
- Colon with numerous juvenile polyps, some with focal low grade dysplasia (see comment)
- Negative for high grade dysplasia or malignancy.
- Eight benign lymph nodes.
- Comment: The findings are consistent with the patient’s reported history of juvenile polyposis. Numerous grossly identifiable polyps were submitted for microscopy, including the largest.
Differential diagnosis
- Similar polyps:
- Can also occur sporadically in nonsyndromic children and adults
- Multiple juvenile type polyps:
- Have also been associated with Cowden syndrome and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (PTEN mutations), as well as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (SMAD4 / DPC4, ENG or ACVRL1 mutations)
- Polyps of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome:
- Histologically similar but intervening mucosa is also involved
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is a criterion for diagnosis of juvenile polyposis syndrome?
- 1 juvenile polyp measuring > 5 cm
- At least 5 juvenile polyps in a patient with a family history of juvenile polyposis
- Juvenile polyps throughout entire GI tract
- More than 25 juvenile polyps
Board review style answer #1