Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Bell P, Findeis-Hosey J. Microsatellite instability pathway. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumormolecularmicrosatellite.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Microsatellites (short tandem repeats) are repetitive DNA sequences composed of repeating motifs of 2 - 10 nucleotides
- When there are defects in mismatch repair (MMR) genes (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6), mutations introduced into microsatellite regions during DNA synthesis are not repaired, which results in microsatellite instability (MSI)
- Microsatellite instability (MSI) is one of the pathways implicated in colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC) carcinogenesis; colorectal cancer with MSI is referred to as MSI / microsatellite unstable or MMR deficient (dMMR) colorectal cancer
Essential features
- Microsatellite instability (MSI) results from abnormal function of one or more mismatch repair genes (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6)
- 10 - 15% of colorectal adenocarcinomas (CRC) are MSI / MMR deficient (dMMR)
- dMMR colorectal cancer arises due to sporadic hypermethylation of the MLH1 promoter or due to germline mutations in MMR genes (Lynch syndrome)
- In pathology, colorectal cancer is initially screened for MSI by assessing the presence of MMR proteins using immunohistochemistry
- Loss of one or more MMR proteins is followed by either MLH1 hypermethylation testing or BRAF mutation testing; the absence of MLH1 hypermethylation or a BRAF mutation prompts germline mutation to assess for Lynch syndrome
- Identifying dMMR colorectal cancer is significant as these tumors have a better stage adjusted survival compared to microsatellite stable (MSS) tumors
Terminology
- Lynch syndrome was formerly known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) syndrome
- Biallelic germline mutation in an MMR related gene is termed constitutional mismatch repair deficiency
Epidemiology
- 10 - 15% colorectal cancer is dMMR (Clin Cancer Res 2012;18:1506)
- 80% of dMMR colorectal cancer is sporadic
- Hypermethylation of MLH1 promoter
- ≥ 60 years old
- F > M
- 20% of dMMR colorectal cancer is familial
- Autosomal dominant, germline mutation (Lynch syndrome)
- ~ 40 - 50 years old
- M = F
- 80% of dMMR colorectal cancer is sporadic
Sites
- dMMR colorectal cancer has predilection for the right colon (Arch Surg 1977;112:170)
- Lynch syndrome related colorectal cancer arises from tubular adenomas (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1144)
- Sporadic dMMR colorectal cancer arises from sessile serrated adenomas / polyps (SSA / P) (Histopathology 2007;50:113)
Pathophysiology
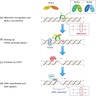
- MMR pathway (see diagram 1) (J Gastroenterol 2020;55:15)
- Corrects DNA base substitution mismatch, insertions, deletions or slippage made during DNA replication
- Errors are corrected through the action of two protein complexes:
- MutSα: heterodimer of mutS homologue 2 (MSH2) and mutS homologue 6 (MSH6) proteins
- MutSβ: heterodimer of MSH2 and mutS homologue 3 (MSH3) proteins
- MutSα or MutSβ bind to the area with the defect and recruit MutLα (heterodimer of mutL homologue 1 [MLH1] and postmeiotic segregation increased 2 [PMS2] proteins)
- PMS2 endonuclease makes a nick at 5’ to the mismatch (upstream)
- Exonuclease 1 is recruited and activated by MSH2 or MLH1
- Catalyzes excision of the nascent DNA strand up to and slightly beyond the mismatch
- DNA excision gap is resynthesized by polymerase δ and nick is sealed by DNA ligase I
- MLH1 is required for the function of PMS2 (when MLH1 is lost, PMS2 must also be lost)
- MSH2 is required for the function of MSH6 (when MSH2 is lost, MSH6 must also be lost)
Etiology
- Also see pathophysiology
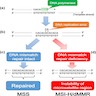
- Colorectal cancer is MSS / MMR proficient (pMMR) or MSI / MMR deficient (dMMR) (see diagram 2)
- pMMR colorectal cancer: intact MMR genes
- dMMR colorectal cancer: abnormality affecting one or more MMR genes
- Sporadic
- MLH1 promoter hypermethylation
- 50% BRAF V600E mutation
- ARID1A may have a role in carcinogenesis (Hum Pathol 2014;45:2430)
- Familial - Lynch syndrome
- Germline mutation followed by somatic mutation in wild type allele
- Mutations in MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6, EPCAM (adjacent to MSH2)
- Other:
- Rare cases with isolated loss of PMS2
- Patients present at an older age and have a lower risk for carcinoma at other sites (J Clin Oncol 2015;33:319)
- dMMR tumors lacking germline mutations and MLH1 hypermethylation
- 70%: double somatic mutations in MMR gene (J Pathol 2014;234:548, Gastroenterology 2014;147:1308)
- Rare cases with isolated loss of PMS2
- Sporadic
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Lynch syndrome is associated with increased risk of carcinoma at other sites
- Gastrointestinal: colon, small intestine, stomach, hepatobiliary, pancreas
- Genitourinary: kidney, bladder, prostate
- Gynecological: endometrium, ovary
Diagnosis
- Clinical assessment
- Patients with dMMR colorectal cancer may be asymptomatic and have an incidentally discovered mass during surveillance colonoscopy, while others may present with signs of MSS colorectal cancer (anemia, fatigue, weight loss, change in bowel habits or hematochezia) - prompting colonoscopy
- If there is clinical suspicion for Lynch syndrome, screening may be done using the Amsterdam Criteria or Bethesda System:
- Amsterdam criteria (Dis Colon Rectum 1991;34:424)
- At least 3 relatives with colorectal cancer (1 is a first degree relative of the other 2)
- At least 2 consecutive generations involved
- At least 1 person with colorectal cancer diagnosed < 50 years old
- Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) excluded
- Bethesda system (revised) (J Natl Cancer Inst 1997;89:1758)
- Colorectal cancer diagnosed < 50 years old
- Presence of other colorectal cancer or other Lynch syndrome associated tumors
- Colorectal cancer with MSI-H phenotype diagnosed < 60 years old (MSI-H versus MSI-L discussed under Molecular / cytogenetics section)
- Patient with colorectal cancer with 2+ first or second degree relatives with a Lynch syndrome associated tumor
- Amsterdam criteria (Dis Colon Rectum 1991;34:424)
- Pathologic assessment (see diagram 3)
- Most institutions test all colorectal cancer cases for MMR deficiency
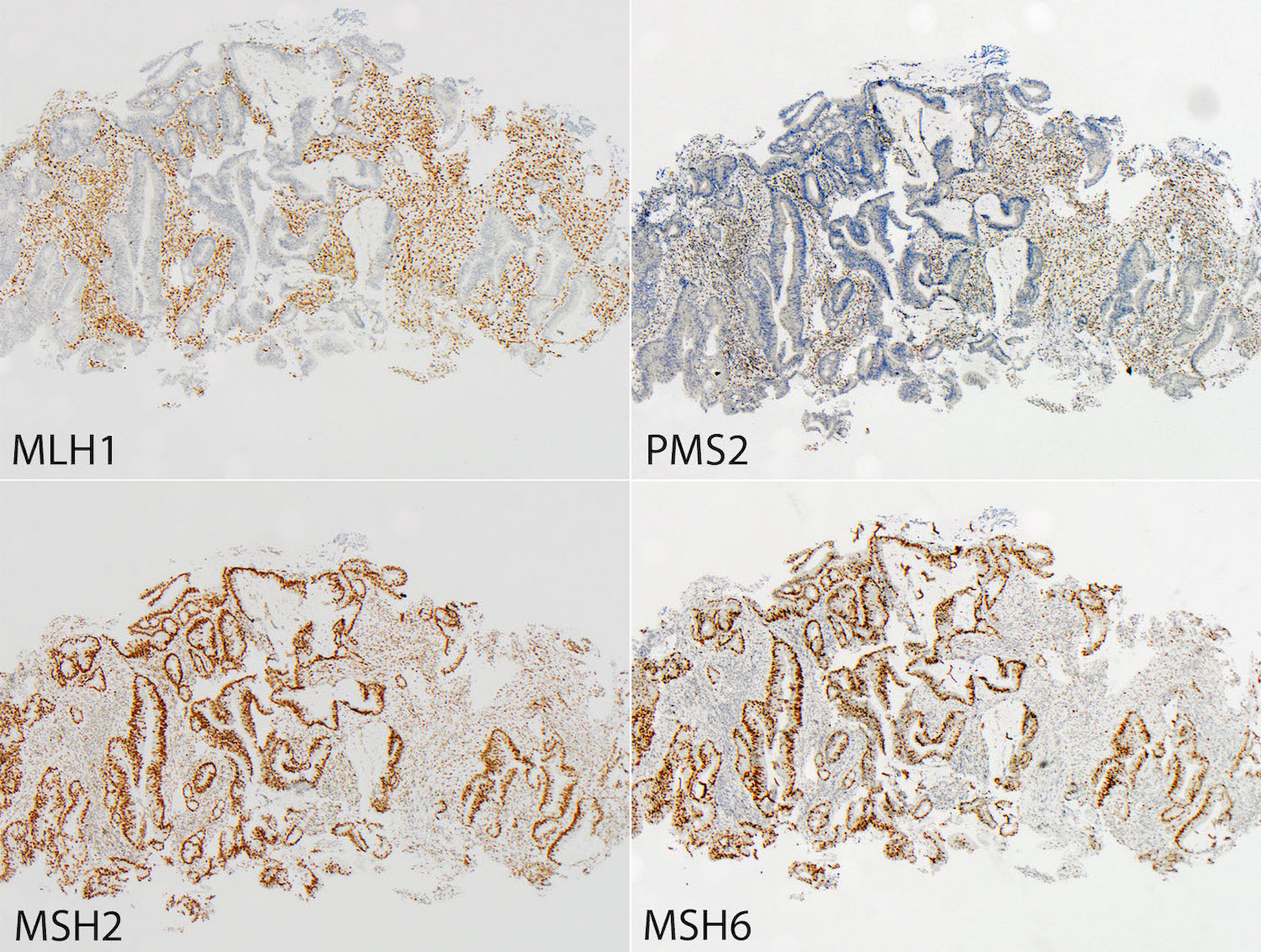
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): IHC markers for MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6
- Loss of one or more markers prompts additional testing
- BRAF mutation status (IHC or PCR)
- MLH1 methylation status
- Absence of methylation or BRAF mutation prompts germline testing
- Next generation sequencing
- Loss of one or more markers prompts additional testing
- Specific staining patterns
- MLH1 / PMS2 loss: favor sporadic
- MSH2 / MSH6 loss: favor familial
- Isolated PMS2 loss: favor familial
- Isolated MSH6 loss: favor familial
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): IHC markers for MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6
- Most institutions test all colorectal cancer cases for MMR deficiency
Laboratory
- Similar to findings as MSS colorectal cancer: anemia with or without elevated CEA
Radiology description
- Similar to findings as MSS colorectal cancer (Radiographics 2000;20:419)
- Luminal obstruction with or without soft tissue mass
- Fat stranding
- Lymphadenopathy
Prognostic factors
- dMMR colorectal cancer
- Better stage adjusted survival compared to MSS tumors (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2001;10:917)
- Prognosis for colorectal cancer associated with Lynch syndrome and MLH1 promoter hypermethylation is the same (Genet Med 2016;18:863)
Case reports
- 57 year old white woman with a history of colon cancer status post hemicolectomy and diagnosis of Lynch syndrome (BMJ Case Rep 2018;2018)
- 61 year old man had a colonoscopy that showed metachronous colorectal carcinoma with massive submucosal invasion (World J Surg Oncol 2017;15:140)
- 62 year old man with mismatch repair deficient metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma, urothelial carcinoma and a history of sebaceous carcinomas (Cancer Biol Ther 2017;18:651)
Treatment
- Surgery
- pMMR colorectal cancer
- Node negative disease = surgical excision
- Higher stage (T3, T4) or LN positive = consider chemotherapy
- dMMR colorectal cancer
- Surgical excision
- Lynch: with or without prophylactic hysterectomy
- pMMR colorectal cancer
- Immunotherapy
- dMMR solid tumor: pembrolizumab (Science 2017;357:409)
- Metastatic dMMR colorectal cancer: nivolumab (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:1182)
- Other
- BRAF mutation = limited response to EGFR targeted therapies (N Engl J Med 2015;372:2509)
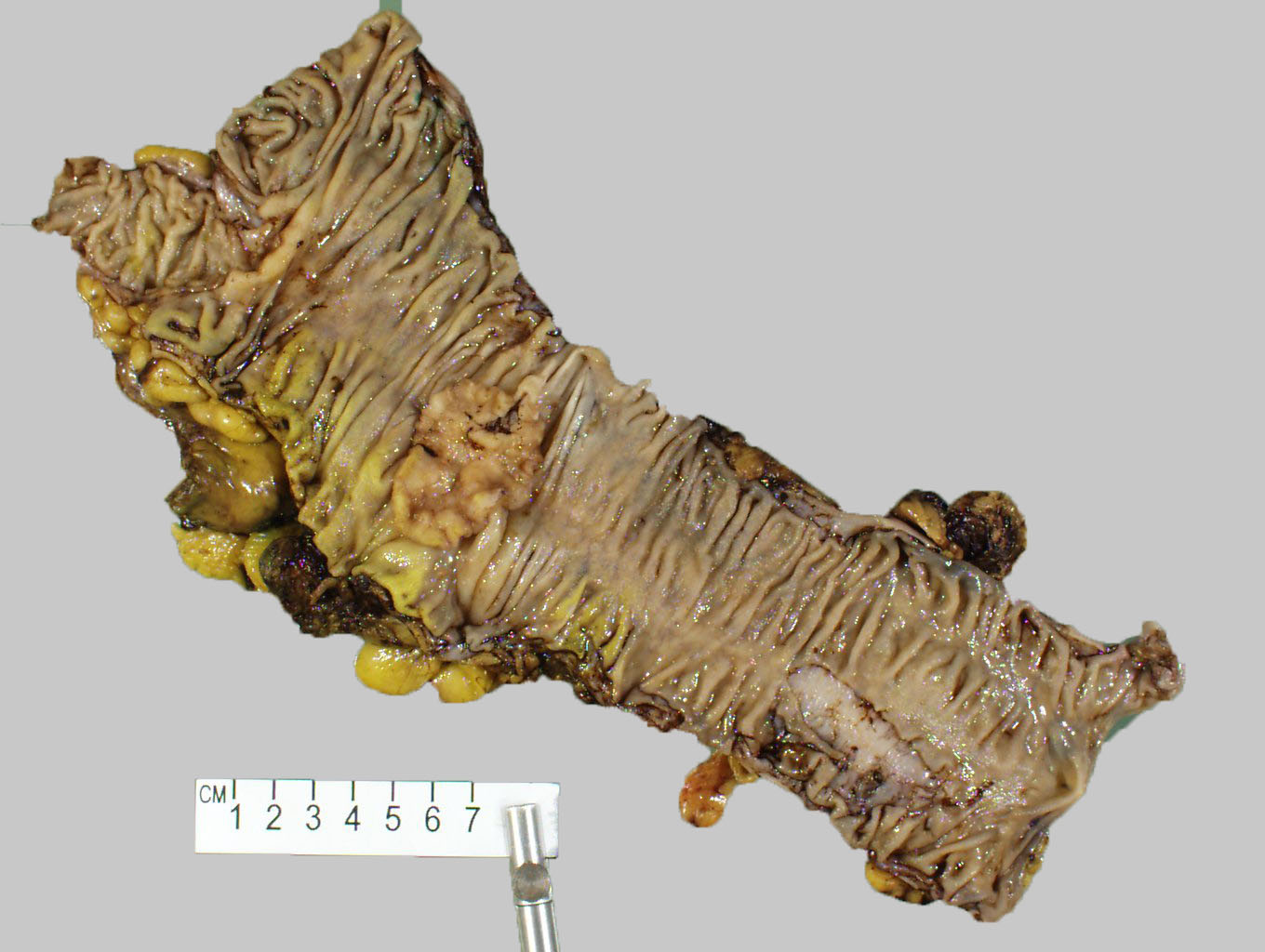
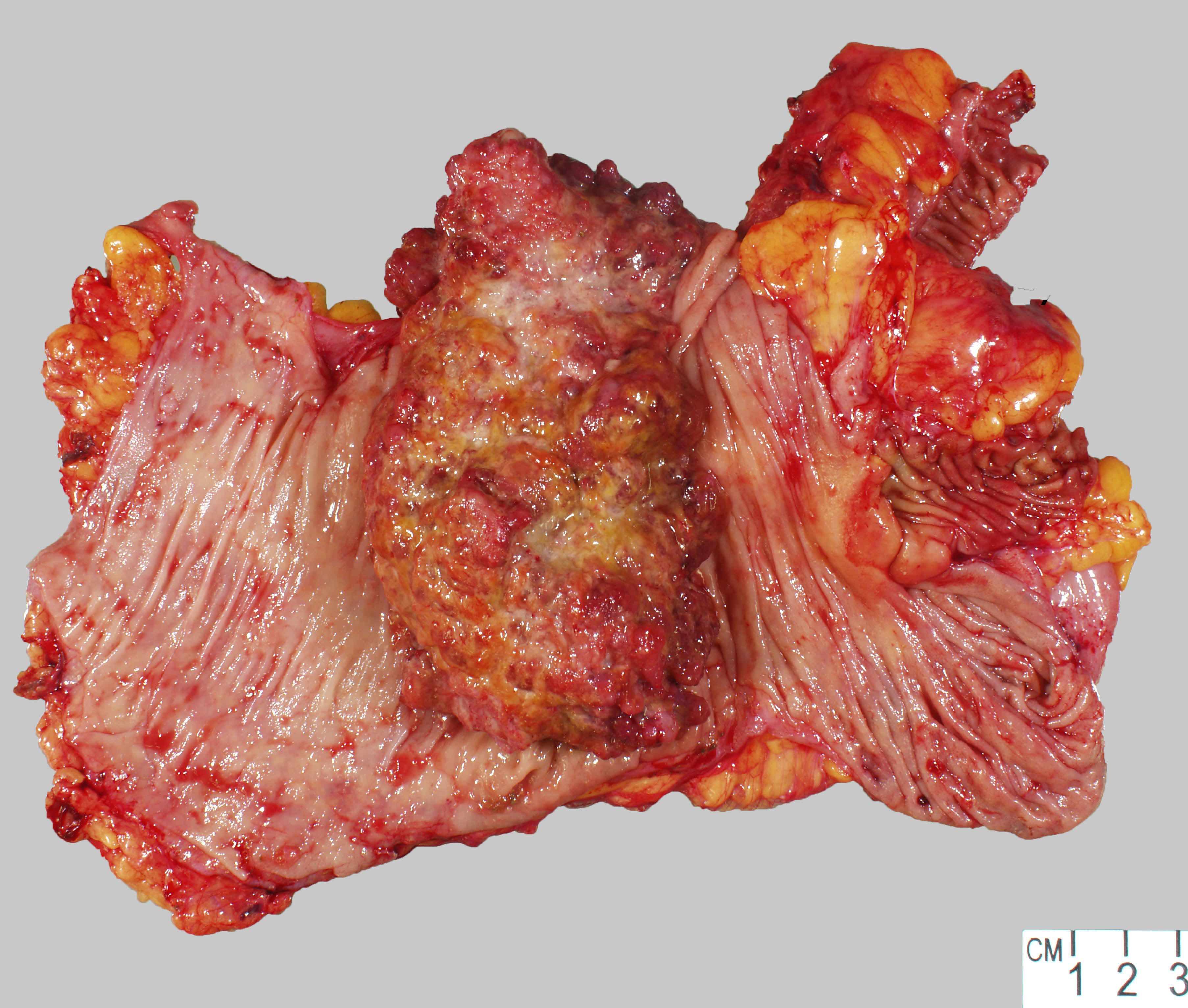
Gross description
- Larger masses with a polypoid / exophytic appearance
- Classic colorectal cancer appearance: ulcerated lesion with heaped up / rolled edges
- Reference: Dis Colon Rectum 1977;20:661
Gross images
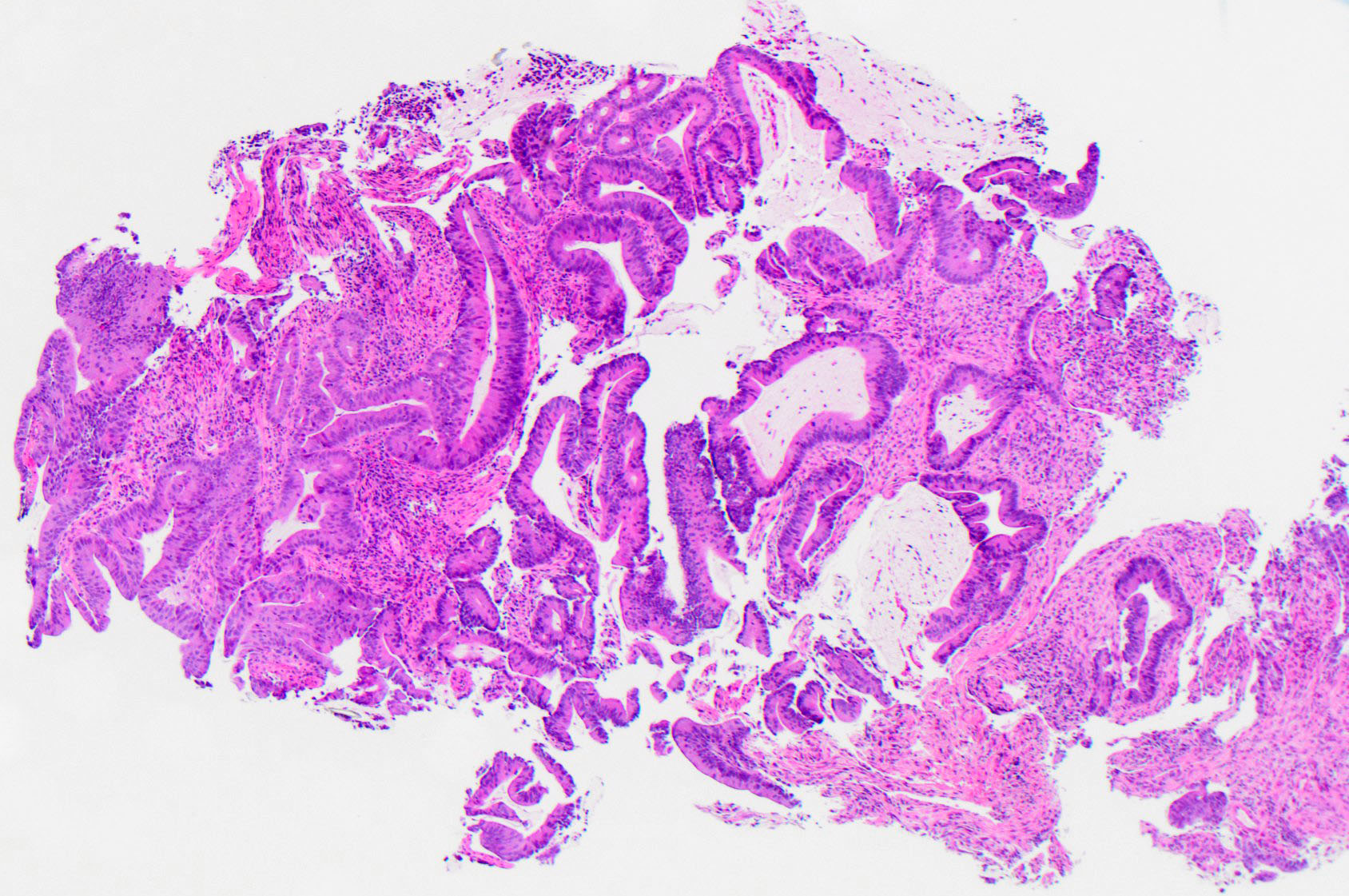
Microscopic (histologic) description
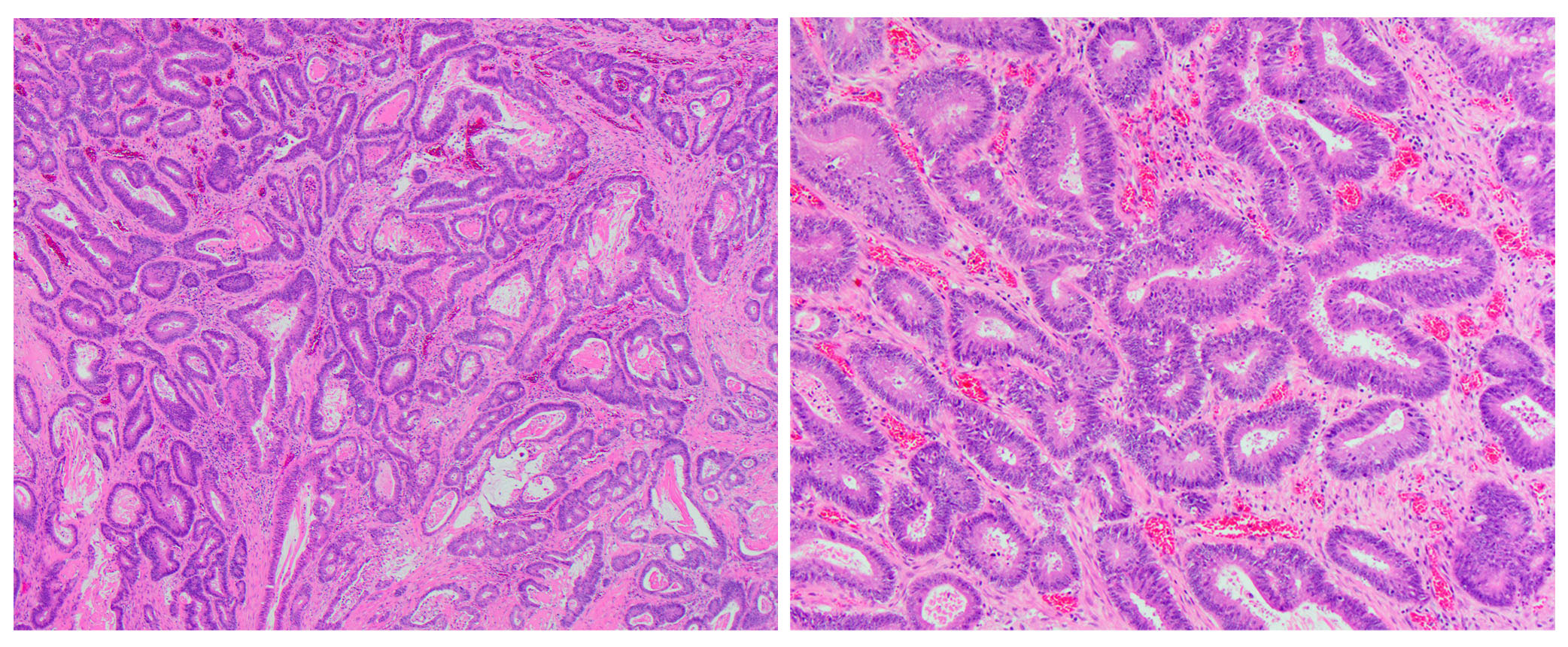
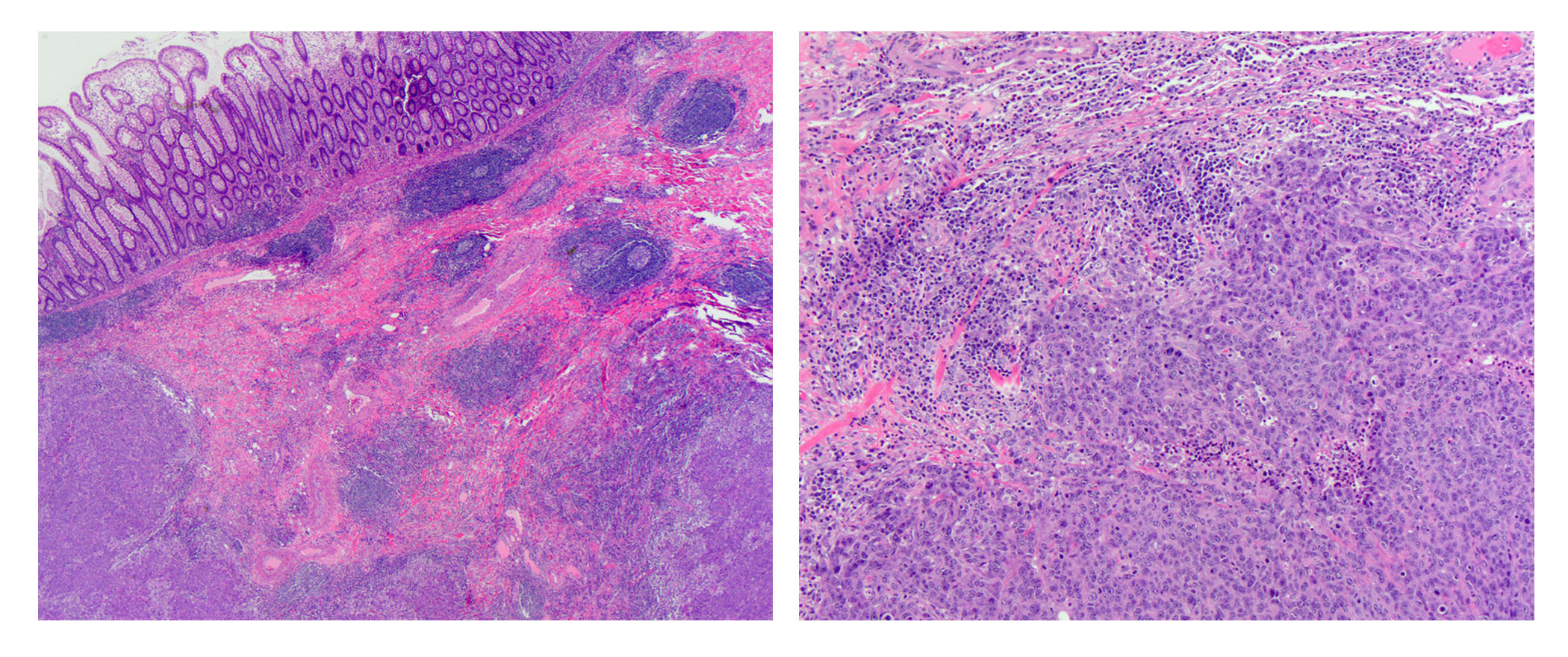
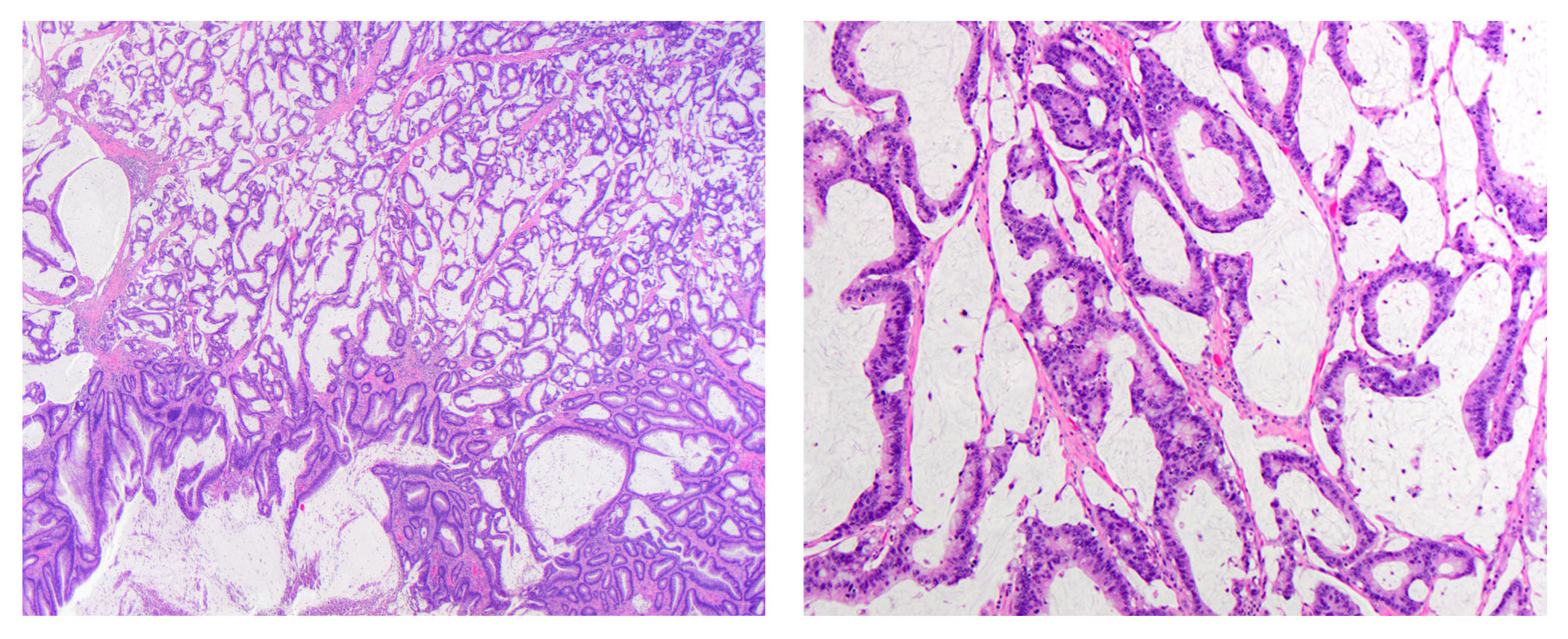
- dMMR colorectal cancer histologic characteristics (Cancer 2001;91:2417, Anticancer Res 1994;14:1631):
- Mucinous, poorly differentiated, signet ring or medullary subtypes
- Increased intratumoral / peritumoral lymphocytes
- Crohn-like reaction
- Relative lack of intraluminal (dirty) necrosis
- Tumoral heterogeneity
- Decreased tumor budding (Hum Pathol 2011;42:1833)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
- MSI / dMMR colorectal cancer: 1 or more MMR proteins absent (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6)
- Note: Several pitfalls exist when interpreting MMR (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- BRAF somatic mutation testing
- DNA change C.1799T>A
- Amino acid change: p.V600E (Val600Glu)
- BRAF mutation absent: send for somatic tests to evaluate tumor for Lynch syndrome
- Germline mutation testing
- PCR amplification of seven markers including five mononucleotide repeat markers (BAT-25, BAT-26, NR-21, NR-24 and MONO-27) and two pentanucleotide repeat markers (Penta C and Penta D) followed by separation of the PCR products by capillary electrophoresis
- ≥ 2 unstable loci = MSI-H, < 1 unstable loci = MSI-L, 0 unstable loci = MSS
- PCR amplification of seven markers including five mononucleotide repeat markers (BAT-25, BAT-26, NR-21, NR-24 and MONO-27) and two pentanucleotide repeat markers (Penta C and Penta D) followed by separation of the PCR products by capillary electrophoresis
- Reference: Cancer Res 1998;58:5248
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Interpretations for MSI immunohistochemistry, BRAF mutation or hypermethylation status should be included in a colorectal adenocarcinoma pathology report. Examples are as follows:
- MSI (by IHC) interpretation:
- pMMR colorectal cancer:
- Immunohistochemical stains for the mismatch repair proteins MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 were performed. The tumor cells demonstrate retained nuclear staining for all four proteins, indicating the tumor is MMR proficient (pMMR) and likely microsatellite stable.
- dMMR colorectal cancer:
- Immunohistochemical stains demonstrate the tumor is mismatch repair protein deficient (dMMR) with loss of expression of MLH1 and PMS2, while nuclear expression of MSH2 and MSH6 is retained. BRAF mutational analysis (or methylation status) is being performed to determine if this represents a sporadic type carcinoma.
- pMMR colorectal cancer:
- BRAF mutation interpretation:
- Absence of mutation:
- BRAF mutational analysis was performed and the V600E mutation was not identified. These are somatic tests being performed to evaluate the tumor phenotype. dMMR tumors may be sporadic or associated with Lynch syndrome / hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Referral to a hereditary cancer screening program is recommended.
- Presence of mutation:
- Molecular testing demonstrated the presence of BRAF V600E mutation, which correlates with sporadic hypermethylation of the MLH1 promoter. However, if there is a strong family history, caution should be exercised in excluding patients from germline screening on the basis of BRAF V600E mutations.
- Absence of mutation:
- MSI (by IHC) interpretation:
Differential diagnosis
- Rectal carcinoma status post neoadjuvant therapy:
- Can lose expression of MSH6 by IHC despite being MSS (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1798)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 64 year old woman presents for routine colonoscopy and a mass is identified in the ascending colon. She undergoes a partial hemicolectomy. Representative histologic sections of the mass are shown. Which of the following features is associated with MSI-H colorectal carcinoma?
- Extensive intraluminal (dirty) necrosis
- Lack of a Crohn-like reaction
- Micropapillary subtype
- Mucinous features
Board review style answer #1
D. Mucinous features. Histologically, traditional MSS colorectal adenocarcinomas are seen as invasive irregular glands surrounded by a desmoplastic stroma. The cells are composed of elongated hyerchromatic nuclei, surrounding luminal (dirty) necrosis. In contrast, MSI / dMMR colorectal carcinomas are associated with mucinous / poorly differentiated / medullary / signet ring cell subtypes, a Crohn-like reaction (dense lymphoid aggregates), increased intratumor / peritumoral lymphocytes, relative lack of intraluminal necrosis and tumoral heterogeneity. Although many institutions regularly test colorectal carcinoma cases for MSI, these features in particular should signal one to consider an MSI / dMMR tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Microsatellite instability pathway
Comment Here
Reference: Microsatellite instability pathway
Board review style question #2
Sporadic MMR deficient colorectal carcinoma is due to promoter hypermethylation of which of the following genes?
- EPCAM
- MLH1
- MSH2
- MSH6
- PMS2
Board review style answer #2
B. Hypermethylation of the MLH1 (heterodimer of mutL homologue 1) promoter is the most common cause of sporadic microsatellite unstable (MSI) CRC. MLH1 is part of a heterodimer, which also includes post-meiotic segregation increased 2 (PMS). MLH1/PMS2 are members of the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway, which fixes mutations in microsatellite regions made during DNA replication. Defects in any of the MMR genes (including MLH1) prevent these mutations from being repaired, resulting in MSI/MMR deficient (dMMR) CRC. In contrast to promoter hypermethylation that leads to sporadic MMR deficient colorectal carcinoma, Lynch syndrome is due to germline mutations in any of the MMR genes.
Comment Here
Reference: Microsatellite instability pathway
Comment Here
Reference: Microsatellite instability pathway