Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Pernick N. Middle ear paraganglioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/earjugulotympanicparaganglioma.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Also called glomus jugulare tumor or glomus tympanicum tumor
- Most common tumor of middle ear
- Usually women, ages 40 - 69 years
- 85% arise in jugular bulb causing mass in middle ear or external auditory canal; 12% arise from tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve (Jacobson nerve) causing middle ear mass; 3% arise from posterior auricular branch of vagus nerve (Arnold nerve) causing external auditory canal mass
- Usually causes conductive hearing loss
- May be locally invasive into temporal bone and mastoid; may cause cranial nerve palsies, cerebellar dysfunction, dysphagia, hoarseness
- Tumors are fed by branches of nearby large arteries; may bleed profusely at biopsy
- Histology usually benign but this does not predict behavior
- Rarely are malignant histologically (necrosis, mitotic activity, vascular invasion) with metastases to cervical lymph nodes, lung, liver (J Laryngol Otol 2000;114:17)
Case reports
- 45 year old man with middle ear mass (Case of the Week #349)
- Patient with tumor with regional metastases and spinal metastases 10 - 13 years after presentation (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1990;114:976)
Treatment
- Complete excision (may be difficult) with possible preoperative embolization or radiation therapy (reduces vascularity, promotes fibrosis)
- 50% recur locally
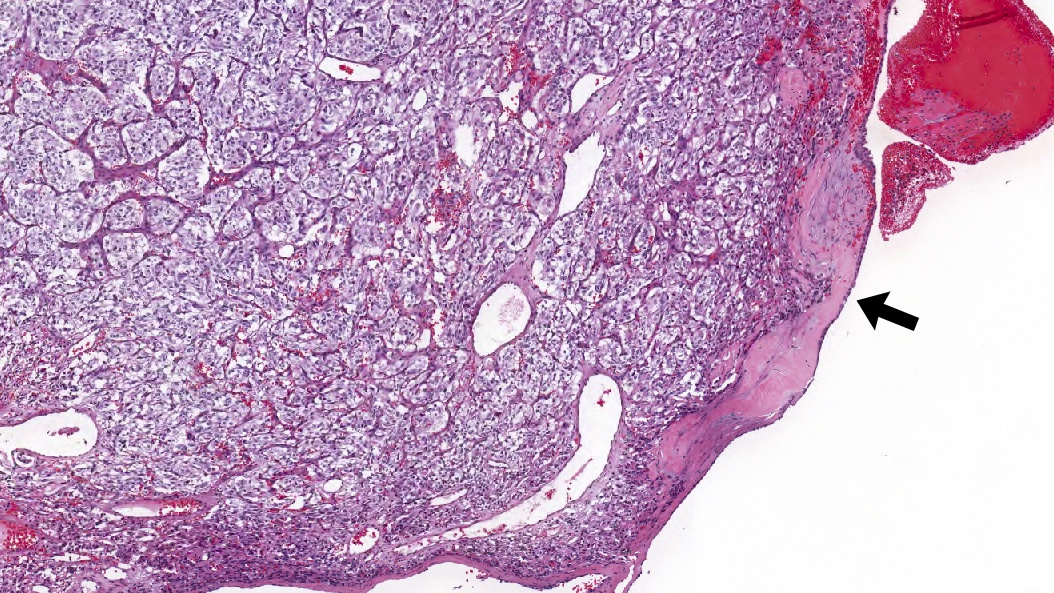
Gross description
- Polypoid, red, friable
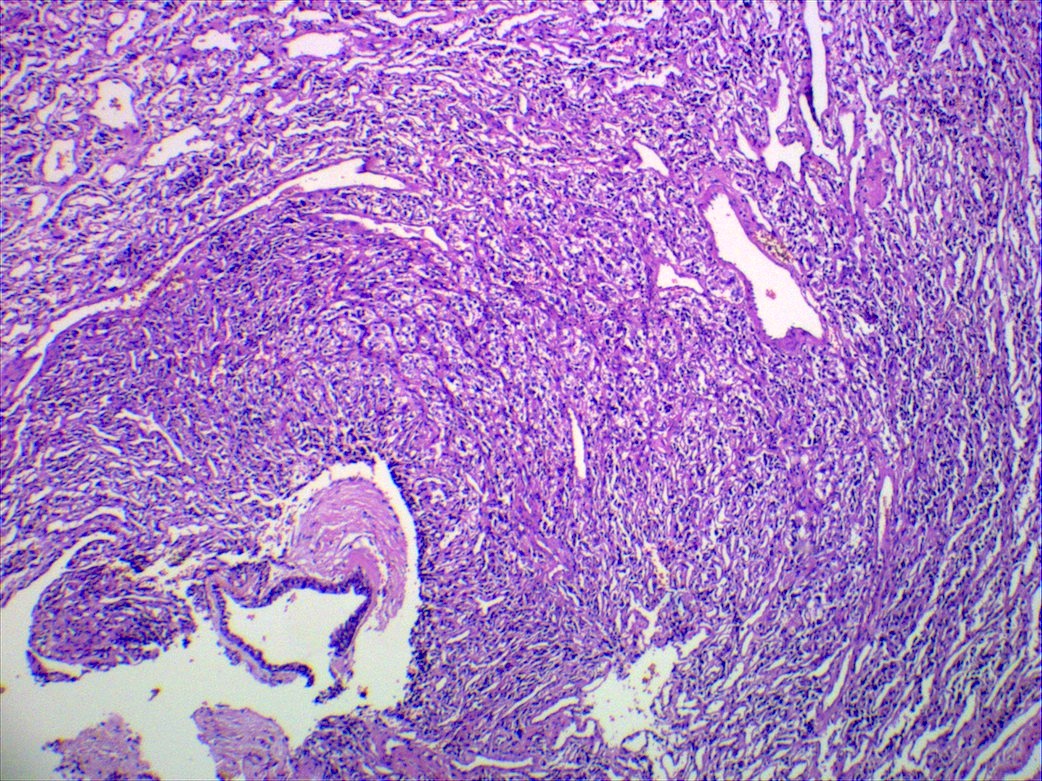
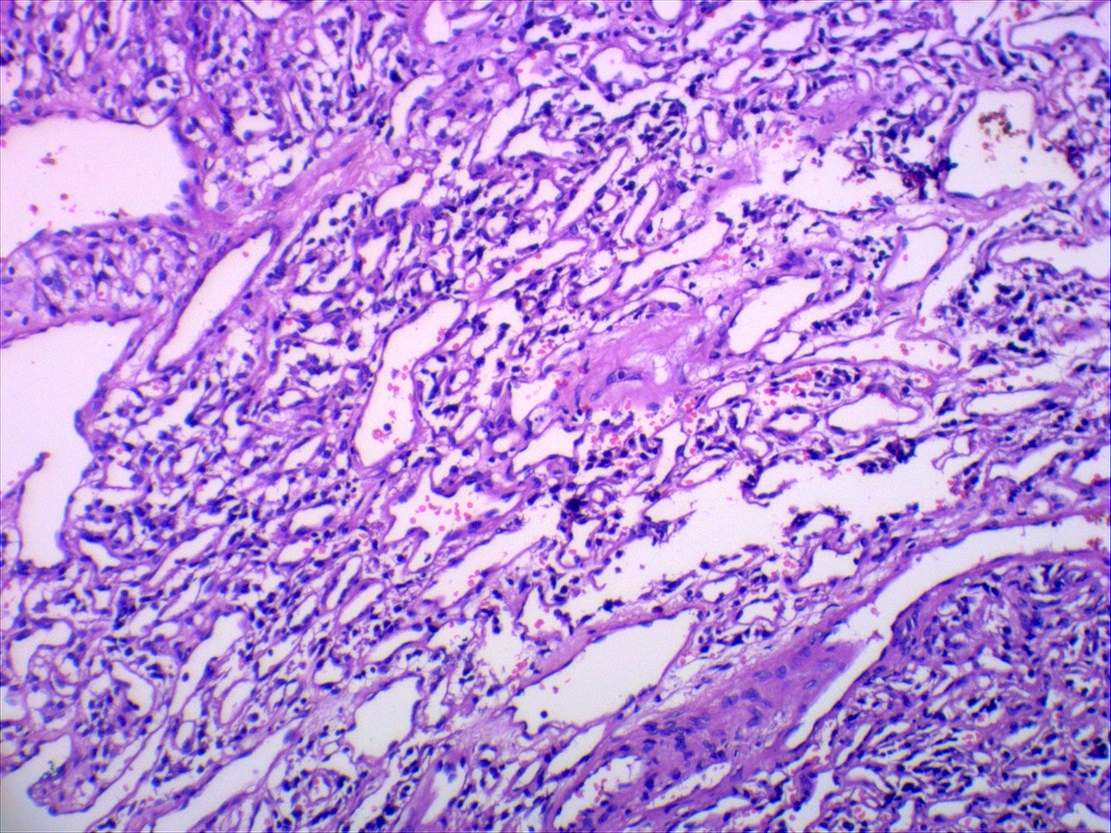
Microscopic (histologic) description
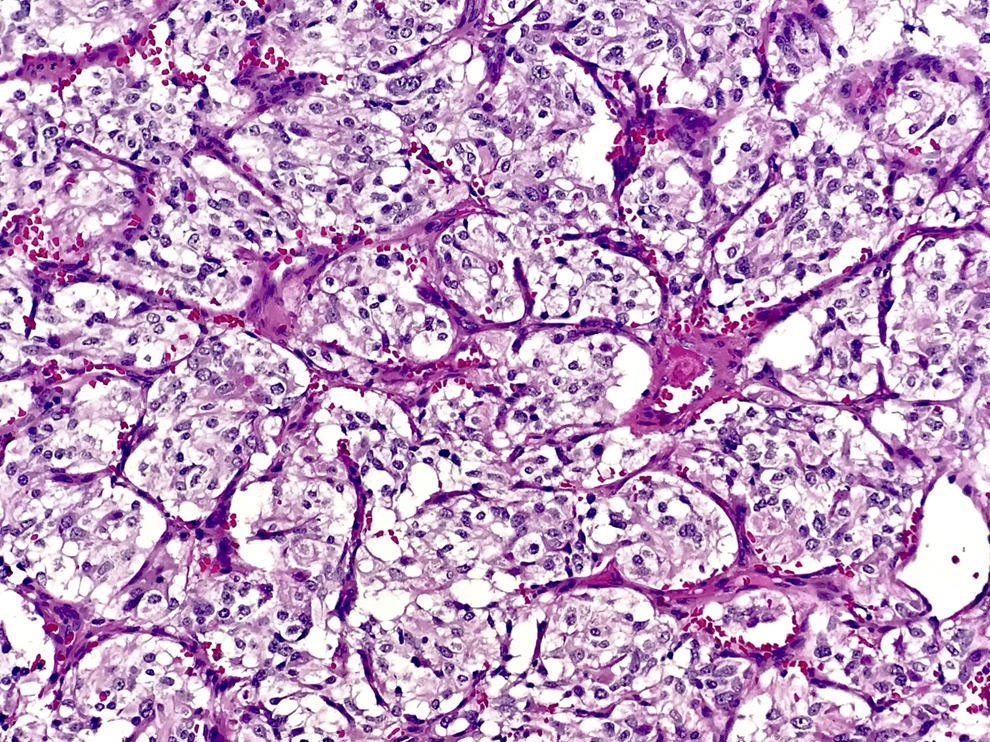
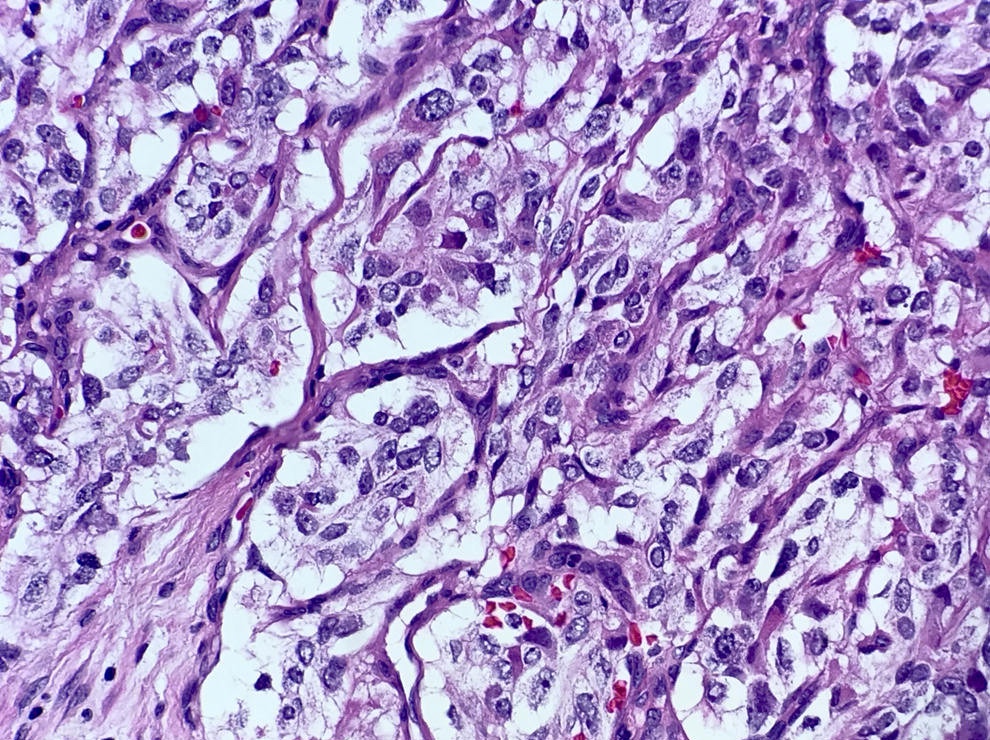
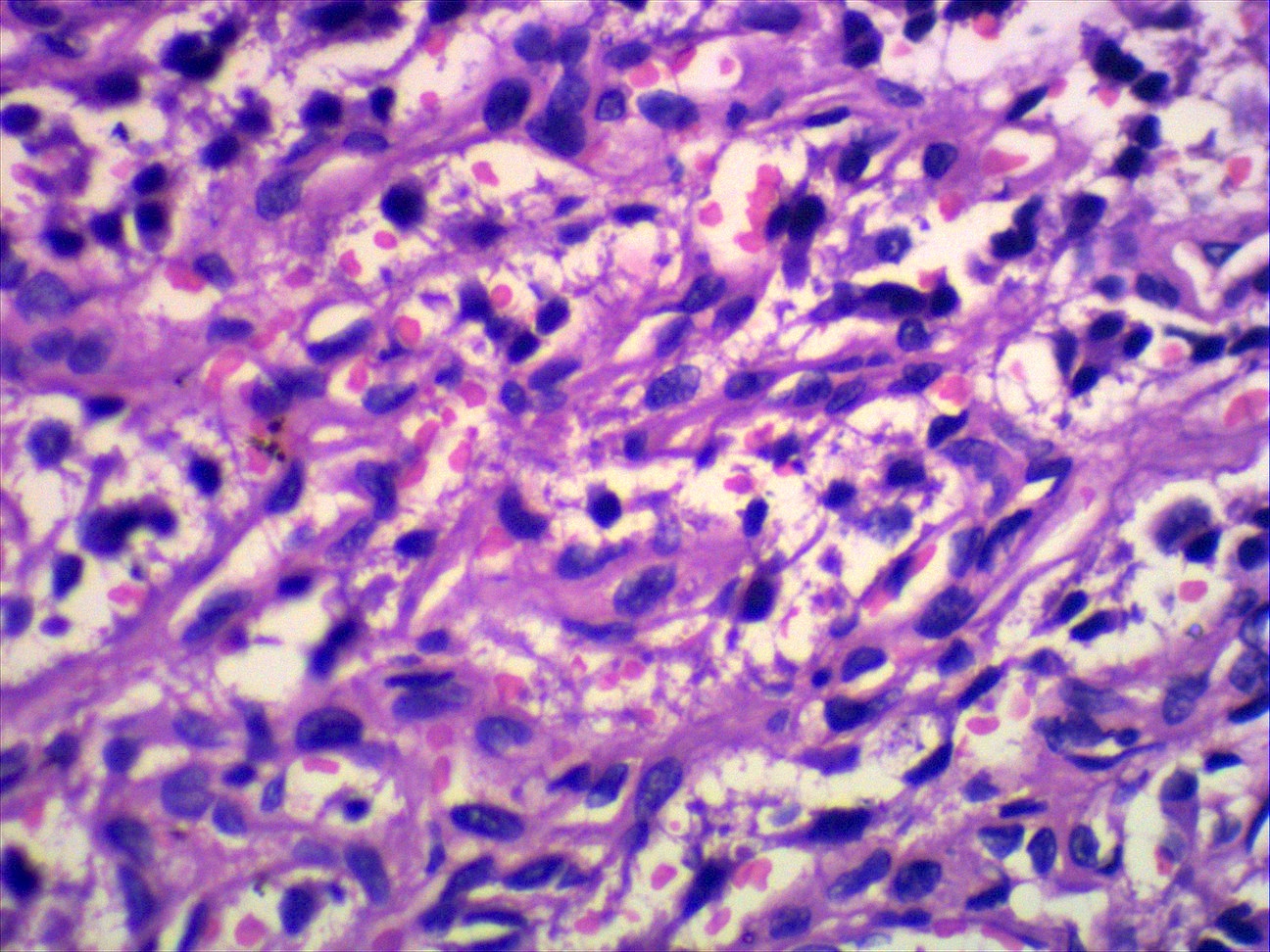
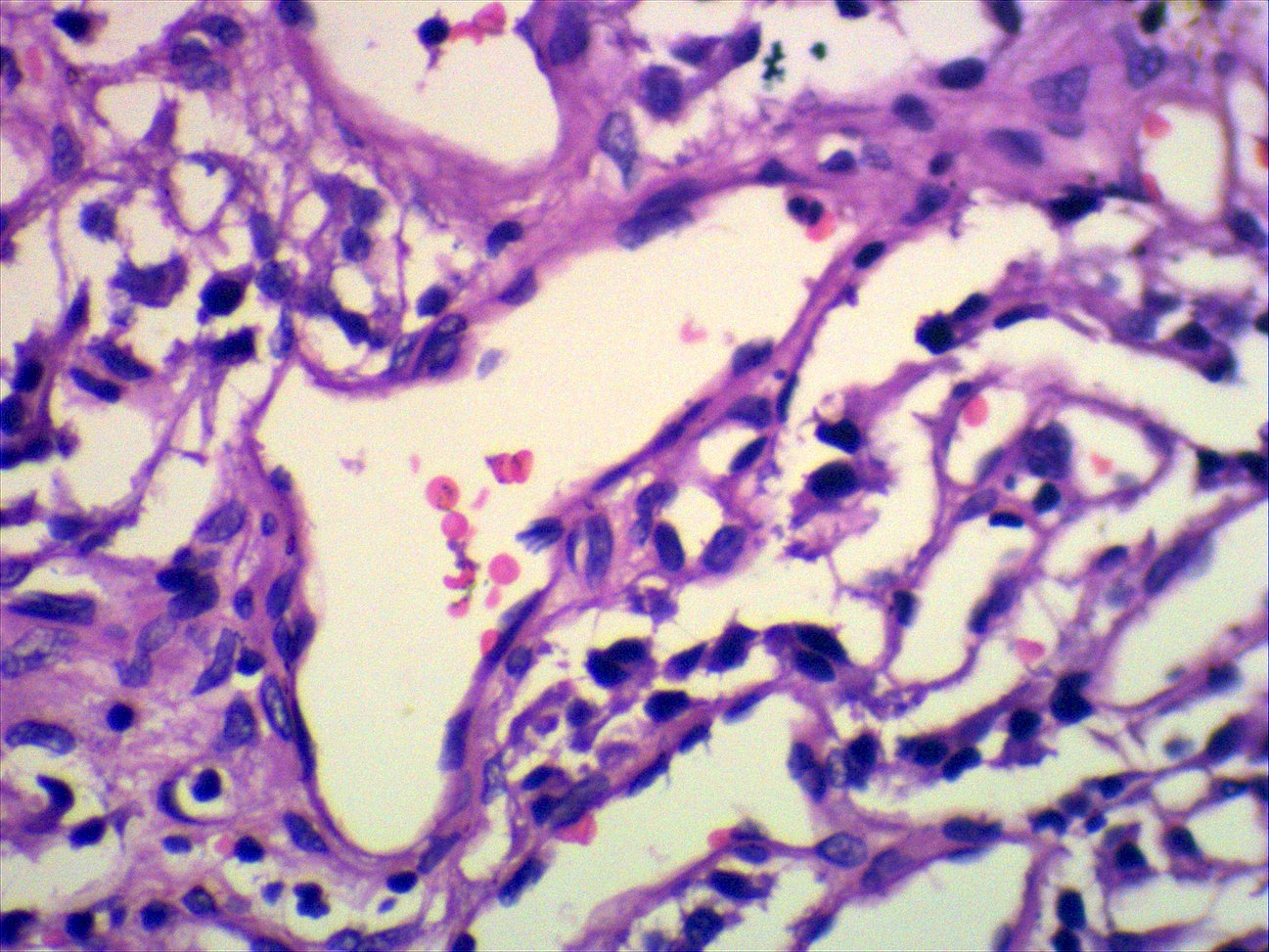
- Classic organoid (zellballen) or nesting pattern of paragangliomas with central round / oval chief cells containing abundant eosinophilic granular or vacuolated cytoplasm, uniform nuclei with dispersed chromatin
- Sustentacular cells (spindled, basophilic, difficult to see with H&E) are present at periphery of nests
- Prominent fibrovascular stroma separates nests
- May have pleomorphism but this does not predict malignant behavior; occasional dense fibrous stroma or apparent infiltrative growth
- Rare mitotic figures or necrosis
- No glandular or alveolar differentiation
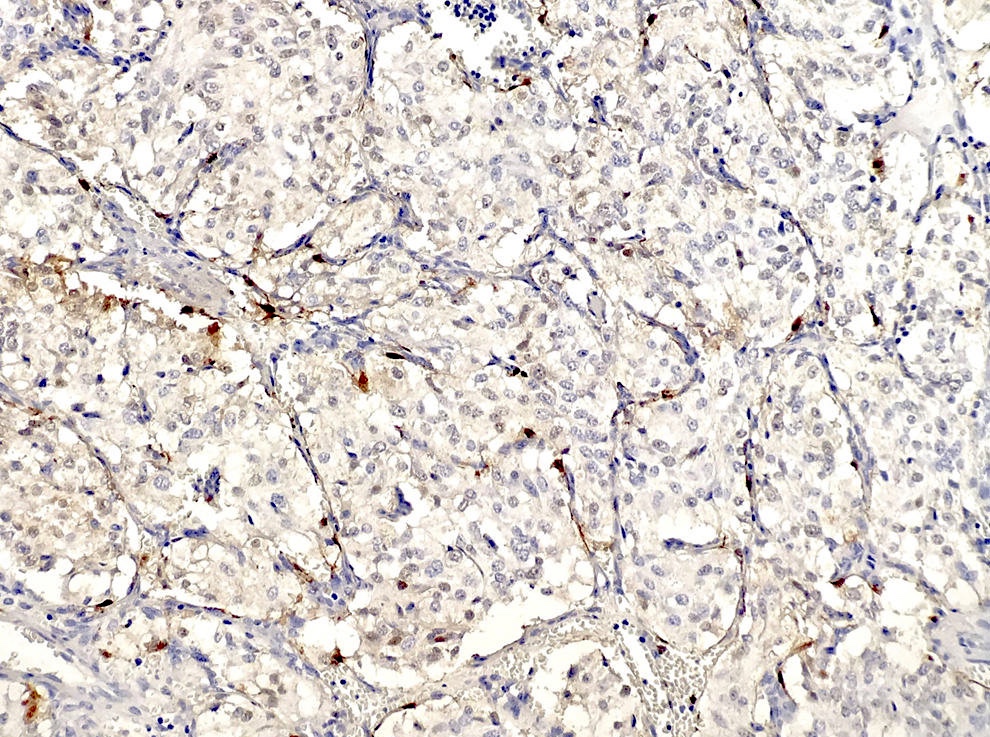
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
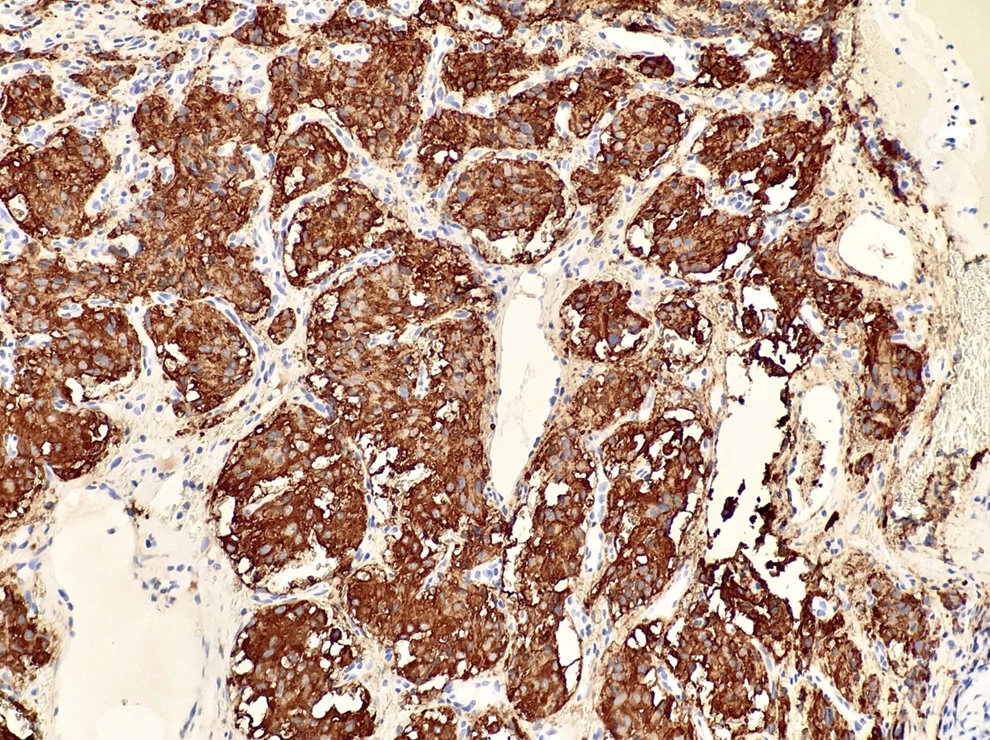
- Chromogranin and synaptophysin (chief cells), S100 (sustentacular cells)
- Reticulin (stains stroma and delineates nesting pattern, particularly helpful with crushed specimens), variable vimentin (both cell types)
Electron microscopy description
- Neurosecretory granules
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Germline mutations for succinate dehydrogenase gene subunits if multiple tumors (Diagn Mol Pathol 2005;14:109)
Differential diagnosis
- Acoustic neuroma
- Carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Meningioma
- Middle ear adenoma
- Other neuroendocrine tumors
Additional references