Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Ma L. Developmental cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/fallopiantubesdevelopmentalcysts.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign developmental cysts arising from remnants of Müllerian and Wolffian ducts as well as from mesothelium
Essential features
- Benign, fluid filled cysts located adjacent to the adnexa (fallopian tube or ovary)
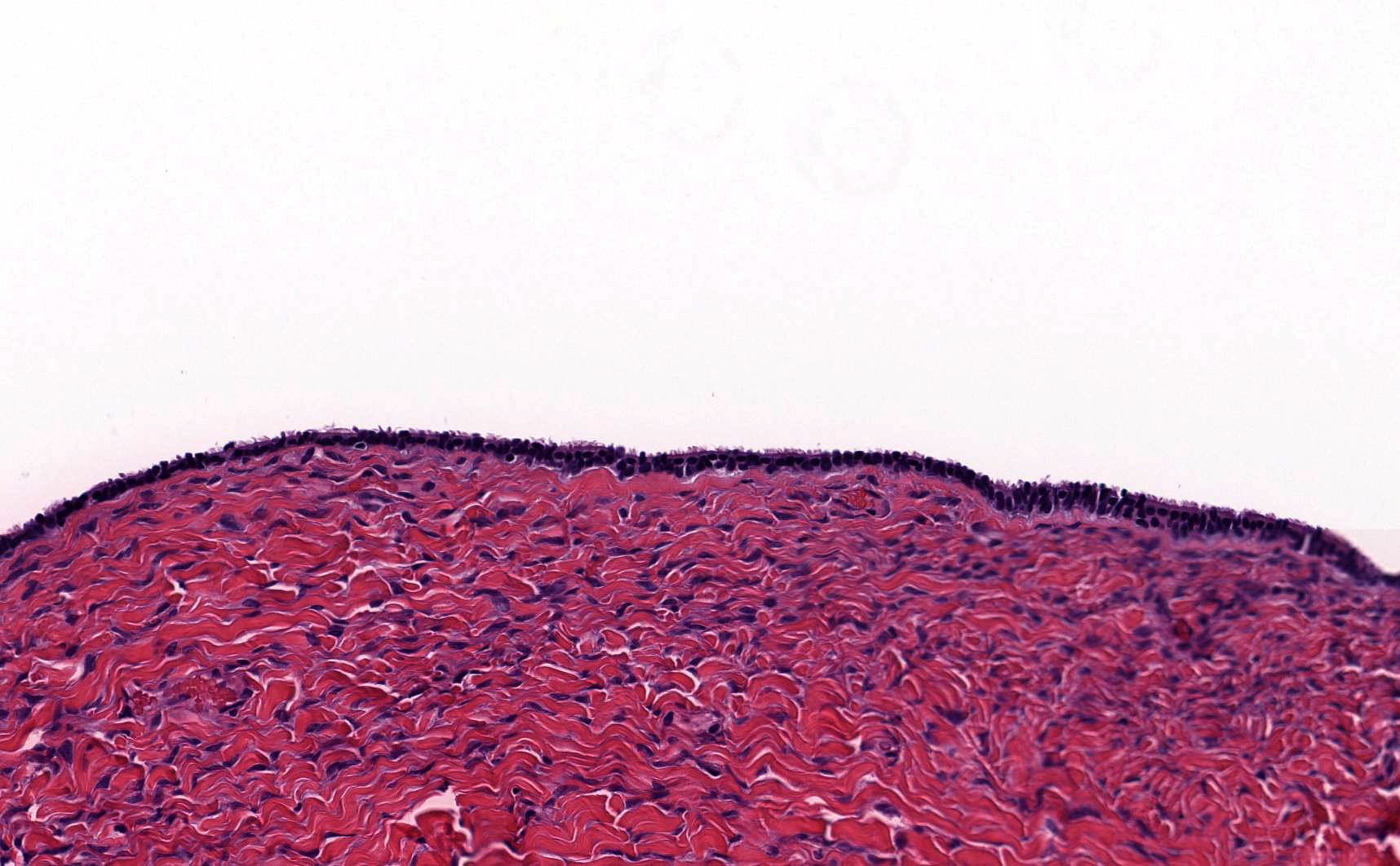
- Cysts are lined by non-stratified epithelium, which can be ciliated (paramesonephric cyst) or flat, cuboidal (mesothelial and mesonephric cysts)
- Usually are incidental findings
Terminology
- Paratubal cysts, paraovarian cysts, mesothelial (or simple) cyst
- Hydatid cyst of Morgagni (no longer recommended): typically refers to pedunculated cyst located near tubal fimbria (Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;285:1563)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- ~10% of all adnexal masses (Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;285:1563)
- Vast majority are Müllerian (paramesonephric) cysts, commonly known as paratubal cysts
- < 2% are Wolffian (mesonephric) cysts (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1977;129:873)
Sites
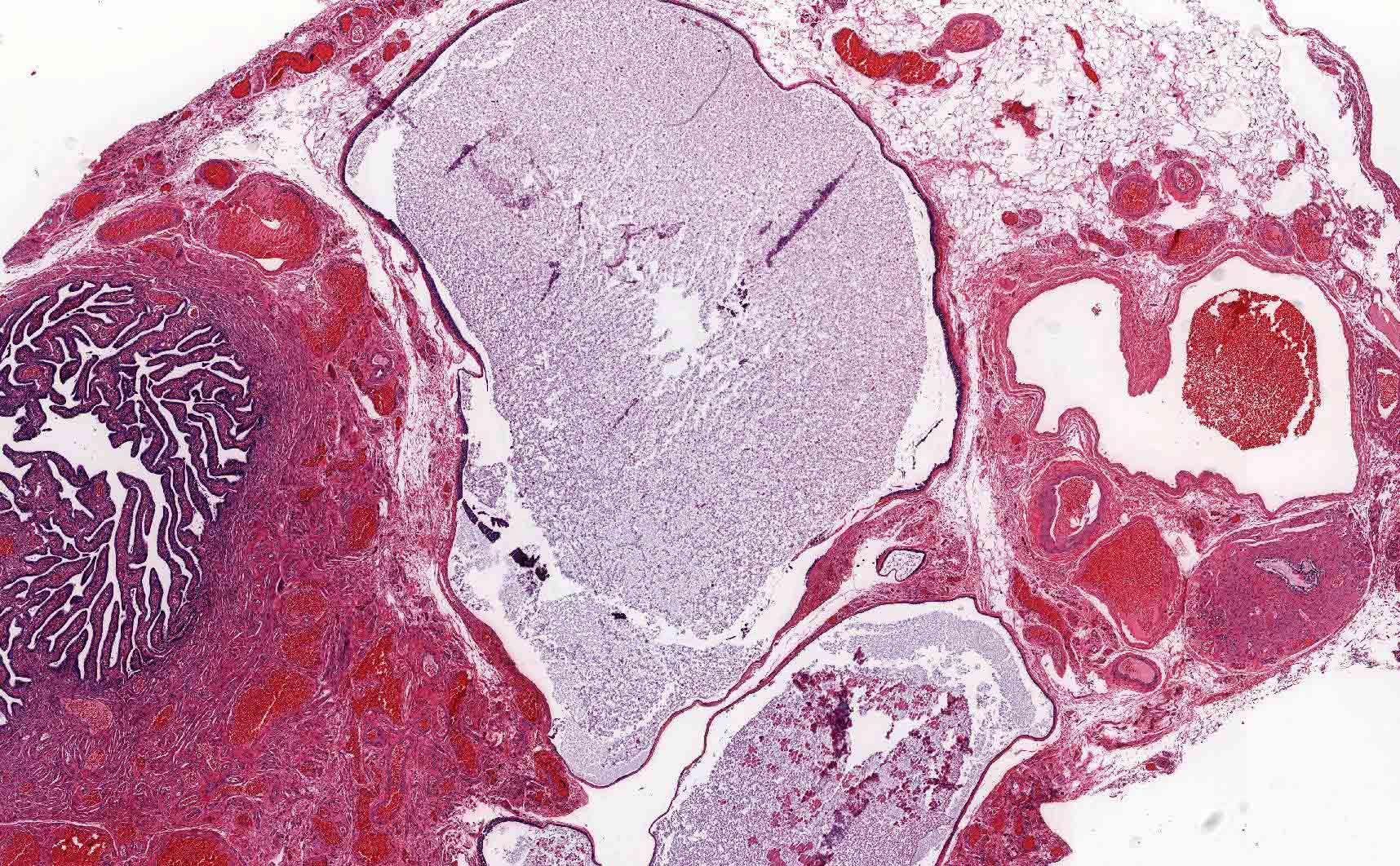
- Adjacent to the adnexa, along broad ligament, between the fallopian tube and the ovary
Pathophysiology
- Müllerian (paramesonephric) and Wolffian (mesonephric) ducts grow mostly in parallel during development
- Müllerian ducts eventually fuse
- Fusion of Müllerian ducts creates a transverse fold, which becomes the broad ligament
- Broad ligament contains Müllerian and Wolffian duct remnants, which can then become cystic
- Reference: Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract, 7th Edition, 2019
Etiology
- Thought to originate from remnants of Müllerian and Wolffian ducts as well as from mesothelium (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1977;129:873, Gynecol Obstet Invest 1981;12:1)
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic and incidentally found
- Large cysts can be painful, bleed, rupture or cause ovarian torsion (Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;285:1563)
Diagnosis
- Incidental finding
- If symptomatic, usually diagnosed by ultrasound
Radiology description
- Ultrasound findings: majority are unilocular cysts without papillations (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;28:330)
- Presence of papillary projections / solid nodule typically indicates neoplastic cysts
Prognostic factors
- Benign
- May rarely give rise to serous borderline tumor and carcinoma (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2020;32:100559, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2017;25:e21)
Case reports
- 13 year old girl with bilateral paraovarian cysts (Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 2021;21:e308)
- 31 year old woman with giant paratubal cyst presented with adnexal torsion (Case Rep Womens Health 2020;27:e00222)
- 85 year old woman with serous borderline tumor arising from a paratubal cyst (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2020;32:100559)
Treatment
- Surgical excision if large or symptomatic
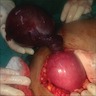
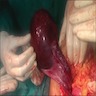
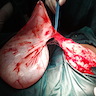
Clinical images
Gross description
- Thin walled, fluid filled cyst(s) located adjacent to fallopian tube or ovary
Microscopic (histologic) description
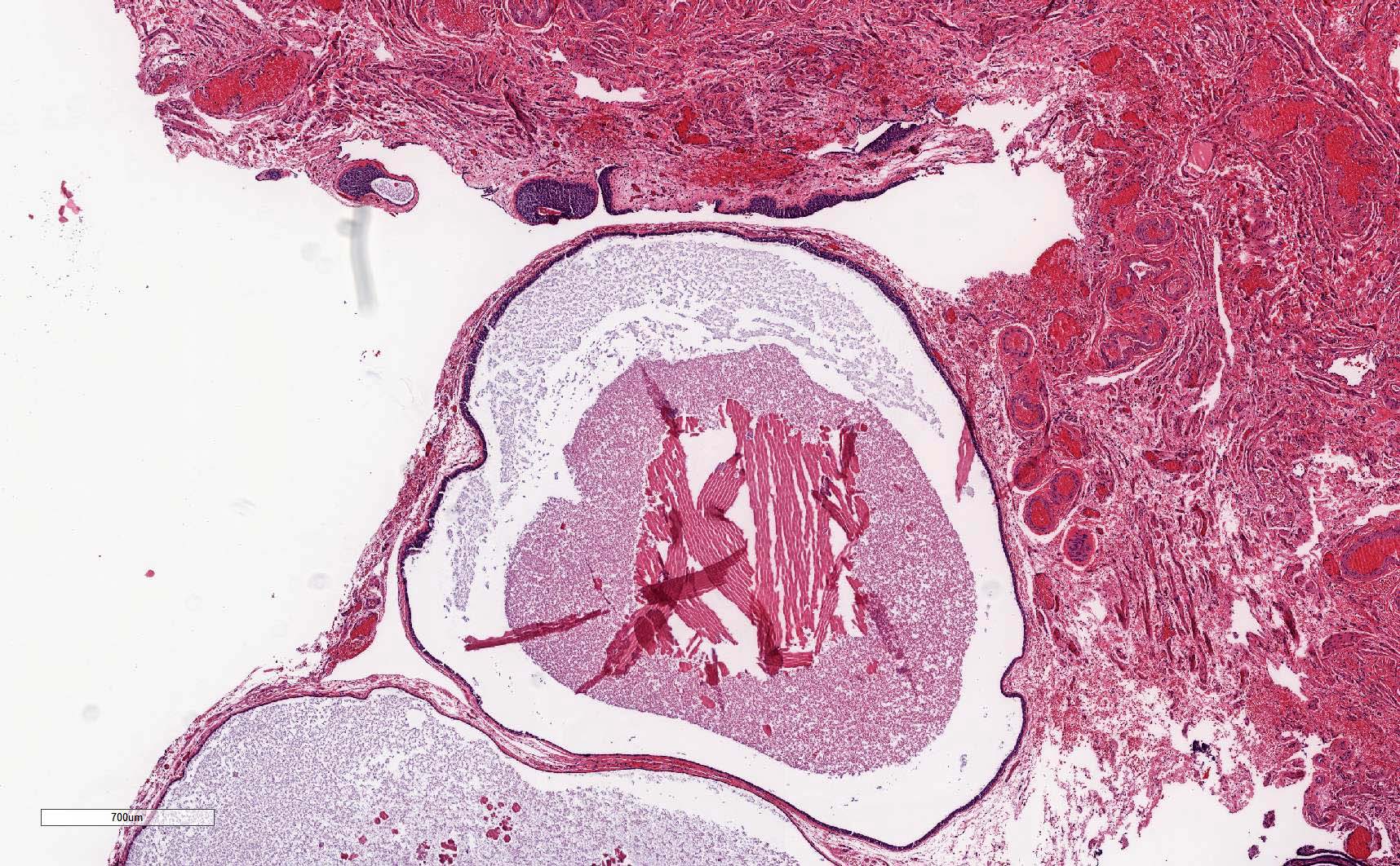
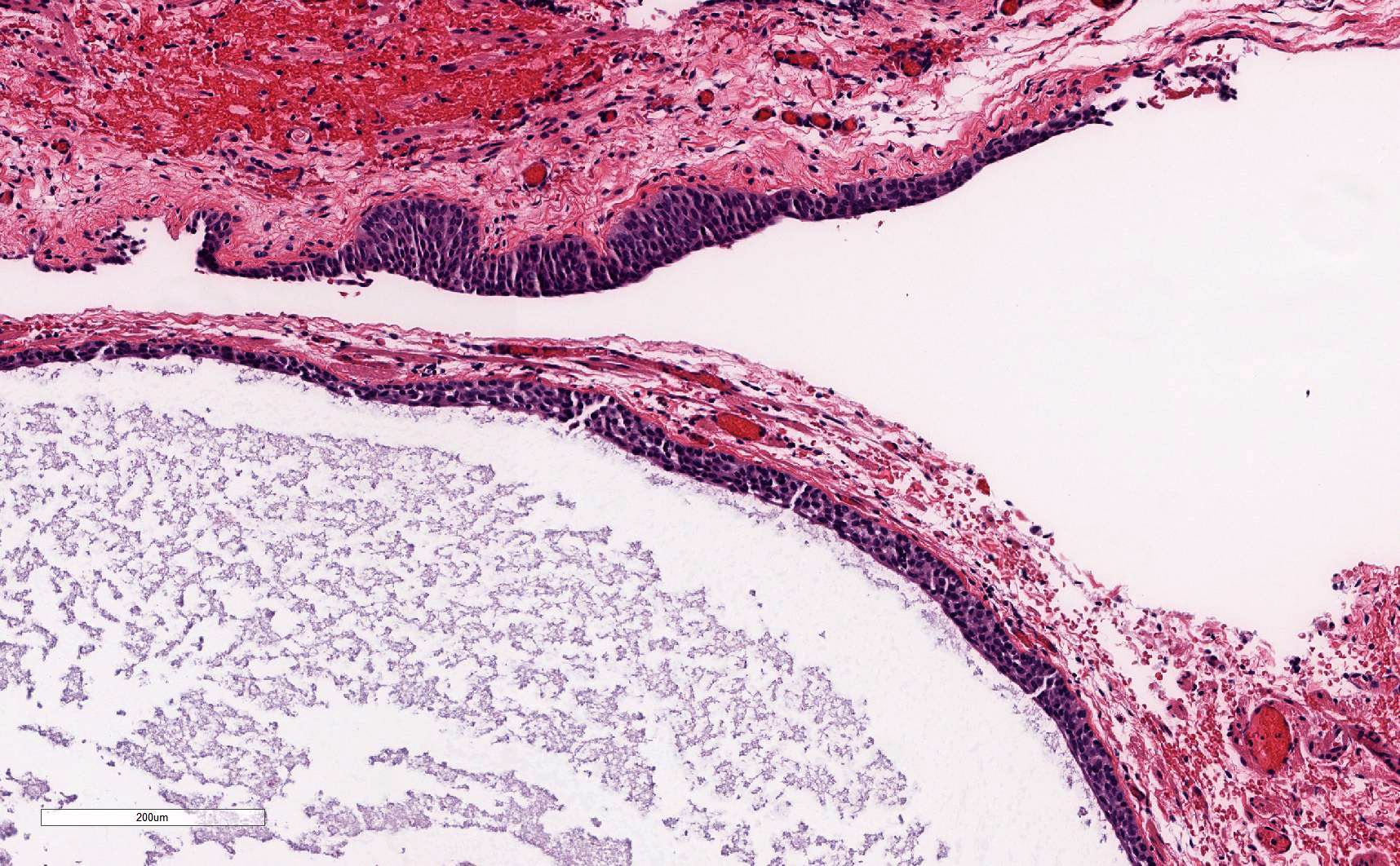
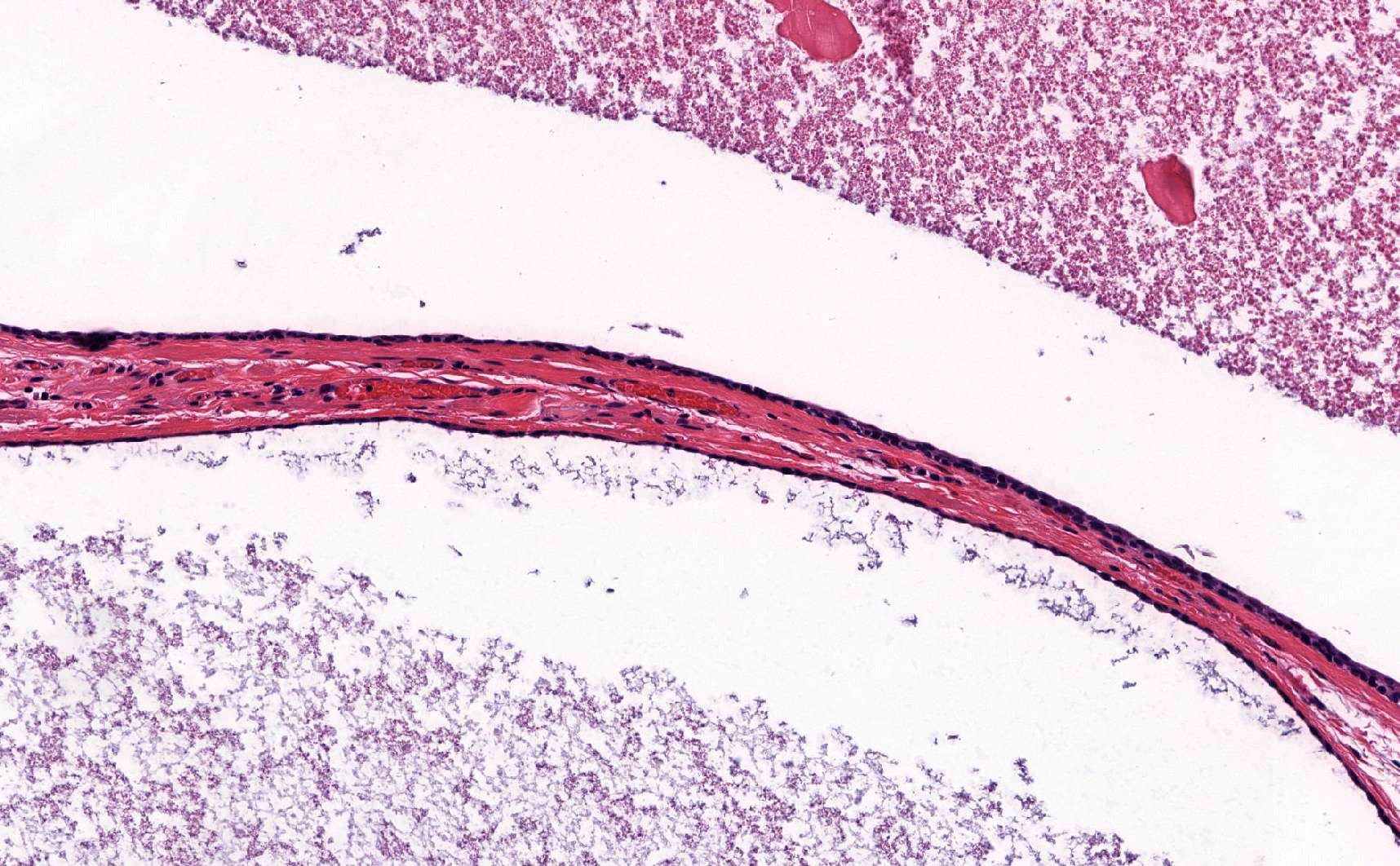
- Paramesonephric cysts are lined by single layer of bland ciliated tubal epithelium
- Mesonephric cysts are lined by single layer of low cuboidal, nonciliated epithelium with occasional clear cells (rare) (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1977;129:873)
- Mesothelial cysts are lined by single layer of flat or cuboidal, nonciliated cells, which may show transitional cell metaplasia (see Walthard cell nests)
- Distinction between the types of cyst may be difficult but has no clinical implications
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Not essential to include in report, particularly if cysts are small and incidental
- Right fallopian tube, salpingectomy:
- Fallopian tube with paratubal cysts
Differential diagnosis
- Serous cystadenoma:
- Presence of dense collagenized cyst wall
- Absence of rudimentary plicae
- Hydrosalpinx:
- Presence of well developed, smooth muscle wall
- Presence of occasional branching plicae with columnar epithelium containing histologic normal ciliated and secretory cells
- Direct communication with nondilated portion of fallopian tube
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old patient underwent total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy for a myomatous uterus. The left adnexa showed the finding in the image above. What is the next step in management regarding this finding?
- Computed tomography (CT) of the chest
- Germline testing
- No additional therapy
- Serial serum CA-125 levels
- Surgical staging
Board review style answer #1