Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Electron microscopy description | Genetics | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Karimi S, Setty S. Chronic pyelonephritis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneychronicpyelo.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Diffuse, patchy tubulointerstitial inflammation and scarring accompanied by blunting of calyces and the renal pelvis
Essential features
- Blunted, deformed, atrophic calyces with scarring due to chronic injury
- Diffuse, patchy lymphoplasmacytic tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis
- Atrophic renal tubules with thyroid type tubular atrophy and intraluminal colloid-like proteinaceous casts
- References: Kumar: Robbins Basic Pathology, 10th Edition, 2017, Urol Case Rep 2018;19:65, Emerg Radiol 2020;27:561
Terminology
- Chronic pyelonephritis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- F > M
- Common in pediatric population with congenital anomalies and vesicoureteral reflux disease
- Most common site: upper pole of the kidney
- Reference: Porter: The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 20th Edition, 2018
Sites
- Renal parenchyma
Pathophysiology
- Reflux of urine and ascending infection into the renal pelvis
- Obstructive uropathy
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Chronic inflammation and infection leading to deformed and atrophic calyces with fibrosis and scarring of the renal parenchyma
- Recurrent damage and scarring leads to renal insufficiency and end stage renal disease (ESRD)
- Complicated chronic pyelonephritis is associated with nephrolithiasis
- Most common bacterial organism associated with chronic pyelonephritis: Escherichia coli
- Reference: Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2017;312:F43, Radiol Med 2021;126:505, Am J Kidney Dis 2016;68:e23, Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006;21:1423
Etiology
- Urinary tract obstruction
- Reflux nephropathy including congenital abnormalities
- Recurrent, untreated pyelonephritis
- Neurogenic bladder
- Long term urethral catheterization
- References: Kumar: Robbins Basic Pathology, 10th Edition, 2017, J Am Geriatr Soc 1994;42:1286
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Nonspecific, generalized malaise and abdominal pain
- Proteinuria in the nephrotic range; if severe, extensive damage to the renal parenchyma
- Silent clinical course if unilateral; presents as hypertension
- Recurrent acute pyelonephritis with fever, abdominal / flank pain
- Involvement of both kidneys can result in hyperchloremic acidosis
- References: Niger Postgrad Med J 2020;27:37, Porter: The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 20th Edition, 2018
Diagnosis
- Helical CT, intravenous urography (IVU)
- CT scan: gold standard for imaging assessment of the severity of pyelonephritis
- Voiding cystourethrogram for neonates, pediatric population with congenital abnormalities
- References: Porter: The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 20th Edition, 2018, Kidney Int 1999;55:1486, Radiographics 2008;28:255
Laboratory
- Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and elevated serum creatinine
- Urinalysis: proteinuria, renal epithelial cells, granular casts, pyuria (acute on chronic, recurrent acute pyelonephritis)
Radiology description
- Focal, polar, coarse cortical scars, calyceal distortion and renal atrophy
- Hypertrophy of residual renal parenchyma, mimicking infarct on imaging
- Ureteral dilation if severe reflux disease is present
- Obstruction with calculi may be present in obstructive nephropathy
- References: Emerg Radiol 2020;27:561, Radiographics 2008;28:255
Prognostic factors
- Slow progression, > 2 decades before consequences of damage are observed
- Can lead to end stage renal disease
- Reference: Porter: The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 20th Edition, 2018
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (Urol Case Rep 2018;19:65)
- 68 year old woman with a nonenhancing left renal sinus mass (J Med Case Rep 2009;3:9054)
- 69 year old woman with primary chronic pyelonephritis (Ann Short Reports 2019;2:1039)
- 73 year old woman with chronic pyelonephritis and renal pyelocalyceal squamous cell carcinoma (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:154)
Treatment
- Surgical intervention: correction of anatomic / congenital abnormalities resulting in reflux
- Medical management: antimicrobial therapy for treatment of recurrent, acute pyelonephritis
- Long term antibiotic prophylaxis with trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, nitrofurantoin, among others
- In pediatric patients who develop end stage renal disease due to reflux, transplant is a treatment modality
- References: Tunis Med 2018;96:495, Porter: The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 20th Edition, 2018
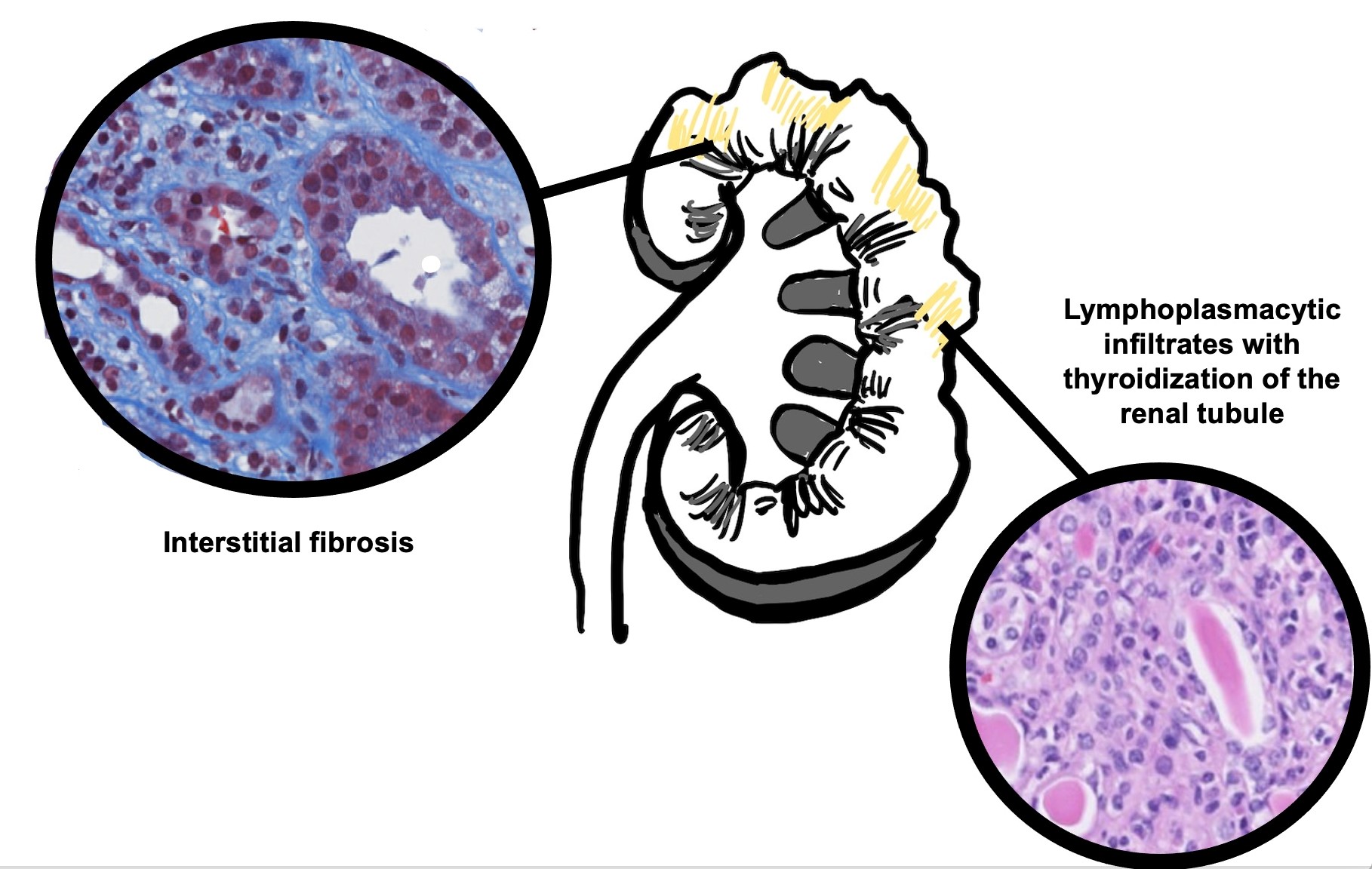
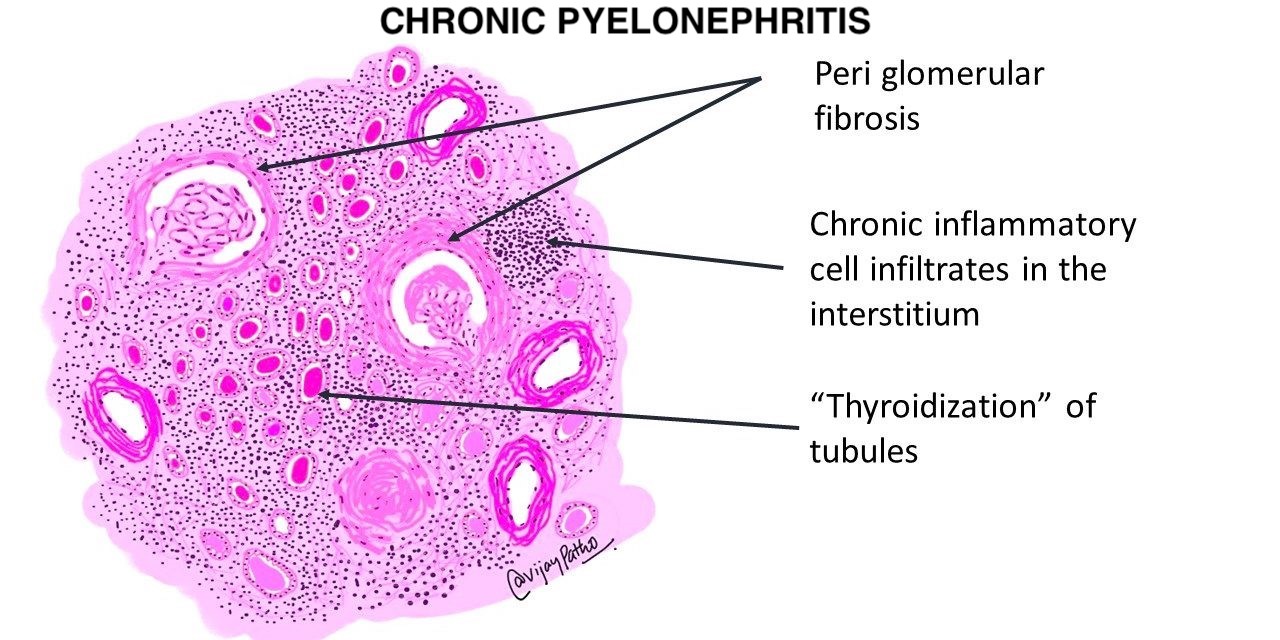
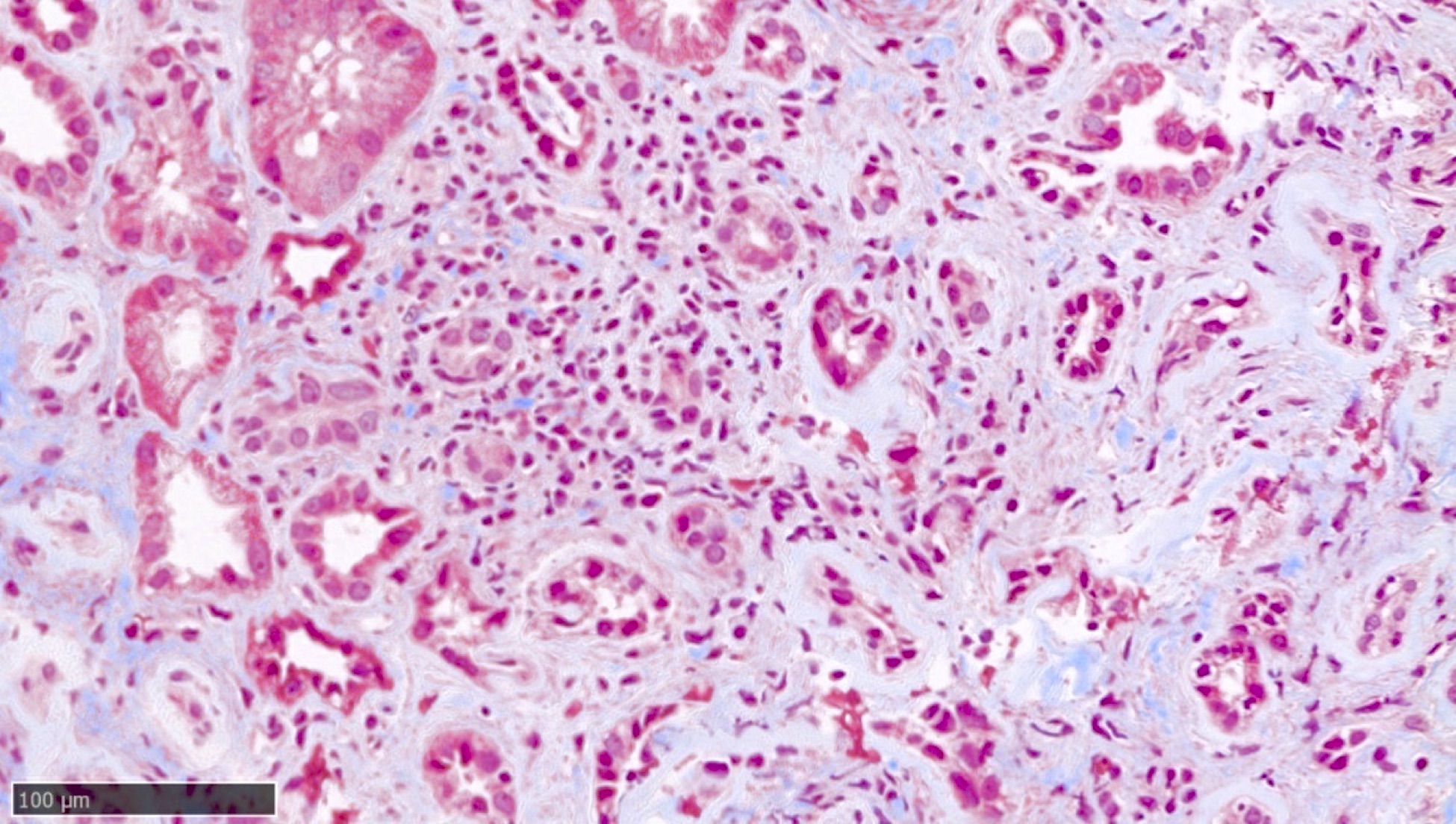
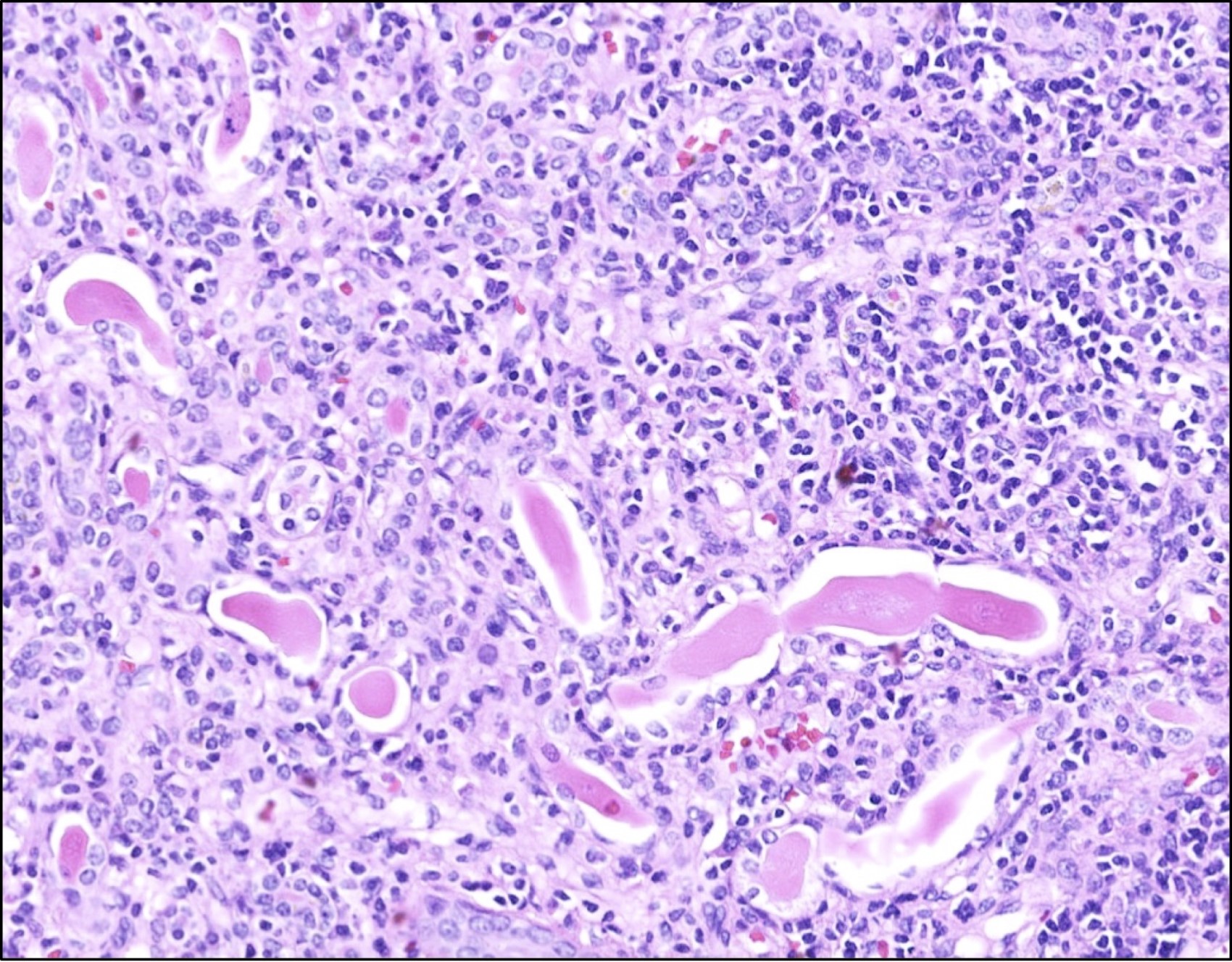
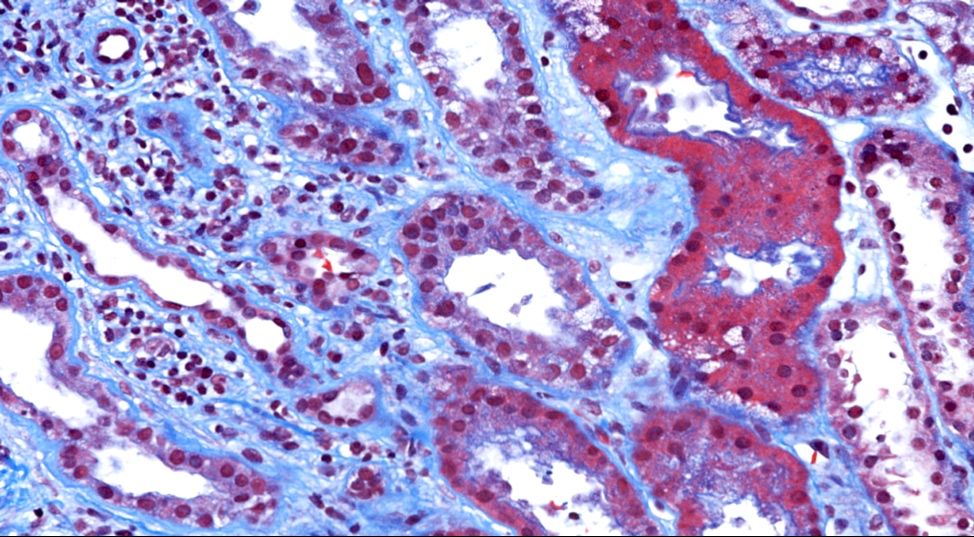
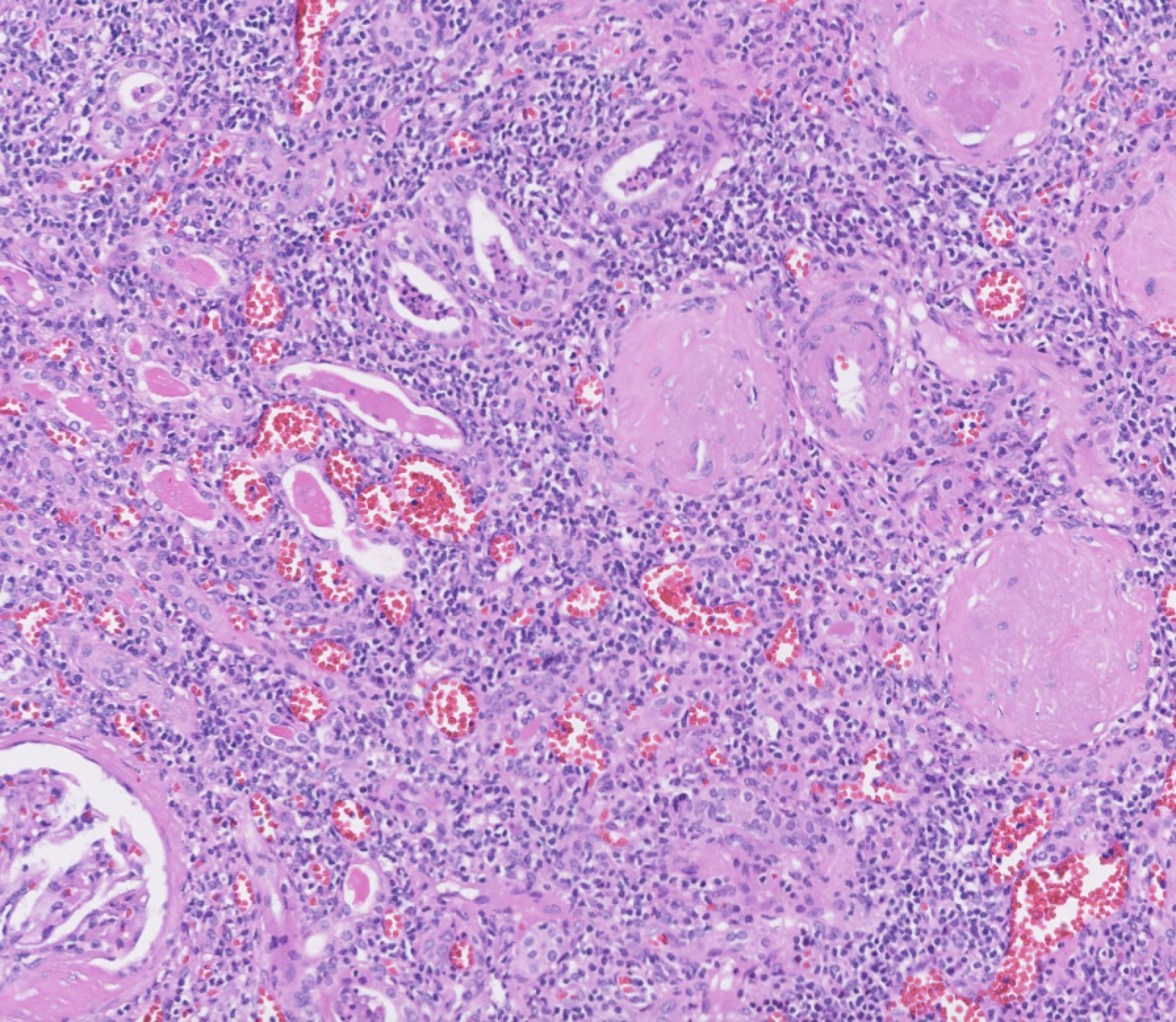
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Patchy interstitial lymphoplasmacytic inflammation with occasional, focal neutrophilic infiltration
- Patchy, well demarcated scarring of the renal pelvis and calyces
- Abundant intraluminal Tamm-Horsfall protein casts
- Tubular atrophy with thyroid type tubular atrophy and interstitial and periglomerular fibrosis
- Secondary segmental glomerulosclerosis
- References: Niger Postgrad Med J 2020;27:37, Yale J Biol Med 1985;58:91, Am J Kidney Dis 2016;68:e23
Microscopic (histologic) images
Electron microscopy description
- No specific findings
Genetics
- Mutant allele 299Gly TLR4 polymorphism
- References: Wiad Lek 2017;70:47, Pediatr Res 2007;61:371, PLoS One 2010;5:e14223
Videos
Overview of chronic pyelonephritis
Histological features of chronic pyelonephritis
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, radical nephrectomy:
- Renal cortical thinning with blunted calyces and scarring
- Global glomerulosclerosis with marked tubular atrophy and thyroid type tubular atrophy of the renal tubules
- Diffuse interstitial lymphoplasmacytic infiltration
- These findings are consistent with chronic pyelonephritis
Differential diagnosis
- End stage renal disease due to other predisposing causes:
- Cortical interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, global glomerulosclerosis and arterionephrosclerosis
- Additional features vary based on the predisposing cause
- Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis:
- Dilated pelvicalyceal system
- Can be associated with multinucleated giant cells
- Sheets of foamy macrophages admixed with inflammatory cell infiltrate
- Hypertensive / vascular injury related renal disease:
- Adherent renal capsule that does not come off easily
- Sclerotic glomeruli with ischemic changes
- Arteriolar hyalinosis, arterial myointimal hyperplasia and arterionephrosclerosis
- References: Indian J Nephrol 2019;29:111, Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2008;17:266, Kumar: Robbins Basic Pathology, 10th Edition, 2017
Board review style question #1
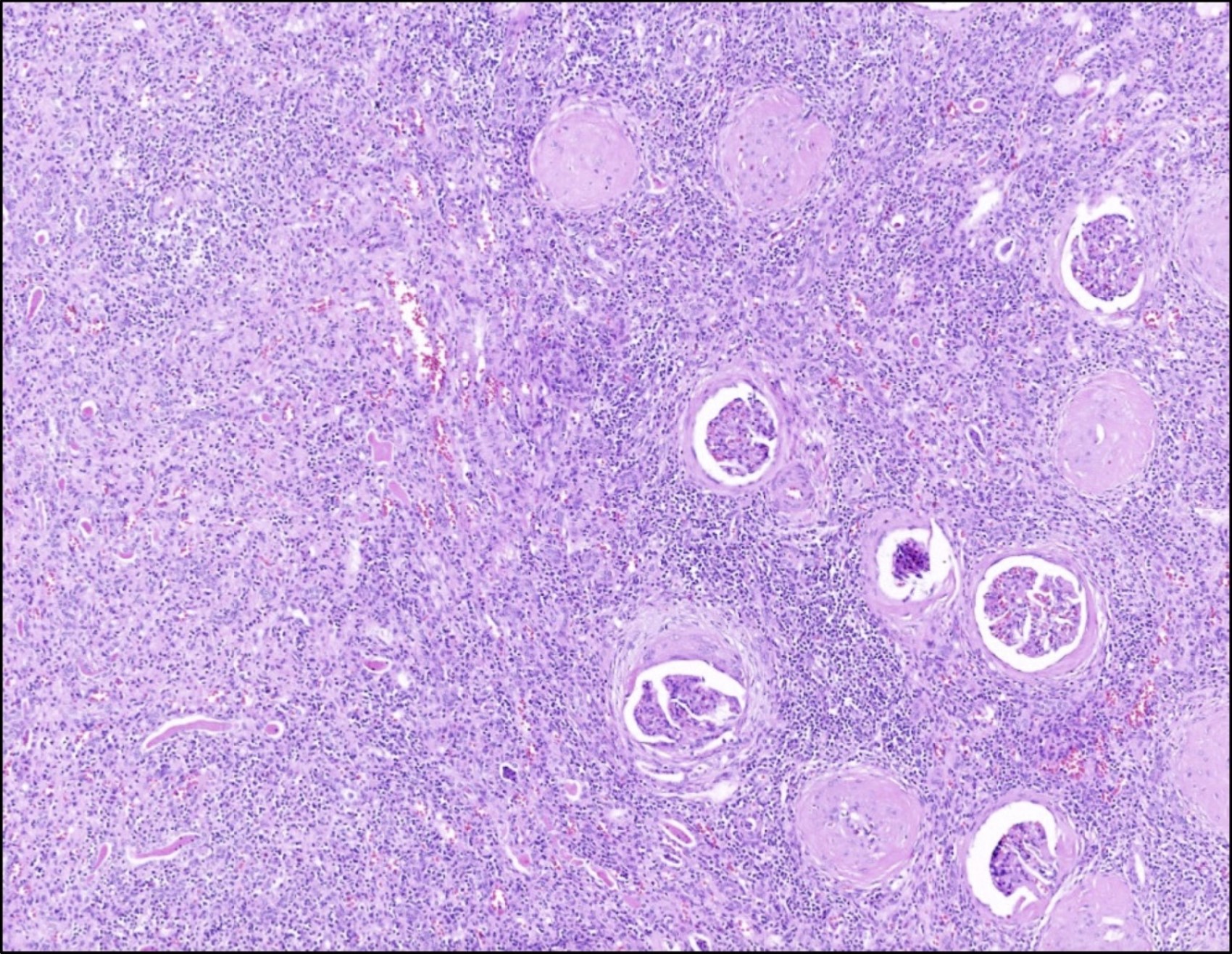
A 79 year old man presented with benign prostatic hyperplasia, obstructive uropathy and lobular segmental hypertrophy of the left kidney. A nephrectomy is performed revealing the histology above. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Chronic pyelonephritis
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Emphysematous pyelonephritis
- Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Board review style answer #1
B. Chronic pyelonephritis. The image shown above illustrates atrophic tubules with luminal casts, diffuse interstitial lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, interstitial fibrosis and globally sclerosed glomeruli. The most likely histologic diagnosis is chronic pyelonephritis.
Comment Here
Reference: Chronic pyelonephritis
Comment Here
Reference: Chronic pyelonephritis
Board review style question #2
Which of the following histologic features are associated with chronic pyelonephritis?
- Glomerular cellular crescents with segmental necrotizing change
- Histiocytes with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and Michaelis-Guttman bodies
- Interstitial dense neutrophilic inflammation and tubular luminal neutrophils
- Tubular atrophy and luminal casts; interstitial lymphoplasmacytic inflammation and fibrosis
Board review style answer #2
D. Tubular atrophy and luminal casts; interstitial lymphoplasmacytic inflammation and fibrosis
Comment Here
Reference: Chronic pyelonephritis
Comment Here
Reference: Chronic pyelonephritis