Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gietzen R, Eyzaguirre E. Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumorrenalmedfibroma.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign kidney tumor
- Asymptomatic, commonly found incidentally
- Arise from renomedullary interstitial cells
- Also known as medullary fibroma
Essential features
- Frequently found at autopsy, incidentally on imaging or resection for other reasons
- Arising from medullary interstitial cells
- Small, well circumscribed, single or multiple gray-white nodules in the renal medulla
- Spindle or stellate cells in basophilic stroma with entrapped tubules
Terminology
- Prior terms include medullary fibroma and renal hamartoma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D30.00 - Benign neoplasm of kidney
Epidemiology
- Incidence between 16% and 46% according to autopsy studies (Hum Pathol 1972;3:559)
- Mean age: 58 years (18 - 92 years), rarely seen in children (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- M = F with similar incidence (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
Sites
- Predominance: right = left kidney (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Bilateral tumors: in 41%, bilateral tumors occurred more in the elderly (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Mostly occur in the renal medulla, occasionally found in renal cortex (Urology 2014;83:1104)
- 60% of patients have multiple interstitial cell tumors, ranging from 1 to 23, mean of 3 (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
Pathophysiology
- Appears to originate as a proliferation of renomedullary interstitial cells between medullary tubules (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Renomedullary interstitial cells are involved in release of renin and regulation of sodium excretion (Eur Urol 2016;70:120)
- As their size increases, cellularity decreases, viscous eosinophilic material is deposited and tubules disappear (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Viscous eosinophilic material is not associated with amyloid but with collagen type III (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- No association with hypertension (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
Etiology
- No statistically significant associated causes (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic, found incidentally during surgery (0.2%), autopsy (16 - 46%) or radiologic investigation (Urology 2014;83:1104)
- May be symptomatic in case reports (e.g. urosepsis or hematuria) (Urology 2014;83:1104)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is made on histology post resection or on core biopsy (Adv Anat Pathol 2000;7:47)
- Imaging modalities are not conclusive and may mimic malignant conditions (Radiographics 2010;30:1525)
Radiology description
- CT: small, nonenhancing noncalcified hypoattenuating solid mass within the renal medulla (Radiographics 2010;30:1525)
- MR imaging: medullary fibromas are hypointense on T1 and T2 weighted images (Radiographics 2010;30:1525)
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognostic factors and mostly asymptomatic (Urology 2014;83:1104)
- After resection, no recurrence (Urology 2014;83:1104)
Case reports
- 20 year old woman with incidental detection at autopsy (Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 2014;8:440)
- 29 year old man found to have a calcium oxalate deposition in a renomedullary interstitial cell tumor at autopsy (Pathol Oncol Res 2003;9:47)
- 32 year old man presented with hematuria, left flank pain and incidental tumor (J Clin Imaging Sci 2013;3:43)
- 50 year old man was found to have renomedullary interstitial cell tumor during a kidney transplant (Indian J Urol 2012;28:202)
Treatment
- Surgical resection is recommended if imaging is inconclusive (Urology 2014;83:1104)
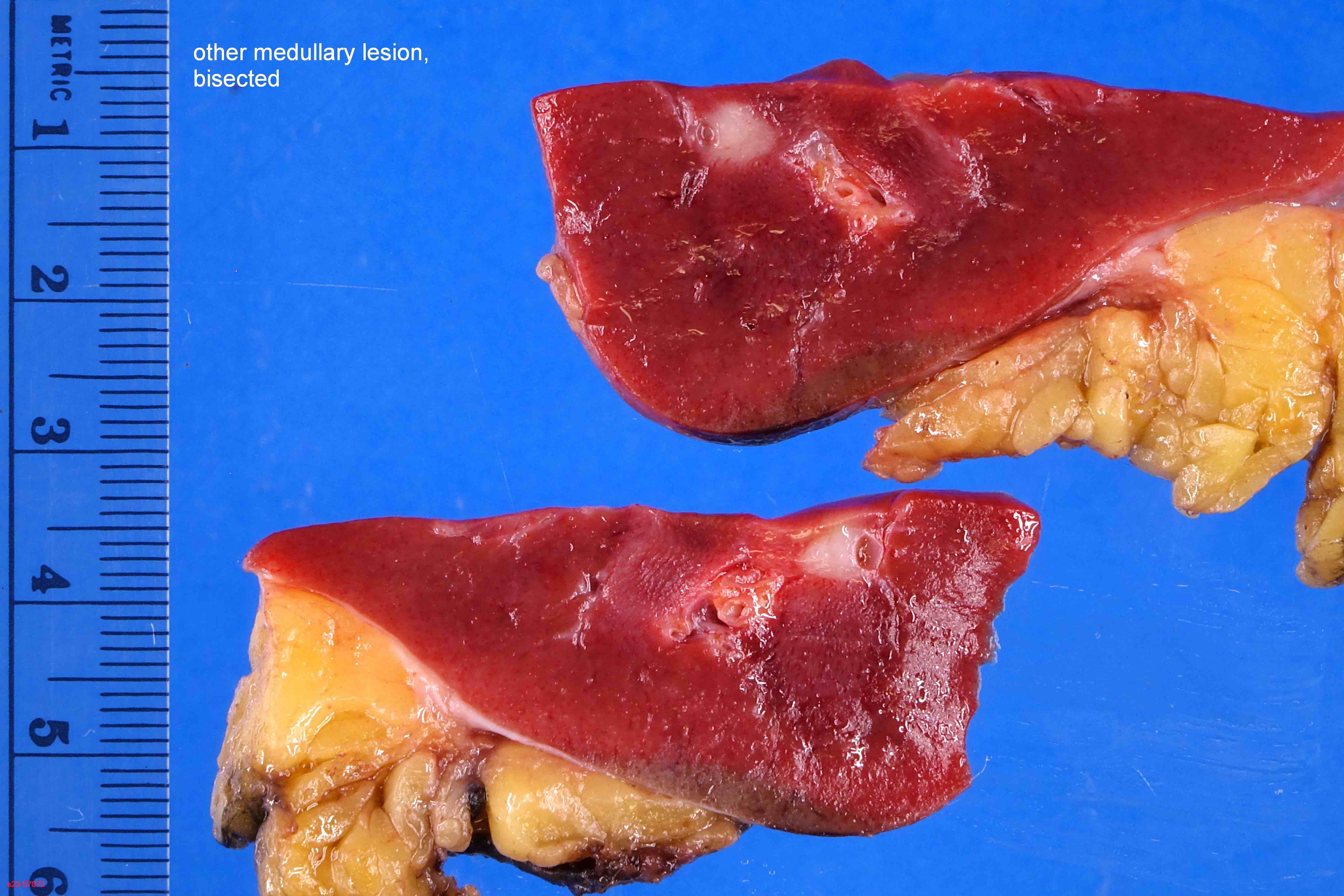
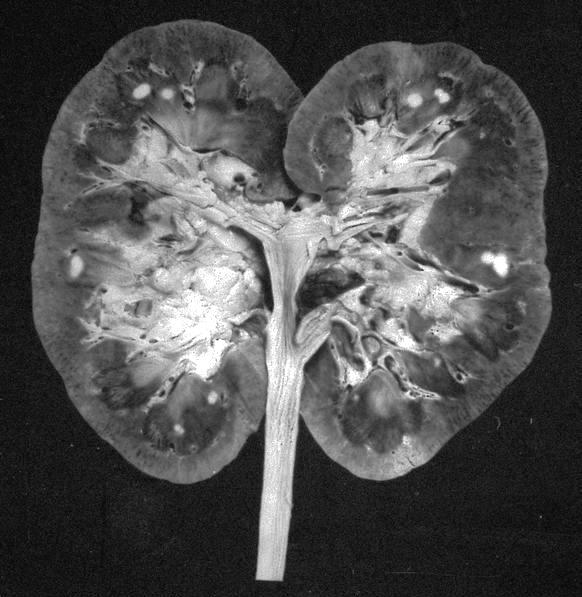
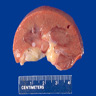
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, homogenenous white / gray-white nodules usually in the medulla
- Small (1 - 13 mm), median tumor size 4 mm and up to 5 cm has been reported in case reports (Hum Pathol 2018;82:46)
- Arises from medulla but occasionally from the cortex (Urology 2014;83:1104)
- Surrounding kidney tissue showed that 47% had normal renal parenchyma, 28% showed slight glomerulosclerosis, 19% moderate and 7% severe glomerulosclerosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
Gross images
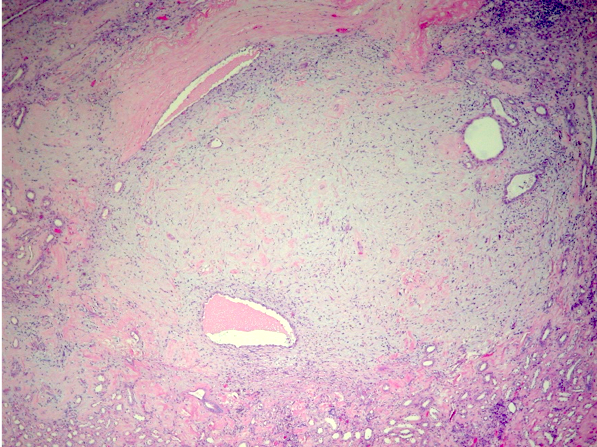
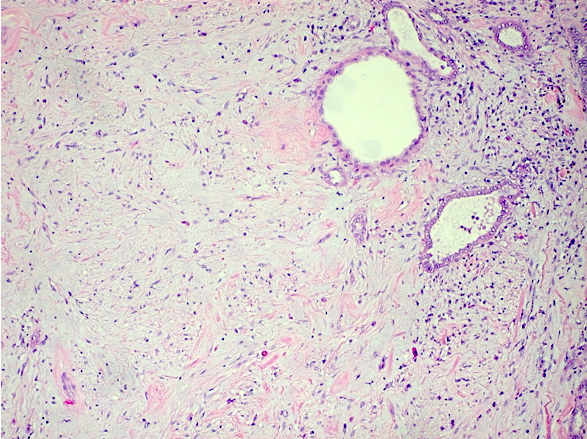
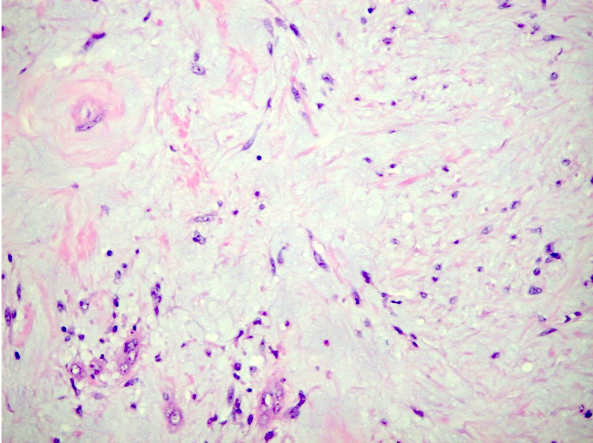
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Small, spindle or stellate cells in a background of loose basophilic stroma or fibrotic stroma with entrapped tubules (Urology 2014;83:1104, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Some cases may contain irregular deposits of amyloid (Eur Urol 2016;70:120)
- Entrapped tubules may be seen diffusely at the periphery and may be cystically dilated (Urology 2014;83:1104, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Nuclear features: open chromatin and minimal atypia or hyperchromasia (Urology 2014;83:1104, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Absent / rare mitotic activity (Urology 2014;83:1104, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
- Surrounding kidney tissue showed that 47% had normal renal parenchyma, 28% showed slight glomerulosclerosis, 19% moderate and 7% severe glomerulosclerosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1693)
Positive stains
- Calponin (weak to moderate)
- Oil Red O and Sudan Black B (Hum Pathol 2018;82:46)
Electron microscopy description
- Resembles renomedullary interstitial cell of kidney with large cytoplasmic lipid droplets (Hum Pathol 1972;3:559)
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, right, laparascopic complete nephrectomy:
- Renal cell carcinoma, clear cell type (see synoptic report)
- Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor
- Kidney, right, mass, needle core biopsy:
- Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor
Differential diagnosis
- Metanephric stromal tumor:
- Concentric rings or collarettes of stromal cells around entrapped renal tubules and blood vessels
- Unencapsulated infiltrative tumor of spindle and epithelioid cells
- Rare in adults
- Scar:
- History of poor renal function, renal stones or prior procedures
- Not well circumscribed
- Less basophilic
- More likely to be associated with inflammation
Board review style question #1
An 85 year old man underwent nephroureterectomy for low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis. A 3 mm white, solid, medullary based incidental lesion is noted on gross examination. Which of the following is true for this tumor?
- They are uncommon tumors seen more frequently in children
- They are typically medullary based tumors composed of stellated interstitial cells immersed in a basophilic matrix with entrapped renal tubules
- Although the majority are benign, rarely metastasis have been described
- Frequently, they present with hematuria and flank pain
Board review style answer #1
B. This is a renomedullary interstitial cell tumor. They are typically medullary based tumors composed of stellated interstitial cells immersed in a basophilic matrix with entrapped renal tubules.
Comment Here
Reference: Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor
Board review style question #2
Which is true about renomedullary interstitial cell tumors?
- Often, these tumors are unifocal, found within the cortex and more than 10 mm in size
- They are asymptomatic and often found incidentally during nephrectomy or at autopsies
- They are CD34 and ER positive and desmin and smooth muscle negative
- Congo red stain is characteristically positive in all tumors
- Specialized myofibroblast is the probable cell of origin
Board review style answer #2
B. They are asymptomatic and often found incidentally during nephrectomy or at autopsies
Comment Here
Reference: Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor