Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Mihova D. AML with minimal differentiation (FAB AML M0). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiaM0.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- No definitive evidence of myeloid differentiation by morphology and light microscopy cytochemistry; need immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, or EM cytochemistry to characterize as myeloid
- Criteria for diagnosis: nongranular blasts; less than 3% of blasts are positive for myeloperoxidase (MPO), Sudan Black B (SBB) or naphthol-ASD-chloroacetate esterase (CAE) by enzyme cytochemistry, although blasts may express myeloperoxidase by EM or immunohistochemistry; blasts do not express classic lymphocyte antigens, but may aberrantly express some lymphocyte antigens
Clinical features
- 5% or less of AML cases; any age, mostly infants or older adults
- Typically presents with anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, marrow failure, but may have leukocytosis with markedly increased blasts
- Children (Blood 2007;109:2314) and adults (Br J Haematol 2001;113:737) may have poorer outcome than other AML subtypes
- Enzyme cytochemistry: negative for nonspecific esterase, although may have nonspecific weak or focal reaction distinct from monocytic cells
Case reports
- 58 year old man with minimally differentiated acute myelogenous leukemia (AML-M0) granulocytic sarcoma in oral cavity (Oral Oncol 2002;38:516)
- Subtelomeric t(5;9)(q35.3;q34.3) and deletion of RB1 gene (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2008;181:36)
- Deletion of (15)(q11.2q22) (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2008;184:57)
Microscopic (histologic) description
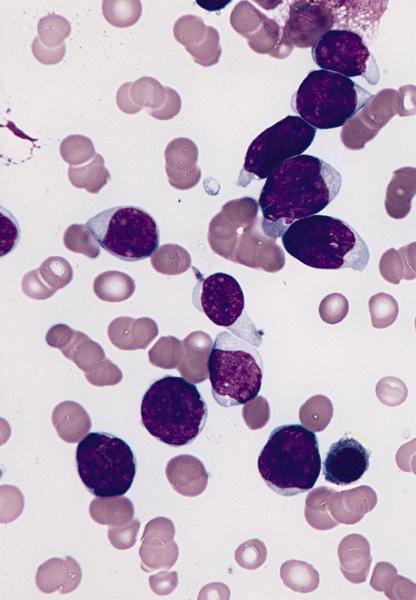
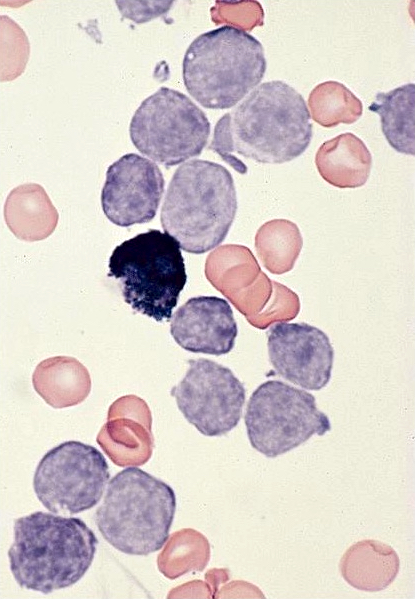
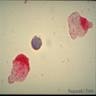
- Medium sized blasts, round or slightly indented nuclei with dispersed chromatin
- One or two nucleoli, agranular cytoplasm with varying degree of basophilia and no Auer rods
- Rarely small blasts with condensed chromatin and scant cytoplasm that may resemble lymphoblasts
- Occasionally, residual normal population of maturing neutrophils may be present
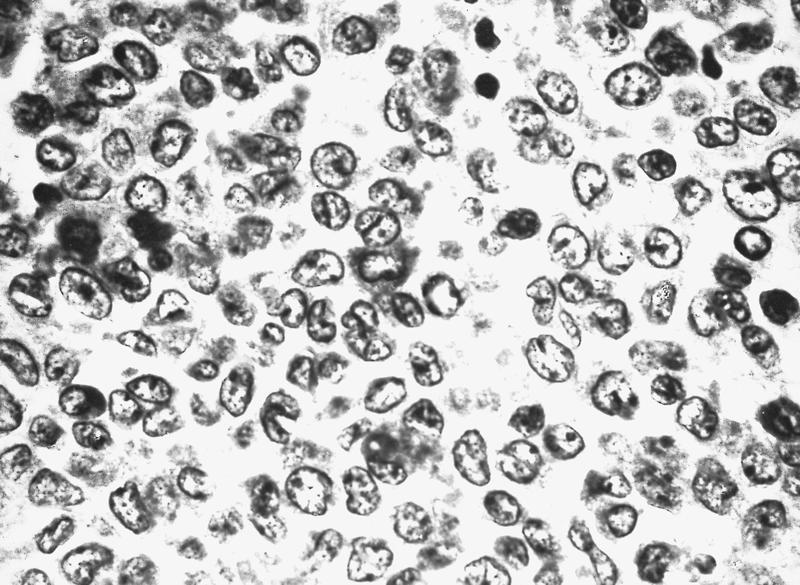
- Bone marrow: markedly hypercellular with poorly differentiated blasts
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
Flow cytometry description
- Pediatric AML-M0 is usually CD33 bright, TdT-, CD34- and CD13-/weak (Am J Clin Pathol 2000;113:193, Clinical Flow Wiki: Acute Minimally Differentiated Leukemia (M0) [Accessed 3 April 2018])
Positive stains
- CD13, CD33 (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:876), CD34, CD117 (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:380), HLA-DR and CD38
- Variable expression of myeloperoxidase, Sudan Black B, TdT (50%), CD2, CD4, CD7 (40%) and CD16 / CD56
Negative stains
- CD11b (usually), CD14 (usually), CD15 (usually), CD36 (usually), CD41, CD61, CD64 (usually, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:748) and most lymphocyte antigens(CD5, cCD3, cCD79a, cCD22)
- Glycophorin A
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Often complex chromosomal abnormalities; tend to have more -5/del(5q), -7/del(7q), +8 and del(11q), but these should be reclassified as AML-MRC
- AML1 / CBFA / RUNX1 (27%) and strong association with trisomy 13 and FLT3 mutation (16 - 22%, Haematologica 2007;92:1123)
- More often trisomy 21 and hypodiploidy than other AML, although outcome is similar (Blood 2007;109:2314)
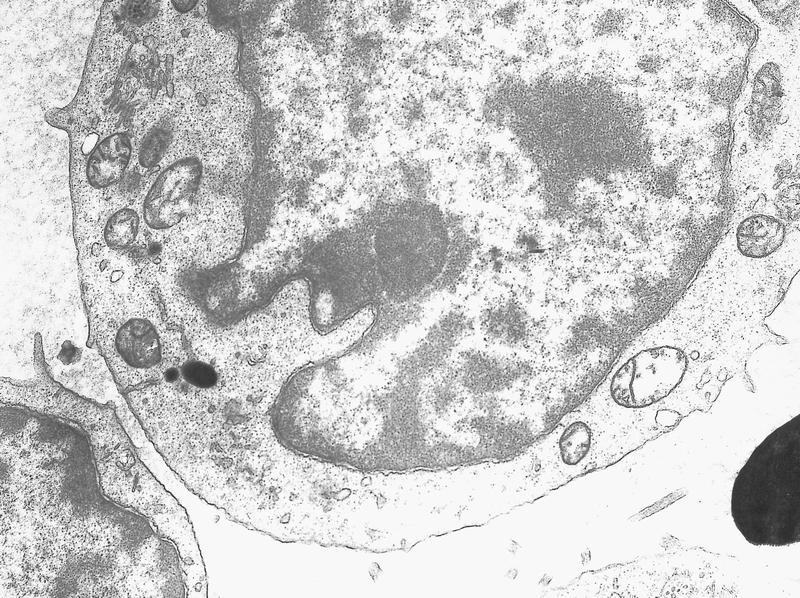
Electron microscopy description
- Resembles myeloblasts; may show focal myeloperoxidase+ granules
Electron microscopy images
Differential diagnosis
- Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage
- ALL
- AML-MRC
- Mixed phenotypic leukemia
- AML-M7 (megakaryoblastic)
- Leukemic phase of large cell lymphoma