Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gonzalez R. Large duct obstruction. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liveracutelargeductob.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Obstruction of the large extrahepatic bile ducts, leading to liver injury
Essential features
- May be caused by stricture, gallstones or malignancy
- Typically a clinical diagnosis; uncommonly biopsied
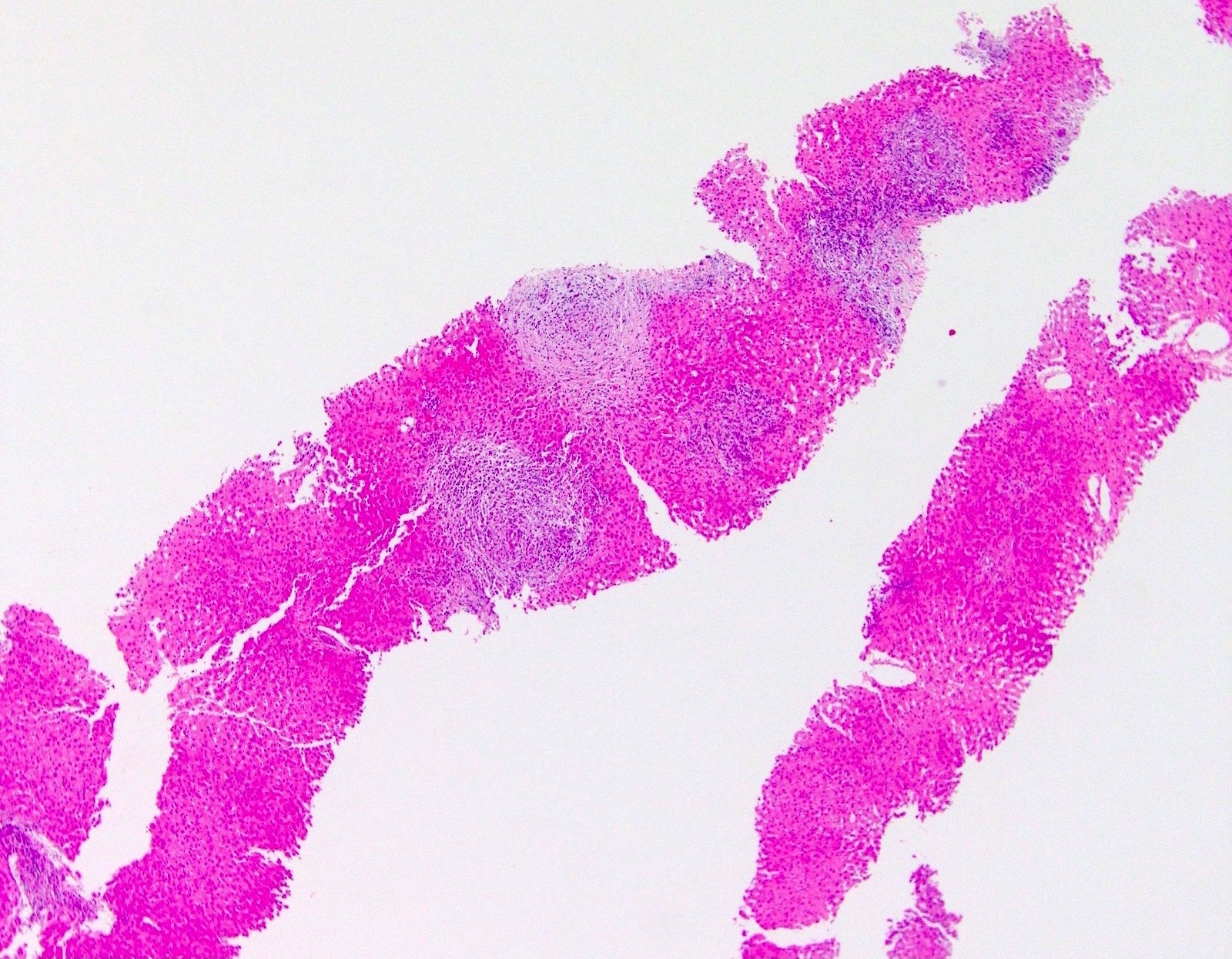
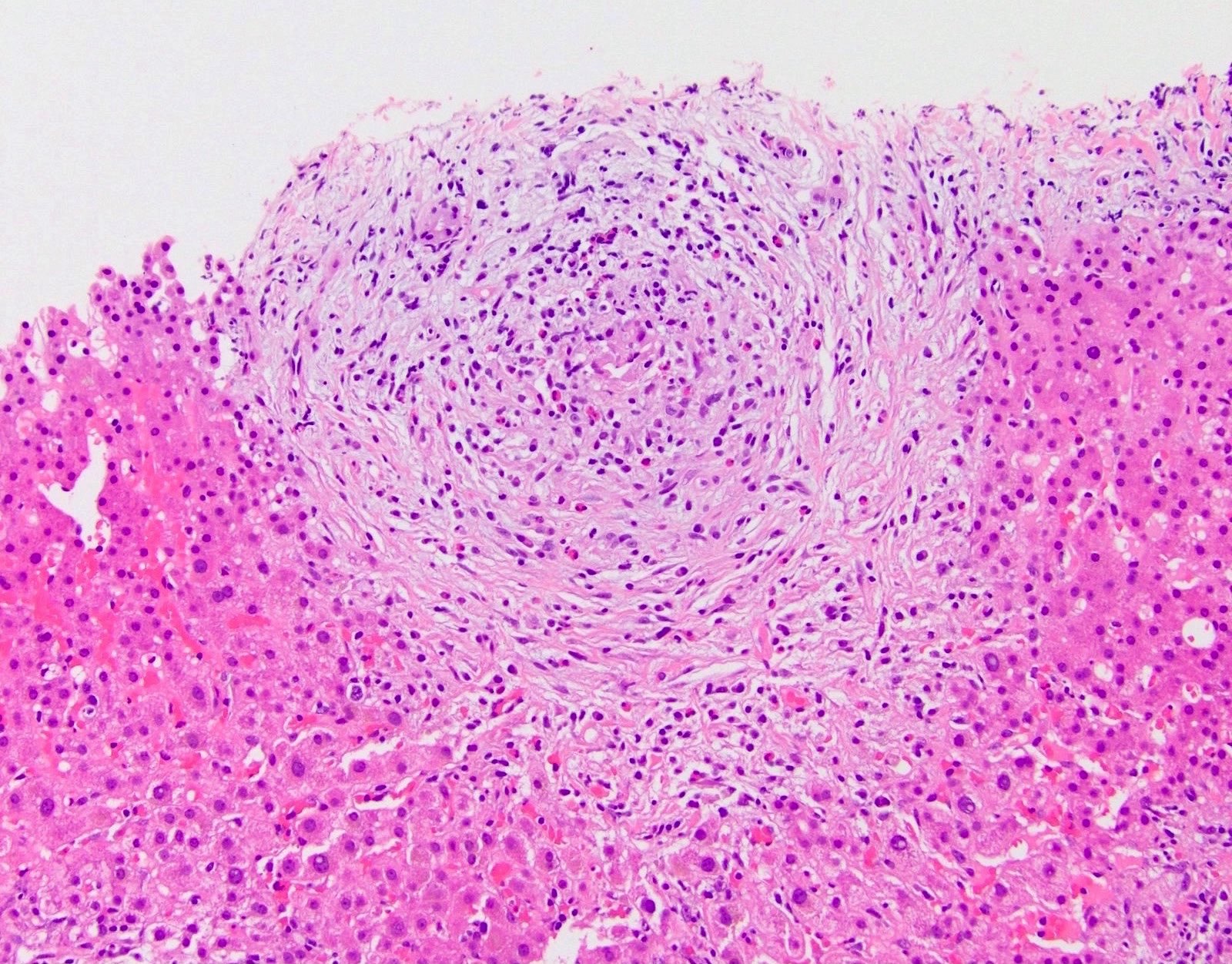
- Histology shows biliary-pattern injury (cholestasis, ductular reaction), often with prominent portal tract edema
Terminology
- May be acute or chronic
- May be termed "mechanical bile duct obstruction"
ICD coding
- ICD10: K83.1 - obstruction of bile duct
Pathophysiology
- Obstruction of bile outflow leads to cholestasis, ductular reaction and liver injury
Etiology
- Usually due to gallstones in common bile duct; other causes include stricture (such as from primary sclerosing cholangitis), malignancy, bile plugs and surgical ligation
Clinical features
- Symptoms include jaundice, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever
- Biopsies have decreased due to improved imaging
- Without treatment, may progress to fibrosis / cirrhosis with duct loss
Diagnosis
- Typically made by clinical presentation (including rapid onset in acute disease) and radiologic findings
Laboratory
- Increased alkaline phosphatase and conjugated bilirubinemia (J Clin Pathol 1994;47:457)
- Normal prothrombin time
- May demonstrate transient increase in ALT and AST
Radiology description
- Etiology may be visible on imaging; also, ducts proximal to obstruction may be dilated
Case reports
- 40 year old woman with hepatic fascioliasis (Pan Afr Med J 2017;28:44)
- 67 year old man with abdominal aortic aneurysm (BMJ Case Rep 2017;2017:220539)
- 77 year old woman with large enterolith (Korean J Gastroenterol 2016;67:150)
- 84 year old man with gastric adenocarcinoma (Med Case Rep 2019;13:72)
Treatment
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) can remove gallstones and stent stricture
- Antibiotics if secondarily infected
- Surgical intervention may be necessary
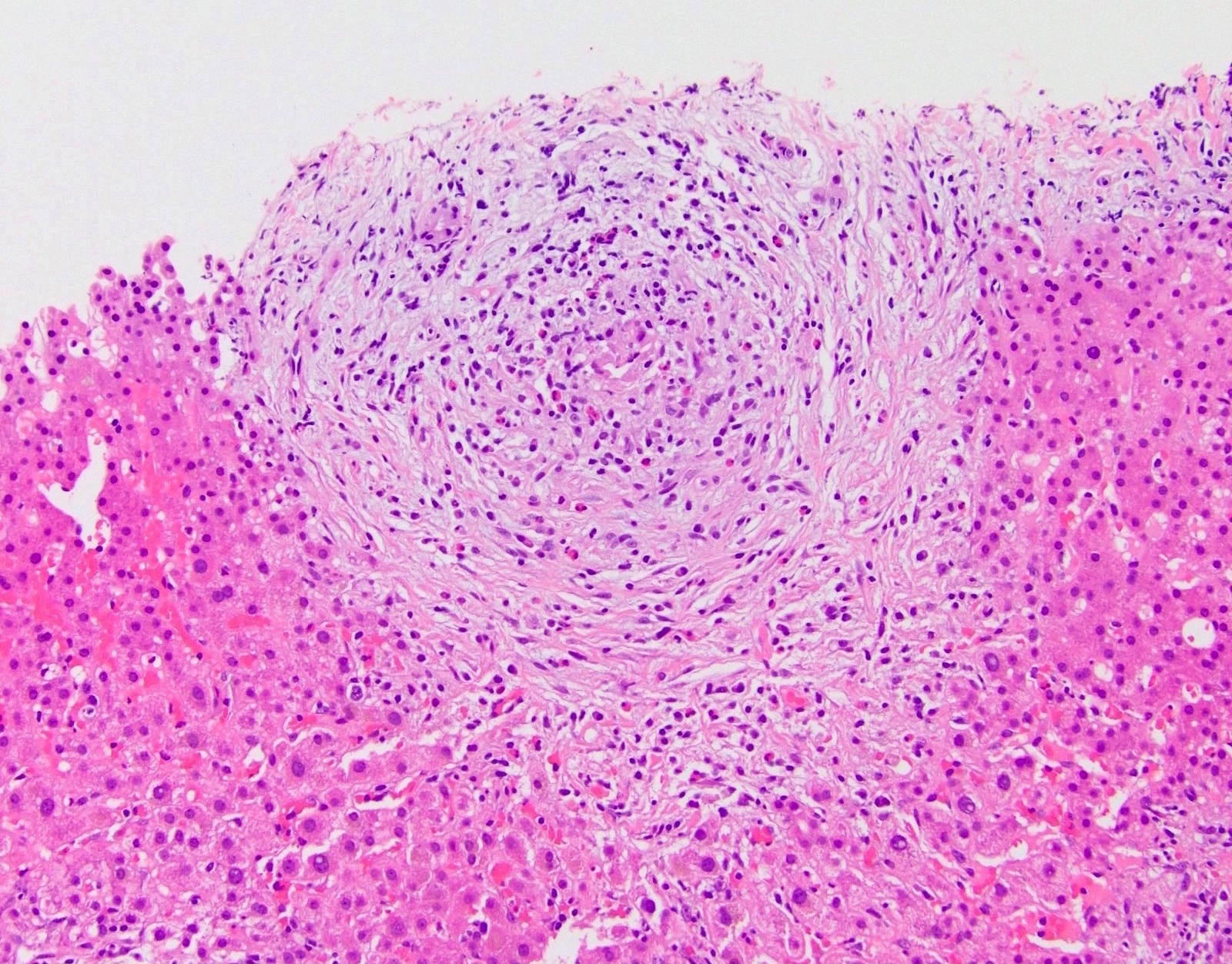
Microscopic (histologic) description
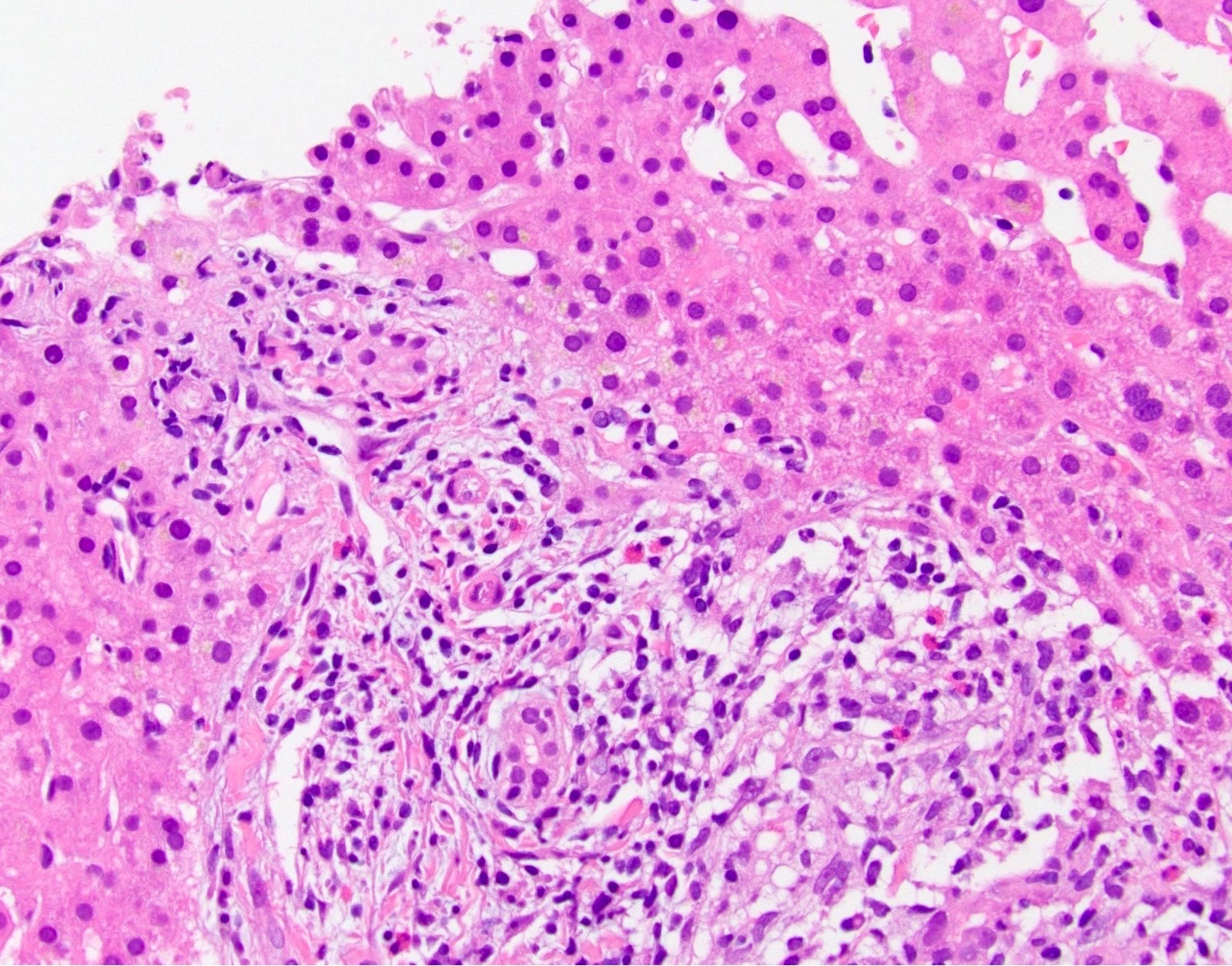
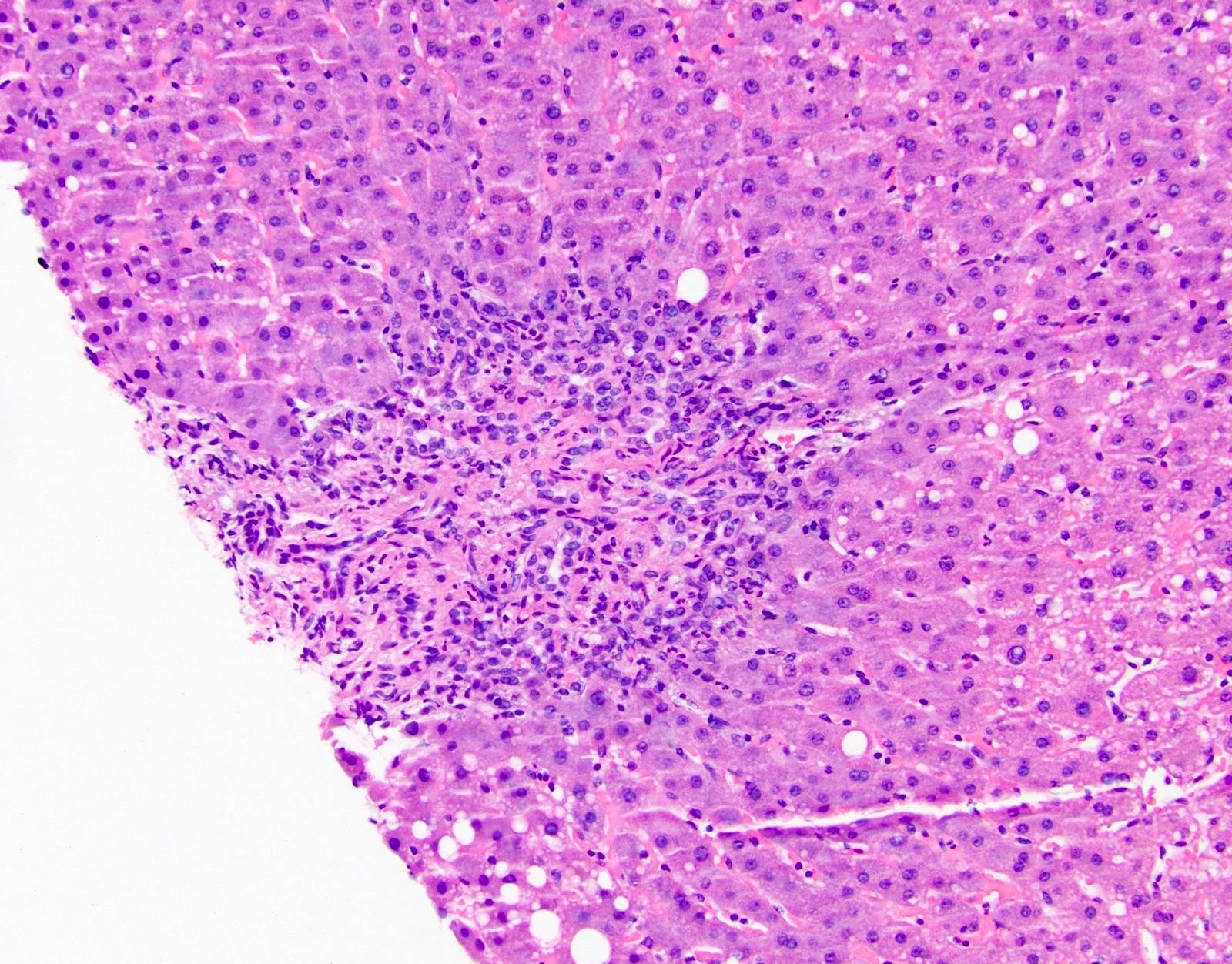
- Acute / early changes: centrilobular canalicular cholestasis, followed shortly by portal tract edema, ductular reaction and mild chronic inflammation
- Chronic / late changes: portal tract fibrosis, feathery degeneration of hepatocytes adjacent to cholestasis, bile in Kupffer cells; may develop bridging fibrosis and ultimately cirrhosis
- Lobules minimally affected since injury occurs via portal tracts
- Bile may leak into parenchyma, with adjacent foreign body giant cell reaction
- Cholestasis may be severe (J Clin Pathol 2018;71:72)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- CK7 highlights ductular reaction (as in all biliary pattern injury)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, biopsy:
- Hepatic parenchyma with prominent portal tract edema, ductular reaction and canalicular cholestasis (see comment)
- Comment: The patient’s history of acute-onset nausea and vomiting is noted, along with increased alkaline phosphatase. The findings are most consistent with acute large duct obstruction. The etiology of the obstruction is not evident in this sample; possibilities include primary sclerosing cholangitis, gallstones, duct structure and malignancy.
- Hepatic parenchyma with prominent portal tract edema, ductular reaction and canalicular cholestasis (see comment)
Differential diagnosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis:
- Onion skinning fibrosis must be distinguished from portal tract edema
- Primary biliary cholangitis:
- Lobular inflammation often present
- Drug reaction:
- Unlikely, but can mimic duct obstruction; clinical correlation necessary
- Hyperalimentation toxicity:
- Can sometimes mimic duct obstruction; clinical correlation necessary
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following is the first finding chronologically in acute obstruction of large bile ducts?
- Canalicular cholestasis
- Ductitis
- Ductular reaction
- Florid duct lesions
- Portal tract edema
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2