Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez R. Portal vein obstruction. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverportalveinobstruction.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Blockage of blood flow through the portal vein into the liver
Essential features
- Malignant and nonmalignant processes may cause portal vein obstruction
- Portal hypertension commonly results
- Biliary abnormalities may also occur
Terminology
- Portal vein obstruction leading to splenomegaly and anemia is termed "Banti syndrome"
- Portal vein obstruction may cause a sclerosing cholangitis-like clinical picture termed "portal biliopathy" (World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:6177, Gut 1992;33:272
Epidemiology
- Relatively rare
Pathophysiology
- Hepatic artery buffer response allows for increased arterial flow to liver when portal vein is obstructed
Etiology
- Prothrombotic disorders, tumor thrombus, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, various infections (e.g. schistosomiasis) (BMC Gastroenterol 2007;7:34)
- Intraabdominal infection and appendicitis are common causes in children
- May be idiopathic
Clinical features
- Signs / symptoms:
- Abdominal pain
- Ascites (massive, intractable)
- Portal hypertension
- Bowel infarction
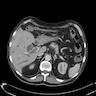
Radiology description
- Dynamic contrast enhanced CT may show filling defect if secondary to thrombus (Abdom Imaging 2008;33:72)
Case reports
- 28 year old man with portal vein thrombosis (J Am Board Fam Med 2008;21:237)
- 34 year old man with cytomegalovirus infection and portal vein thrombosis (Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:e13)
- 43 year old woman with portal vein thrombosis (Oncol Lett 2015;9:2495)
Treatment
- Anticoagulation if caused by acute portal vein thrombosis (Neth J Med 2009;67:46)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sinusoidal dilation, increased portal tract vessels and hepatocyte atrophy may be seen (Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1989;415:61)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, native, orthotopic transplantation:
- Liver with portal vein thrombosis and patchy sinusoidal dilation and zone 3 necrosis (see comment)
- Comment: The parenchymal findings are mild, as is often the case with portal vein obstruction. Trichrome and iron stains are unremarkable.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A patient develops portal vein thrombosis secondary to appendicitis.
Based on this information, which of the following is most likely true regarding the patient?
- Has an allograft liver
- Has situs inversus
- Has von Willebrand disease
- Is a child
- Is a woman
Board review style answer #1