Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Wu R. Lipoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumorlipoma.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Very rare; usually endobronchial, usually men ages 50+ (Chest 2003;123:293)
- Benign neoplasm composed of mature adipose tissue
- Treatment of choice is bronchoscopic removal
Essential features
- Endobronchial lipomas may show focal cytologic atypia and fibrosis but molecular evidence suggests similarity to lipomas of other sites
- Endobronchial lipomas clinically mimic other tumors and may cause obstructive symptoms
- Pulmonary lipomas lack the cartilage, myxoid matrix, entrapped bronchial epithelium, or other mesenchymal components seen in pulmonary hamartomas
Epidemiology
- Very rare, 0.1 to 0.5% of all lung tumors
- Older men, mean age 65, majority with smoking history
- May be associated with obesity
Sites
- Usually endobronchial (large bronchi), very rarely parenchymal
- More common in right lung
Pathophysiology
- Typically sporadic
Etiology
- Endobronchial lesions may arise from peribronchial or submucosal adipocytes
- Parenchymal lesions may arise from adipocytes of subsegmental bronchi or subpleural fatty tissue
Clinical features
- Slow growing, indolent
- Discovered incidentally by imaging or during bronchoscopy for other reasons
- Larger endobronchial lesions may present with cough, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, empyema, hemoptysis
- May mimic endobronchial carcinoid, malignancy or asthma / COPD
Diagnosis
- CT or MRI can suggest diagnosis
- Bronchoscopic biopsy or excision for endobronchial lesions
Radiology description
- High signal intensity of fat in all MRI sequences
- CT shows smooth, non-enhancing, homogenous mass with fat density
- May see peripheral air trapping on CT with obstructive endobronchial lesions
Prognostic factors
- Benign, but large lesions may cause obstructive complications
Case reports
- 26 year old woman with peripheral intrapulmonary lipoma (Pol J Pathol 2011;62:113)
- 52 year old man with endobronchial lipoma mimicking asthma and malignancy (Prim Care Respir J 2010;19:281)
- 54 year old woman with peripheral intrapulmonary lipoma (Tuberk Toraks 2006;54:374)
- Peripheral intrapulmonary lipoma (Br J Radiol 2004;77:60)
- Endobronchial lipoma (Ther Adv Respir Dis 2014;8:162)
- Intraparenchymal pulmonary lipoma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:244)
Treatment
- Resection is curative
Gross description
- Endobronchial tumors are generally < 3 cm
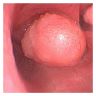
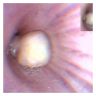
- Well circumscribed, polypoid or sessile, yellowish mass on bronchoscopy
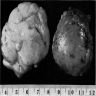
- Yellow-grey mass with firm capsule
- Intraparenchymal lesions are well circumscribed, soft, lobulated, yellow
Microscopic (histologic) description
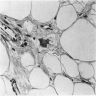
- Mature adipose tissue underlying respiratory epithelium, with scattered lymphocytes and histiocytes
- May show fibrosis and hyperchromatic stromal cells
- Rarely has osteocartilaginous metaplasia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HMGA1 or HMGA2 rearrangements seen in endobronchial lipomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1715)
Differential diagnosis