Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Kajtár B. CLL / SLL. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaCLL.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Indolent mature B cell lymphoma
- Clonal proliferation of B cells with characteristic phenotype
Essential features
- Indolent mature B cell lymphoma
- Most common adult leukemia in the Western world
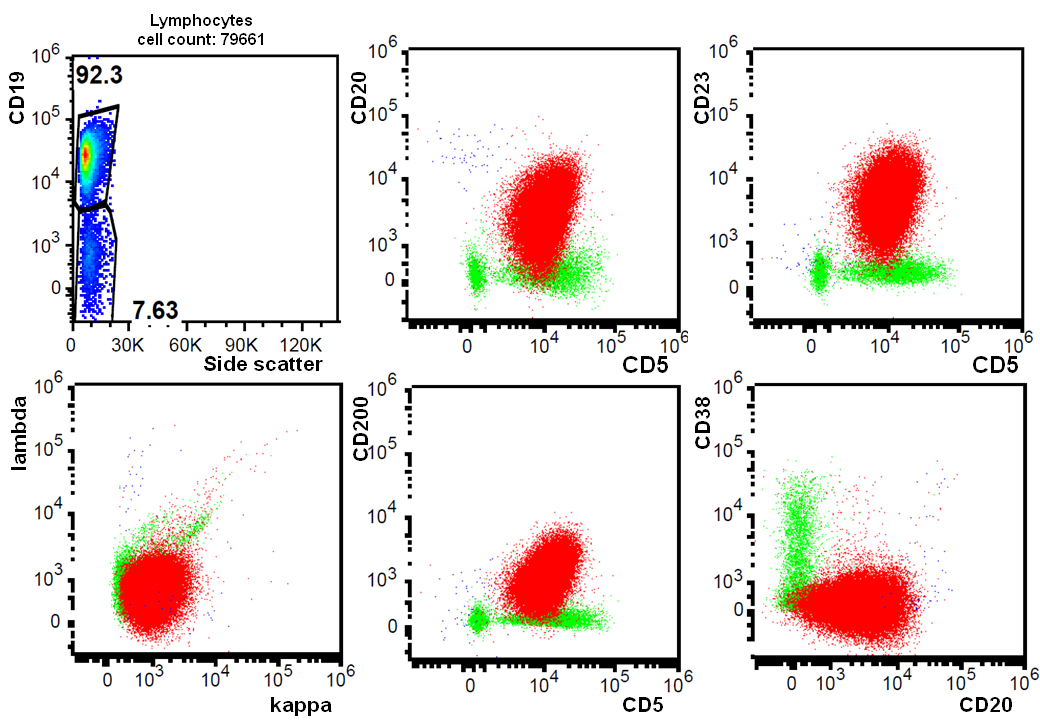
- Characteristic immunophenotype with CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, CD200 positivity
- 2 types with distinct biological behavior based on mutation status of rearranged IGH gene
Terminology
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): neoplasm of mature B cells with characteristic immunophenotype showing peripheral lymphocytosis (≥ 5 x 109/L) with or without nodal or extranodal manifestation (Blood 2016;127:2375)
- Monoclonal B cell lymphocytosis: clonal B cells with or without CLL-like immunophenotype in peripheral blood < 5 x 109/L and without nodal manifestation (see B cell monoclonal lymphocytosis)
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL): < 5 x 109/L CLL-like cells in peripheral blood with nodal or extranodal manifestation, usually with bone marrow involvement
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Most common adult leukemia in the Western world (Future Oncol 2017;13:1873)
- Median age is between sixth and seventh decade, practically nonexistent in children
- Male preponderance (M:F = 1.5 - 2:1)
- Incidence is low in Asian countries (Int J Oncol 2013;43:561)
Sites
- Lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen and peripheral blood
- Usually widespread disease, clinical staging system is used
Pathophysiology
- Clonal restriction of specific B cell populations with reduced competition of remaining B cell clones due to aging
- B cell receptors show evidence of selection by antigens, B cell receptor signaling is crucial in survival of CLL cells (Front Oncol 2020;10:592205)
- Evidence for autoreactivity of B cell receptors (antigens recognized by studies are related to normal tissue maintenance, apoptosis, atherosclerosis, common infections, etc.) (Front Oncol 2020;10:592205)
- Some evidence indicating self stimulation by B cell receptors (Cell Res 2013;23:182)
- 30% of cases show stereotyped B cell receptors with identical or nearly identical structure (Leukemia 2019;33:287)
- 2 types of CLL that do not show conversion during disease course:
- CLL-UM (unmutated): few mutations in the IGH gene (≥ 98% homology with germline sequence), associated with more proliferation, more aggressive disease course
- CLL-MUT (mutated): many mutations in the IGH gene (< 98% homology), associated with less proliferation, better prognosis
- Gradual accumulation of genetic alterations, however, no clear malignant transformation event recognizable
Etiology
- Incidence is not increased following radioactive incidents
- Familial predisposition in 5 - 10% cases
Clinical features
- Frequently no symptoms
- Lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly are common
- Anemia, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia related symptoms frequently occur
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is common (Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2010;23:47)
- Extramedullary involvement may occur; liver, skin, GI mucosa, kidneys are most commonly involved
Diagnosis
- Laboratory diagnosis of lymphocytosis
- Detection of generalized adenopathy or splenomegaly
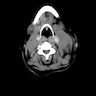
- CT scans are helpful to detect lymph node enlargement
- Immunophenotyping is essential: flow cytometry of peripheral blood or bone marrow or immunohistochemistry of biopsy material
- Lymph node biopsy is not generally required, unless to establish diagnosis of Richter transformation (Blood 2018;131:2745)
Laboratory
- Lymphocytosis
- Anemia, thrombocytopenia are common
- Monoclonal gammopathy may occur
- Hypogammaglobulinemia commonly occurs (Blood 2015;126:573)
Prognostic factors
- Clinical stage (based on physical manifestations and blood parameters): Rai and Binet systems
- Beta-2 microglobulin: high levels associated with high tumor burden and adverse prognosis
- TP53 mutation / 17p deletion is adverse, is associated with poor response to traditional chemotherapeutic regimens; patients may respond to newer agents (J Oncol Pract 2017;13:371)
- Unmutated IGH gene is adverse
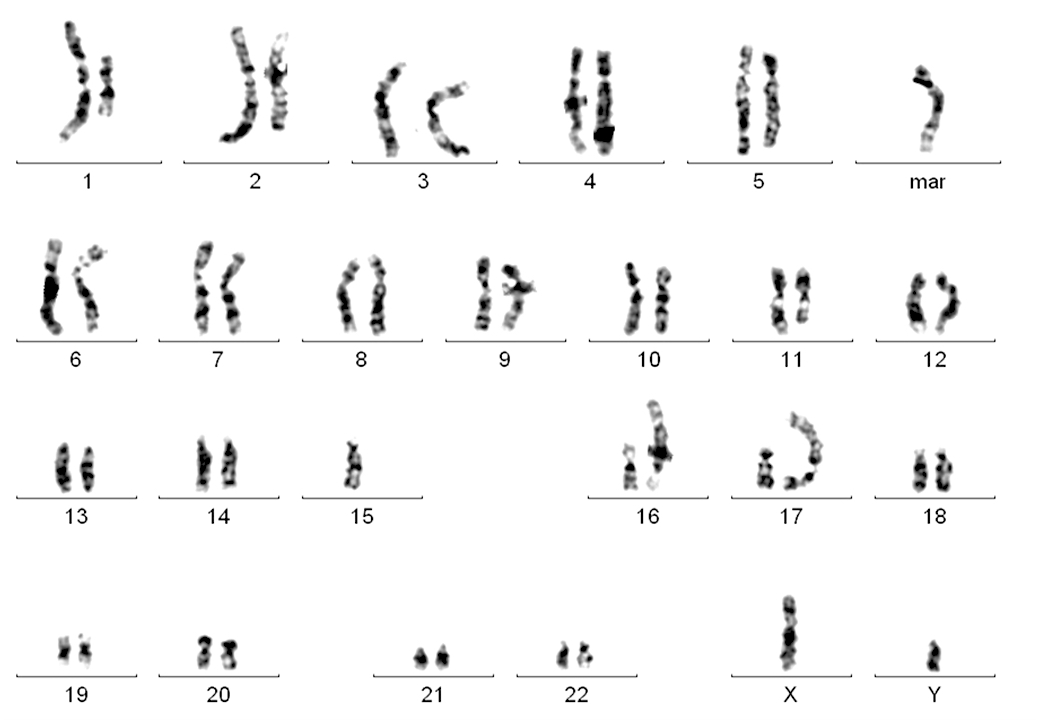
- Complex karyotype (10 - 15%, 3 or more unrelated abnormalities) is adverse (Blood 2019;133:1205)
- 13q deletion is favorable, 11q deletion is unfavorable, trisomy 12 is associated with intermediate prognosis
- CD38 (> 30% positive in CLL cells by flow cytometry) is adverse, ZAP70 expression (> 20%) is adverse
- CD49d (> 30% positive in CLL cells) has been associated with progression (Blood 2020;135:1244)
- Large, confluent proliferation centers (adverse) (Blood 2016;127:2375)
- Methylation profile, various gene mutations may correlate with epigenetic maturation status, response to therapy or prognosis but are not currently used in clinical practice (Nat Genet 2016;48:253)
- Pattern of bone marrow infiltration is no longer considered important
Case reports
- 47 year old man with clonal evolution, treatment resistance and progression to Richter transformation (Haematologica 2019;104:e38)
- 58 year old man with CLL showing focal cyclin D1 expression (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:92)
- 66 year old man with Hodgkin transformation (Blood 2017;130:2151)
- 71 year old woman with Richter transformation after 6 years of complete remission of CLL (BMJ Case Rep 2016;2016:bcr2016214361)
Treatment
- Treatment is tailored based on clinical progression (progressive bone marrow failure, progressive or bulky lymphadenopathy, short lymphocyte doubling time, etc.), biological fitness of patient, presence of TP53 mutation / 17p deletion and IGH mutation status (Curr Oncol Rep 2020;22:36)
- Cytostatic agents: chlorambucil, fludarabine, bendamustine, cyclophosphamide, etc.
- Monoclonal antibodies: rituximab, obinutuzumab (anti-CD20), alemtuzumab (anti-CD52)
- Kinase inhibitors: ibrutinib, acalabrutinib (Btk inhibitors), idelalisib (PI3K inhibitor)
- BCL2 inhibitors: venetoclax
- Lenalidomide
Gross description
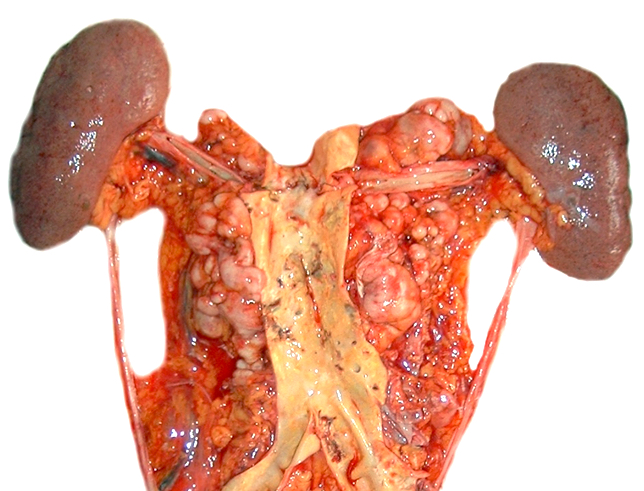
- Lymph node: enlarged lymph node with homogeneous, fleshy cut surface
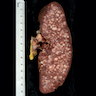
- Spleen: often miliary pattern of white pulp expansion, homogeneous infiltration with massive splenomegaly also occurs (Am J Clin Pathol 2003;120:335)
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Diffuse infiltrate of small, mature lymphocytes with inconspicuous nuclei and scant cytoplasm
- Immunophenotyping is necessary for diagnosis
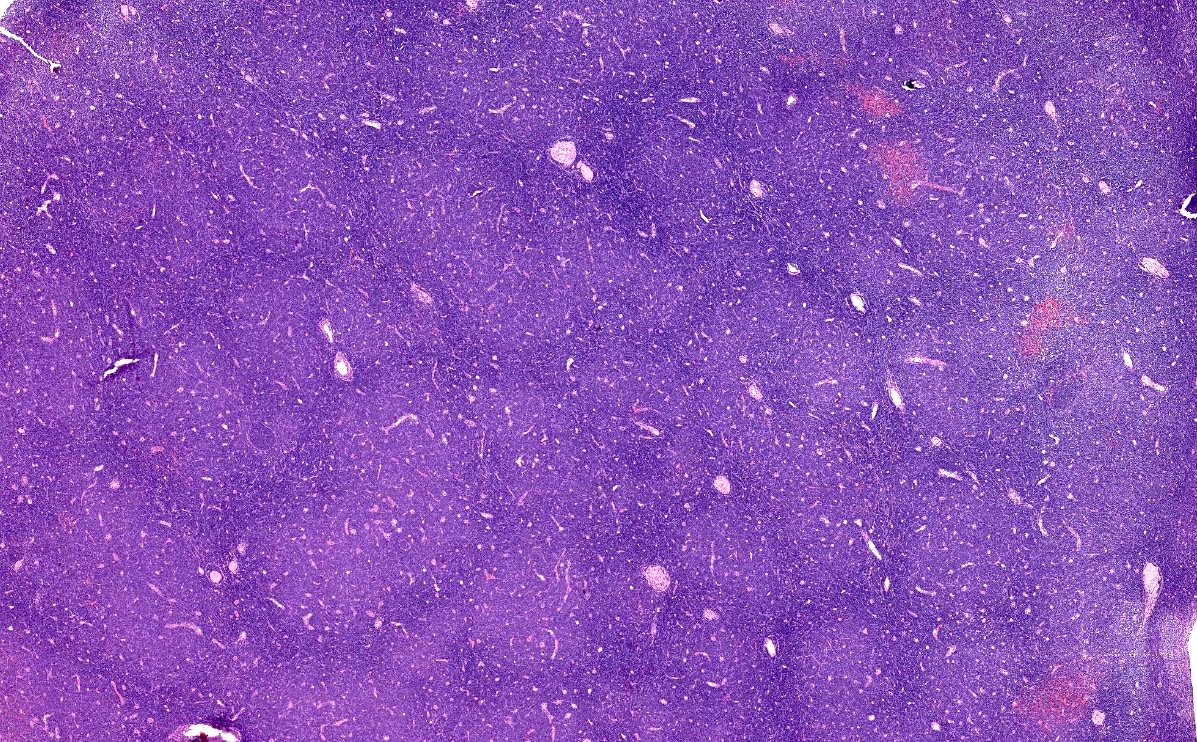
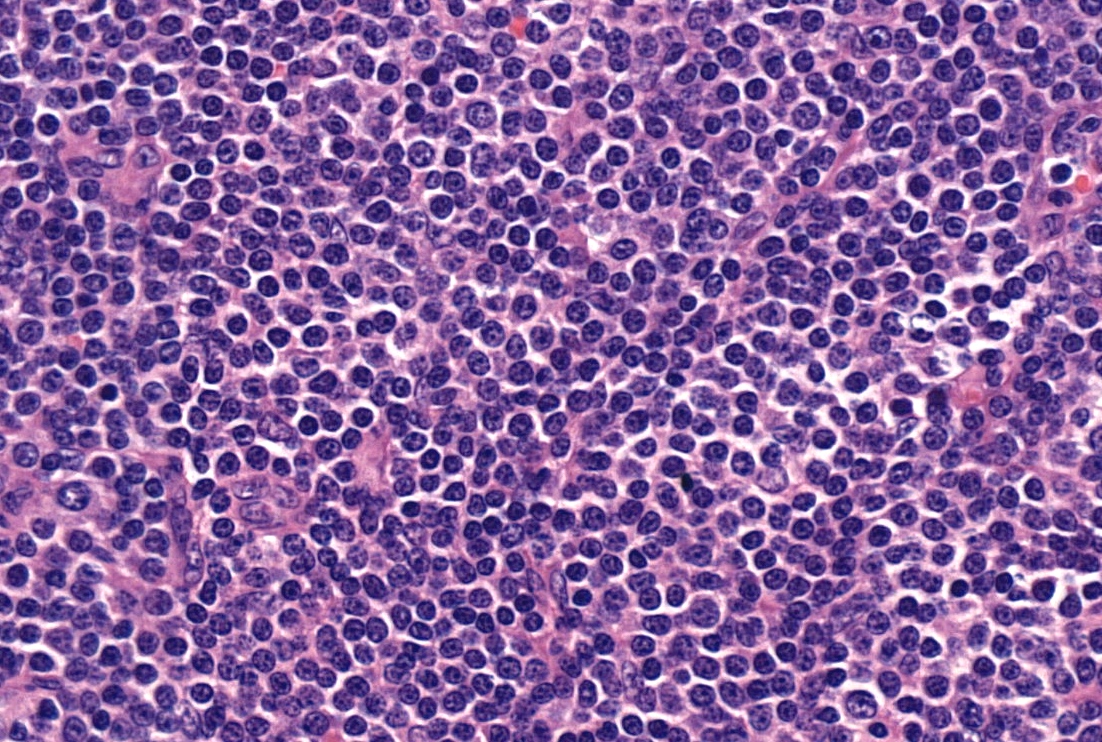
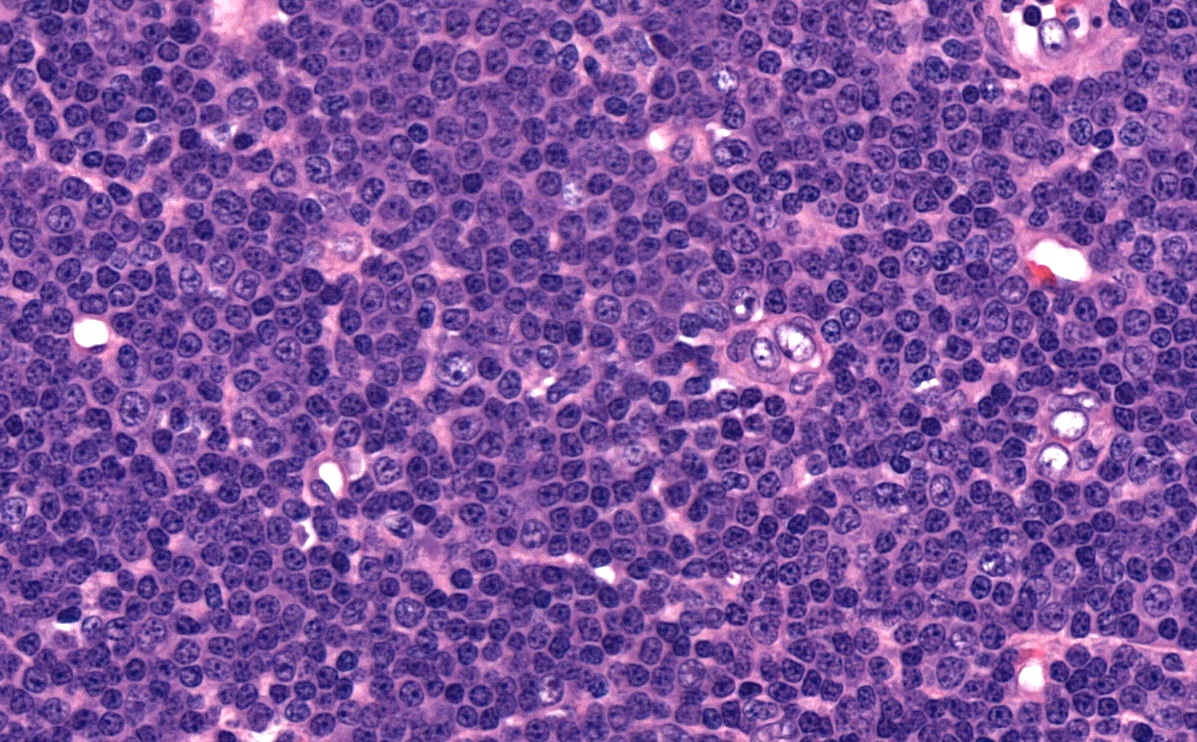
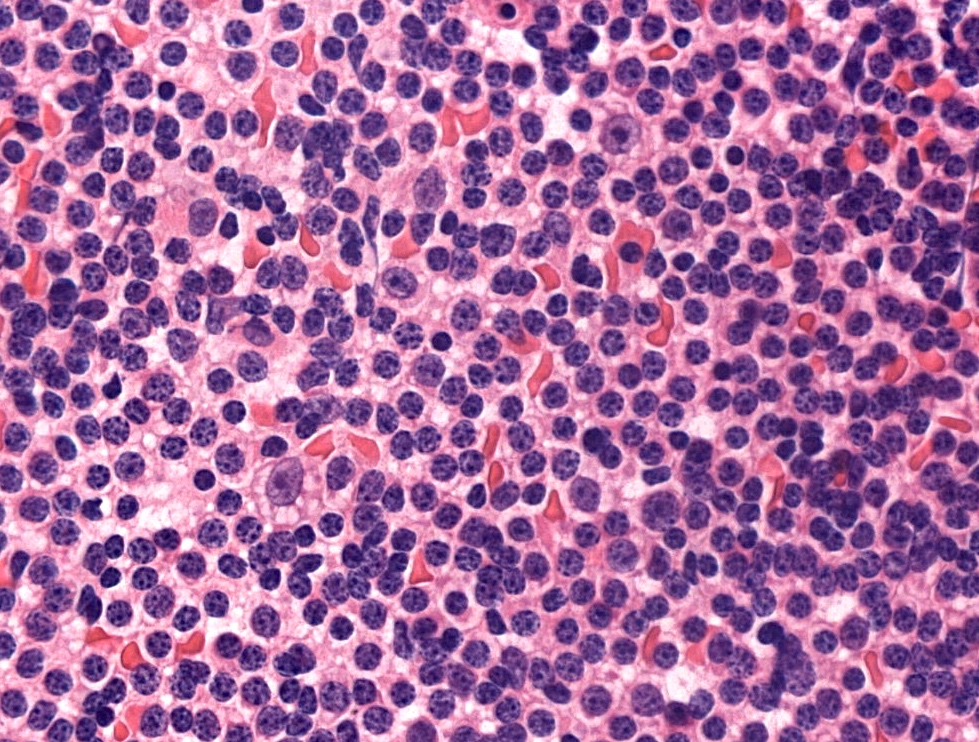
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Diffuse effacement of parenchyma by small, mature lymphocytes
- Round nucleus, clumped chromatin with only small nucleoli and scant cytoplasm
- Ill defined, pale proliferation centers (pseudofollicles) are common, composed of prolymphocytes and paraimmunoblasts
- Bone marrow: nodular or diffuse infiltration; paratrabecular aggregates are not common
Notes:
- Occasionally extensive plasmacytoid differentiation
- Partial lymph node infiltration is possible with perifollicular or interfollicular infiltration (Haematologica 2011;96:1144)
- Prolymphocyte: small to medium sized mature lymphocyte with clumped chromatin, somewhat larger central nucleolus
- Paraimmunoblast: large cell with round nucleus, dispersed chromatin and central, enlarged nucleolus, often with basophilic cytoplasm
- No grading system is used, prolymphocytic transformation is defined based on peripheral blood
- Histologically aggressive CLL: confluent or very large proliferation center or > 40% Ki67 index; not the equivalent of Richter transformation (Blood 2018;131:2761)
- Richter transformation: usually high grade B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) appearing in the context of CLL; confluent areas of large cells are required for diagnosis
- Hodgkin transformation: rare form of Richter transformation, usually clonally unrelated and EBV positive, requires classical Hodgkin lymphoma pattern; scattered Reed-Sternberg cells may be present in CLL (Blood 2018;131:2761)
- Prolymphocytic transformation: ratio of prolymphocytic cells in peripheral blood increases (< 55%), transformation into B cell prolymphocytic leukemia does not occur, by definition
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Small, mature lymphocytes with round nucleus, clumped chromatin and only small nucleoli
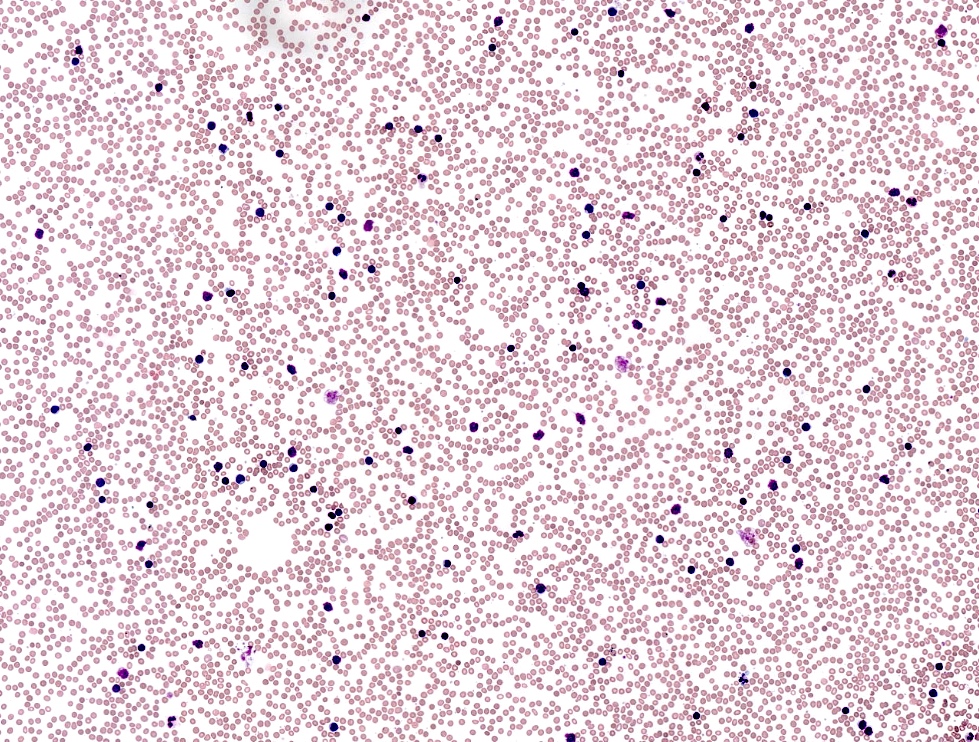
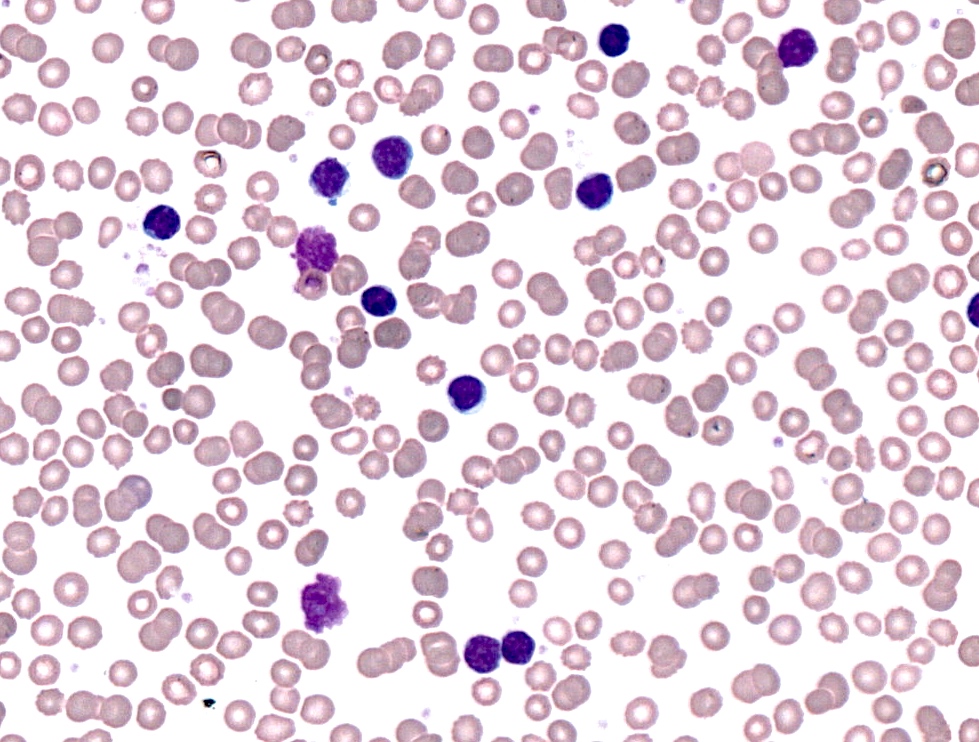
Peripheral smear description
- Lymphocytosis composed of small, mature lymphocytes with round nucleus, clumped chromatin and only small nucleoli
- Smudged cells (Gumprecht cells) commonly seen representing mechanically damaged cells (J Clin Oncol 2009;27:1844)
- Prolymphocytes usually < 15%; 15 - 55% in case of atypical CLL; > 55% defines B cell prolymphocytic leukemia (see Prolymphocytic leukemia)
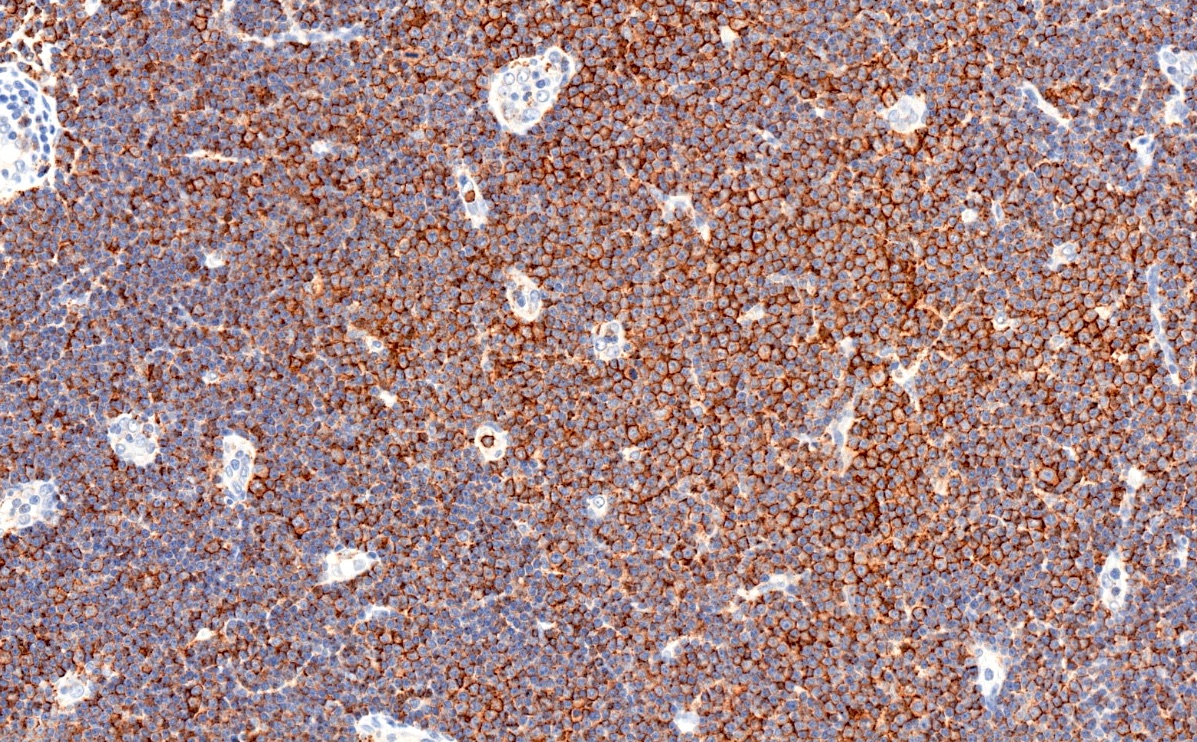
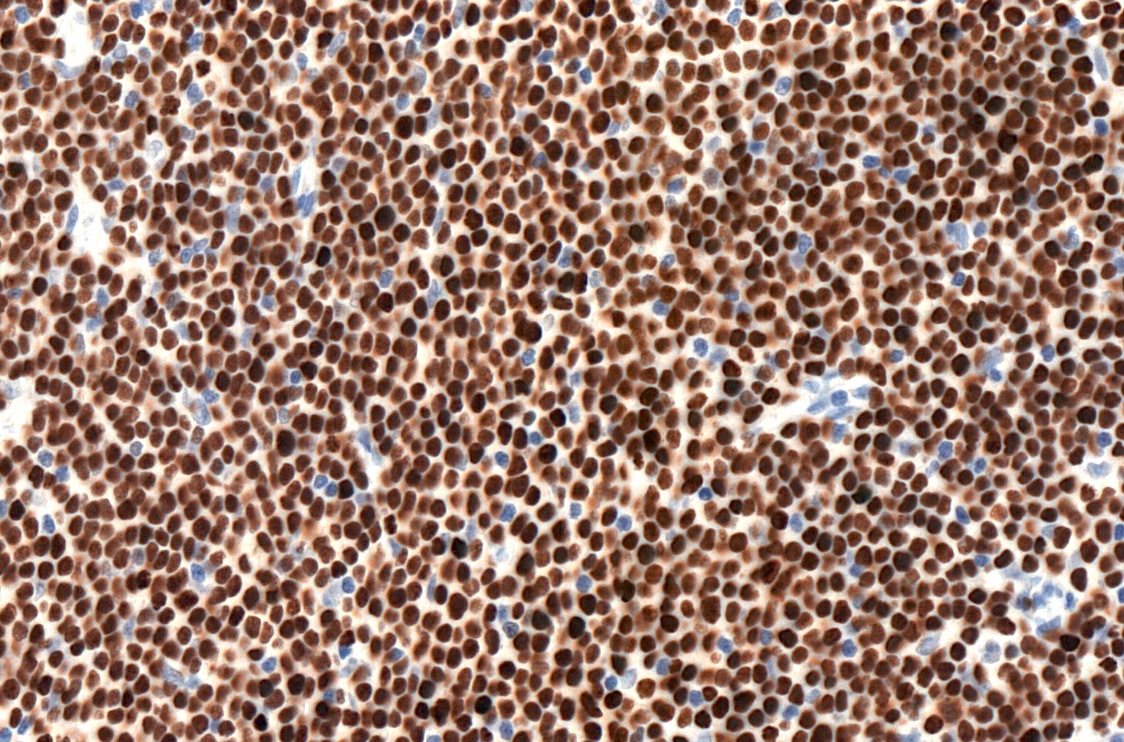
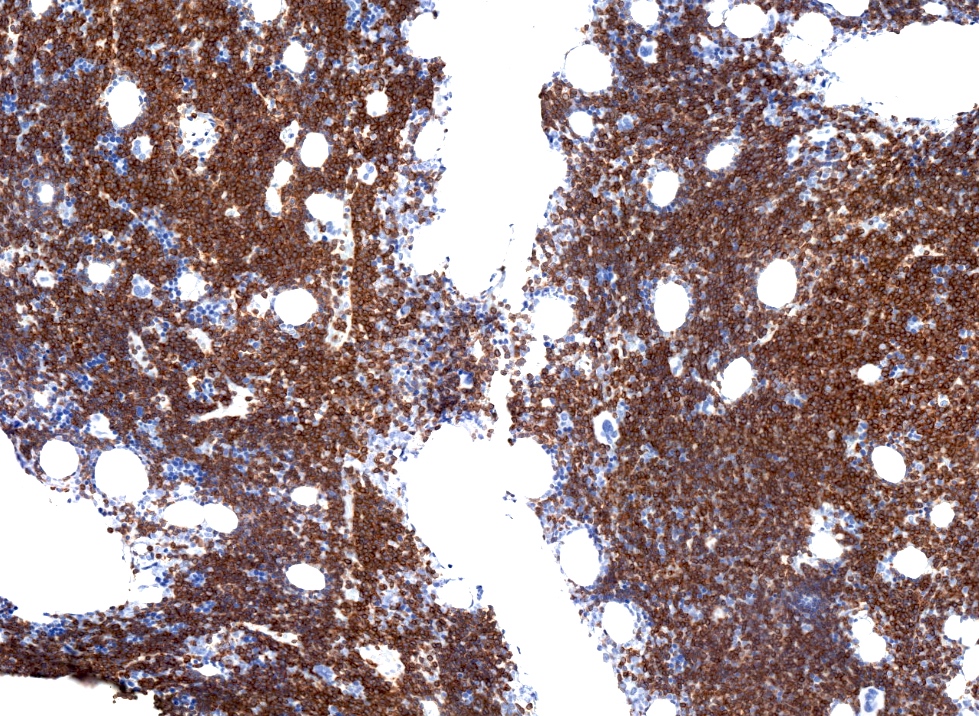
Positive stains
- CD5 (rarely negative), CD79a, CD20 (dim), CD23, CD19, PAX5, CD200, BCL2, LEF1, CD43, IgM / IgD (dim) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1666)
- CD38, ZAP70, CD49d may be positive; they are associated with worse prognosis (Blood 2011;118:3470, Leukemia 2003;17:2426, Blood 2020;135:1244)
- MUM1 may be positive, considered as adverse prognostic factor by some
- Richter transformation: only 30% are CD5 positive, CD23 only in 15%, most are nongerminal center type (Blood 2018;131:2761)
Negative stains
- CD10, BCL6, SOX11 (Haematologica 2009;94:1563)
- CD20 may appear negative or very dim
- Cyclin D1 may be positive in scattered prolymphocytes, may show dim staining on proliferation centers, never shows diffuse, strong labeling (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:132, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:92)
Flow cytometry description
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Unmutated IGH (sequencing) (40 - 60% of cases), testing is necessary before treatment
- TP53 mutations (sequencing) 10% at diagnosis, 30% at relapse, testing is necessary before treatment (Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2016;2016:149)
- 17p deletion (5 - 30%) may be independent from TP53 mutation, testing is necessary before treatment
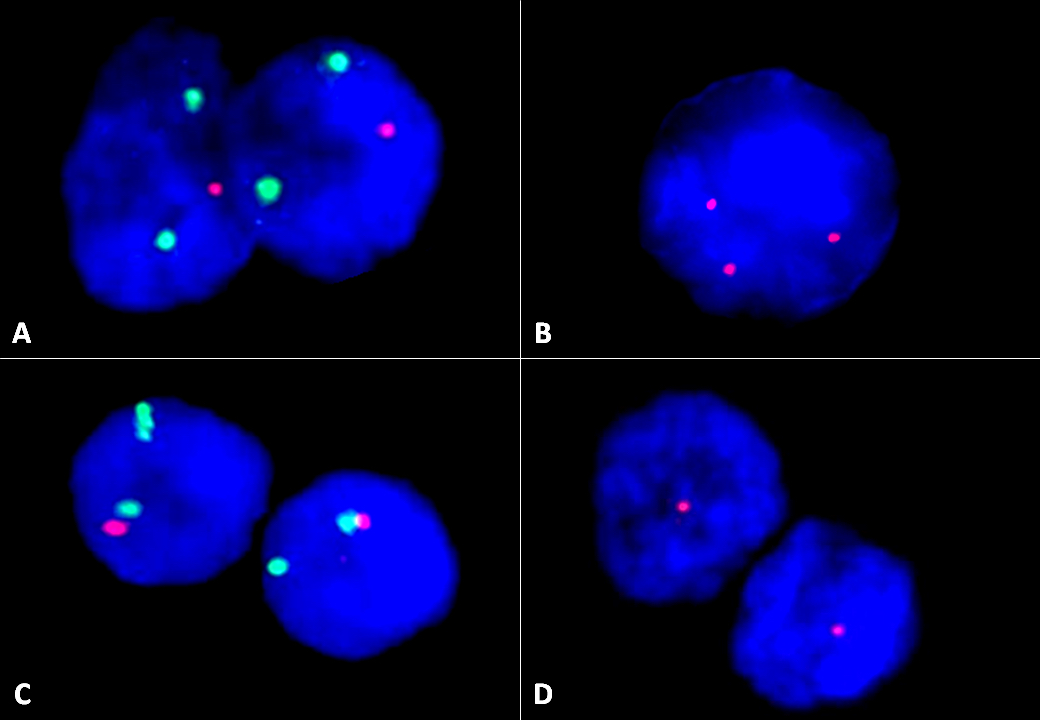
- 13q deletion (50 - 55%), 11q23 deletion (5 - 20%), 12 trisomy (10 - 20%), 6q deletion by FISH is recommended (Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:435983, Blood 2018;131:2745)
- Karyotyping to show complex karyotype is recommended in clinical studies, not generally indicated in routine clinical practice (Blood 2018;131:2745)
- IGH translocations rarely occur, IGH-BCL2+ CLL does exist (2 - 5%) (Am J Hematol 2019;94:338)
Sample pathology report
- Bone marrow, left posterior iliac crest, core biopsy, clot section, aspirate smears and peripheral blood smears:
- Hypercellular bone marrow with maturing hematopoietic activity and 85% diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate with immunophenotype consistent with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (see comment)
- Comment:
- Flow cytometric analysis of bone marrow demonstrates 62% lymphocytes with CD19+, CD5+, CD10-, CD43+, CD23+, CD200+, CD38-, CD20(dim)+, sIgL-kappa(dim)+ immunophenotype consistent with CLL. Peripheral blood smears indicate > 5 x 109/L CLL cells.
- FISH showed biallelic 13q14 deletion in 58%, 11q23 monoallelic deletion in 32% of cells, no 12 trisomy or 17p deletion was noted (see details in separate cytogenetic report).
- Additional molecular studies (TP53 and IGH sequencing) are in progress and will be reported separately.
- Peripheral smear: Manual review of the peripheral blood shows unremarkable platelets, no morphological alteration of red blood cells and lymphocytosis with few smudged cells. 12% of lymphocytes show enlarged nuclei and nucleoli (prolymphocytes). A manual 500 cell differential count reveals 87% lymphocytes, 2% monocytes, 10% neutrophils and 1% eosinophils.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Quality: adequate. Cellularity: 80%. Hematopoiesis: trilineage maturation is present but diminished without dysplastic features or increased blasts. Megakaryopoiesis: normal, cell number is reduced. Granulopoiesis: normal, no blast increase. Erythropoiesis: normal. Infiltrate: 85% diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate composed of mature lymphocytes, approximately 15% are prolymphocytes. Special stains: Reticulin: loose network of reticulin without significant intersections (minimal reticulin fibrosis). Trichrome: negative for collagen deposition.
- Bone marrow clot section: Quality: adequate. Cellularity: 80% morphologic features are similar to those observed in the core biopsy.
- Bone marrow aspirate: Quality: adequate. Granulocytes: decreased; normal maturation; no dysplastic features. Erythrocytes: decreased, normal maturation, no dysplastic features, no ringed sideroblasts. Megakaryocytes: significantly decreased; no dysplastic features. Blasts: less than 1% of nucleated cells. Infiltrate: diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate (78%) consisting of small, mature lymphocytes as well as 13% prolymphocytes. A manual 500 cell differential count reveals 23% erythroblasts, 1% myelocytes, 7% metamyelocytes, 2% neutrophils, 1% eosinophils and 66% lymphocytes (of which 13% are prolymphocytes).
Differential diagnosis
- Monoclonal B cell lymphocytosis:
- Less than 5 x 109/L B cells in peripheral blood
- Mantle cell lymphoma:
- Marginal zone lymphoma:
- Prolymphocytic B cell leukemia:
- Variable immunophenotype, bright CD20 and sIg
- > 55% of lymphoid cells are prolymphocytes in peripheral blood
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following constitutes Richter transformation?
- Appearance of complex karyotype as part of progression of CLL
- Appearance of TP53 mutation as part of progression of CLL
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma appearing as progression of CLL
- Nodal CD5+ diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Unmutated CLL turning into mutated CLL
Board review style answer #2