Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Magliocca K, and Martinez A. Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillaPigNEtumor.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- A rare, locally aggressive biphasic tumor composed of a small round blue cell (neuroblast-like) component along with larger, melanin producing epithelioid cells
Essential features
- A rapidly growing lesion in infants (usually in the first year of life) that can be associated with elevated VMA
- Histologically is a biphasic tumor composed of a small round blue cell neuroblast-like component and larger, melanin producing epithelioid cells
Terminology
- Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy (MNTI)
- Other synonyms the current WHO no longer recommends:
- Melanotic progonoma
- Retinal anlage tumor
Epidemiology
- Rare, > 90% are in infants
- Median age 5 months
- Slightly more common in males (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2015 Oct;73:1946)
Sites
- Most cases occur in the craniofacial region, most commonly the maxilla ( > 60% of cases)
Etiology
- Thought to be neural crest origin, based on:
- Secretion of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), characteristic of other neural crest tumors such as pheochromocytoma and neuroblastoma
- VMA levels generally return to normal when excised
Clinical features
- Usually presents as a pigmented, rapidly expansile mass
Diagnosis
- Based on clinical, radiographic and pathologic features, but most important is biphasic components with histology
Laboratory
- Can show elevated vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) levels
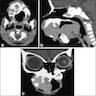
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Wide range of recurrence rates:
- One large study found local recurrence rates after resection of 10 - 15% (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006;102:204)
- Others indicate recurrence rate is > 35% (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2006;25:59)
- A systematic review found a metastatic rate of 6.5% (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006;102:204)
Case reports
- 2 month old female with mass arising in fibula (BMC Cancer 2016;16:629)
- 3 month old girl with swelling of the upper gums (J Clin Diagn Res 2016;10:ZJ07)
- 3 month old with MNTI involving anterior maxilla (Ann Maxillofac Surg 2015;5:234)
- 10 month old with soft tissue mass near right elbow (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:13584)
Treatment
- Complete local excision with clear margins
- Adjuvant therapy for recurrent or residual tumor
Clinical images
Gross description
- Lesions are usually gray to blue, firm and lobulated
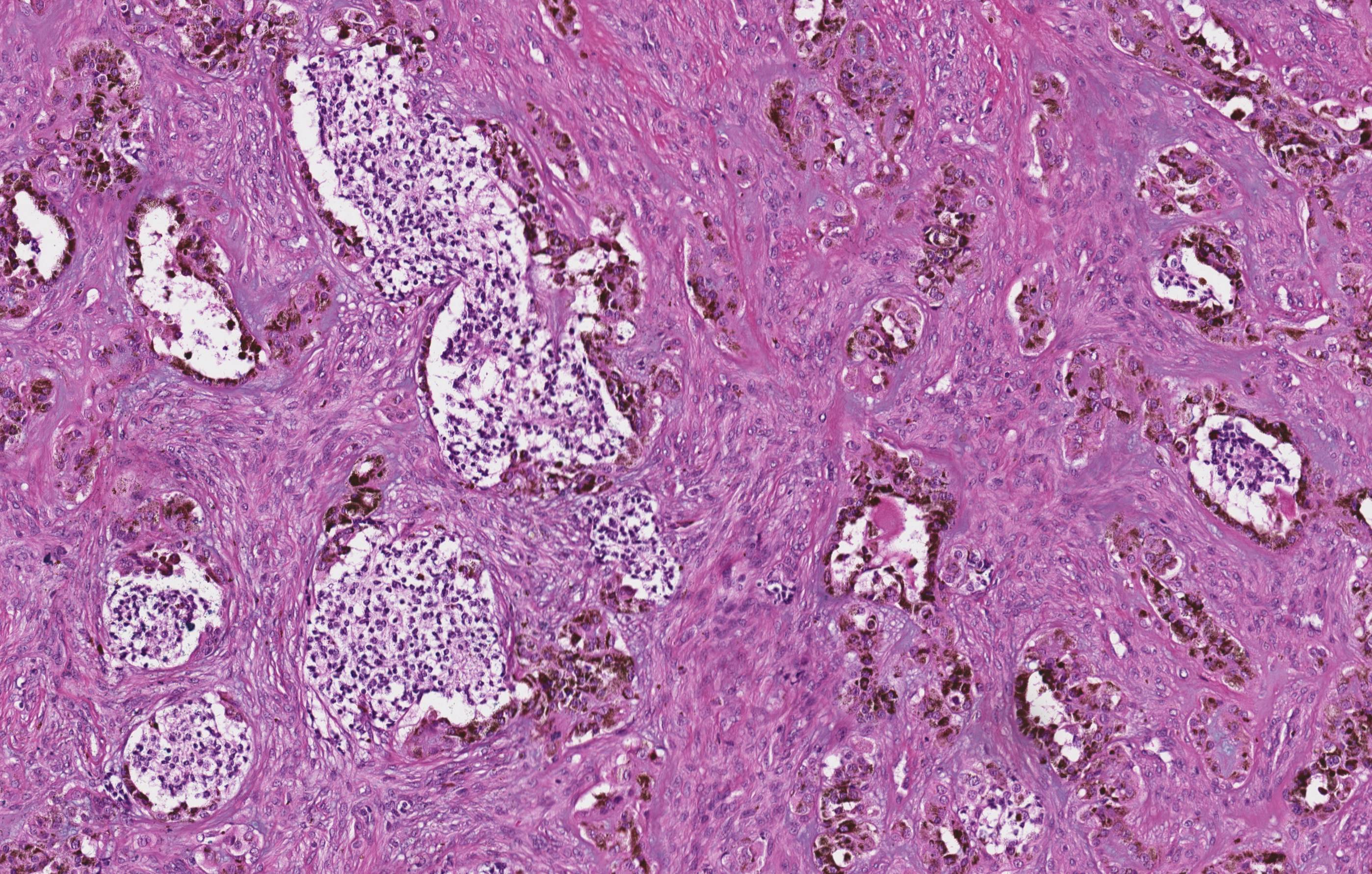
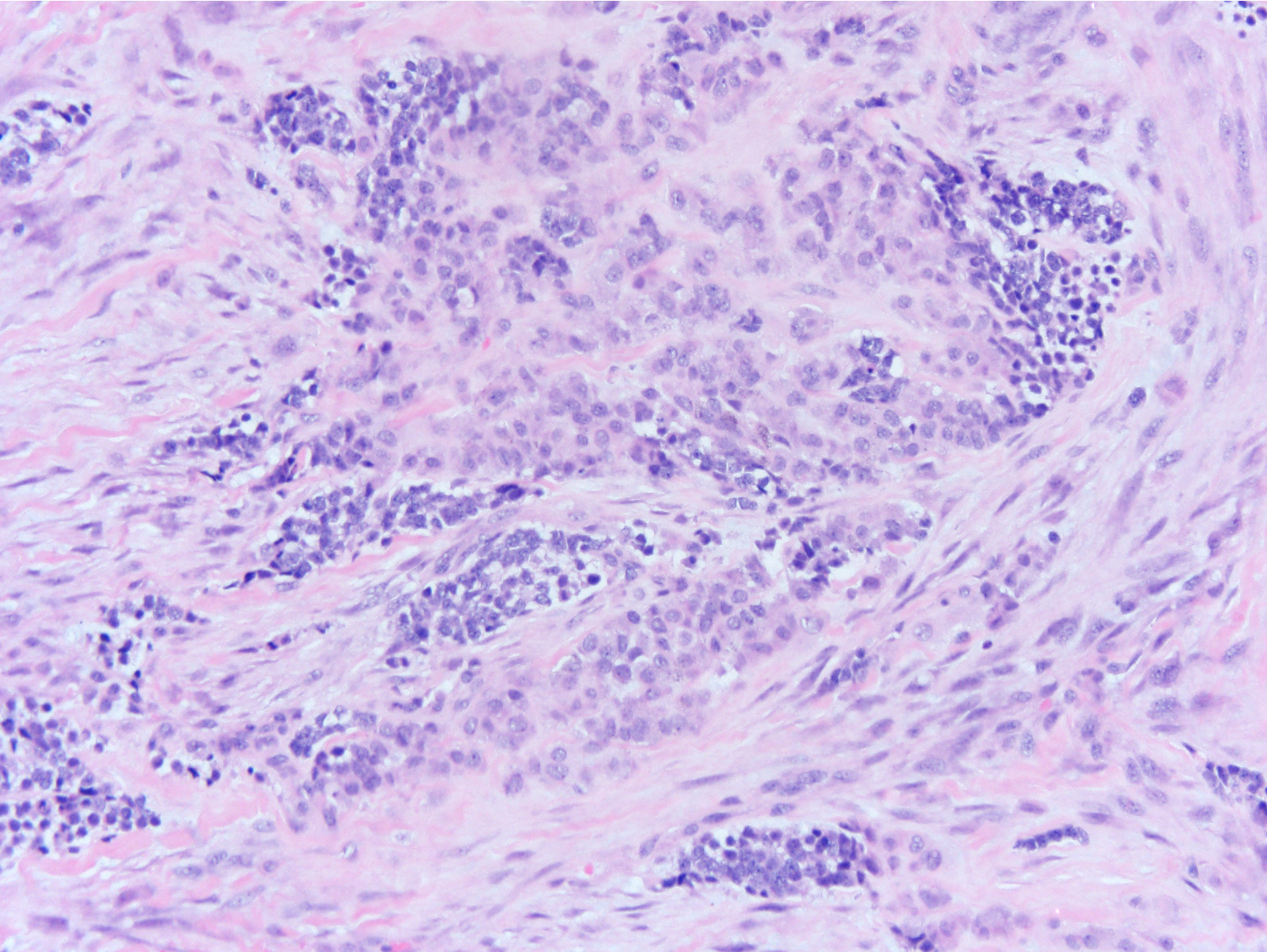
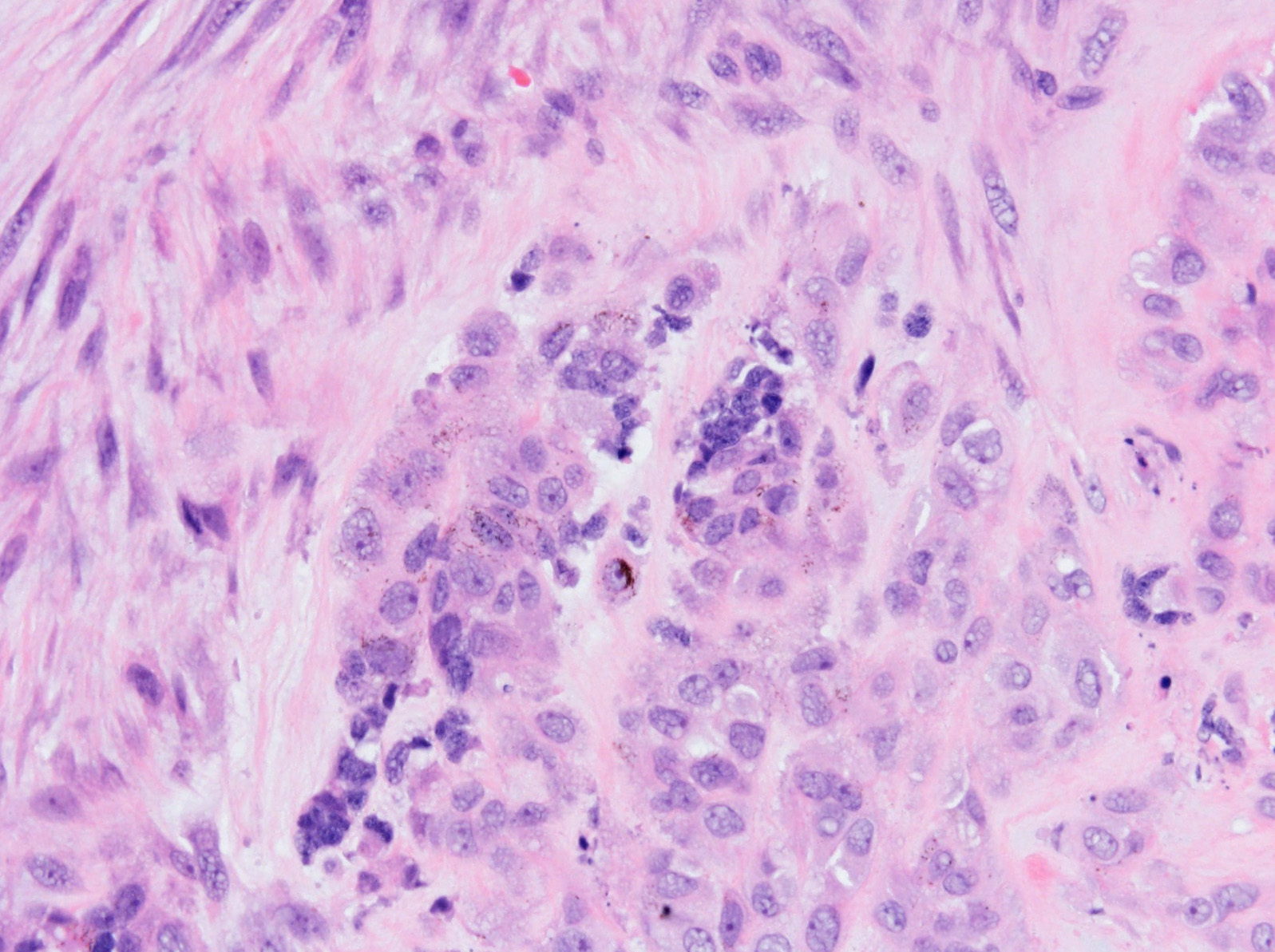
Microscopic (histologic) description
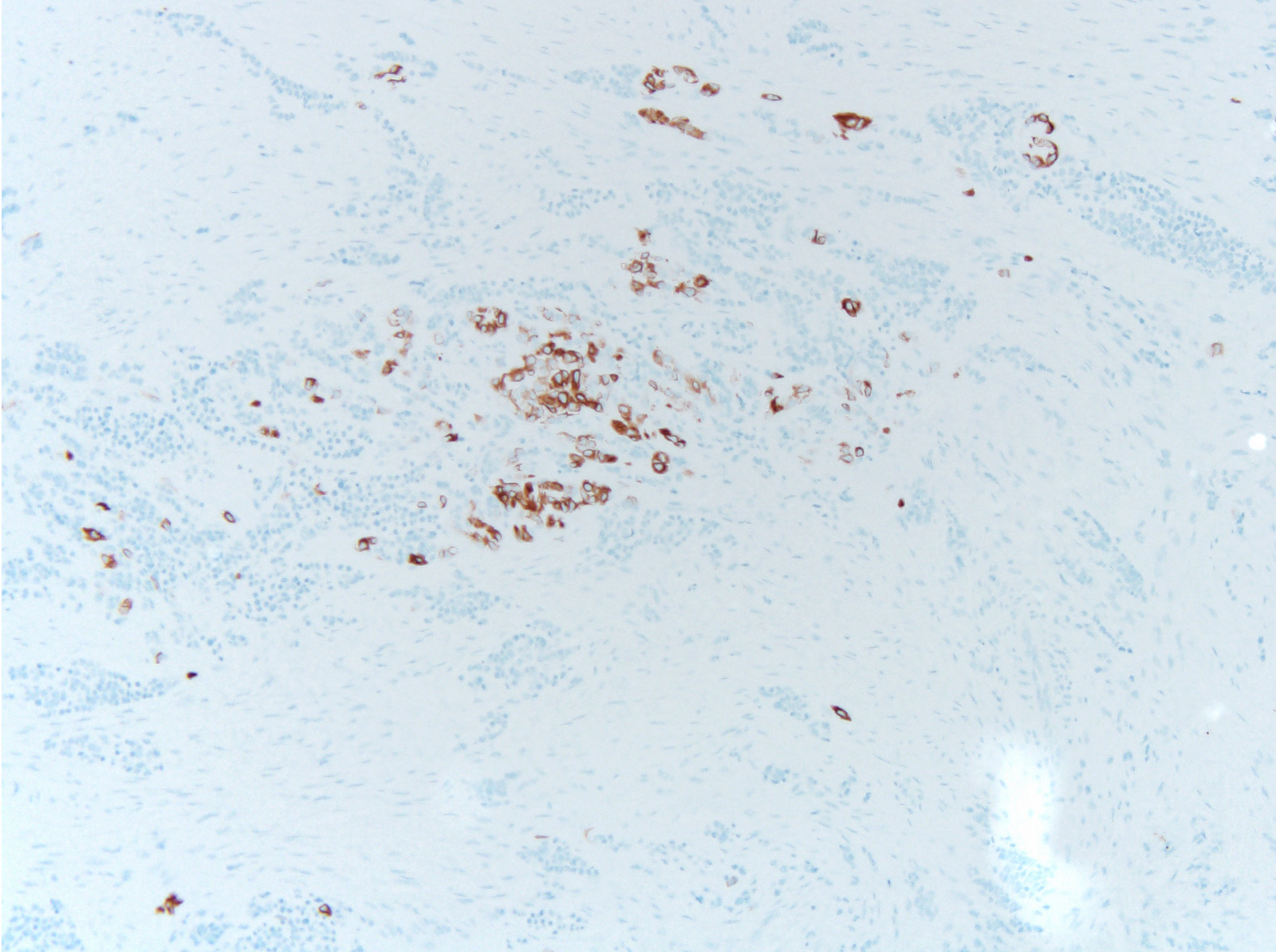
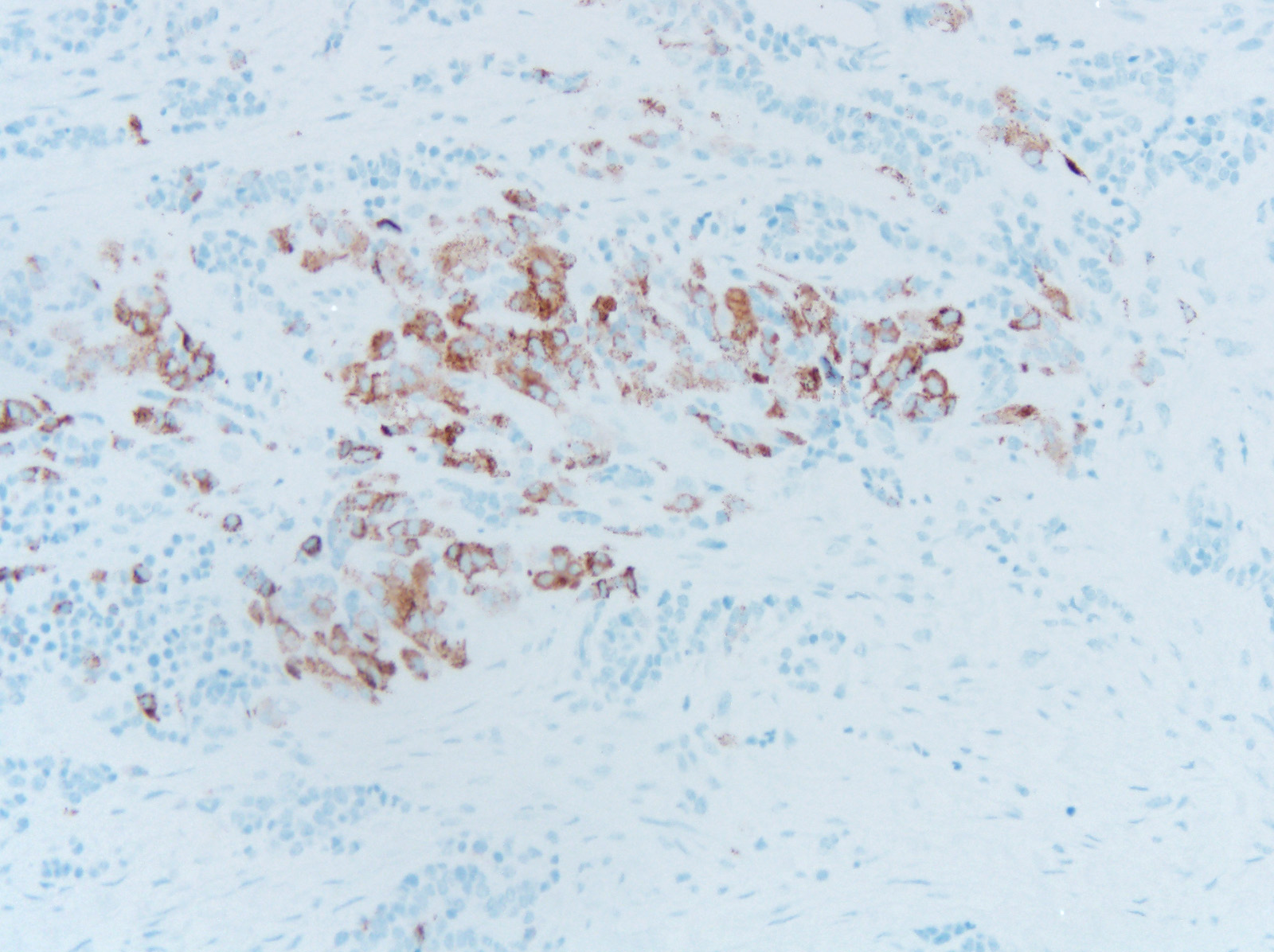
- Biphasic population of cells composed of:
- Nodules of round blue cells that are small and hyperchromatic with scant cytoplasm, often termed “neuroblastoma-like”
- A second population of larger epithelioid cells arranged in
cords and nests composed of abundant pale cytoplasm and round nuclei with vesicular
chromatin
- Within the cytoplasm is melanin pigment, although it can be focal and difficult to identify
- The background consists of dense fibrosis creating the appearance of third component.
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Usually negative for S100, chromogranin
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Limited data but occasional mutations identified:
- Germline mutation of CDKN2A and a novel RPLP1- C19MC fusion identified in 1 case (BMC Cancer 2016;16:629)
- A BRAFV600E mutation was found in 1 case (Pediatrics 2015;136:e267)
Differential diagnosis
- Ewing sarcoma
- Only 2 - 10% develop in the head and neck
- Small round blue cell tumor that grows in sheets and nests
- Can have similar appearance to “neuroblast-like” component of MNTI, but lacks the epithelioid component
- Should have rearrangements of EWSR1, unlike MNTI
- Olfactory neuroblastoma
- Most common during fifth and sixth decades
- Typically involves the cribriform plate, nasal concha and septum
- Also composed of small round blue cells
- Can have Homer-Wright rosettes imparting biphasic
morphology, but they are all the same population of cells
- These will also stain with NSE and synaptophysin like the primitive component of MNTI
- No epithelioid component with melanin pigment
- Can have Homer-Wright rosettes imparting biphasic
morphology, but they are all the same population of cells
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumor
- Rare, aggressive tumor, usually in abdomen of adolescents
and young adults
- More commonly affects men
- Composed of nests of round blue cells with variable amounts of cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei surrounded by desmoplastic stroma
- Should not have the epithelioid component with melanin pigment
- Also shows EWSR1 rearrangement as in Ewing sarcoma
- Rare, aggressive tumor, usually in abdomen of adolescents
and young adults
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Individuals tend to be older at presentation than MNTI
- More commonly involves sinonasal tract
- Also composed of small primitive round blue cells but with scattered rhabdomyoblasts
- Embryonal most common subtype in younger children
- Should be positive for myogenic markers such as myogenin and myoD1
- Should not have the epithelioid component with melanin pigment of MNTI
- Lymphoma
- Approximately 16% of NHLs involve the jawbones
- 2/3 are diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) which usually occur in an older age group
- Main lymphoma mimics for MNTI are lymphoblastic lymphoma or Burkitt lymphoma, which feature monotonous, small to medium size round cells, without a biphasic component
- Flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry (such as Tdt) and molecular studies would help classify and risk stratify the patient
- Approximately 16% of NHLs involve the jawbones
Board review style question #1
What rearrangement has been described in melanotic neuroectodermal
tumor of infancy?
A. EWRS1-FLI1
B. EWSR1-WT1
C. PAX3-FOXO1
D. RPLP1-C19MC
A. EWRS1-FLI1
B. EWSR1-WT1
C. PAX3-FOXO1
D. RPLP1-C19MC
Board review style answer #1
D. RPLP1-C19MC has been described in one case of melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy. EWRS1-FLI1 is seen in Ewing sarcoma, EWSR1-WT1 is seen in desmoplastic small round cell tumor and PAX3-FOXO1 is seen in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
Comment Here
Reference: Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy