Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Jewett FC, Nelson BL. Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxilladentinogenicghost.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign, locally aggressive odontogenic neoplasm of maxilla and mandible with a predominantly solid pattern of growth
Essential features
- Neoplasm with predominantly solid growth of islands of odontogenic and ameloblastoma-like epithelium
- Ghost cells composed of anucleate epithelial cells with pale cytoplasm
- Focal stellate reticulum-like epithelium
- Varying levels of calcified material to include products of odontogenesis and calcification of the ghost cell
- Locally aggressive with high rates of recurrence
- Histopathologic overlap with calcifying odontogenic cysts
Terminology
- Epithelial odontogenic ghost cell tumor
- Calcifying ghost cell odontogenic tumor
- Previously classified along with calcifying odontogenic cyst (J Periodontol 1985;56:340)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D16.4 - benign neoplasm of bones of skull and face
Epidemiology
- Broad age range (11 - 79 years old); peak 40 - 60 years old
- M:F = 1.8:1 (J Oral Pathol Med 2018;47:721)
- Rarity may affect demographics
Sites
- Intraosseous sites: posterior maxilla and mandible
- Rarely reported as gingiva or alveolar mucosal tumor
Pathophysiology
- Wnt signaling pathway may have a role in the development similar to calcifying odontogenic cyst since beta catenin gene mutations and beta catenin overexpression are also identified in DGCT (PLoS One 2017;12:e0180224, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2007;103:97)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Patients frequently present with asymptomatic swelling of the jaw
Diagnosis
- Radiologic and histopathologic correlation required for diagnosis
Radiology description
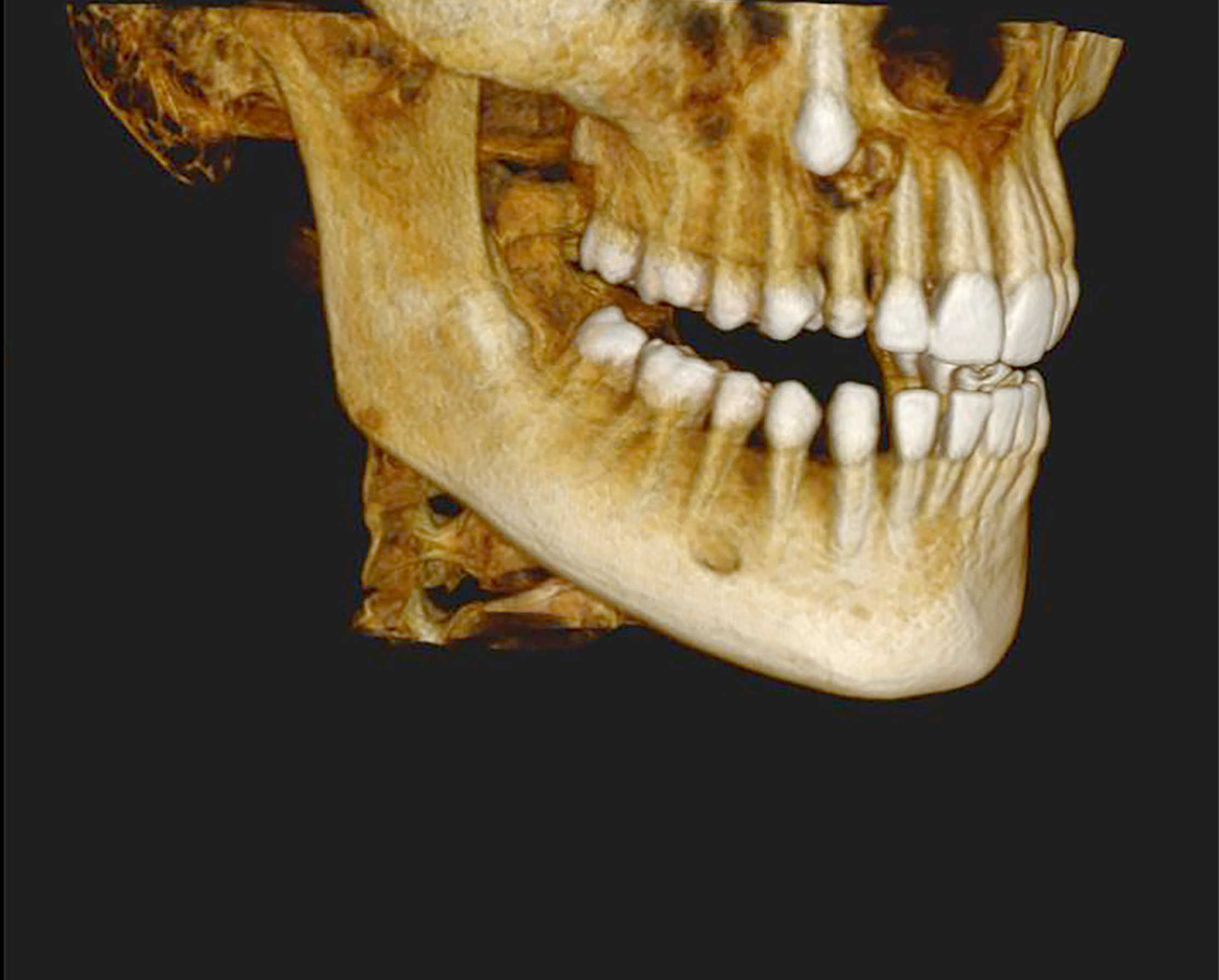
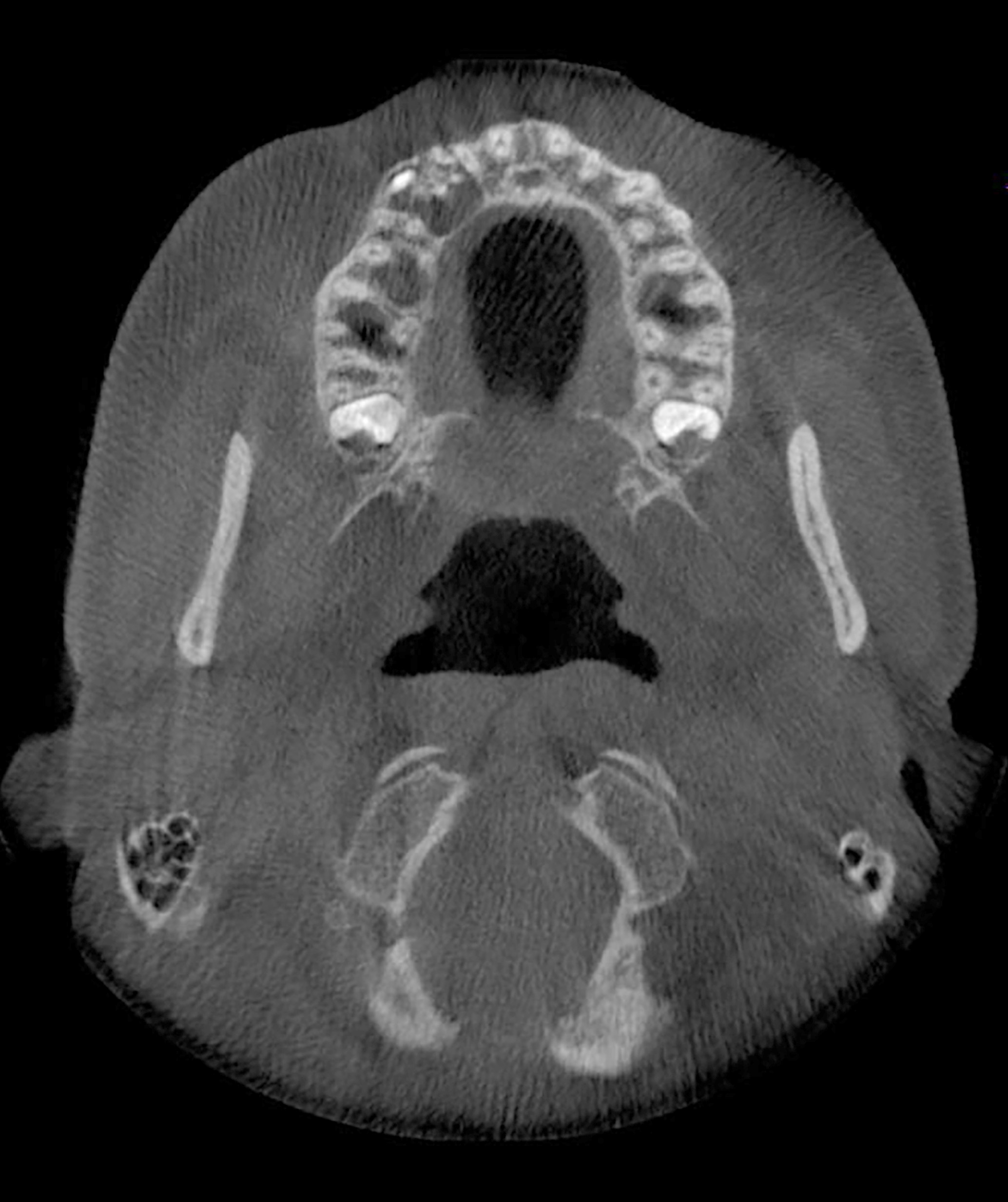
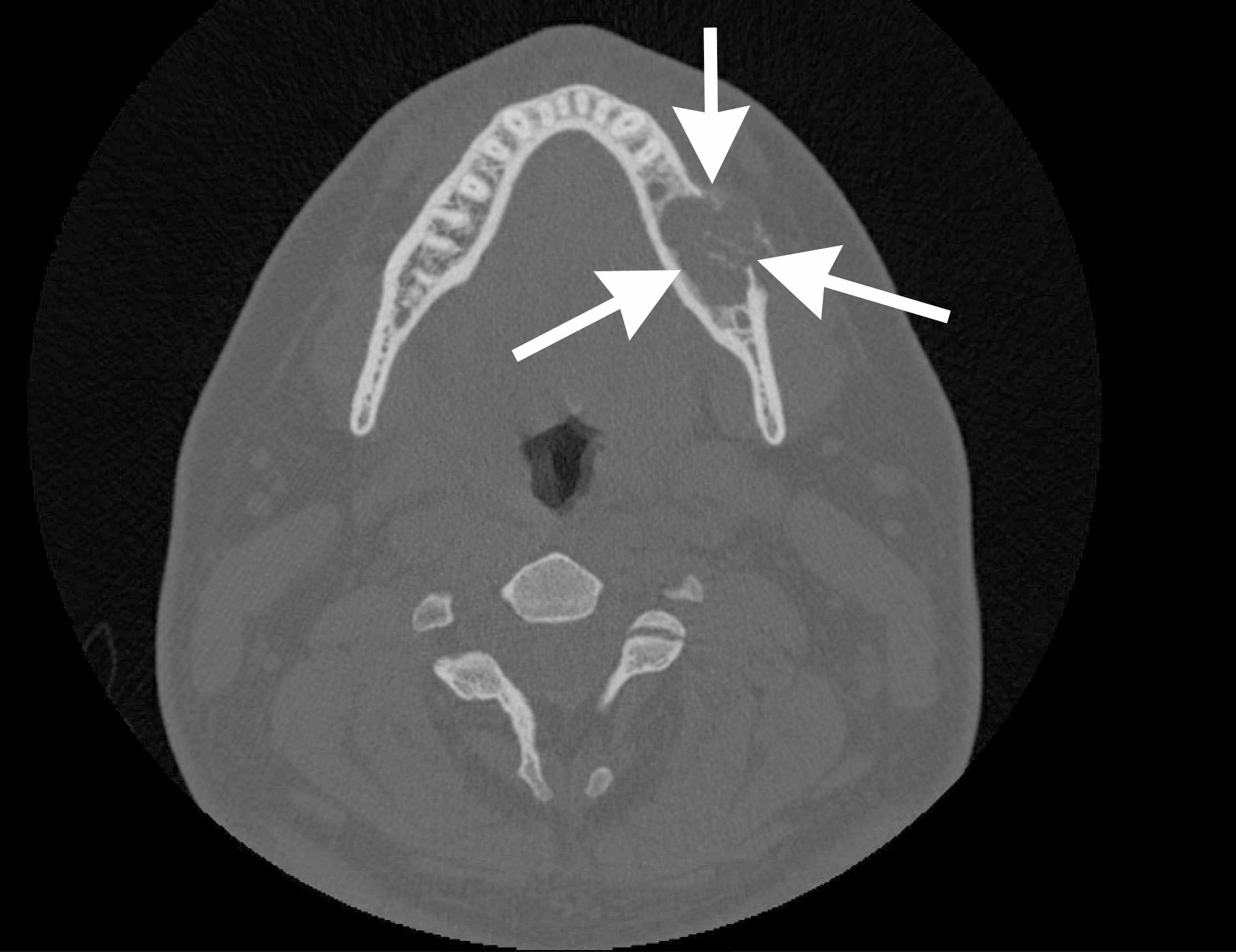
- Majority present as radiopaque lesions with well defined borders and a mixed radiodensity due to varying levels of calcification
- Rarely associated with odontomas, similar to calcifying odontogenic cyst (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006;101:356)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- High rates of recurrence with simple enucleation (up to 73%) (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016;74:307)
- Lower but still significant rates of recurrence with more extensive procedures (up to 33%) (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016;74:307)
- Limited reported cases may affect knowledge of true prognosis
Case reports
- 18 year old man reported with recurrent swelling and pain in upper jaw (World J Clin Oncol 2019;10:192)
- 26 year old man with a growth in the upper left front part of the jaw (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2018;22:150)
- 40 year old man with swelling on the right side of the face (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;23:478)
- 40 year old woman with swelling in the front region of the lower jaw for 2 years (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;23:66)
- 68 year old man with a soft tissue growth in lower anterior region of the jaw for 3 years (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2016;20:163)
Treatment
- Rarity of this tumor limits study of the optimal form of treatment
- Simple enucleation, curettage: recurrence rate of up to 73% after a follow up period of 1 - 20 years
- Recurrence rates vary by surgical approach; recent recommendation includes wide local resection
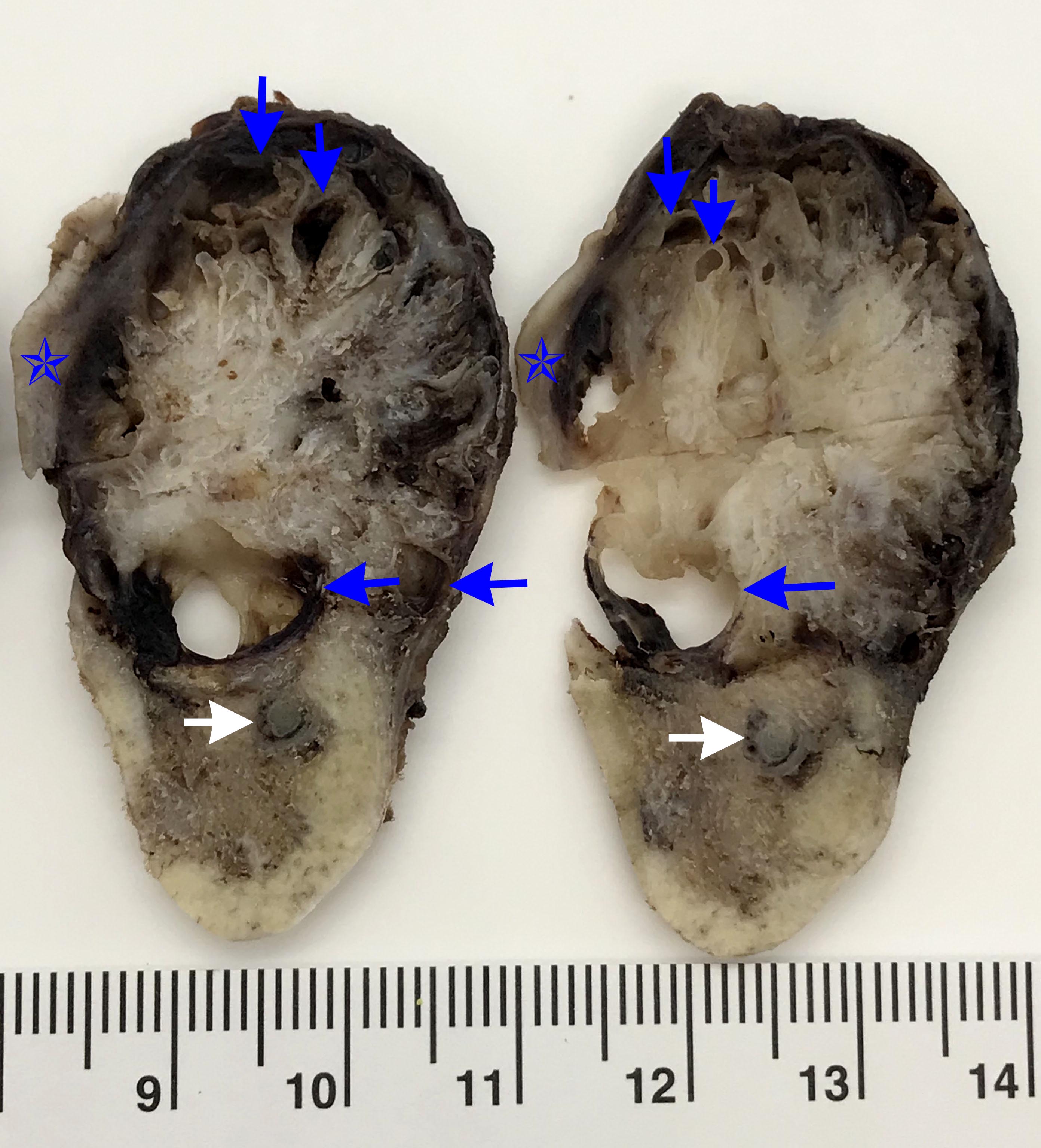
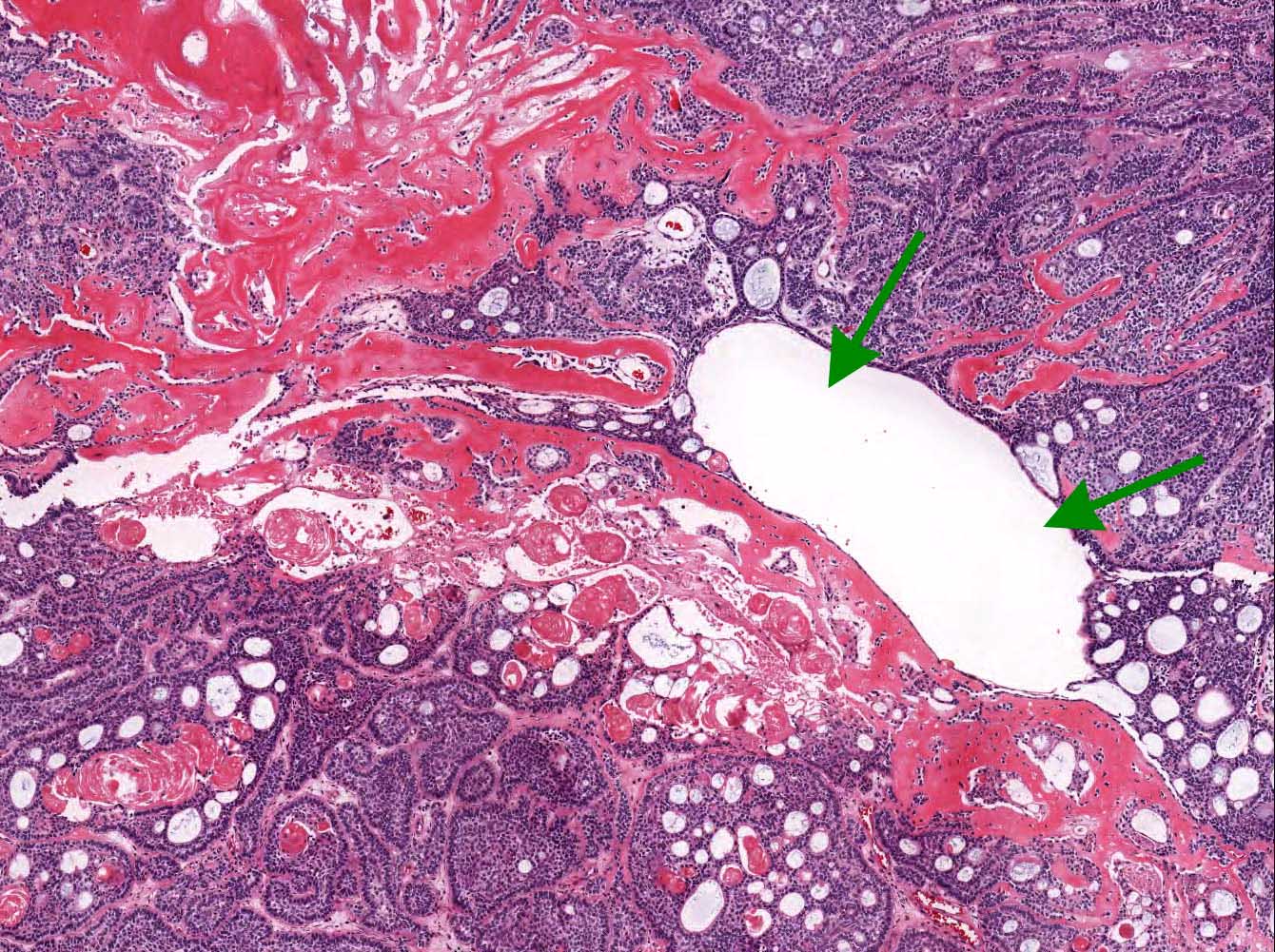
Gross description
- Predominantly solid tumor; limited macrocystic change
Microscopic (histologic) description
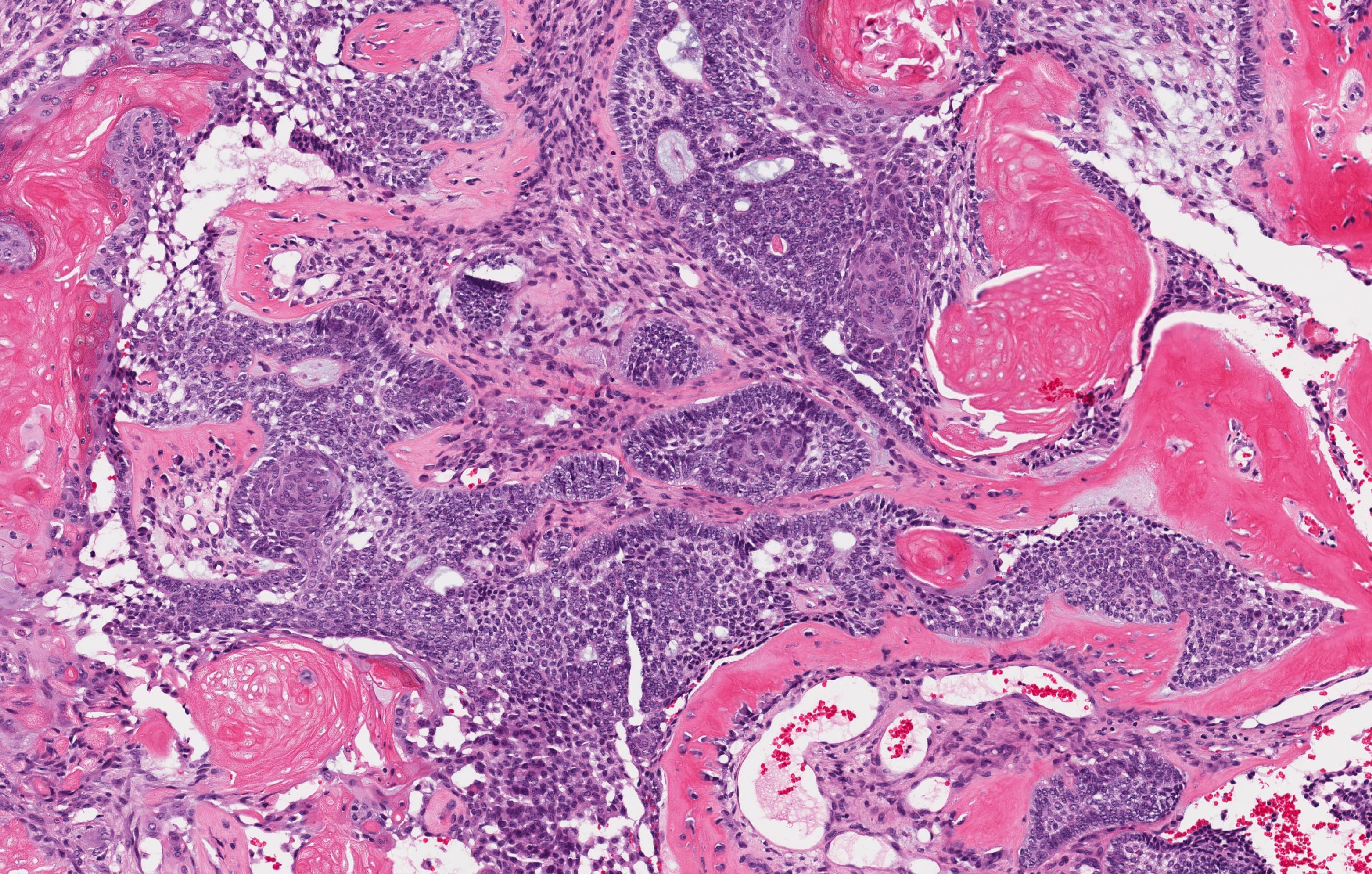
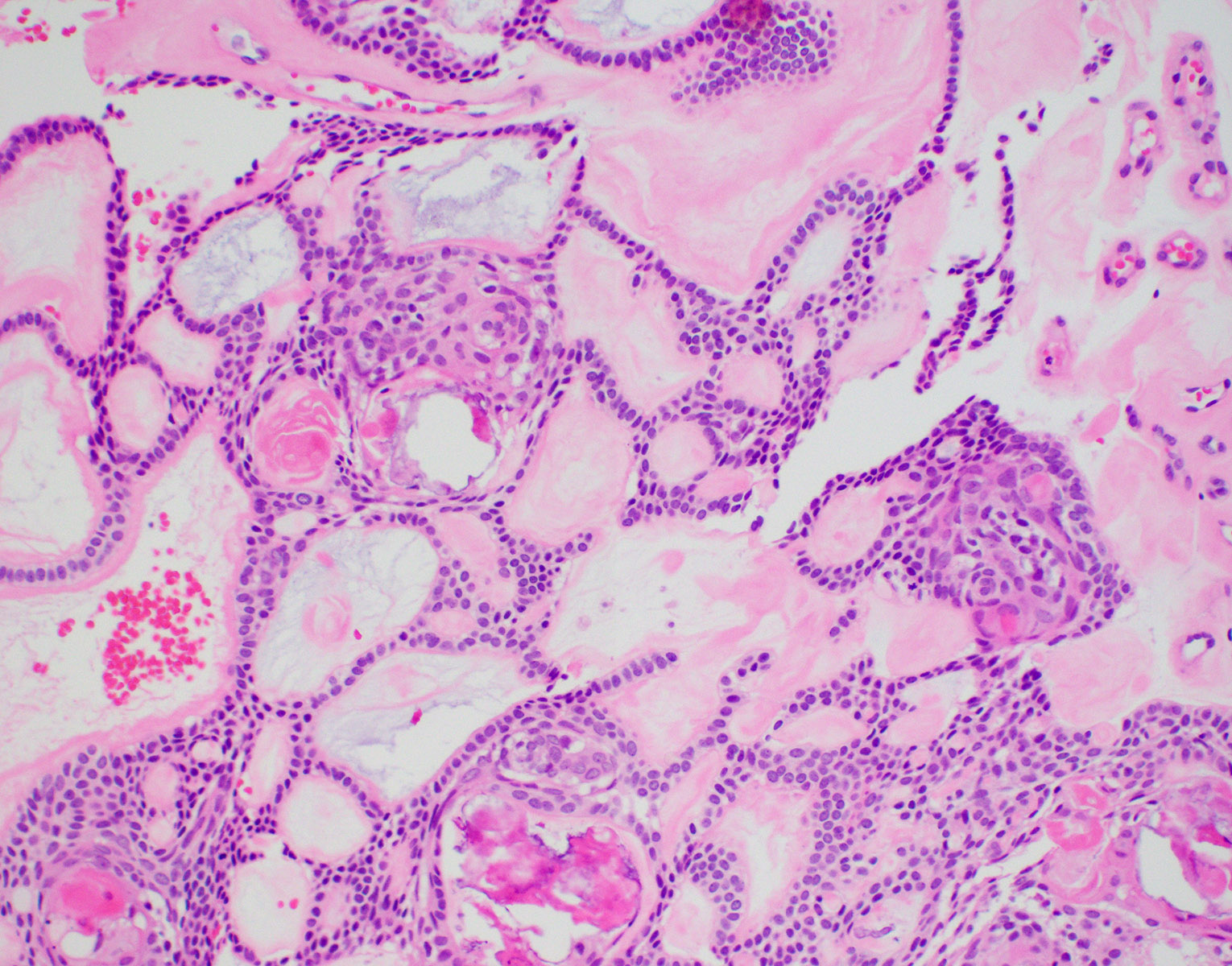
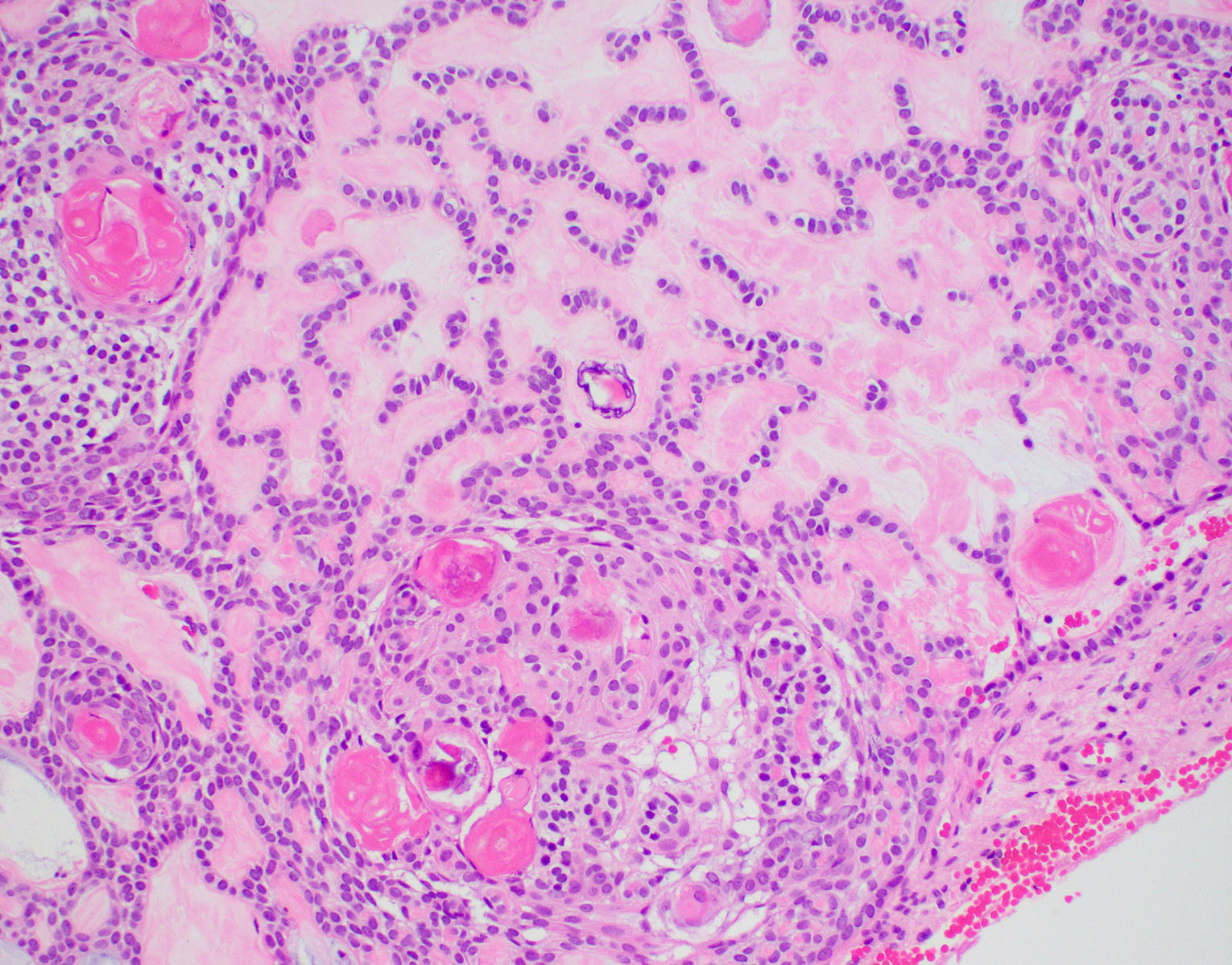
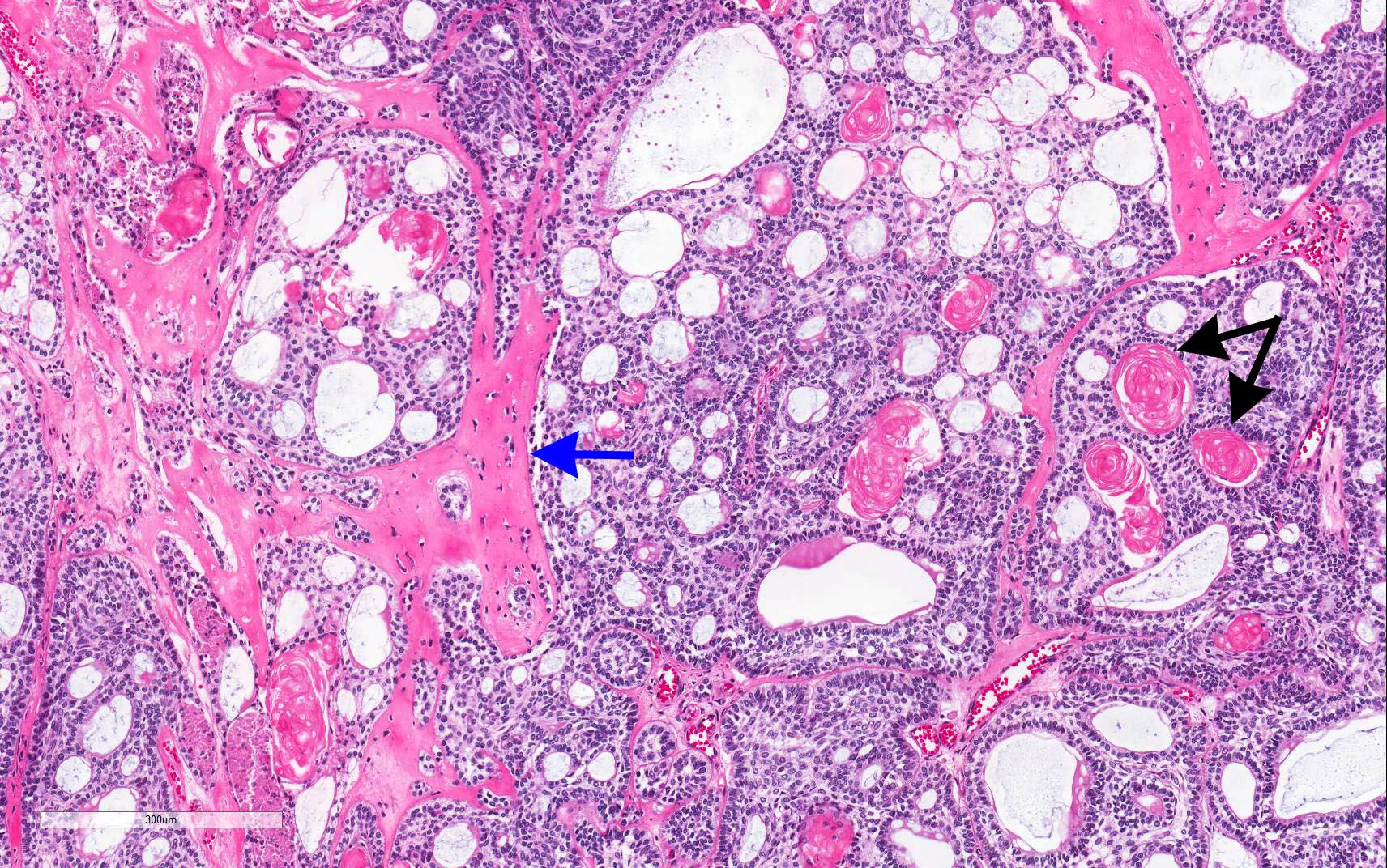
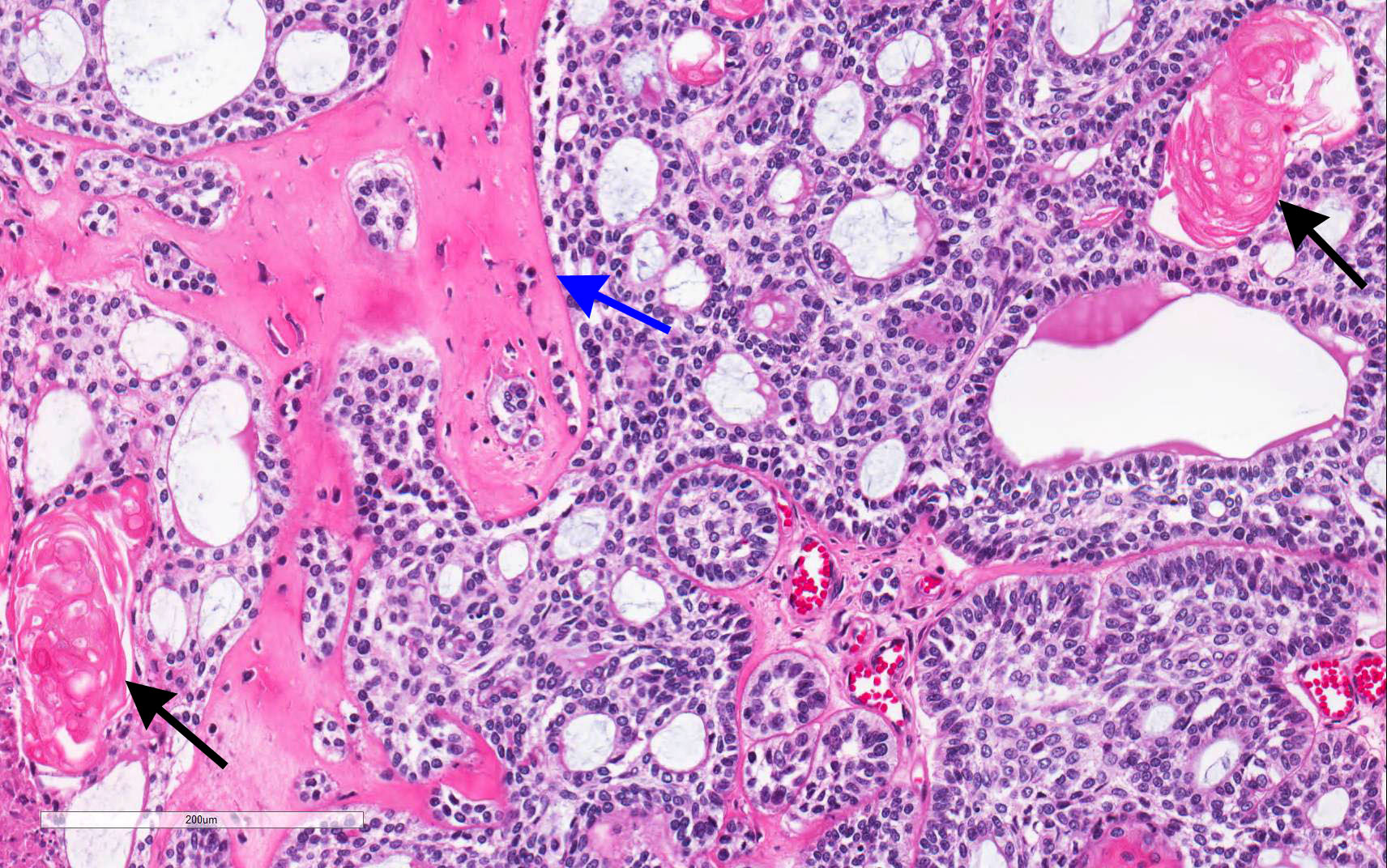
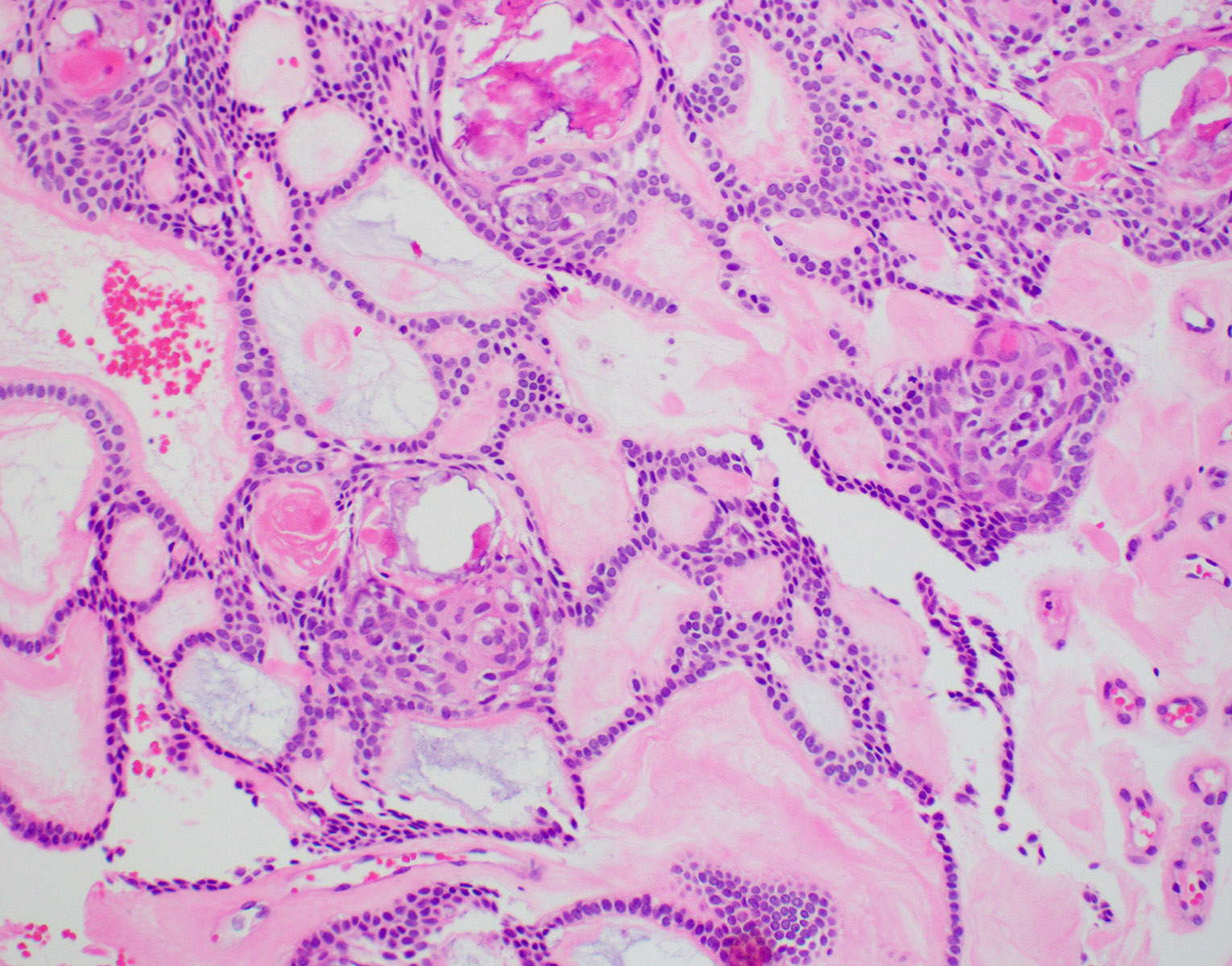
- Predominantly solid mass consisting of sheets of anastomosing cords and strands of odontogenic epithelium; microcystic development possible
- Admixed ghost cells: anucleate epithelial cells with pale cytoplasm containing cytoplasmic clearings representing the location of a previously resorbed nucleus or organelles
- Interspersed with islands of swirling cells with squamous differentiation
- Ameloblastic-like areas with palisading of basaloid cells
- Odontogenic epithelial cells demonstrate round uniform basophilic nuclei and pale eosinophilic to clear cytoplasm
- Background stellate reticulum-like proliferation
- Varying levels of dentinoid and cementum-like calcified collagenous matrix
- Mitosis rare
- Reference: J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016;74:307
Microscopic (histologic) images
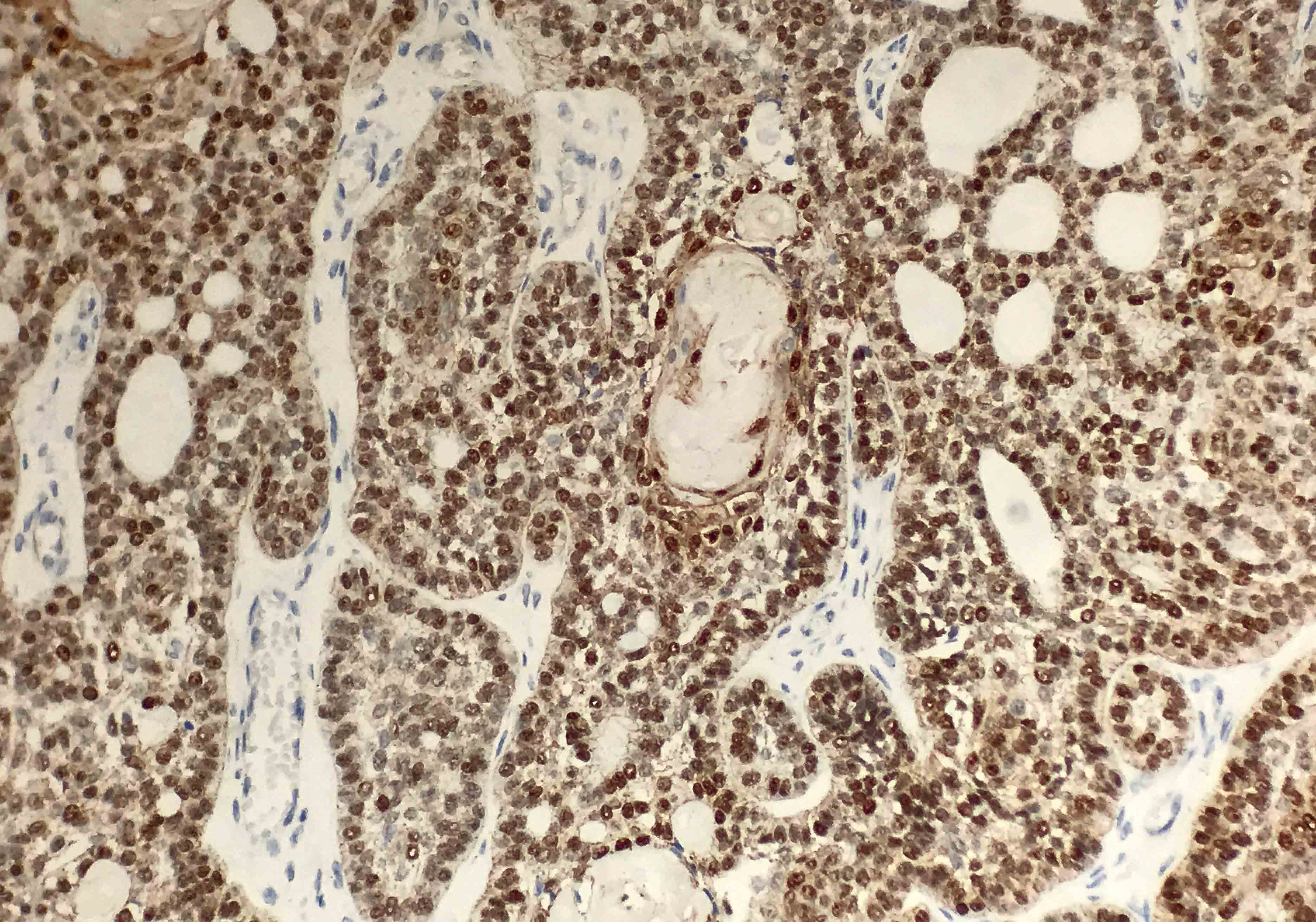
Positive stains
- Positive but nonspecific:
- Beta catenin (nuclear and cytoplasmic)
- LEF1 (nuclear)
Negative stains
- Negative but nonspecific:
Sample pathology report
- Posterior mandible, right, segmental mandibulectomy:
- Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor (3.2 cm) (see comment)
- Comment: Tumor confined to bone and measures 0.5 cm from anterior and posterior bone margins
- Posterior mandible, right, excision / curettage:
- Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor, in fragments
Differential diagnosis
- Ameloblastoma:
- Second most common odontogenic tumor; however, most clinically significant odontogenic tumor after odontoma
- May have similar basaloid epithelial cells, reverse polarity, stellate reticulum but no ghost cells
- Typically does not have calcifications
- Conventional (nonunicystic), commonly solid and multilocular
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst:
- Similar histology, ameloblast-like epithelium, stellate reticulum-like proliferation, ghost cells, dentinoid and calcifications
- Grossly, predominantly cystic; small satellite cysts, islands of epithelium or ghost cells may be seen in the fibrous capsule
- Likely on a spectrum with dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
- Craniopharyngioma:
- Similar histology, ghost cells and islands of squamous cells present but originates in the sella turcica
- Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma:
- Extremely rare with only isolated case reports
- Demonstrates pleomorphism and malignant cytology with invasive features
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Predominantly solid pattern of growth. Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor and calcifying odontogenic cyst have significant histopathologic overlap. Both demonstrate amelobastic-like epithelium, ghost cells, stellate reticulum, squamous differentiation and varying levels of dentin and calcification; however, dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is a predominantly solid neoplasm and calcifying odontogenic cyst is a single chamber, unilocular cyst.
Comment Here
Reference: Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
Board review style question #2
Which radiographic features distinguishes an ameloblastoma from a dentinogenic ghost cell tumor?
- Air fluid levels
- Calcifications
- Cystic spaces
- Invasive features
Board review style answer #2
B. Calcifications. Ameloblastoma and dentinogenic ghost cell tumor have significant radiographic and histopathologic overlap; however, radiographically ameloblastoma generally does not have calcifications. Radiographically, ameloblastoma typically demonstrates a multilocular appearance. Ameloblastoma is the most common clinically significant odontogenic tumor and by far more common than dentinogenic ghost cell tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
Back to top