Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Morrison, A, Magliocca K. Gingival cyst (adult). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillagingivalcystadult.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Gingival cysts of adults occur along gingiva of older adults, arise from dental lamina epithelial rests
Epidemiology
- Rare, approximately 0.5% of all odontogenic cysts
- Arise in middle aged or elderly adults, peak incidence in fifth to sixth decade of life
- More common in females
Sites
- Most common location is facial gingiva of mandibular canines and premolars
- Maxillary gingival cysts usually found in facial gingival incisor, canine, premolar region
Pathophysiology
- Arise from epithelial rests of dental lamina epithelium (rests of Serres) within soft tissue
- Cause of cystic degeneration of this epithelium is unknown
- Is considered the soft tissue counterpart of lateral periodontal cyst
Clinical features
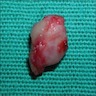
- Solitary, well circumscribed, usually less than 0.5 cm
- Rarely bilateral
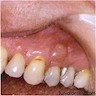
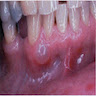
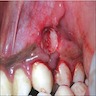
- Bluish, smooth surfaced, dome shaped swelling on attached gingiva or unattached alveolar mucosa
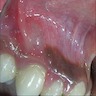
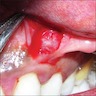
- May cause superficial pressure resorption of underlying alveolar bone (See "Bone defect" in Clinical images)
Radiology description
- Cyst may cause a superficial "cupping out" of alveolar bone, usually not detected on a radiograph but apparent when cyst is excised
- If more bone is missing or the pre-operative lesion is visible on a radiograph, one could argue that the lesion may be a lateral periodontal cyst that has eroded the cortical bone rather than a gingival cyst that originated in the mucosa
Case reports
- 16 year old boy with gingival cyst (J Indian Soc Periodontol 2012;16:465)
- Gingival "surgical cyst" developing post-subepithelial connective tissue graft (J Periodontol 1997;68:392)
- Bilateral gingival swellings in mandibular canine-premolar areas (J Am Dent Assoc 1990;120:71)
- Gingival cyst of adult with bilateral presentation (J Periodontol 1987;58:796)
Treatment
- Local surgical excision, typically do not recur
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
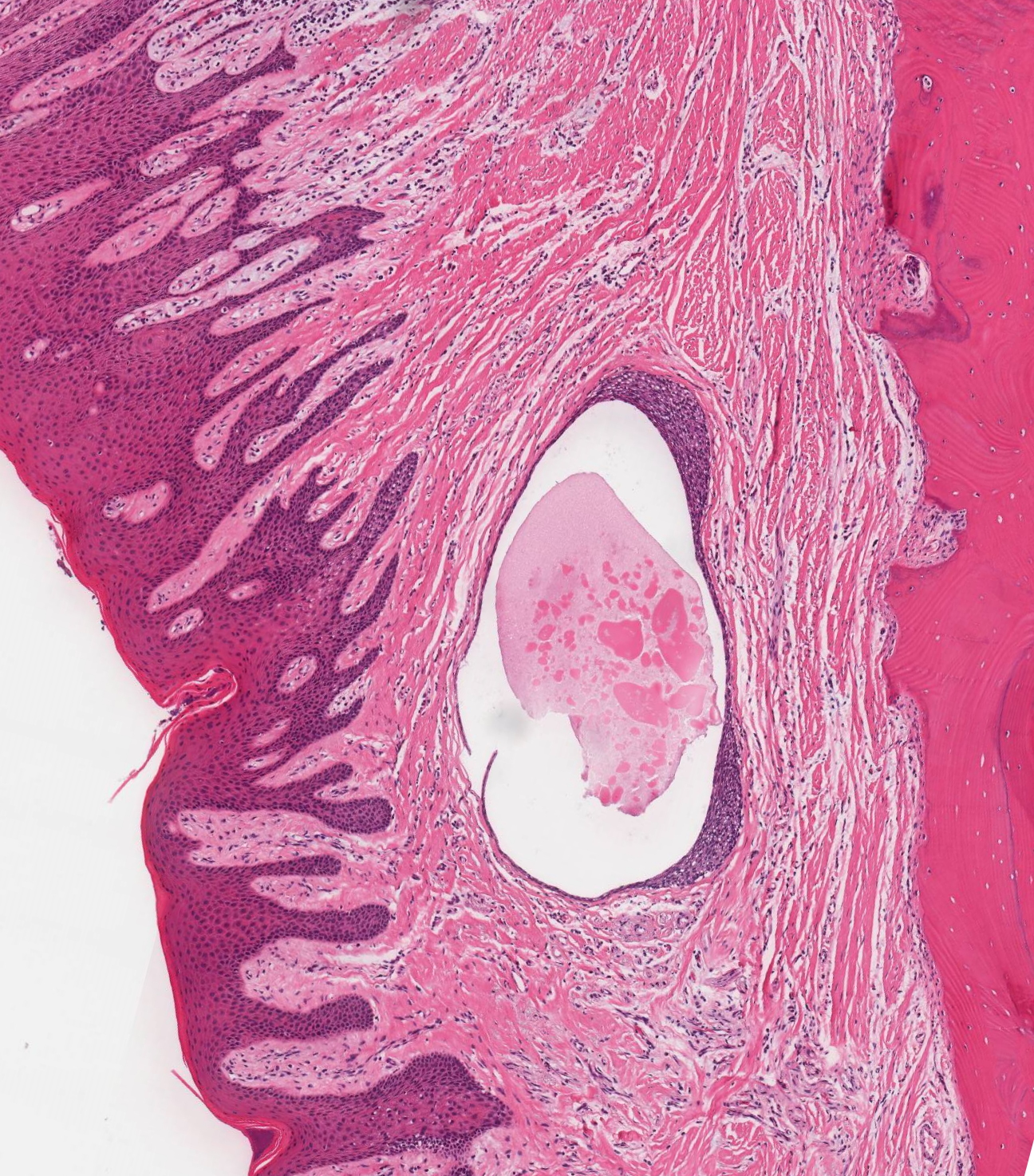
- Unicystic structure lined with attenuated, non-keratinized low cuboidal or stratified squamous epithelium
- Cyst lining may be with or without contiguous epithelial plaques (focal thickened areas of epithelium) which may have clear cells
- Surrounding fibrovascular stroma is relatively uninflamed, except biopsy includes a portion of junctional epithelium
- Variable inflammation
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Cyst of incisive papilla: only occurs in soft tissues of midline anterior hard palate between central incisor teeth
- Epidermoid cyst: usually floor of mouth, large size
- Epithelial inclusion cyst: after gingival graft
- Lateral periodontal cyst: originates within bone
- Odontogenic keratocyst: occasionally reported in soft tissues
- Salivary duct cyst: occurs in non-gingival, salivary gland bearing tissues