Table of Contents
Definition / general | Laboratory | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Sangle N. MDS with excess blasts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/myeloproliferativeRAEB.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Myeloblasts are 5 - 19% of bone marrow differential
- Usually cytopenias in 2 or 3 lineages
- Considered high risk MDS
- Type 1: 5 - 9% blasts in bone marrow or 2 - 4% blasts in peripheral blood, no Auer rods, < 1 billion/L monocytes
- Type 2: 10 - 19% blasts in bone marrow or 5 - 19% blasts in peripheral blood or Auer rods in any MDS, < 1 billion/L monocytes; more aggressive, greater tendency to progress to AML (Am J Clin Pathol 2005;124:191)
- Refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation (RAEB-T): classified as AML under WHO classification
- Median survival of 16 months for RAEB-1 and 9 months for RAEB-2 (Br J Haematol 2006;132:162)
Laboratory
- Anemia (normochromic, normocytic or macrocytic), usually neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
Case reports
- 31 year old man with cutaneous involvement (Cutis 2007;80:223)
- 64 year old woman with extensive myocardial infiltration (BMC Blood Disord 2006;6:4)
Microscopic (histologic) description
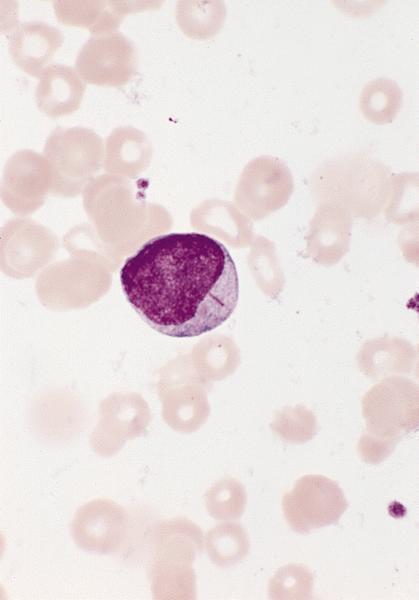
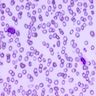
- Peripheral blood: nucleated red blood cells, immature granulocytes, neutrophilic hyposegmentation, pseudo-Pelger-Huet cells and hypogranulation, myeloblasts 2 - 4% (RAEB-1) or 5 - 19% (RAEB-2), occasional micromegakaryocytes
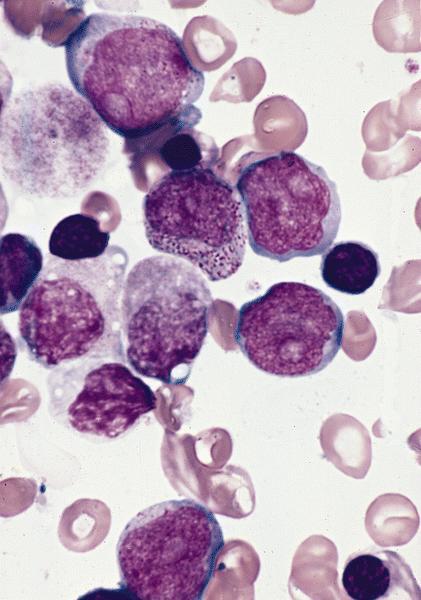
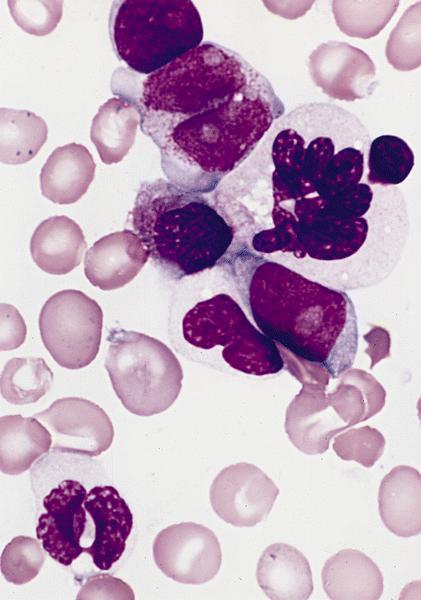
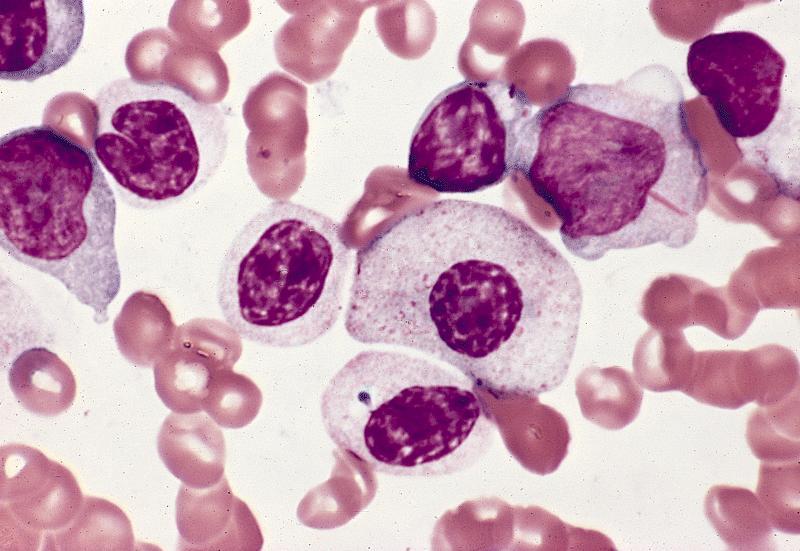
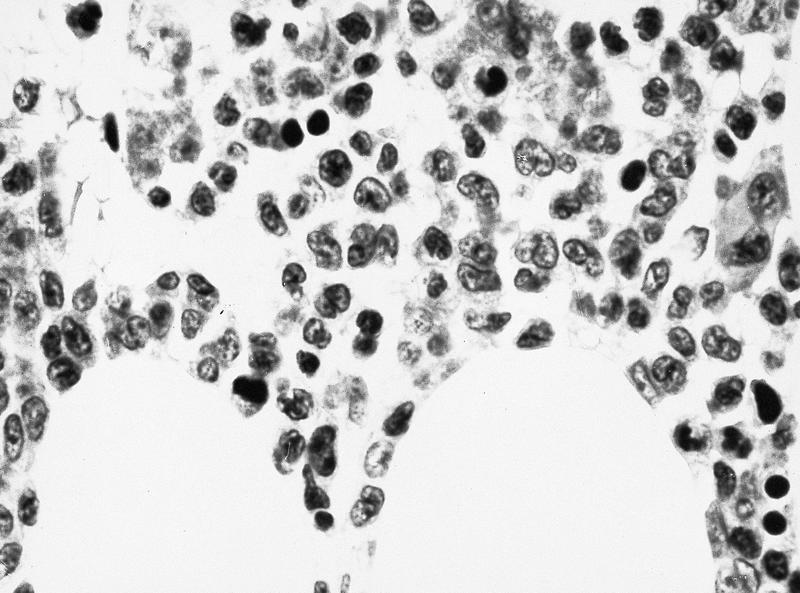
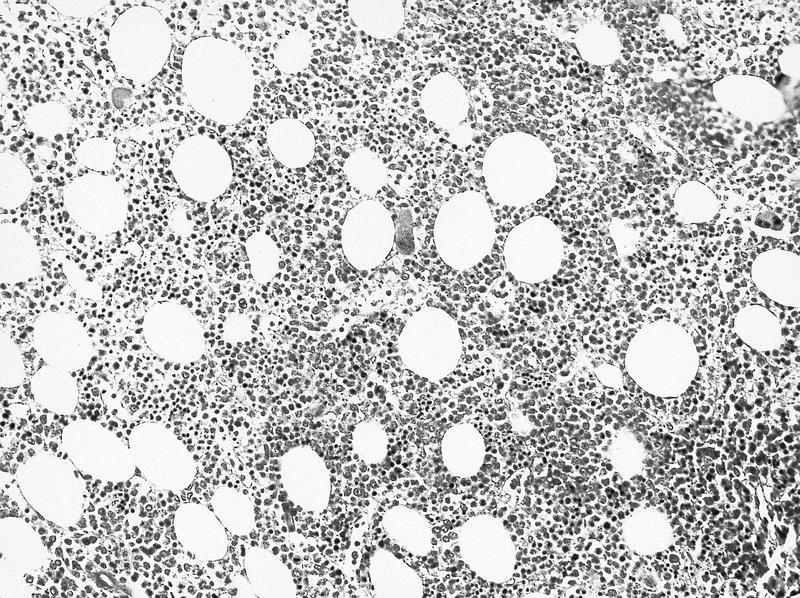
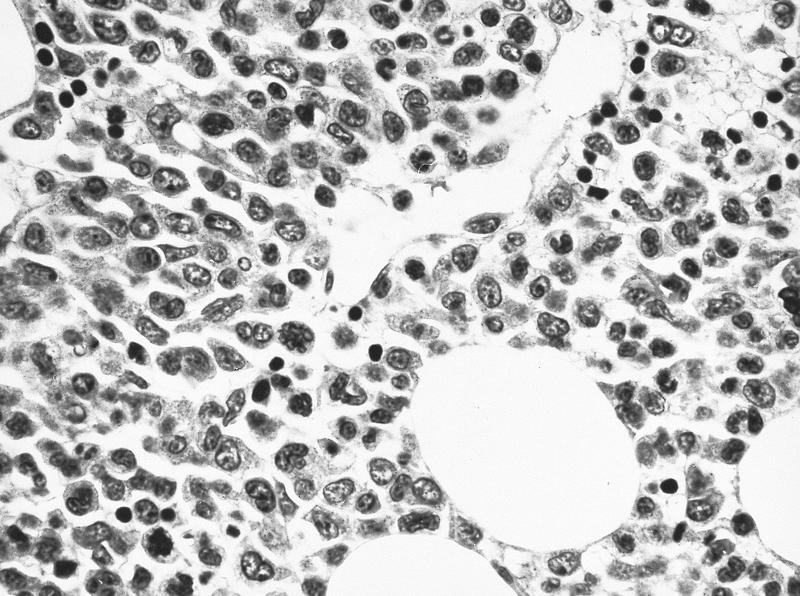
- Bone marrow: normocellular or hypercellular; hyperplasia of granulocytes or erythrocytes; myeloblasts comprise 5 - 9% (RAEB-1) or 10 -19% (RAEB-2) of white blood cells; Auer rods often seen; severe dysplastic changes in all 3 lineages, more severe than other MDS; abnormal localization of immature precursors (ALIP / clusters or aggregates of blasts located away from bone trabeculae and vascular structures); may have increased reticulin fibers
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
Peripheral smear images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No specific abnormality (Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics)
Differential diagnosis
- Copper deficiency: reduced copper levels (Leuk Res 2008;32:495)