Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Vidis LJ, Bentz JL. Embryonal carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorembryonal.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Primitive appearing ovarian tumor that is histologically similar to embryonal carcinoma of the testis
- Often a component in a malignant mixed germ cell tumor of the ovary; the pure form is exceedingly rare
Essential features
- Median age is 14 - 15 years; patients often present with precocious puberty, vaginal bleeding, infertility, amenorrhea and mild hirsutism (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- Both serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and beta human chorionic gonadotropin (βhCG) can be elevated (which can result in a positive pregnancy test) (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
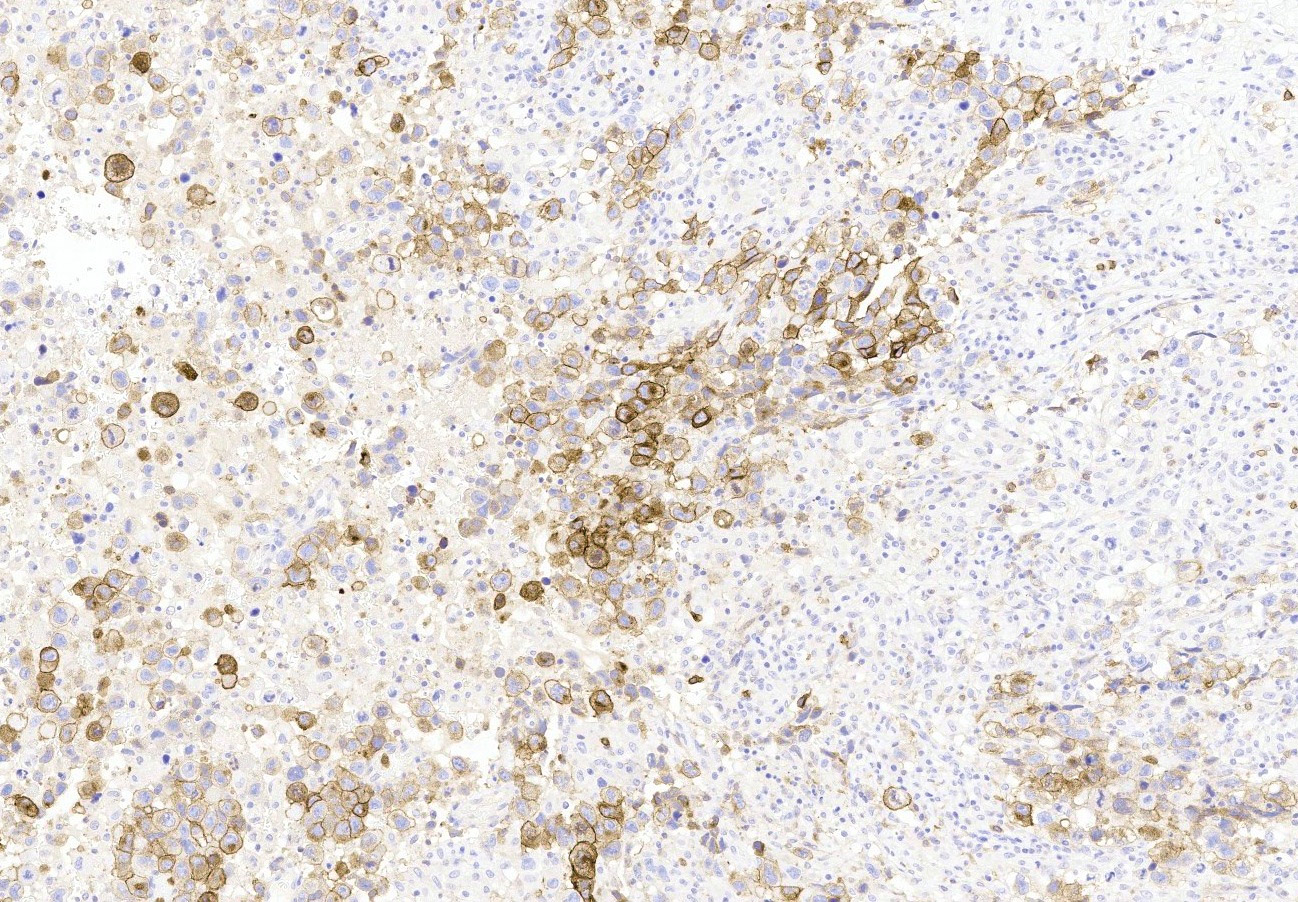
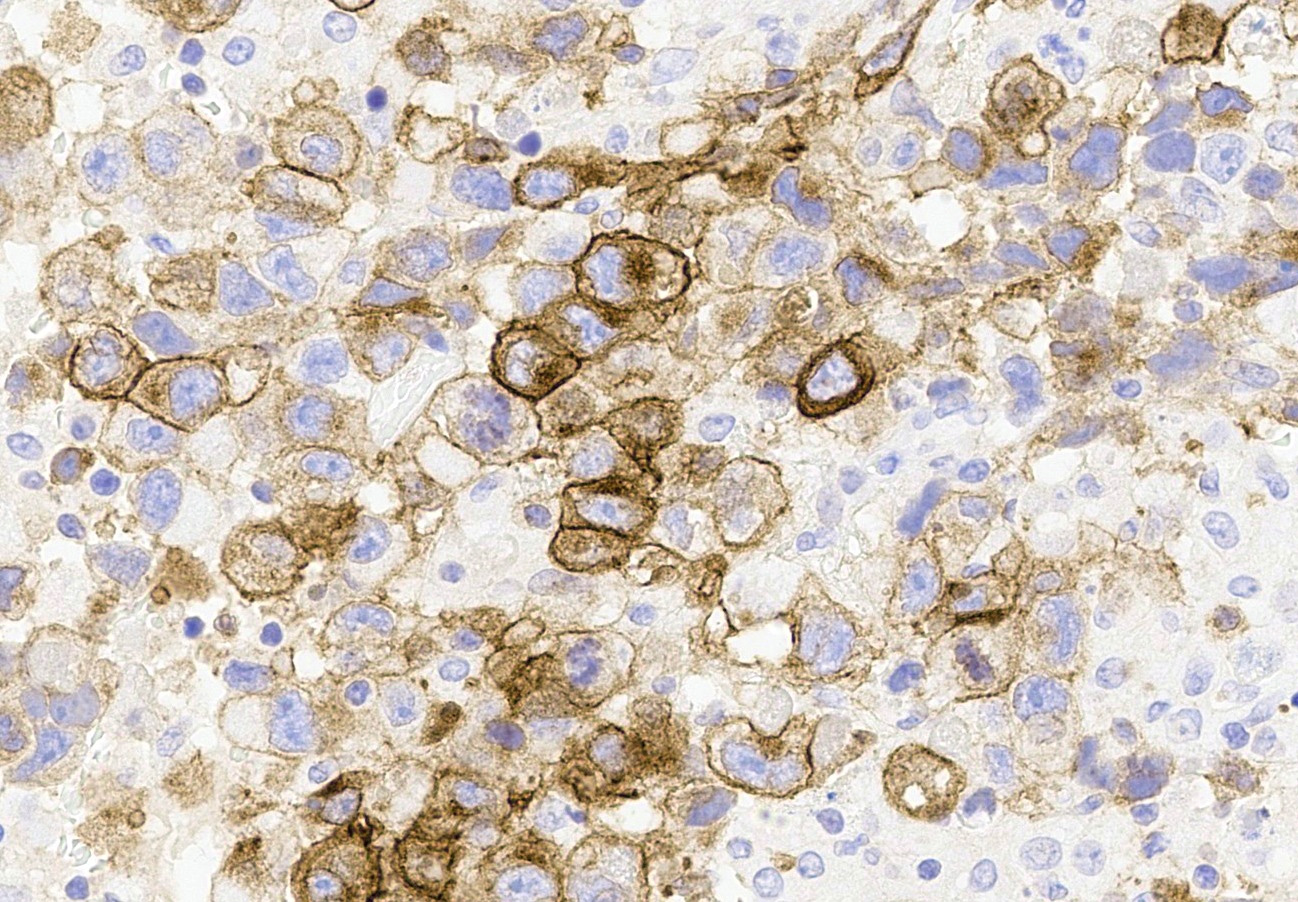
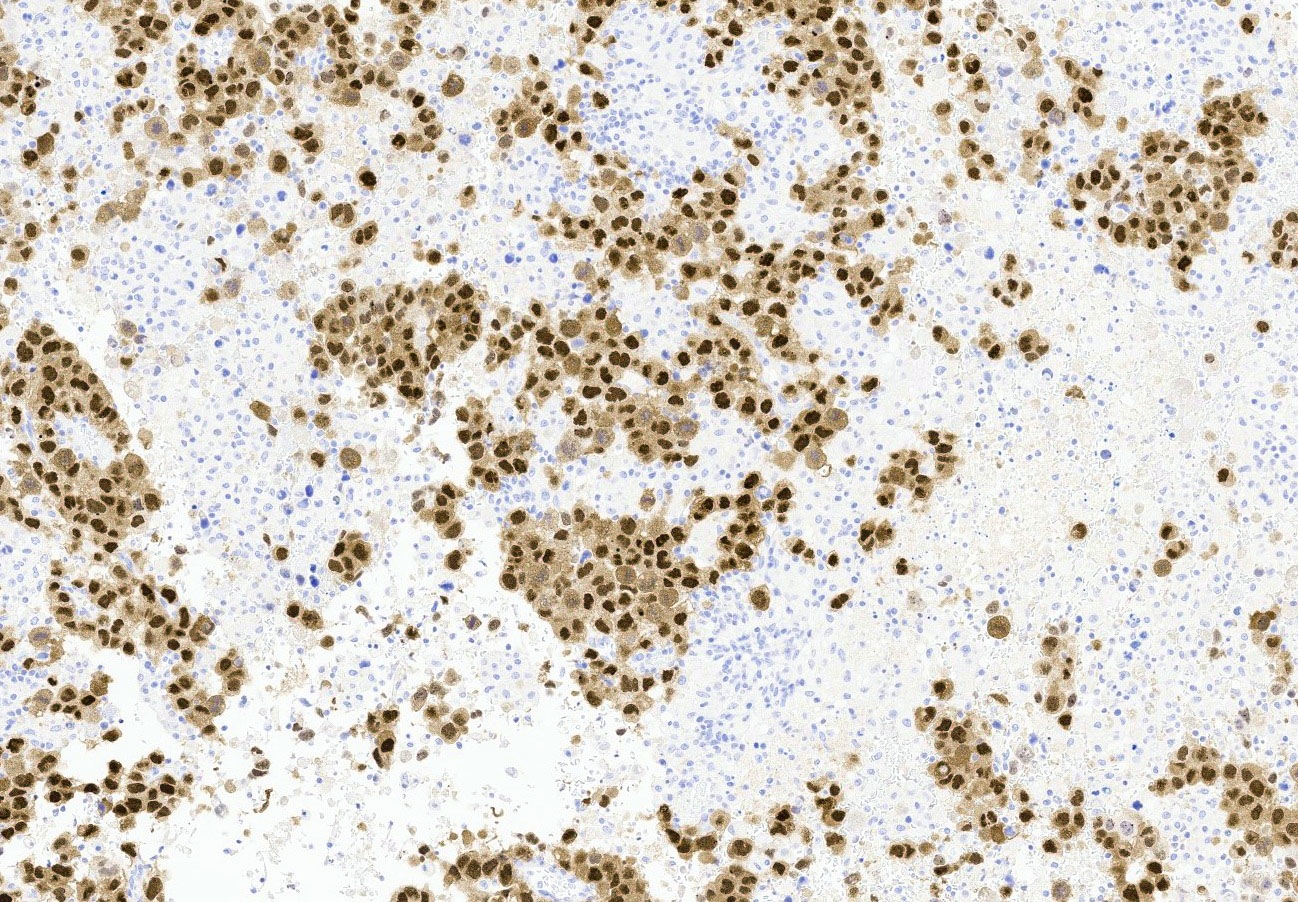
- Positive IHC expression with OCT 3/4, CD30, SOX2, SALL4 and βhCG (if syncytiotrophoblast is present); negative for glypican and CD117
- Worst prognosis among germ cell tumors, even at low stage (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
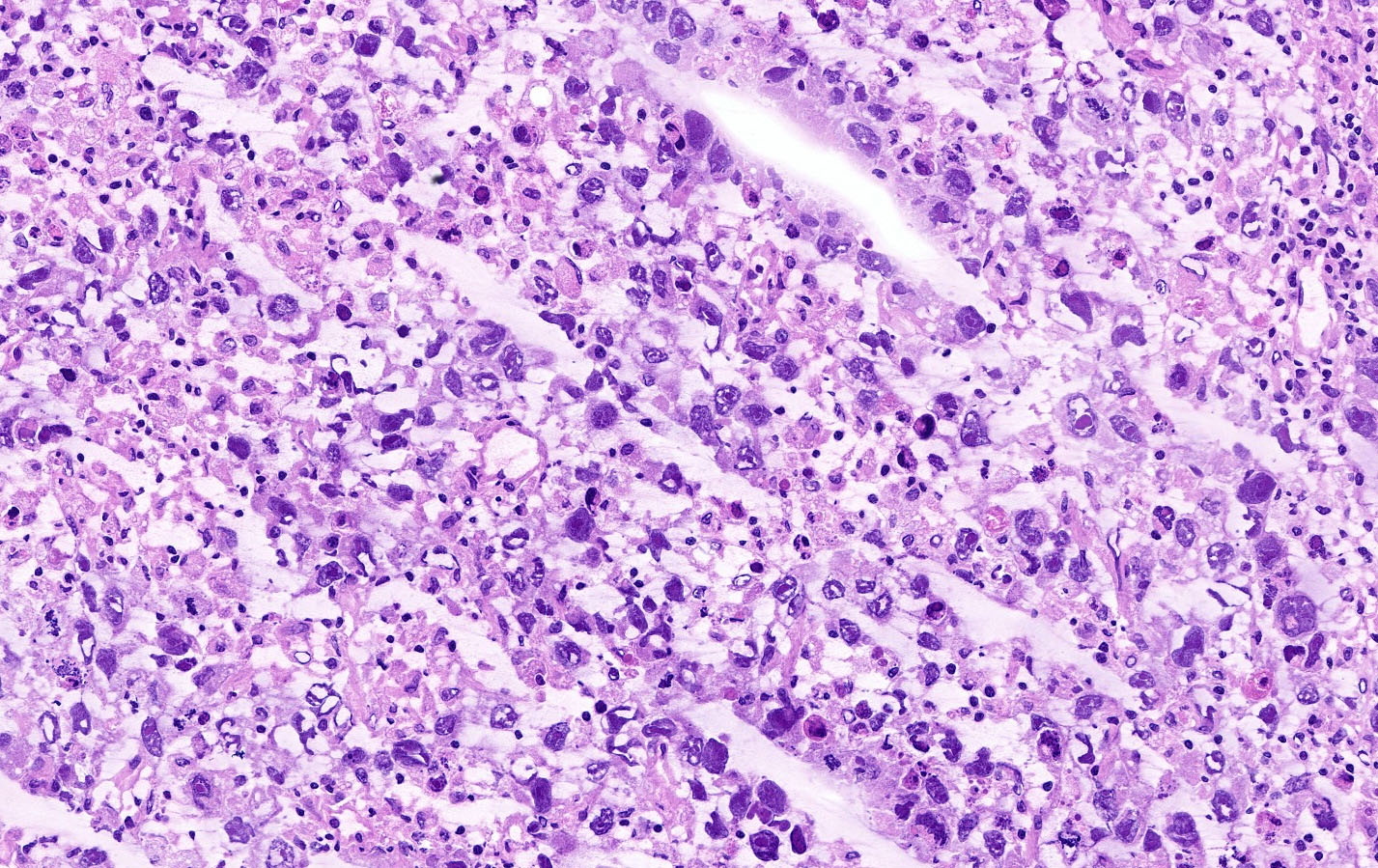
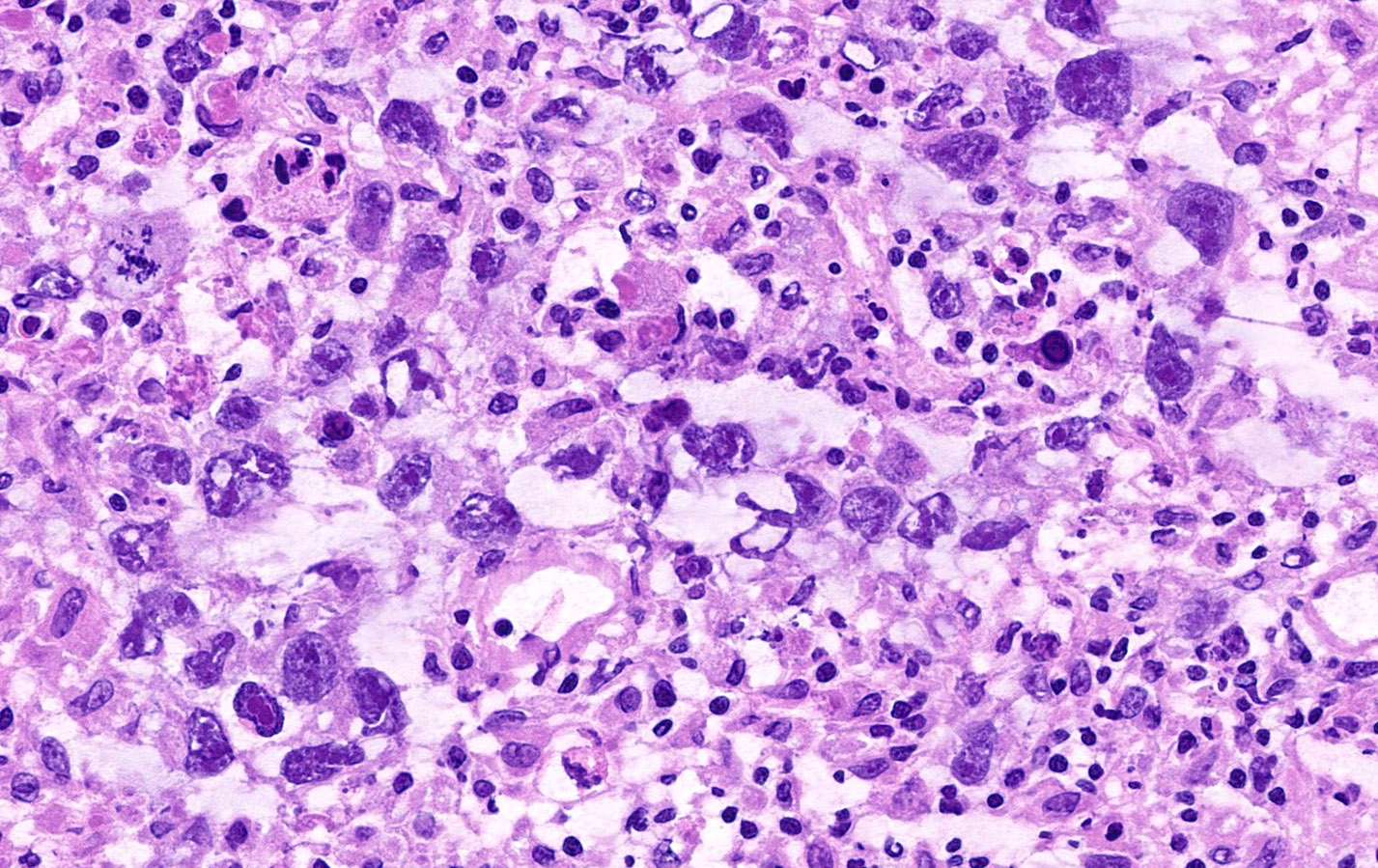
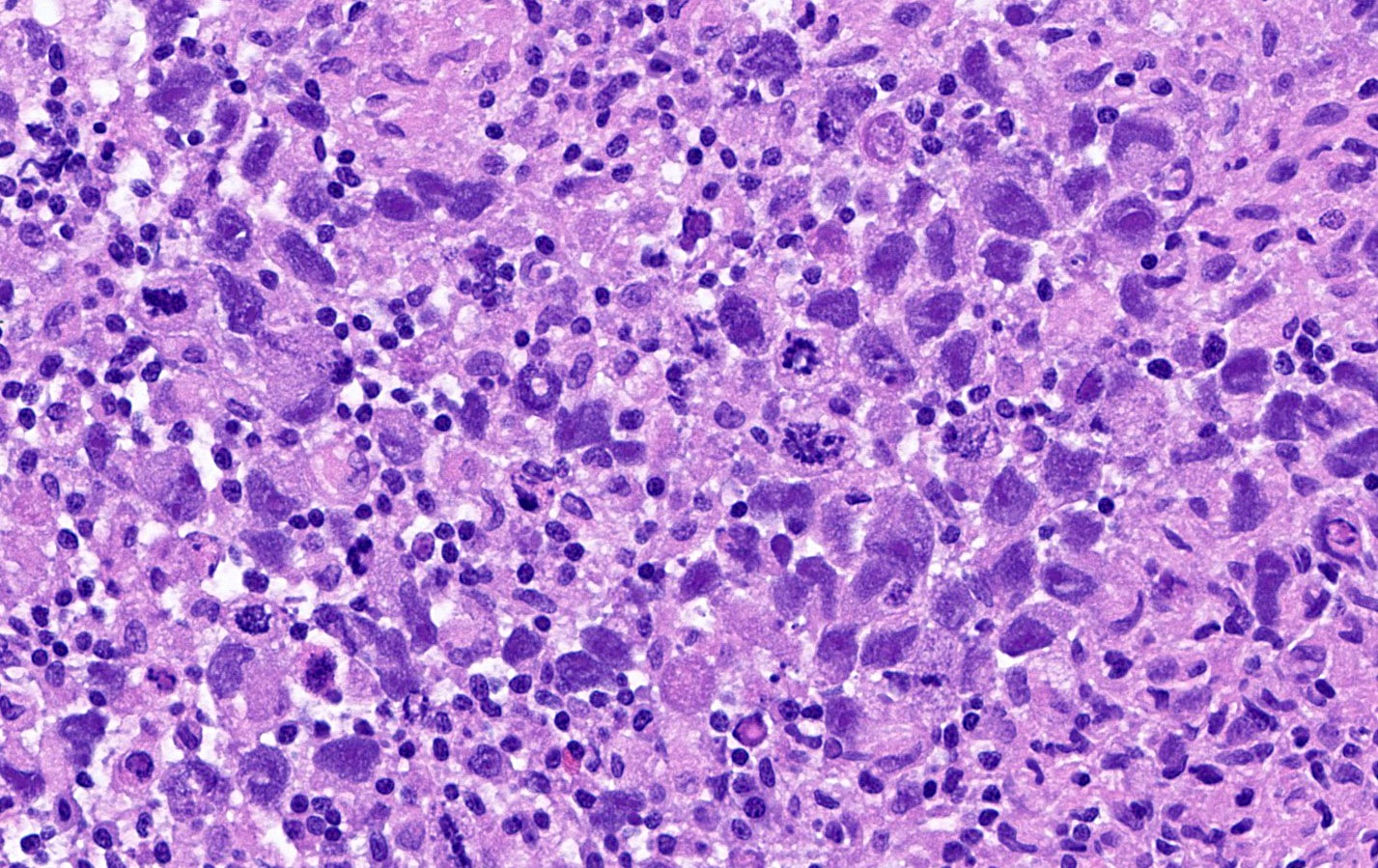
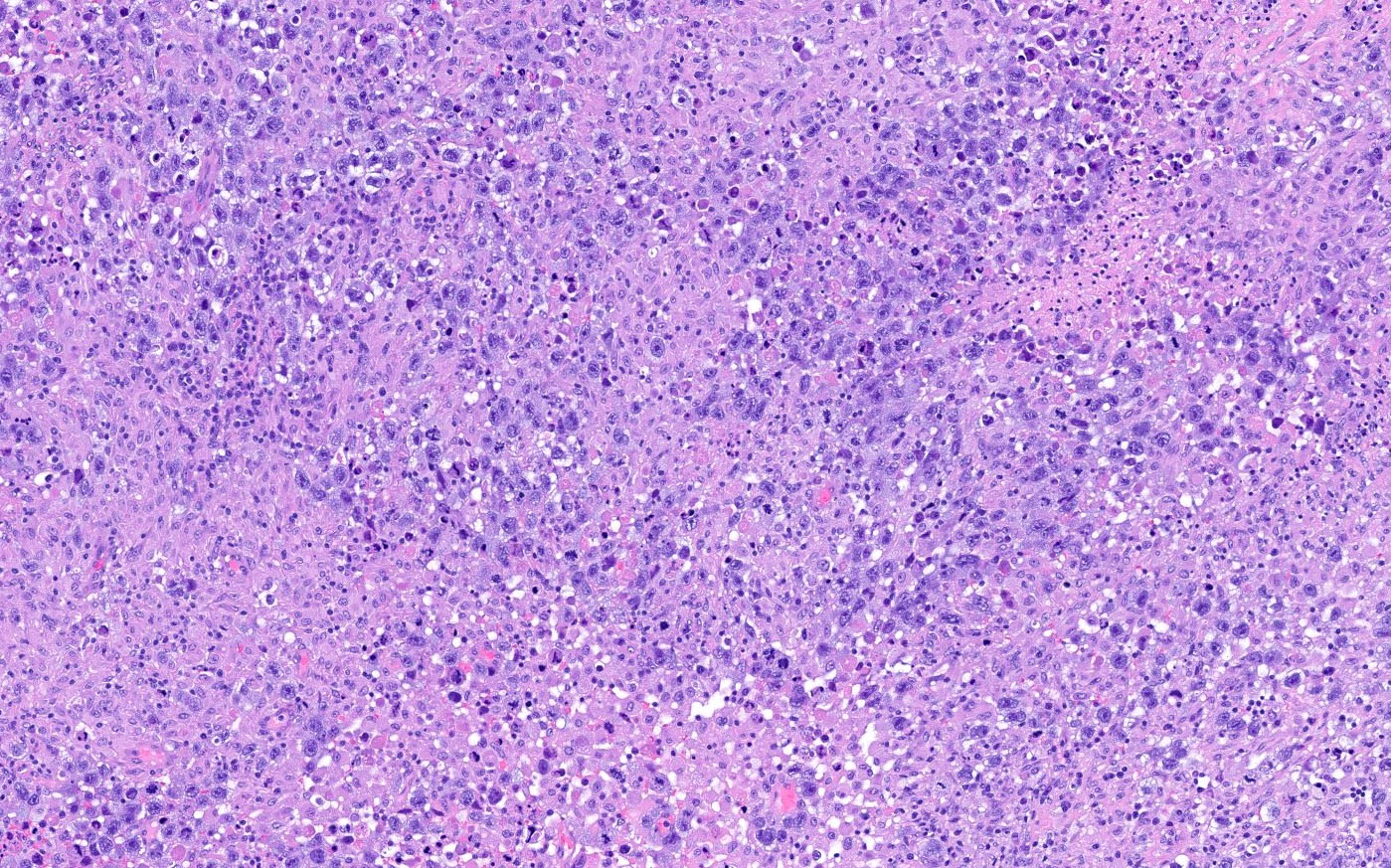
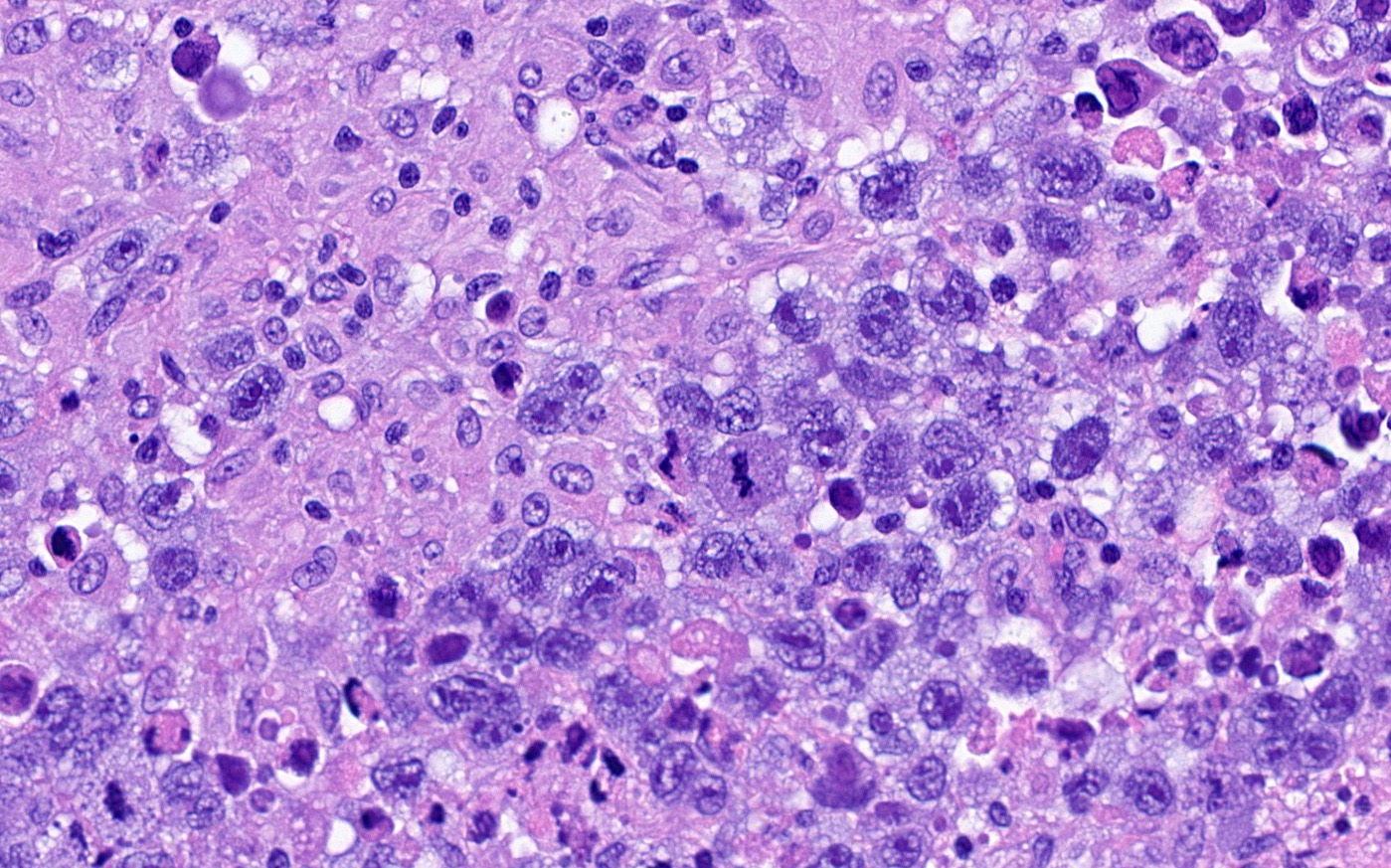
- Large, primitive pleomorphic cells with abundant cytoplasm arranged in sheets and nests
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9070/3 - embryonal carcinoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2C73.Y & XH8MB9 - other specified malignant neoplasms of the ovary & embryonal carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Primarily in adolescents and young women with average age of 14 - 15 years (Cancer 1976;38:2420, Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- First described in 1976 by Kurman and Norris as a distinct type of malignant germ cell neoplasm to distinguish from endodermal sinus tumor of ovary (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Estimated to account for < 1% of malignant ovarian germ cell tumors (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
Sites
- Ovary
- Metastasis is possible to liver, lungs, retroperitoneal lymph nodes, peritoneal surfaces in up to half of all cases (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
Pathophysiology
- Chromosome 12 abnormalities in 5 of 6 cases analyzed by FISH (iscochromosome 12p or 12p amplification) (Hum Pathol 2010;41:716)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Hormonal manifestation, including precocious puberty, vaginal bleeding, infertility, amenorrhea and mild hirsutism, in approximately half of patients (Cancer 1976;38:2420, Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- May show serum elevation of AFP or βhCG with positive pregnancy test
- Palpable unilateral abdominal or pelvic mass in 80% of patients (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- May present with abdominal pain, fever, menstrual irregularities or weight loss (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Clinical evidence of an endocrinopathy is seen in approximately half of patients (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
Diagnosis
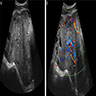
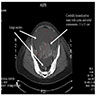
- Large, unilateral abdominal or adnexal mass on imaging (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2021;57:987, Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Pregnancy test may be positive (increased βhCG) (Cancer 1976;38:2420, Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- AFP may be increased (Cancer 1976;38:2420, Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- Definitive diagnosis made by histologic examination of surgical specimen (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
Laboratory
- Serum βhCG elevation resulting in positive pregnancy test (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- Serum AFP may be elevated
Radiology description
- Unilateral, solid mass with cystic areas, irregular margins, rich vascularization (Radiographics 2014;34:777, Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2021;57:987)
- No reported preference for right or left ovary (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- 1 embryonal carcinoma of the ovary measured at 216 mm (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2021;57:987)
Prognostic factors
- Worst prognosis among germ cell tumors
- 5 year survival rate for stage I cases: 50% (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22, Cancer 1976;38:2420)
Case reports
- 11 year old girl with large abdominal mass and ascites (Med Arch 2018;72:371)
- 13 year old girl with abdominal pain and 25 cm mass (Iran J Pathol 2016;11:66)
- 19 year old woman with abdominal pain and massive ascites (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2011;24:e1)
- 53 year old woman with irregular menses, pelvic pain and positive pregnancy test (Gynecol Oncol 1996;63:133)
Treatment
- Surgery with adjuvant chemotherapy
- Bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin (BEP) most common chemotherapy regimen (Ann Oncol 2018;29:iv1)
Gross description
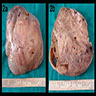
- Large, with median size of 17 cm (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Cut surface is gray-white or yellow (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- With or without cysts containing hemorrhage or necrosis (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
Frozen section description
- High grade malignant neoplasm with necrosis
Frozen section images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Similar to embryonal carcinoma of the testis (Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Often mixed with other malignant germ cell tumor components (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22, Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Sheets and nests of large, primitive pleomorphic cells with abundant cytoplasm (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22, Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Round nuclei with coarse membranes, at least 1 prominent nucleolus and brisk mitotic activity (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- Occasional papillae and gland morphology (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
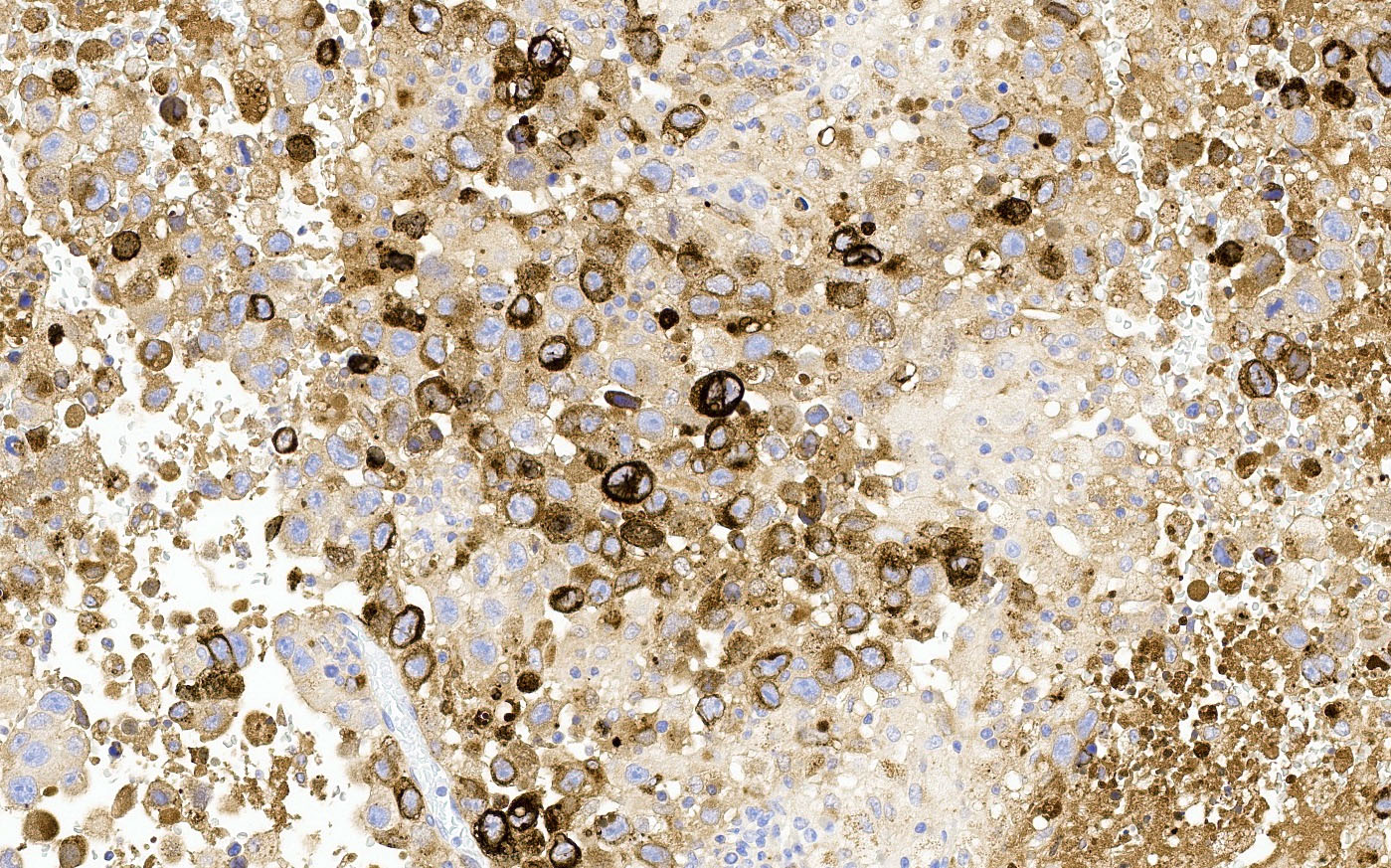
- Syncytiotrophoblast-like tumor cells are seen (hCG+) around sheets of tumor cells or within stroma (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22, Cancer 1976;38:2420)
- Hyaline globules, similar to yolk sac tumor, may also be present (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- Glandular pattern may mimic endometrial carcinoma or glandular morphology of a yolk sac tumor (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Immunofluorescence description
- Chromosome 12p overrepresentation
- Isochromosome 12p
Positive stains
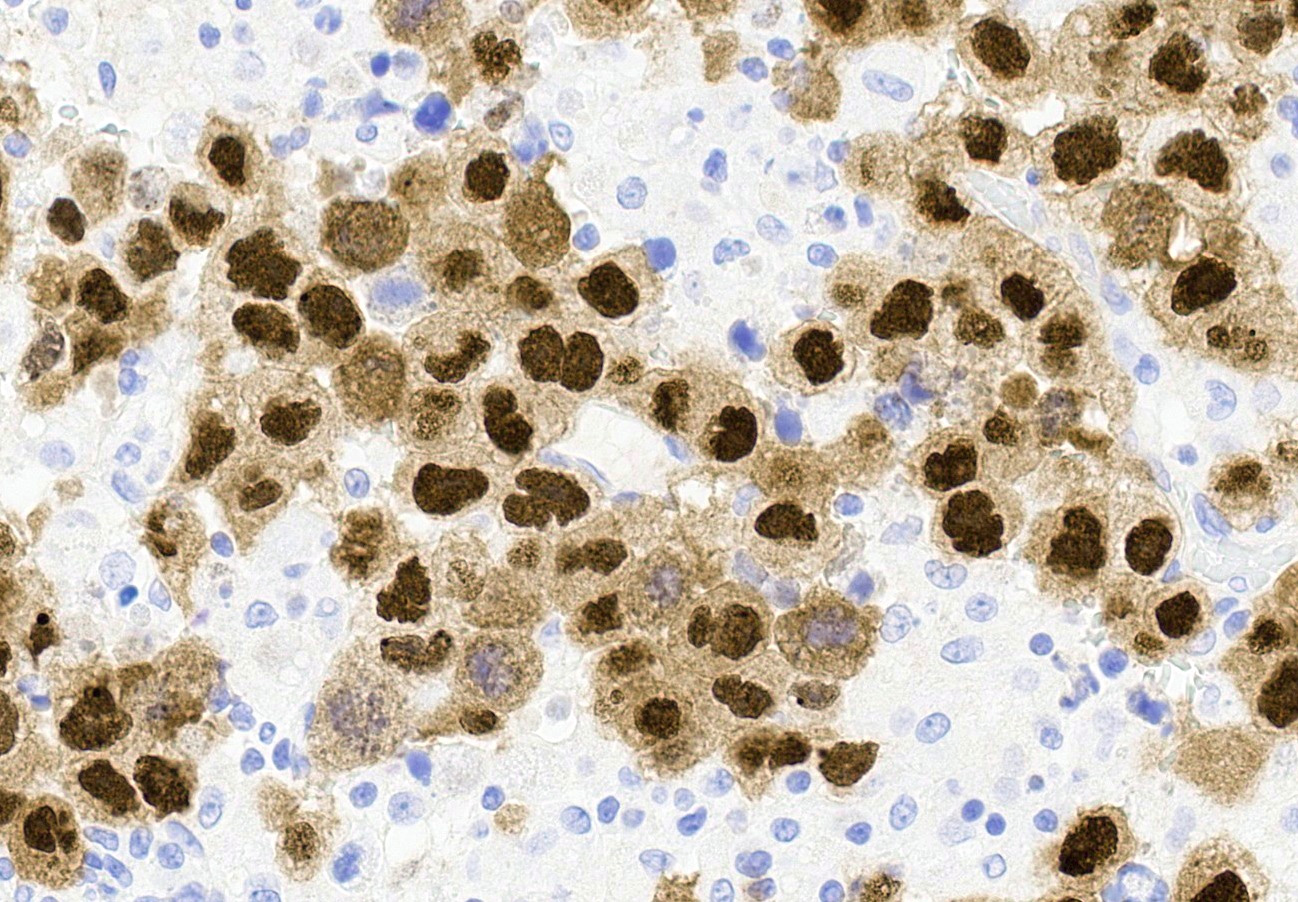
- SALL4, OCT 3/4 and SOX2 nuclear positivity (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:894, Histopathology 2013;62:71)
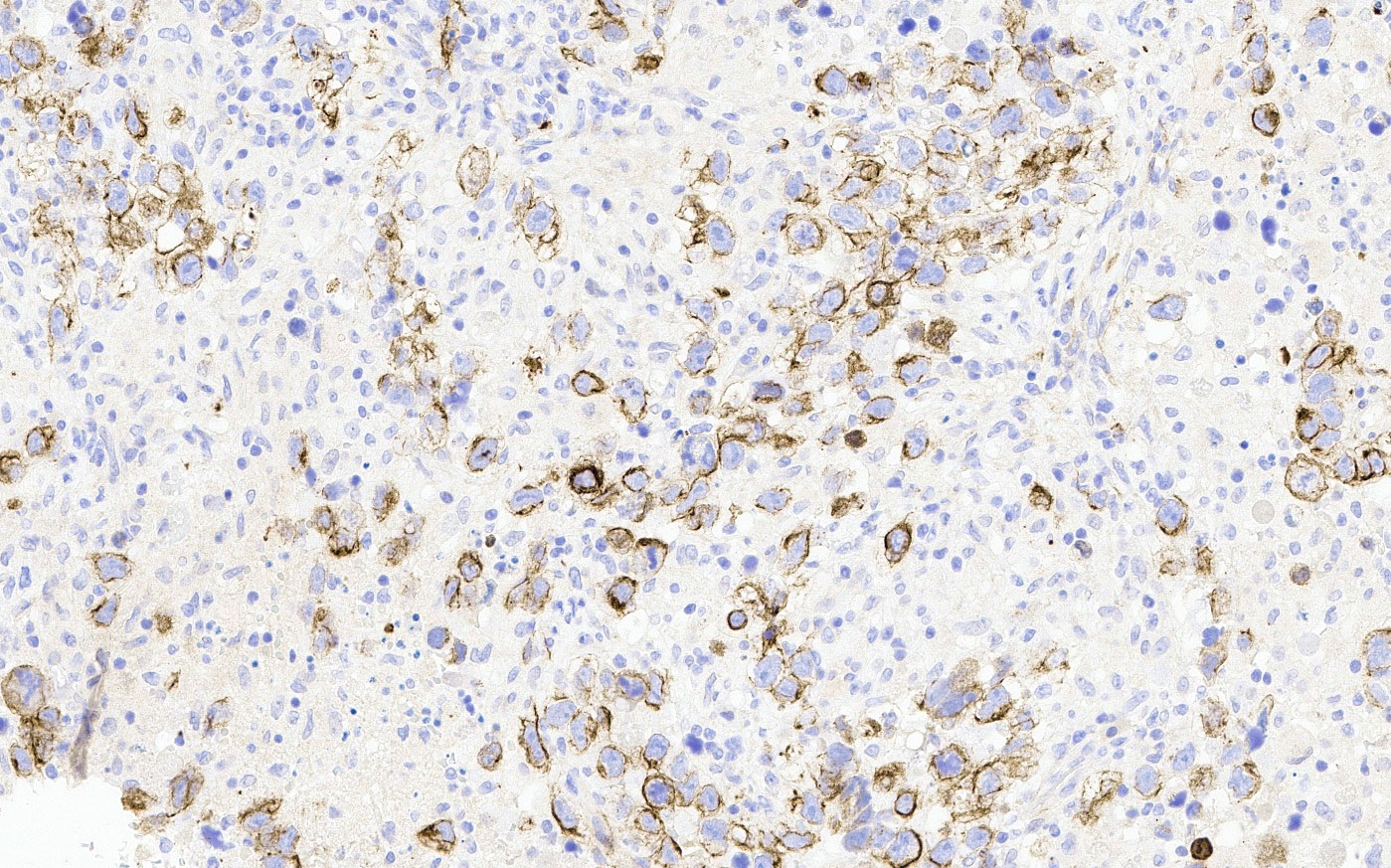
- CD30 membranous positivity (Hum Pathol 2010;41:716)
- OCT 3/4 more sensitive than CD30 but can also be expressed in dysgerminoma (Histopathology 2013;62:71)
- AE1 / AE3 (Histopathology 2013;62:71)
- βhCG positive in syncytiotrophoblastic cells (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- AFP may be expressed in both tumor cells and hyaline globules (Semin Diagn Pathol 2023;40:22)
- CD30 expression might decrease after chemotherapy (Hum Pathol 2006;37:662)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Chromosome 12p FISH can be helpful in establishing a diagnosis in conjunction with IHC (Hum Pathol 2010;41:716)
Sample pathology report
- Left ovary and fallopian tube, left salpingo-oophorectomy:
- Malignant mixed germ cell tumor (see comment)
- Comment: The ovarian tumor is compatible with a malignant mixed germ cell tumor composed of embryonal carcinoma (__%) (e.g., yolk sac tumor __%; immature teratoma __%; with or without choriocarcinoma __%). Sheets of pleomorphic, primitive cells with brisk mitotic activity, tumor cell necrosis and positive expression of OCT 3/4 and CD30 are consistent with a component of embryonal carcinoma. Syncytiotrophoblastic cells are present (hCG+), which can raise concern for a component of choriocarcinoma; however, the presence of isolated syncytiotrophoblastic cells has been reported in embryonal carcinoma and there is no evidence of choriocarcinoma in examined sections of this extensively sampled ovarian tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Yolk sac tumor:
- Microcystic / reticular, polyvesicular vitelline and festoon-like patterns
- Less nuclear pleomorphism
- Positive expression with AFP and glypican 3
- Negative for OCT 3/4 or SOX2
- Dysgerminoma:
- Choriocarcinoma:
- Poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma:
- Juvenile granulosa cell tumor:
- Follicle-like spaces with luteinized tumor cells
- Lack of syncytiotrophoblast
- Positive for inhibin, calretinin and negative for AFP
- Poorly differentiated Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor (SLCT):
- Portion of the tumor will contain a better differentiated component of SLCT
- Positive for inhibin and calretinin
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. CD30. CD30 is the most specific marker for embryonal carcinoma of the ovary. Answer A is incorrect because AFP is a marker for yolk sac tumor. Answer D is incorrect because CD117 highlights dysgerminoma. Answer B is incorrect because βhCG is a marker for syncytiotrophoblast and choriocarcinoma. Answer E is incorrect because while OCT 3/4 can stain embryonal carcinoma of the ovary, it also stains dysgerminoma, whereas dysgerminoma should be negative for CD30.
Comment Here
Reference: Embryonal carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Embryonal carcinoma
Board review style question #2
The glandular pattern of embryonal carcinoma, particularly if present with hyaline globules, can mimic which of the following tumors?
- Choriocarcinoma
- Dysgerminoma
- Leydig cell tumor
- Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
- Yolk sac tumor
Board review style answer #2
E. Yolk sac tumor. The glandular pattern of embryonal carcinoma can mimic a yolk sac tumor, particularly in the presence of hyaline globules. Glandular architecture can also mimic a poorly differentiated carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because choriocarcinoma will have a mixture of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast without a prominent glandular architecture. Answer B is incorrect because dysgerminoma will not show a glandular architecture and will have fibrous septa with lymphocytic or granulomatous infiltrate. Answer D is incorrect because Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors will not show a prominent glandular architecture and stain with inhibin / calretinin. Answer C is incorrect because Leydig cell tumors are rare and arise in the hilum and have Reinke crystals.
Comment Here
Reference: Embryonal carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Embryonal carcinoma