Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Feroze A, Bhalla R. Condyloma acuminatum. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotumcondyloma.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) associated, nonneoplastic tumor-like growths
- Typically considered benign
Essential features
- HPV (6 and 11) associated lesions
- Frequently occurs in young, sexually active men
- Soft, flesh colored, cauliflower-like, raised or flat lesions
- Hallmark of the lesion is koilocytic atypia
- Benign course with high recurrence rate
Terminology
- Genital wart
- Anogenital wart
- Usual condyloma
- Flat condyloma
- Venereal wart
- References: Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022, Partin: Campbell-Walsh Urology 12th Edition Review, 3rd Edition, 2020
Epidemiology
- Most frequently occurs in men between 25 and 29 years of age
- Spread by direct skin to skin contact
- Transmitted sexually
- If found in children, sexual abuse should be suspected
- Autoinfection is common after initial infection
- References: Cheng: Urologic Surgical Pathology, 4th Edition, 2019, Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e15109, Drugs Context 2018;7:212563
Sites
- Occurs most commonly on the penis, scrotum, perineum and anus
- Usual site of occurrence on the penis is the glans, followed by foreskin and penile shaft
- 5% of patients demonstrate urethral involvement, which may extend to the prostatic urethra
- Urinary bladder is rarely involved
- Giant condyloma acuminatum (Buschke-Löwenstein tumor) occurs in the urethra, coronal sulcus, frenulum or shaft
- Reference: Partin: Campbell-Walsh Urology 12th Edition Review, 3rd Edition, 2020, Drugs Context 2018;7:212563, J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2016;9:S2
Pathophysiology
- Microabrasions cause HPV virus inoculation into the epithelial structures
- Virus replicates in the epithelial basal layer
- Warty plaques or papules form due to viral replication
- Viral genome of HPV has 6 early open reading frames (E1, E2, E4, E5, E6, E7) as well as 2 late open reading frames (L1, L2)
- Early open reading frames play a role in regulating and coding of proteins involved in viral replication and cell transformation
- High risk HPV strains directly integrate their genetic material into the host cell, resulting in uncontrolled activation of E6 and E7 genes, transcription of oncoproteins and inactivation of p53 and retinoblastoma tumor suppressor genes
- HPV integration into host cells causes formation of atypical and altered morphological cells called koilocytes
- Viral gene amplification occurs with migration of infected basal layer cells to adjacent layers
- Site of assembly of virions is in the superficial layer of the epithelium, from which they are released and infect their own or foreign adjacent tissues
- Viral effects on epithelium causes condyloma's exophytic phenotype
- Reference: Rom J Morphol Embryol 2021;62:369
Etiology
- Contagious disease
- Transmission by oral, genital and anal sex, through skin contact
- Nononcogenic mucosal HPV types 6 and 11 are detected in 75 - 100% of condylomas
- 15% are coinfected with high risk HPV (16 and 18) types
- HPV 16 and 18 can lead to squamous cell carcinoma
- Factors associated with higher rates of infection with HPV include
- Absence of circumcision
- Multiple sexual partners
- Lack of condom use
- Smoking
- References: Partin: Campbell-Walsh Urology 12th Edition Review, 3rd Edition, 2020, Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022, Heliyon 2020;6:e03547
Clinical features
- Soft and friable papillomatous growth
- May occur singly or in moruloid clusters
- Giant condyloma acuminatum can become as large as 15 cm, destroying normal tissue and imparting a cancerous appearance
- Reference: Partin: Campbell-Walsh Urology 12th Edition Review, 3rd Edition, 2020
Diagnosis
- Detection is through thorough clinical history, physical examination and biopsy
- Subclinical disease and flat lesions, which may not be obvious on inspection, may be detected by application of 5% acetic acid solution to the penis, followed by inspection with a magnifying glass
- Lesions will turn white
- These acetowhite lesions should be confirmed by biopsy, since not all these lesions are caused by HPV
- Virus can be identified by immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization and PCR
- Reference: Partin: Campbell-Walsh Urology 12th Edition Review, 3rd Edition, 2020, Drugs Context 2018;7:212563
Prognostic factors
- Benign course with high recurrence rate
- Posttreatment recurrence is seen in 38 - 73% patients with usual benign lesions
- Spontaneous regression is common
- Malignant transformation is rare; more frequently seen in longstanding giant condylomas
- Reference: Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022, Drugs Context 2018;7:212563
Case reports
- 26 year old White man with 6 months history of papillomatous lesions on the glans penis and orificium urethrae (Open Access Maced J Med Sci 2018;6:110)
- 26 year old Lebanese man with hypopigmented lesions on the penis (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2016;82:572)
- 29 year old man with 1 month history of papillary lesions on the coronary sulcus of the penis (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e15109)
- 62 year old man with 6 year history of warty lesions on the genital areas (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:117)
- 62 year old man with urinary obstruction (Am J Case Rep 2018;19:1522)
Treatment
- Commonly used treatment modalities include
- Podophyllotoxin 0.5% solution or gel (used historically)
- Trichloroacetic acid 35 - 85%
- Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen
- Electrofulguration
- CO2 laser therapy
- Imiquimod cream (5%) - topical treatment of choice
- Surgical approaches include electrofulguration, cryosurgery, laser ablation for smaller lesions, local excision for medium sized lesions and wide local excision or penectomy for giant condylomas
- Significant rates of recurrence have been noted despite using laser, electrocautery or cryotherapy treatment options
- References: Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022, Partin: Campbell-Walsh Urology 12th Edition Review, 3rd Edition, 2020, J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2016;9:S2, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2019;33:1006
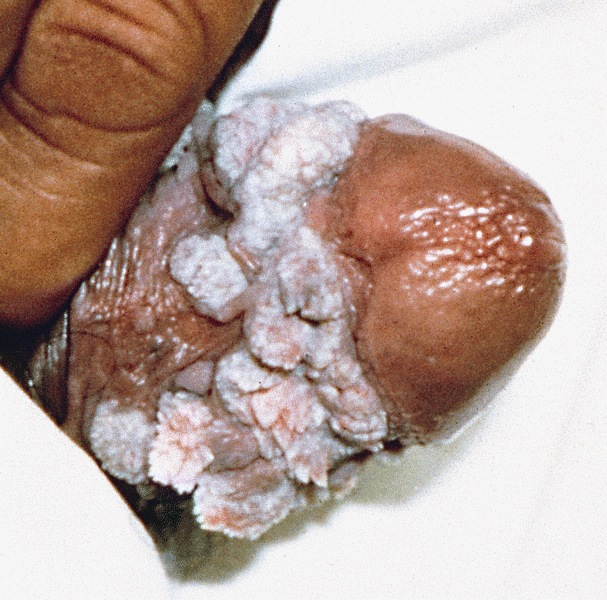
Clinical images
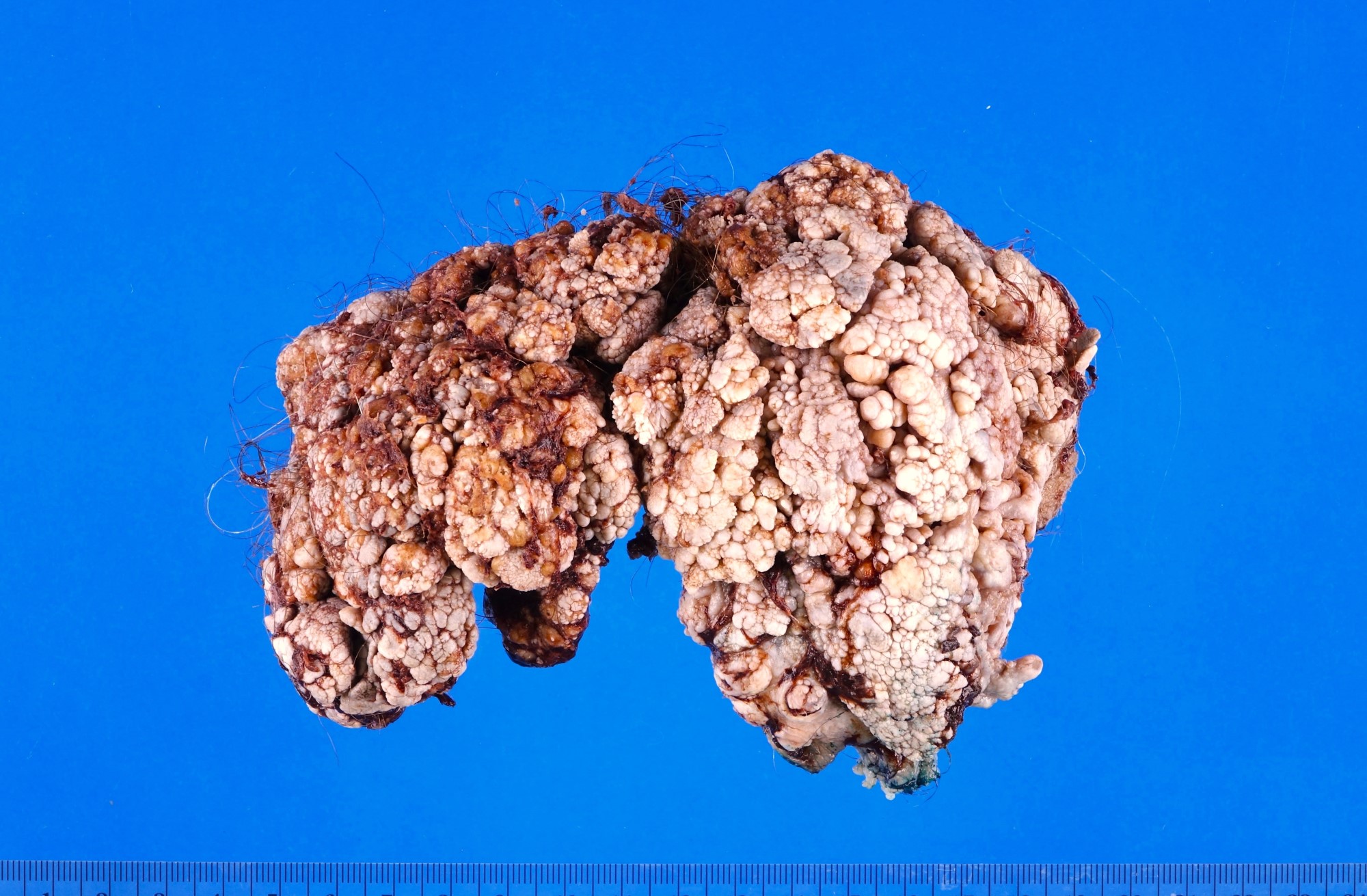
Gross description
- Soft, flesh colored lesions
- Can be flat, delicately papillary or warty and cauliflower-like
- References: Cheng: Urologic Surgical Pathology, 4th Edition, 2019, Heliyon 2020;6:e03547
Microscopic (histologic) description
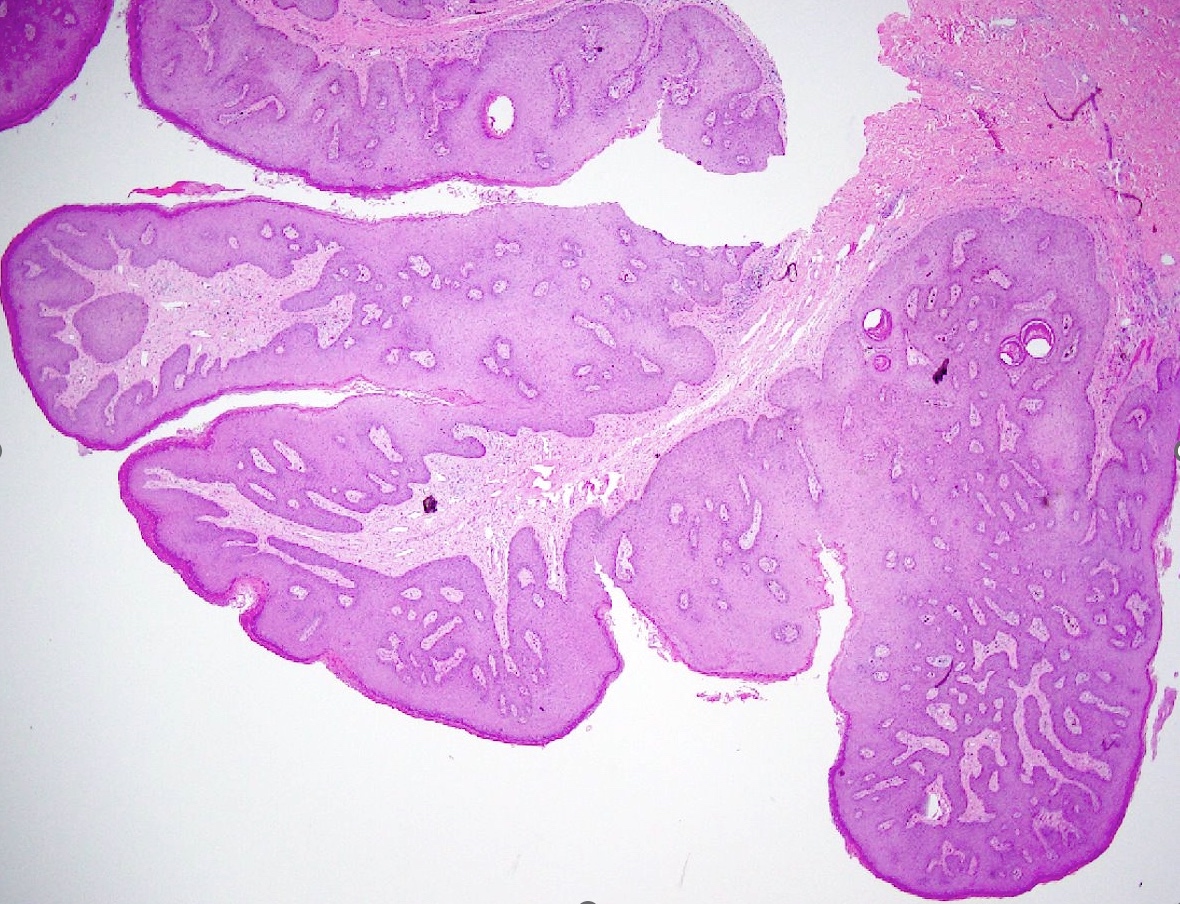
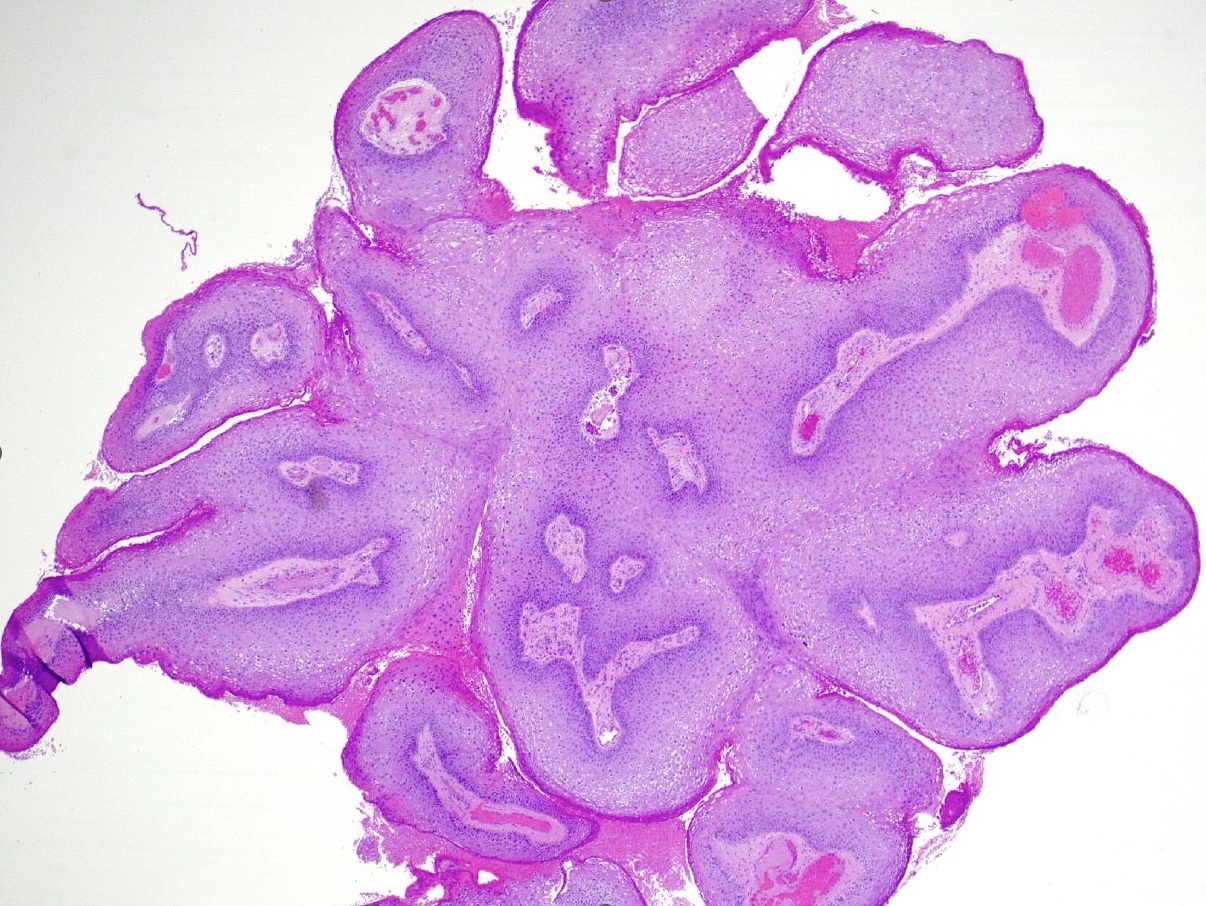
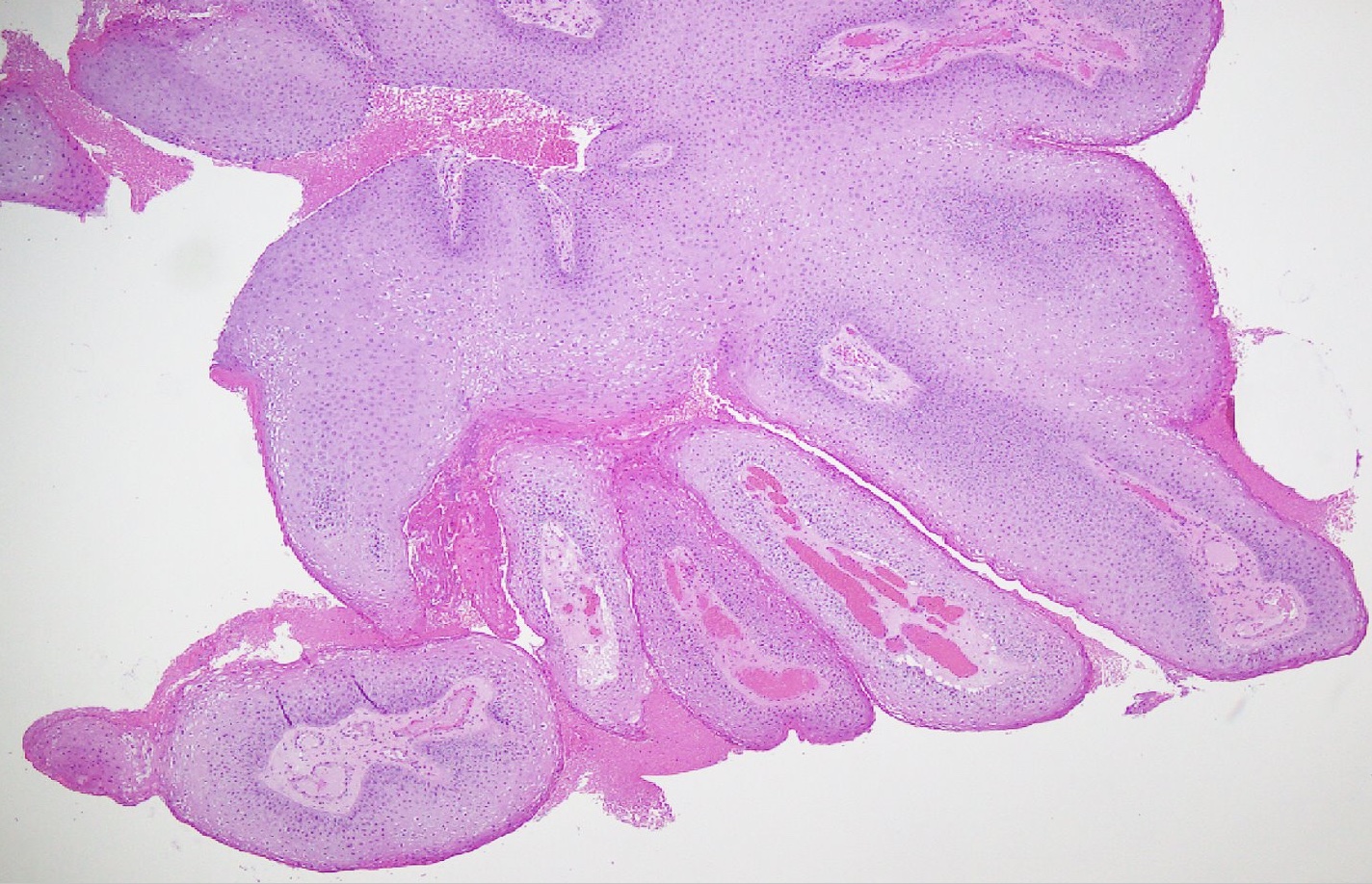
- Lesions show papillomatosis, acanthosis with a well demarcated bulbous base
- Prominent central fibrovascular cores with branching patterns
- Surface hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis are frequently seen in the papillae
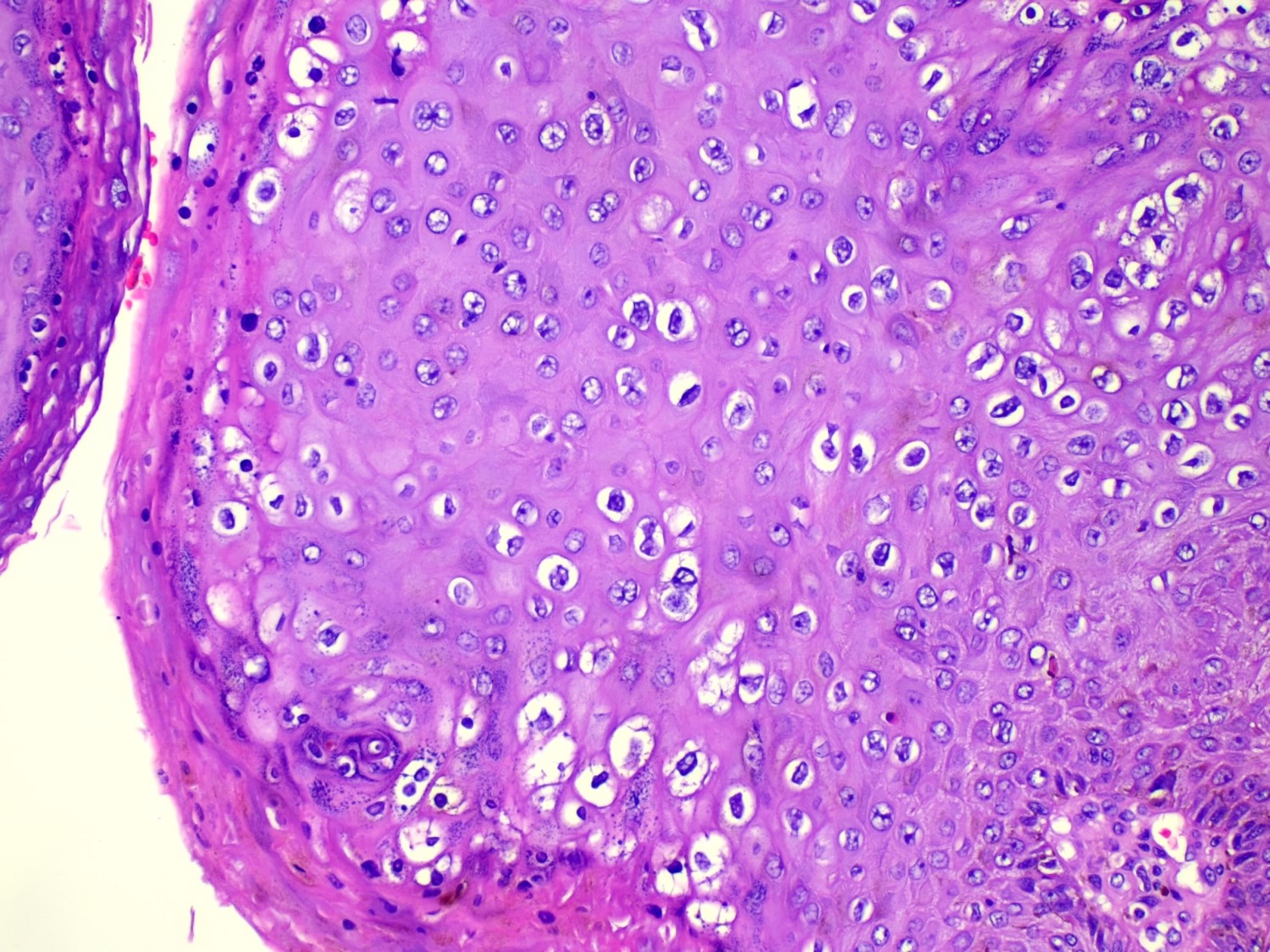
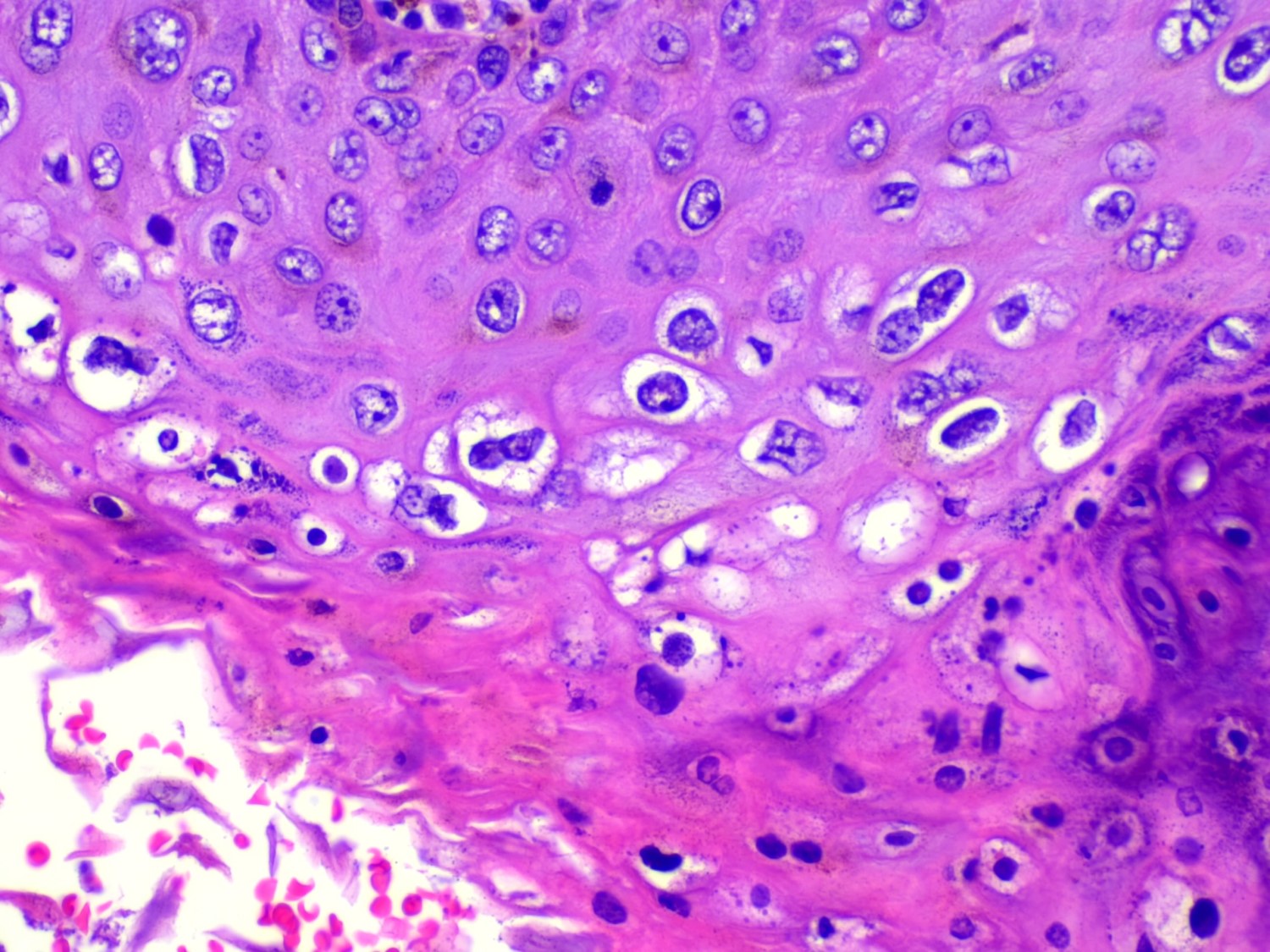
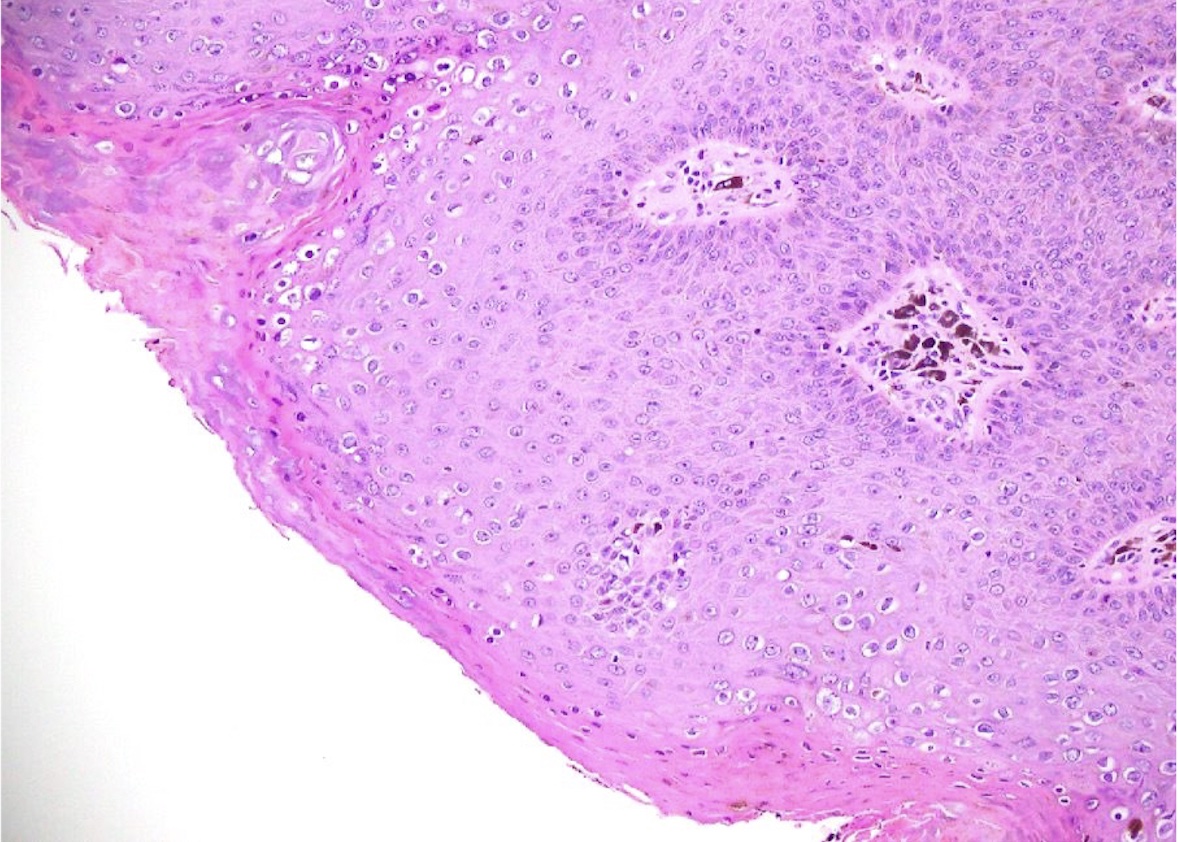
- Koilocytic atypia is the hallmark of the lesions
- Koilocytes have enlarged, wrinkled nuclei surrounded by a perinuclear halo
- Dyskeratotic cells with binucleation and multinucleated forms may be seen
- Koilocytic changes are more prominent on the upper levels of the epithelium
- Despite being the most classic and best recognized feature, koilocytes are not always prominent
- Sessile (flat) and inverted patterns are rare
- Prominent degenerative changes such as vacuolization, nuclear enlargement, numerous necrotic keratinocytes in the lower half of the epidermis and an increased number of mitotic figures are seen in condyloma acuminata that has been previously treated with topicals (e.g., podophyllum resin, also known as podophyllin)
- References: StatPearls: Condyloma Acuminata [Accessed 29 February 2024], Rom J Morphol Embryol 2021;62:369
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Immunochemistry is not routinely used, although positivity for p16 in condylomas is associated with high risk HPV (Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2021;22:3219)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HPV, which are usually low risk types, can be detected by in situ hybridization and PCR
Videos
Condyloma histopathology
Genital warts under microscope
Sample pathology report
- Penis, lesion, biopsy:
- Condyloma acuminata (see comment)
- Comment: Koilocytic cells are seen within papillomatous lesion. There is no high grade dysplasia or malignancy identified.
Differential diagnosis
- Early penile plaques:
- Hyperkeratosis
- No koilocytosis
- HPV negative
- Pearly penile papules:
- Also known as papillomatosis of glans corona
- Monomorphic yellow-white papules on the coronal sulcus and penile corona in uncircumcised men
- Thick epithelial covering over fibrovascular cores, resembling angiofibromas
- HPV negative
- References: Cheng: Urologic Surgical Pathology, 4th Edition, 2019, Rom J Morphol Embryol 2021;62:369
- Acrochordons:
- Also known as skin tags
- Soft, flesh colored, sessile or pedunculated lesions
- Occasionally may be hyperkeratotic or warty appearing (Drugs Context 2018;7:212563)
- HPV negative
- Seborrheic keratosis:
- Acanthosis, papillomatosis and occasional hyperpigmentation
- HPV negative
- Warty carcinoma (Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022):
- Papillary squamous cell carcinoma:
- Exophytic invasive squamous cell carcinoma with complex irregular papillae possessing jagged interface with the underlying stroma
- Irregular wide areas of keratinization are present between adjacent papillae
- Condylomas with malignant transformation (Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022):
- Rare event for common condylomas
- Usually associated with longstanding giant condylomas
- Malignant foci are composed of conventional squamous cell carcinoma and tend to occur at tumor base or front
- Molluscum contagiosum (Cheng: Urologic Surgical Pathology, 4th Edition, 2019, Drugs Context 2018;7:212563, Rom J Morphol Embryol 2021;62:369):
- Diagnosis is usually made clinically
- Caused by molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a pox virus
- Smooth, dome shaped, 1 - 5 mm papules with central umbilication
- Cytoplasmic inclusions (molluscum bodies) are seen in cells of the stratum malpighii and progressively enlarge as they reach the surface
- Verrucous carcinoma (Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, 3rd Edition, 2022):
- Condyloma latum (Cheng: Urologic Surgical Pathology, 4th Edition, 2019, Rom J Morphol Embryol 2021;62:369):
- Cutaneous lesion of secondary syphilis caused by Treponema pallidum
- Appear as wet, sometimes weepy plaques
- Dark field microscopy can be used to visualize spirochetes
- Prominent epithelial hyperplasia that may become pseudoepitheliomatous with ulceration and neutrophilic exocytosis
- Plasma cell infiltrate and capillary endothelial proliferation
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Condyloma acuminatum. The clinical presentation along with the microscopic findings of koilocytosis, acanthosis and hyperkeratosis are classic for condyloma acuminatum caused by HPV infection. Answer B is incorrect because condyloma latum is a cutaneous lesion of secondary syphilis caused by treponema pallidum, which would show prominent epithelial hyperplasia with plasma cell infiltrate and capillary endothelial proliferation. Answer C is incorrect because molluscum contagiosum would have molluscum bodies. Answer D is incorrect because verrucous carcinoma would show endophytic growth with a broad based pushing pattern of invasion and absent koilocytic atypia.
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma acuminatum
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma acuminatum
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
C. Smoking. Smoking is one of the risk factors associated with higher rates of infection with HPV.
Answers A, B and D are incorrect because lack of multiple sexual partners, safe sex practices (use of condoms) and circumcision decrease risk of acquiring HPV infection.
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma acuminatum
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma acuminatum
Board review style question #3
Which of the following is true regarding the pathogenesis of condyloma acuminatum?
- E6 and E7 viral gene activation causes inactivation of p53 and retinoblastoma tumor suppressor genes
- Viral effects on the epithelium causes condyloma's endophytic phenotype
- Virus does not integrate into host cells
- Virus remains confined to the basal cell layer
Board review style answer #3
A. E6 and E7 viral gene activation causes inactivation of p53 and retinoblastoma tumor suppressor genes.
Answer B is incorrect because viral effects on the epithelium cause exophytic growth. Answer C is incorrect because viral integration into host cells does occur, causing koilocyte formation. Answer D is incorrect because although the viral replication happens in the basal layer, the infected basal layer cells migrate to adjacent layers causing amplification and the assembly of the virions takes place in the superficial layer of the epithelium.
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma acuminatum
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma acuminatum