Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Norgan AP, Roberts DJ. Acute chorioamnionitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentachorioamnionitis.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acute chorioamnionitis is defined by the presence of acute inflammation (neutrophils) within the chorion or amnion (or both) of the extraplacental membranes or chorionic plate (maternal inflammatory response [MIR]), with or without acute inflammatory cell extravasation from the umbilical cord vasculature or chorionic plate vessels (fetal inflammatory response [FIR])
Essential features
- Acute chorioamnionitis is due to a maternal (with or without accompanying fetal) inflammatory response
- Fetal inflammatory response (inflammatory cell extravasation from umbilical or chorionic plate vessels) is associated with longer term and more severe infections
- Commonly associated with ascending bacterial or fungal cervicovaginal flora infecting the amniotic fluid
- Uncommonly associated with hematogenously disseminated bacteria (e.g., Listeria)
- Associated with risk of neonatal sepsis and poor neonatal outcomes especially when there is a fetal inflammatory response
Terminology
- Histologic chorioamnionitis
- Necrotizing chorioamnionitis
- Chorionitis
- Subchorionitis
- Umbilical vein vasculitis
- Umbilical artery vasculitis
- Fetal vasculitis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- More common in younger, nulliparous women
- Risk factors include:
- Longer duration rupture of membranes (Clin Infect Dis 1993;17:S100)
- Extended length of labor (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1024)
- Number of intrapartum digital vaginal examinations (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1024)
- Use of indwelling devices around labor (intracervical balloon catheter, fetal monitors) (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:304)
- Cervical insufficiency (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:746)
- Bacterial vaginosis (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:672)
- Group B Streptococcus colonization (J Infect Dis 1983;148:802)
- Meconium stained amniotic fluid (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:746)
- Pregnancy with a foreign body in situ (e.g., cerclage, IUD) (J Perinat Med 2010;38:45)
Sites
- Extraplacental membranes: chorion or amnion (MIR)
- Umbilical cord: vein or arteries (FIR)
- Chorionic plate: chorion or amnion (MIR) and vessels (FIR)
Pathophysiology
- Amniotic fluid infection by ascending cervicovaginal flora (common) or hematogenously or postprocedurally infecting organisms (uncommon) causes activation of material and fetal inflammatory responses
- In the maternal inflammatory response, maternal neutrophils migrate from the decidual circulation into the extraplacental decidua, chorion and amnion, or the intervillous circulation into the chorionic plate and overlying amnion
- In the fetal inflammatory response, fetal neutrophils extravasate from fetal vessels in the umbilical cord or chorionic plate and migrate toward the amniotic fluid (amniotropic)
- Release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators can lead to rupture of membrane or onset of labor
- Reference: Pediatr Res 2022;91:289
Etiology
- Amniotic fluid infection is typically polymicrobial, often involving 2 or more organisms from vaginal or enteric flora; single pathogens may be seen in hematogenously disseminated infections or when 1 organism in a polymicrobial infection outcompetes the others
- Organisms that are commonly isolated from amniotic fluid infections include (J Infect Dis 1988;157:113):
- Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis (Clin Infect Dis 1993;17:S100)
- Gram negative anaerobic vaginal flora (e.g., Bacteroides spp., Gardnerella sp.)
- Group B Streptococcus
- Peptostreptococcus spp.
- Escherichia coli
- Enterococci
- Fusobacterium spp.
Clinical features
- Can be clinically silent
- Maternal fever > 37.5 °C, uterine tenderness, abdominal pain, foul smelling vaginal discharge, maternal and fetal tachycardia (BJOG 2017;124:775, J Perinat Med 2016;44:5, J Perinat Med 2016;44:23)
- Associated with fetal infection, neonatal sepsis, stillbirth, spontaneous preterm birth and fetal central nervous system injury (Semin Perinatol 2015;39:2)
- Fetal inflammatory response associated with multiorgan injury, including chronic lung disease, periventricular leukomalacia and cerebral palsy (Front Immunol 2020;11:531543, Clin Perinatol 2010;37:339, Am J Obstet Gynecol 2020;223:745.e1, Am J Reprod Immunol 2018;79:e12803)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis (Obstet Gynecol 2016;127:426, J Perinat Med 2016;44:23):
- Clinical chorioamnionitis (or intrauterine inflammation or infection) is diagnosed by a combination of physical examination findings and laboratory results
- Isolated maternal fever:
- Clinically documented fever ≥ 39.0 °C once or ≥ 38.0 °C (oral) twice
- Suspected intrauterine inflammation or infection:
- Fever (as above), plus 1 or more of the following:
- Fetal tachycardia (greater than 160 beats per minute for 10 minutes or longer)
- Elevated maternal white blood count (> 15,000 per mm3; in the absence of corticosteroids)
- Purulent fluid from the cervical os
- Fever (as above), plus 1 or more of the following:
- Confirmed intrauterine inflammation or infection:
- Suspected intrauterine inflammation or infection findings, plus:
- Positive amniotic fluid Gram stain or culture
- Low amniotic fluid glucose (e.g., ≤ 14 mg/dL)
- Elevated amniotic fluid white cell count (> 30 cells/mm3; in the absence of red blood cells indicating blood contamination)
- Histopathologic evidence of acute chorioamnionitis
- Suspected intrauterine inflammation or infection findings, plus:
Laboratory
- Positive:
- Amniotic fluid Gram stain
- Amniotic fluid culture
- Placental tissue culture
- Fetal tissue culture (e.g., lung tissue) in cases of fetal demise
- Placental tissue (fresh or FFPE) molecular testing (e.g., PCR)
- Neonatal blood cultures within day 1 of life
Prognostic factors
- Unfavorable factors:
- Necrotizing chorioamnionitis
- Fetal inflammatory response
- References: Front Immunol 2020;11:531543, Am J Reprod Immunol 2018;79:e12803, Neurotoxicology 2017;61:47
Case reports
- 25 and 34 year old women with chorioamnionitis with placental listeriosis (Obstet Gynecol Sci 2018;61:688)
- 26 year old woman chorioamnionitis caused by S. marcescens (Open Med (Wars) 2020;16:81)
- 31 year old woman with necrotizing chorioamnionitis due to Kingella kingae (Diagnostics (Basel) 2021;11:243)
- 36 year old woman with Klebsiella pneumoniae chorioamnionitis (Microorganisms 2021;9:96)
- 41 year old woman with Candida chorioamnionitis (Case Rep Womens Health 2020;27:e00239)
Treatment
- Maternal and neonatal antibiotic therapy (Clin Microbiol Infect 2011;17:1304, Pediatrics 2016;137:e20152323)
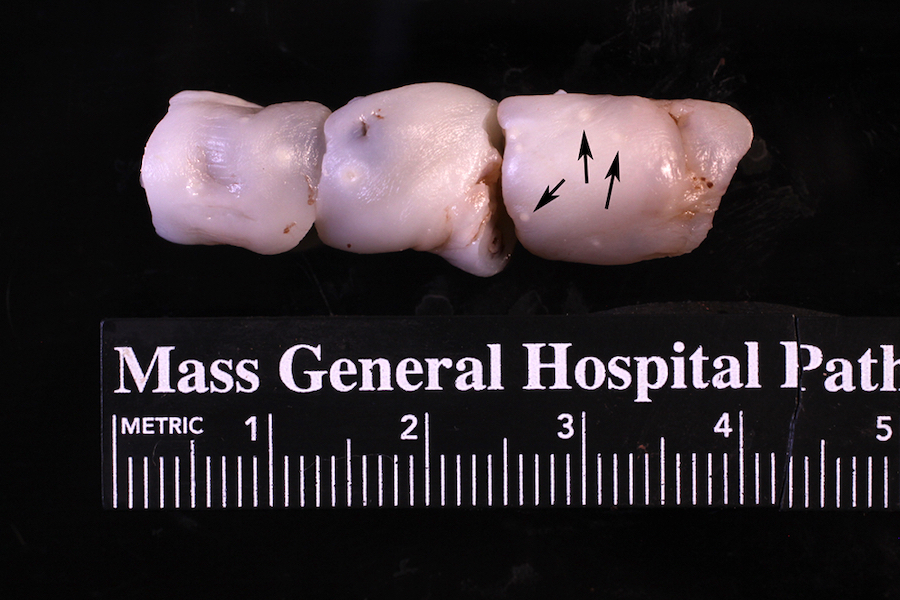
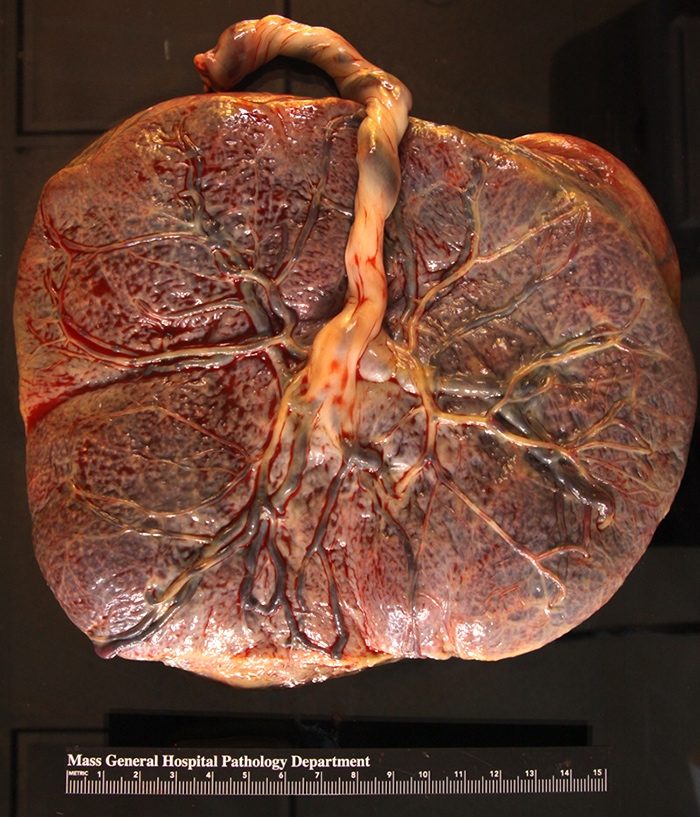
Gross description
- Dull, opaque membranes with yellow-green discoloration and cloudy amniotic fluid, possibly with purulent exudate
- Can be grossly normal
- Acute marginal hemorrhage in preterm deliveries (ISRN Obstet Gynecol 2012;2012:856971)
- Multifocal umbilical cord surface microabscesses in C. albicans infections (APMIS 2018;126:570)
Gross images
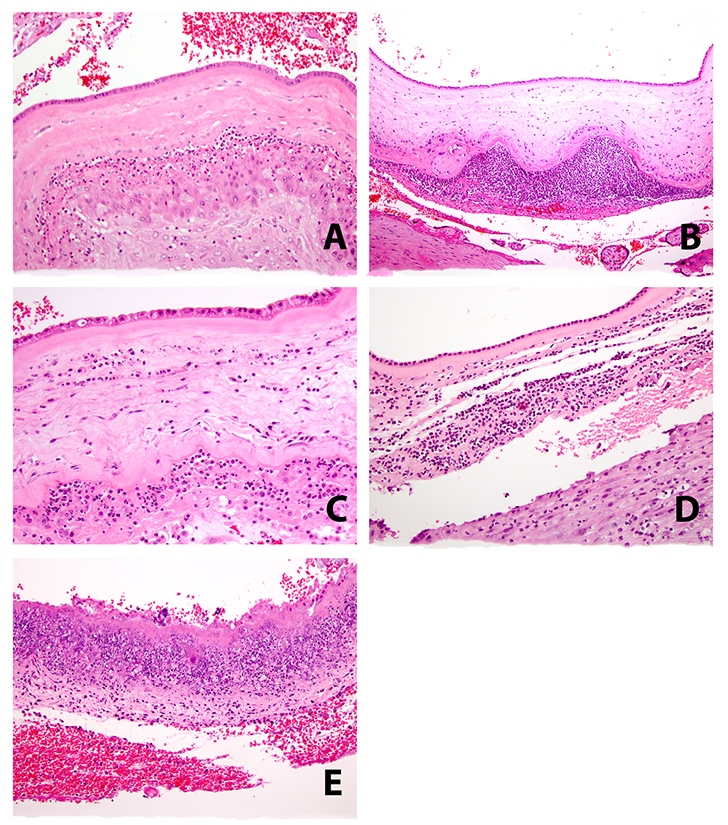
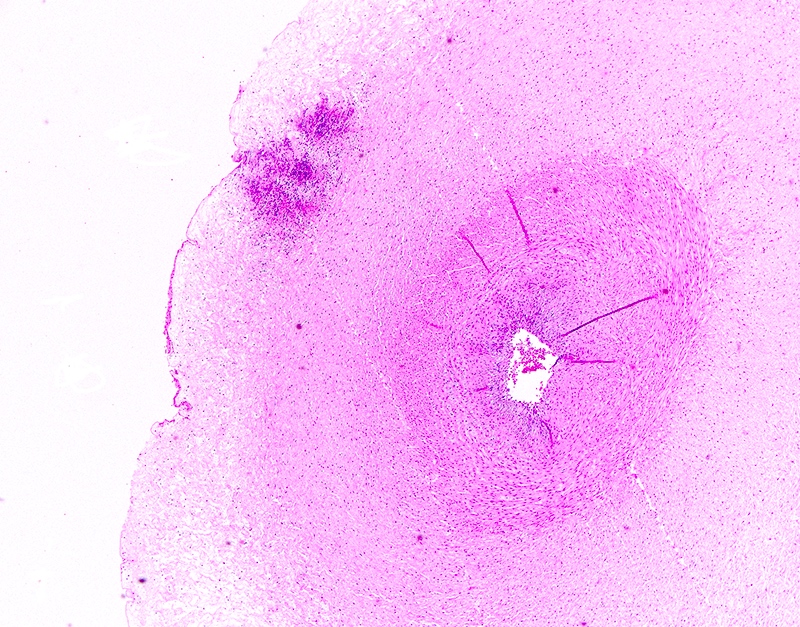
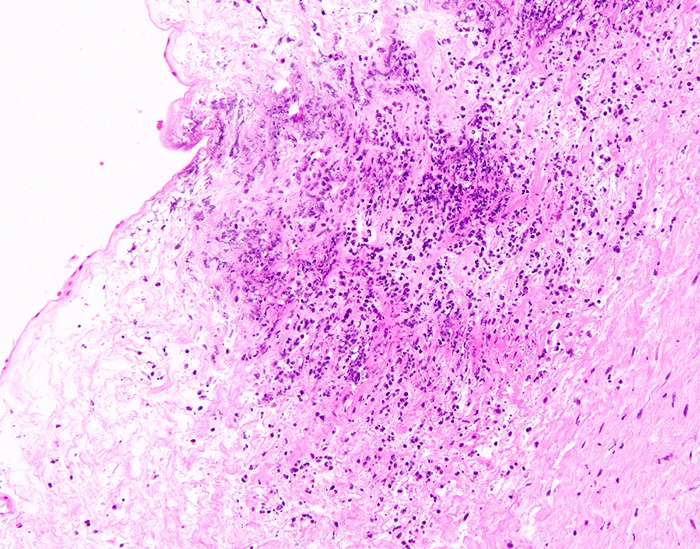
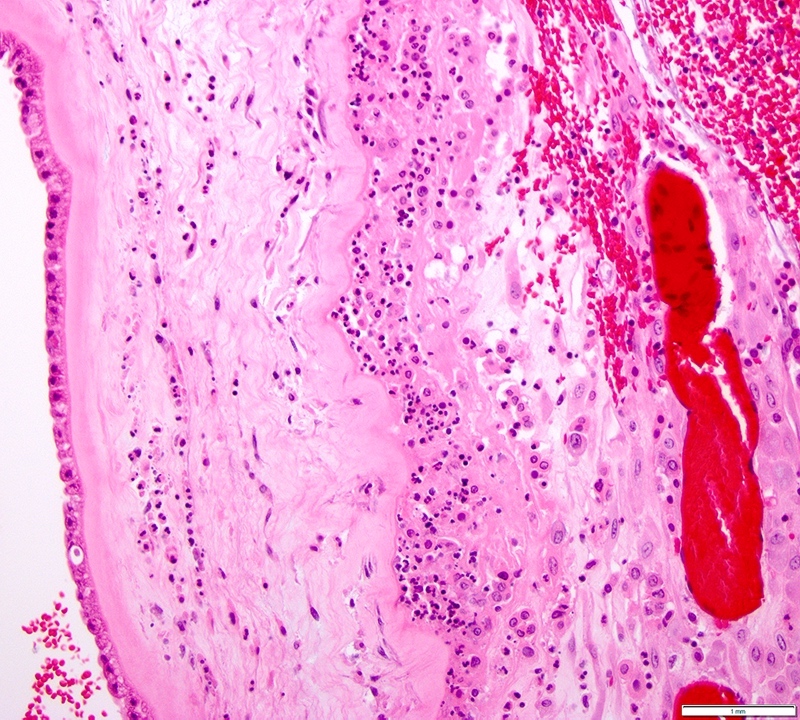
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Acute chorioamnionitis should be staged and graded based on MIR and FIR (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:698, Roberts: Atlas of Placental Pathology, 2021)
- MIR stage (location):
- Stage 0 (preacute chorioamnionitis): neutrophils in the subchorial intervillous space beneath the chorionic plate (subchorionitis)
- Stage 1 (early): neutrophils in chorion laeve of the extraplacental membranes (chorionitis)
- Stage 2 (intermediate): neutrophils within chorionic or amnionic mesoderm
- Stage 3 (advanced): stage 2, plus necrosis of amnionic epithelium or neutrophil necrosis
- MIR grade (severity):
- Grade 1 (mild to moderate): anything less than severe, as described below
- Grade 2 (severe): confluent neutrophils or > 3 foci of > 200 neutrophils
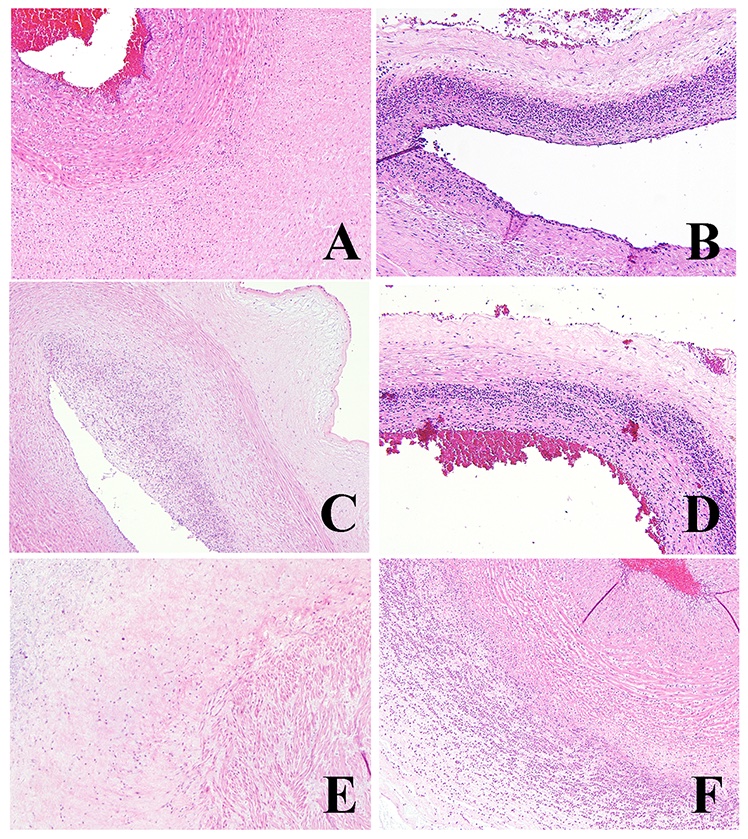
- FIR stage:
- Stage 1 (early): fetal inflammatory cells within chorionic plate vessel walls (fetal vasculitis) or umbilical vein vessel wall (umbilical vein vasculitis)
- Stage 2 (intermediate): fetal inflammatory cells within umbilical arteries (umbilical artery vasculitis) or vein
- Stage 3 (advanced): necrotizing funisitis (perivascular bands of necrotic Wharton jelly containing dense neutrophils)
- FIR grade:
- Grade 1 (mild to moderate): anything less than severe, as described below
- Grade 2 (severe): confluent fetal inflammatory cells with attenuation / degeneration of smooth muscle
- Accompanying findings:
- Acute intervillositis: aggregates of neutrophils in the intervillous space; often due to Listeria monocytogenes
- Peripheral funisitis: wedge-like foci of neutrophils with necrosis at the periphery of the umbilical cord; often due to Candida
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Sample pathology report
- Singleton placenta, delivery:
- Acute chorioamnionitis (maternal stage X; grade X) with fetal vascular involvement (fetal stage X; grade X)
Differential diagnosis
- Chronic chorioamnionitis:
- Mononuclear infiltrate in the chorion laeve or chorion and amnion
- Often associated with villitis of unknown etiology
- Thought to be a host versus graft-like reaction
- Has a recurrence risk
- Meconium histiocytic infiltrate:
- Meconium pigment within histiocytes in the membranes
- Often accompanies acute chorioamnionitis
- Acute inflammation in the space between the amnion and chorion:
- Inflammation is not within the soft tissue or epithelium but in the space between the 2 membranes
- Often associated with vernix caseosa or loose meconium
- Not true acute chorioamnionitis unless the inflammatory cells are within tissue
- Acute deciduitis:
- Acute inflammation retained only within the decidua capsularis or parietalis, not in the chorion laeve epithelium
- Feature of labor, not infection
Board review style question #1
A yellow / green discolored and cloudy placenta shows which of the following histologies of the membranes and umbilical cord?
- Stage 0 grade 1 acute chorioamnionitis, maternal inflammatory response with a fetal inflammatory response stage 1 grade 1
- Stage 1 grade 1 acute chorioamnionitis, maternal inflammatory response with a fetal inflammatory response stage 2 grade 1
- Stage 2 grade 2 acute chorioamnionitis, maternal inflammatory response with a fetal inflammatory response stage 2 grade 1
- Stage 3 grade 2 acute chorioamnionitis, maternal inflammatory response with a fetal inflammatory response stage 2 grade 2
Board review style answer #1
C. Stage 2 grade 2 acute chorioamnionitis, maternal inflammatory response with a fetal inflammatory response stage 2 grade 1
Comment here
Reference: Acute chorioamnionitis
Comment here
Reference: Acute chorioamnionitis
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2