Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) descriptionCite this page: Kowalski PJ. Furcate insertion. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentafurcate.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
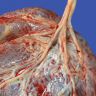
- Grossly visible branching of the umbilical vessels before their insertion onto the placental surface
Terminology
- May be associated with cord insertions at the disk margin (marginal insertion) or insertions in the membranes (velamentous insertion)
Pathophysiology
- Protective substance, known as Wharton jelly, which covers the umbilical cord is lost at the cord's insertion end
- Cord displays less tubular integrity and the umbilical vessels divide or branch before reaching the placental surface
- Umbilical vessels unsupported by Wharton jelly are more subject to shearing forces potentially causing rupture or hemorrhage
Etiology
- There are no known causative factors
Clinical features
- Usually, no clinical significance is associated with furcate insertion
- Very rarely, fetal hemorrhage has been described
Radiology description
- Furcate insertion can be detected on an ultrasound scan
Prognostic factors
- Generally very good, unless the rare situation of hemorrhage from the unprotected portions of vessel occur
Case reports
- Furcate insertion resulting in late third trimester bleeding and fetal death (Int J Legal Med 2009;123:509)
- 2 patients with furcate insertion diagnosed prenatally (J Reprod Med 2015;60:365)
Gross description
- Umbilical vessels are seen to divide before reaching the placental surface, usually only involving the distal most 1 - 4 cm of the cord
- Hemorrhage surrounding the vessels may very rarely indicate vascular rupture
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Usually no significant microscopic changes are observed