Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Talwar A, Jalaly JB. Cystadenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandscystadenoma.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare neoplasm of salivary glands (1 - 4% of all salivary gland neoplasms)
- Papillary and cystic-like architecture
Essential features
- Unilocular or multicystic lesion
- Cyst is frequently lined by papillary projections
- Frequently oncocytic cells but minimal or absent lymphoid tissue
- No atypia, mitoses or invasion (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:354, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:53)
Terminology
- Not recommended: Lymphocyte poor Warthin tumors, monomorphic adenoma, cystic duct adenoma, intraductal papillary hyperplasia
- Subtypes: oncocytic cystadenoma, oncocytic cystadenoma, mucinous cystadenoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- F > M
- Fifth to seventh decades
Sites
- 45% in the parotid; clinically indistinguishable from other primary benign cystic salivary gland lesions
- Minor salivary gland neoplasms mimic mucocele; lip and buccal mucosa most common sites among minor salivary glands
Pathophysiology
- No clear pathogenesis
Clinical features
- In major salivary glands: usually a painless slow growing mass or lump
- In minor salivary glands: usually painless and compressible, mimicking mucocele
- Slightly higher incidence in women (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:354, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:53)
Diagnosis
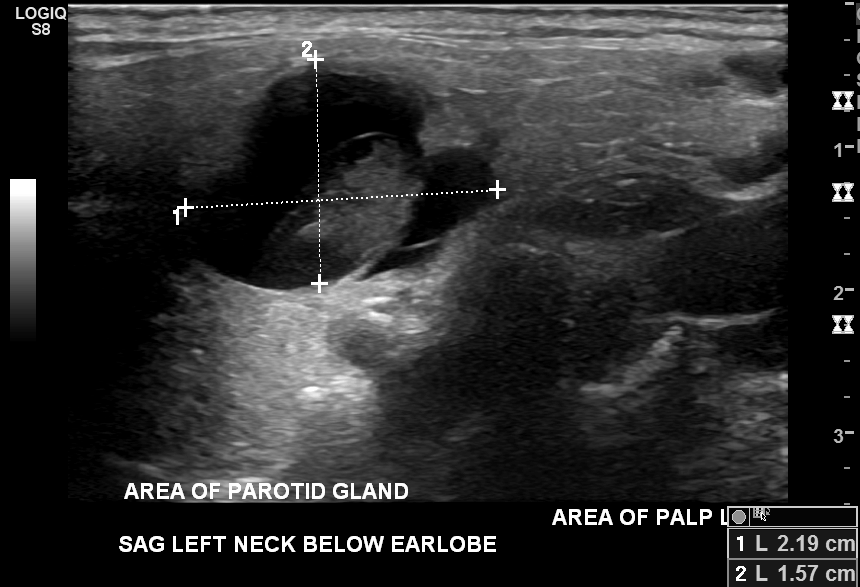
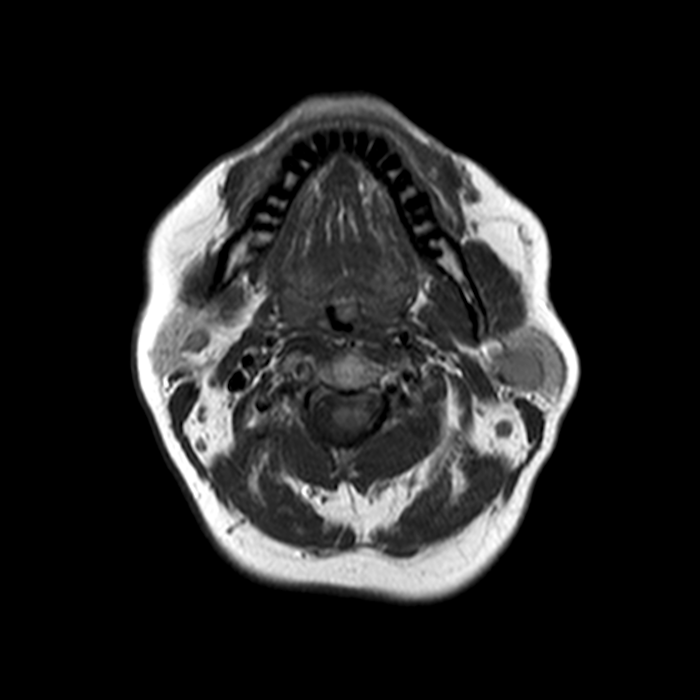
- Cystic or solid well circumscribed masses on ultrasound, CT or MRI
- May appear solid due to internal hemorrhage or infection
- No other typical imaging patterns
Laboratory
- No distinct serologic testing available
Radiology description
- Well circumscribed mass with a clear capsule
- Cystic or solid without internal flow
- Capsule may show contrast enhancement if infected (Cancer Imaging 2007;7:52)
Prognostic factors
- Simple excision of the lesion is curative
Case reports
- 19 year old man with asymptomatic swelling of roof of mouth (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2008;105:e28)
- 40 year old woman with swelling below right ear (J Clin Diagn Res 2016;10:ED01)
- 52 year old man, a smoker with 2 lesions of the right parotid gland (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2019;60:993)
- 58 year old woman with tumor of the right temporomandibular joint (World J Clin Cases 2019;7:366)
- 63 year old man with nodule on right side of tongue (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa269)
Treatment
- Simple excision is curative; recurrence is rare
Gross description
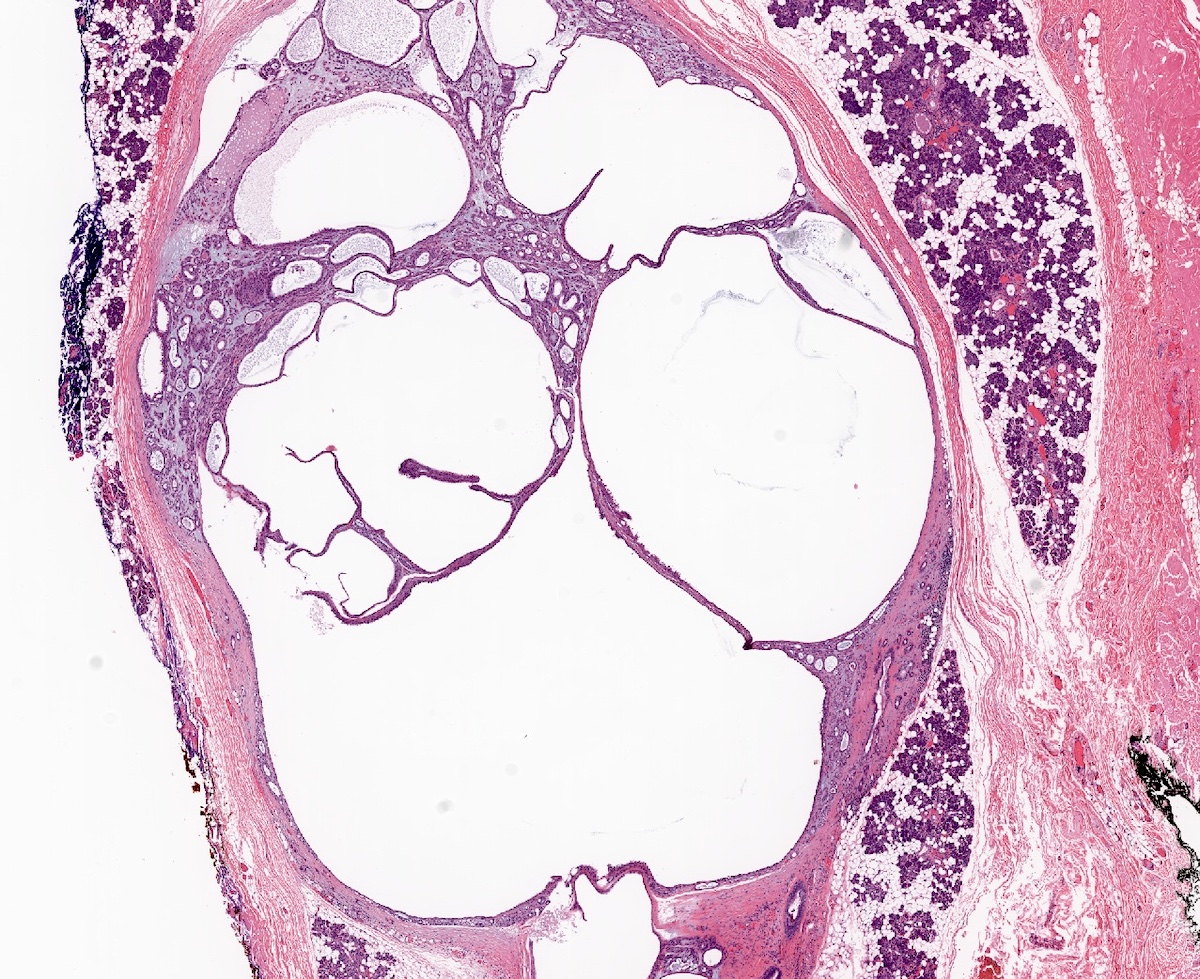
- Uni or multicystic spaces within salivary gland tissue, well circumscribed
Frozen section description
- Cyst wall with simple lining of glandular cells, oncocytic cells or squamous cells
- Papillae lack lymphoid infiltrate seen in Warthin tumor
- Should not see infiltration, atypia or mitoses
- Mucinous or intermediate cells should bring up the differential of mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Oncocytic variant may be confused with macrocystic secretory carcinoma (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:354, Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Journal 2017;8:28, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:53)
Frozen section images
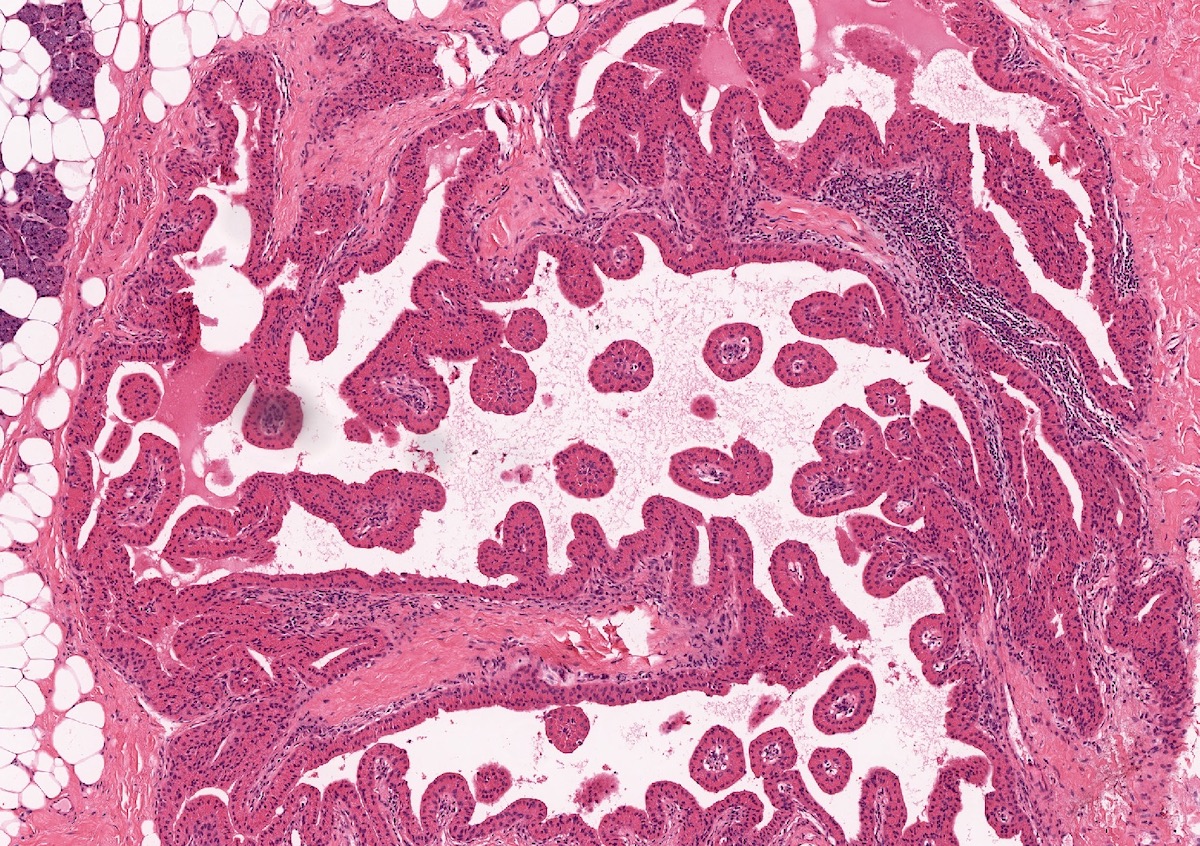
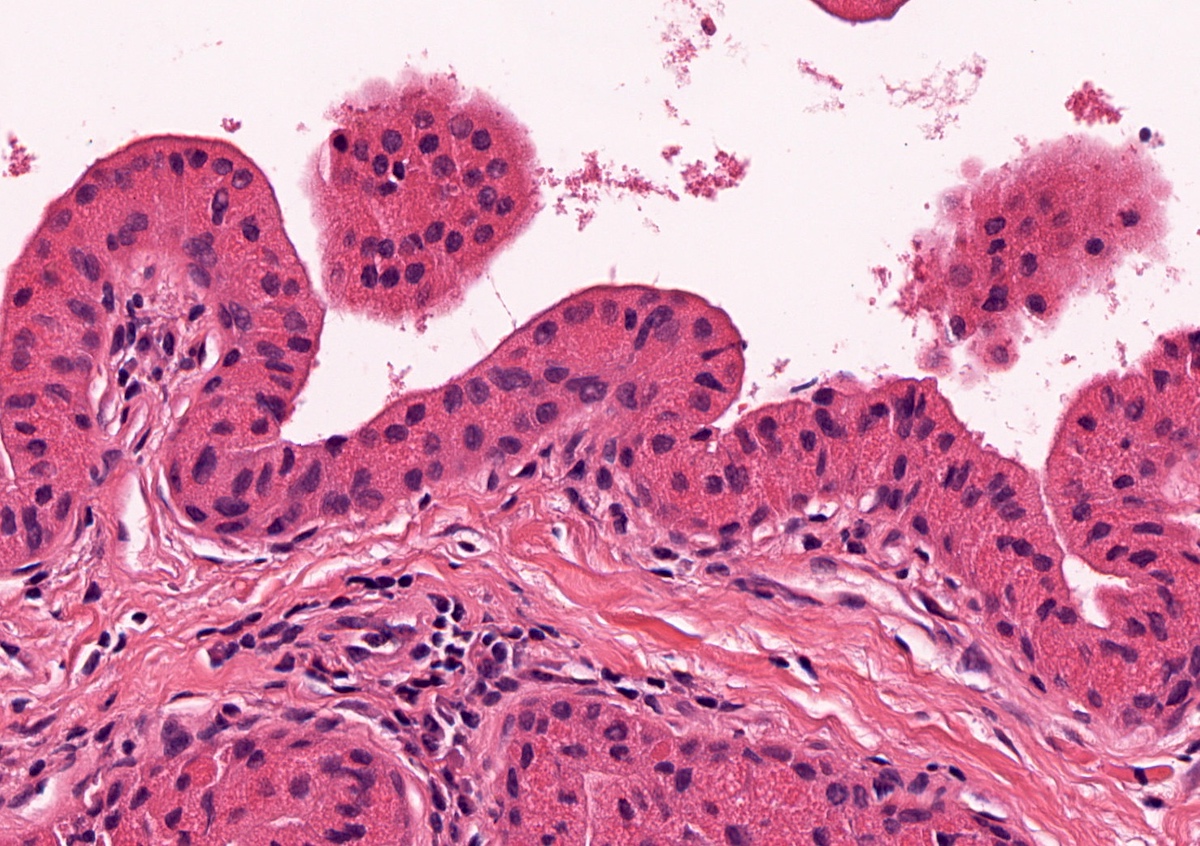
Microscopic (histologic) description
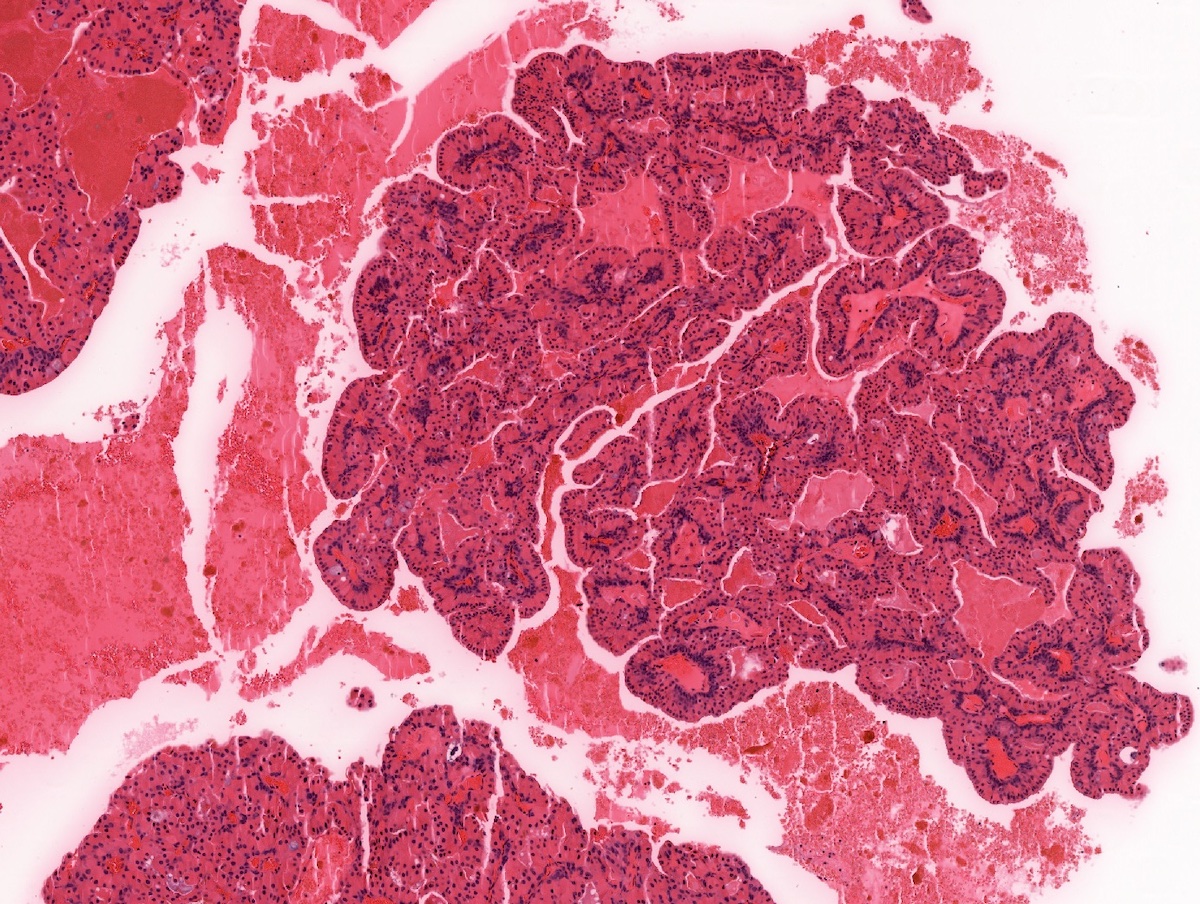
- Uni or multiloculated cystic lesion (multiloculated growth is more common)
- Well circumscribed, with peripheral entrapment of benign salivary gland tissue
- Simple papillary architecture, should not have complex architecture, mitoses or atypia
- Lining epithelial cells are commonly a mixture of columnar, cuboidal and oncocytic cells
- May also see mucinous, squamous and rarely ciliated cells
- Mucinous cystadenoma is rare; lacks architectural and nuclear atypia
- Consider unicystic mucoepidermoid carcinoma in the differential diagnosis
- Prominent multiloculated / multicystic growth pattern gives a low power appearance of more lumens than epithelial cells
- Simple papillary projections and true papillae are common; however, complex papillary tufting should alert the pathologist to other differential diagnoses (e.g. intraductal carcinoma)
- Immunohistochemical stains are useful to rule out macrocystic secretory carcinoma and intercalated type intraductal carcinoma (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:354, Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Journal 2017;8:28, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:53)
Microscopic (histologic) images
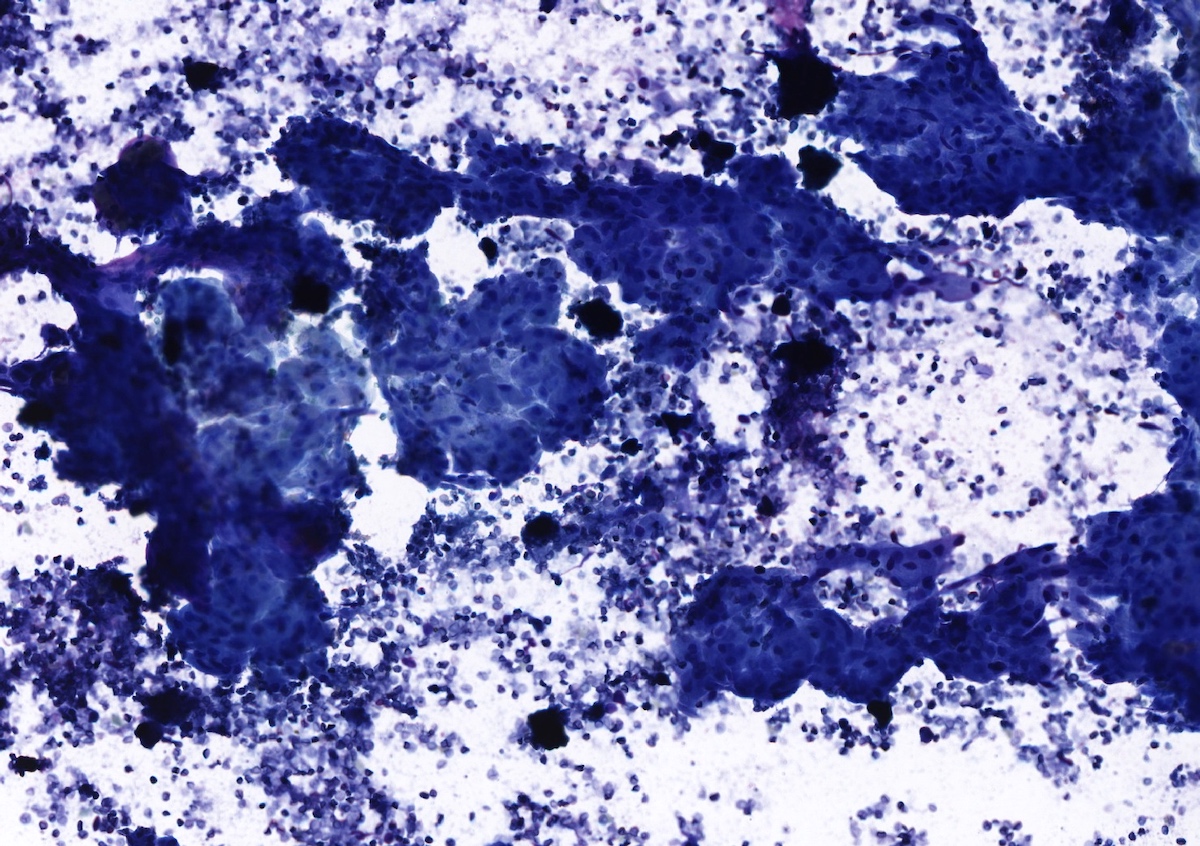
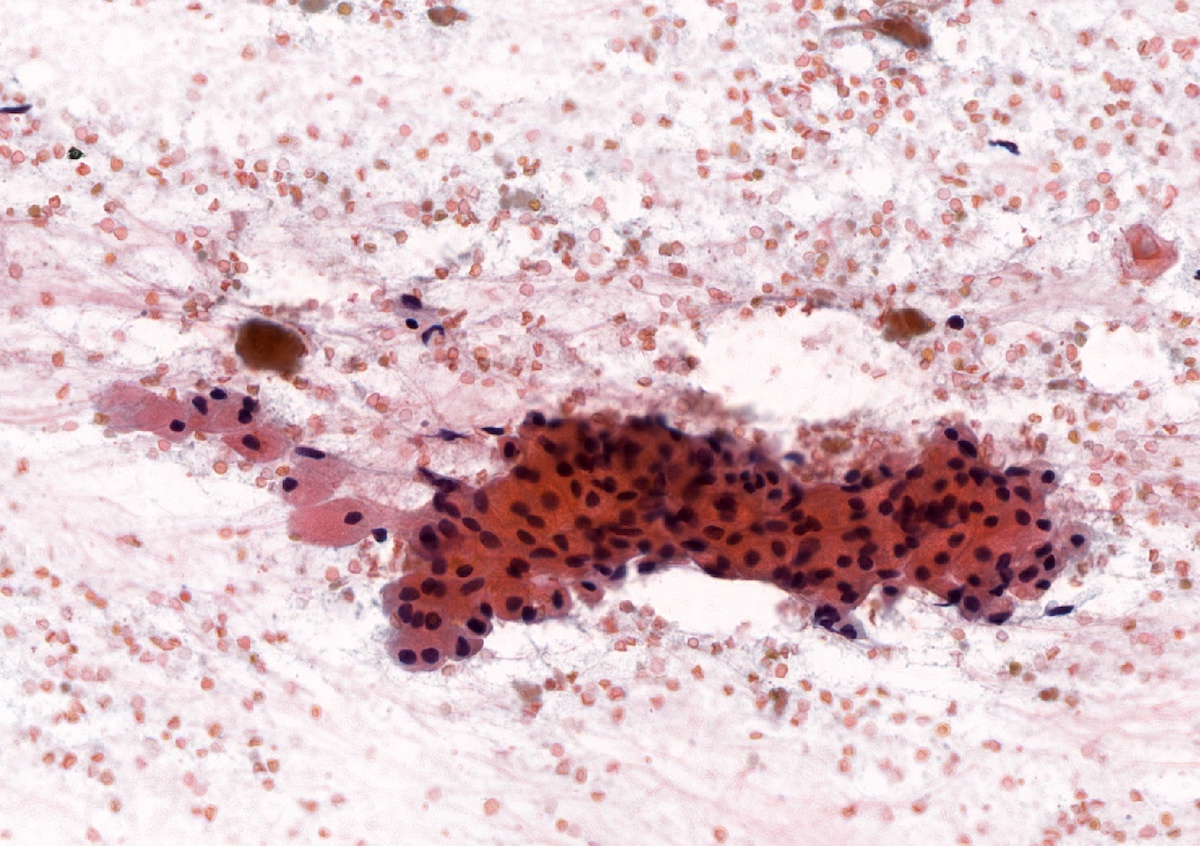
Cytology description
- Cohesive groups of epithelial cells
- Oncocytic variants will have ample granular cytoplasm, well defined cell borders and central nuclei
- May see squamous differentiation as well
- Squamous or mucinous differentiation should bring a low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma in the differential diagnosis (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2008;105:e28)
Cytology images
Negative stains
- S100, SOX10 (negative or patchy in basal cells)
- Mammaglobin
- GATA3
Sample pathology report
- Parotid gland, right, superficial parotidectomy:
- Cystadenoma, 1.3 cm, not present at inked margin
- Background salivary gland tissue with no specific pathologic change
Differential diagnosis
- Ductal ectasia:
- Ductal dilation, due to obstruction or stones
- May see squamous metaplasia
- May also see duct wall fibrosis, hyalinization and inflammatory infiltrate
- Cystic oncocytic mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Nuclear atypia, infiltrative border and 3 cell types of MEC (mucous cells, epidermoid cells and intermediate cells)
- Warthin tumor:
- Bilayer of oncocytic cells and prominent inflammatory infiltrate in papillary cores
- Cystic oncocytic myoepithelioma:
- Myoepithelial in origin, usually no papillary architecture
- Macrocystic secretory carcinoma:
- Characteristic ETV6-NTRK3 translocation
- Eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm
- CK7, GATA3, mammaglobin, SOX10 and S100 positive
- Low grade apocrine intraductal carcinoma:
- Resembles apocrine intraductal carcinoma of the breast with monotonous population of neoplastic cells usually filling the duct space with large nuclei and prominent nucleoli
- May have cribriform, micropapillary or solid growth pattern
- Intraductal papilloma:
- Resembles intraductal papilloma of breast with arborizing fibrovascular cores lined by ductal epithelial cells
- Salivary duct cyst / oncocytic salivary duct cyst:
- Due to obstruction, most common sites are labial and buccal mucosa
- May represent a true developmental cyst, rather than secondary cyst formation due to obstruction
- Intercalated duct type intraductal carcinoma:
- Prominent complex or arborizing papillae and tufting
- Mucocele:
- Reactive extravasation of mucin lined by compressed granulation tissue containing muciphages and inflammatory cells
- Not a true cyst with epithelial lining, although adjacent ductal epithelium may be seen
- Most commonly found in the lower labial mucosa / buccal mucosa
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. MAML2 is positive in up to 80% of low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Mucinous metaplasia may occur in cystadenoma. Typically, these cases will lack intermediate cells and infiltrative edges seen in cases of mucoepidermoid carcinoma. However, for equivocal cases, a negative MAML2 FISH analysis can provide additional support to exclude malignancy.
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
A. A panel type approach is often beneficial in salivary gland tumors. GATA3 is a nuclear stain that is positive in many malignancies, particularly breast and urothelial carcinomas. In the salivary gland, GATA3 stains secretory carcinoma, salivary duct carcinoma and other types of salivary gland neoplasms (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:311). The addition of S100+, SOX10+ and MUC4+, in addition to mammaglobin+ weighs against cystadenoma and with the correct morphology, supports macrocystic secretory carcinoma. Nuclear stains are generally easier to interpret than cytoplasmic stains, like mammaglobin, due to high background staining. S100 stains most salivary gland neoplasms including secretory carcinoma and is not specific for it. KIT is seen in adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma