Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Roy SF, McNiff JM. Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticmultinucleatecellangio.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Uncommon cutaneous lesion
- Vascular and fibrohistiocytic lineage are hypothesized
- Characterized by odd multinucleated fibroblasts, superficial fibrosis and thickening of superficial papillary dermal vessels
Essential features
- Presence of odd multinucleated fibroblasts
- Presence of superficial parallel fibrosis
- Presence and thickening of superficial papillary dermal vessels
- Absence of perifollicular fibrosis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- M = F according to the largest series with histopathological review (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- But F > M according to prior literature review (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:222)
- Mean age 56 years for both sexes (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- 2 cases associated with chronic hepatitis B and C (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563, J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:678)
- Certain authors postulate that MCAH-like changes can exist, although not as a distinct solitary papule clinically and more as a focal histologic finding aside or within another dermatologic process (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:415)
- Generalized form may be associated with systemic disease or abnormal immune states (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:125)
Sites
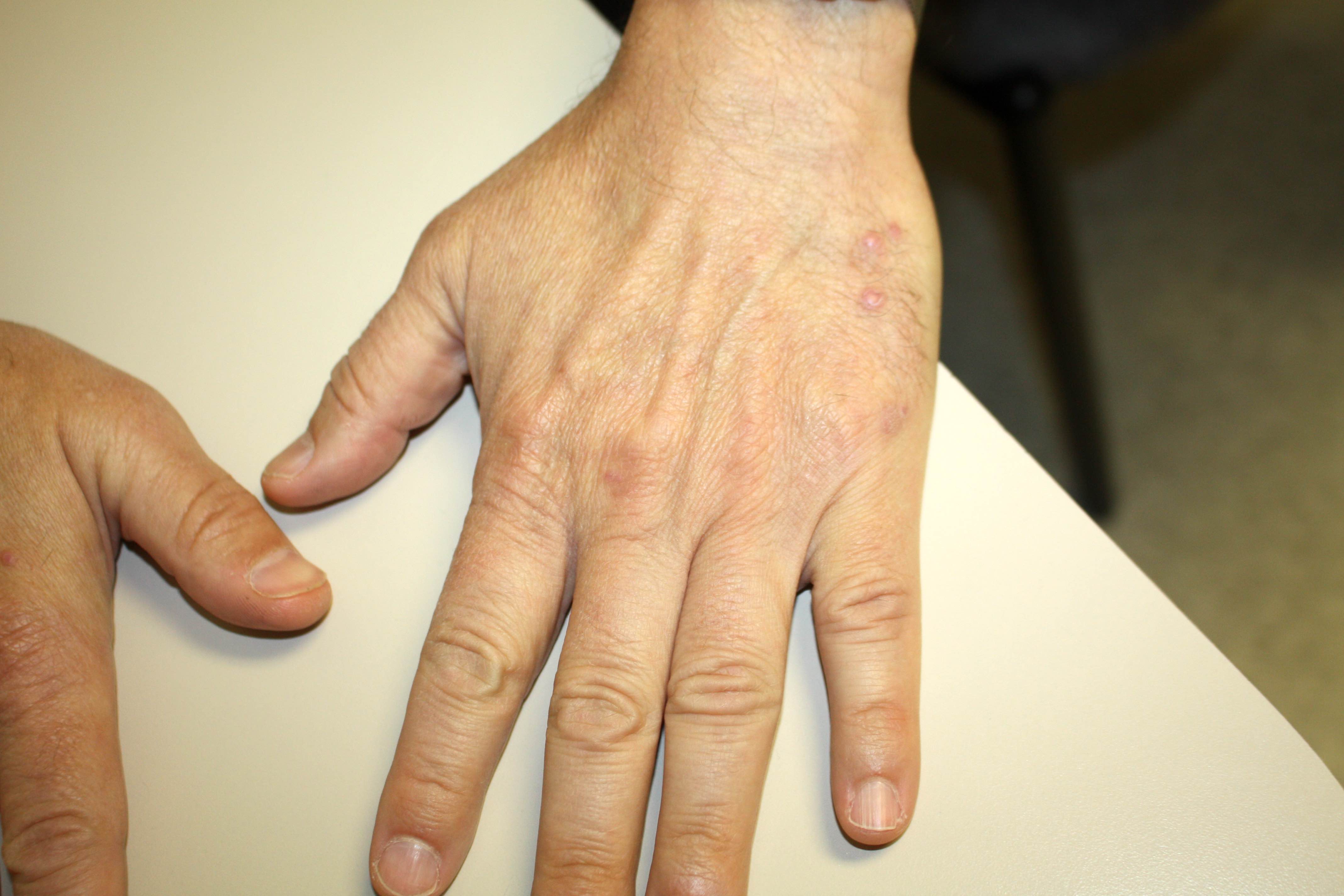
- Dorsal hands or fingers most frequent; when multiple lesions are found, they are most likely to affect the hands or fingers (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- Lower extremities
- Trunk or back
- Head and neck (rare, most often these are fibrous papules with multinucleated stromal cells, not multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma)
Pathophysiology
- Currently unknown
- Role for increased mast cells had been postulated but when mast cell counts were compared with counts of normal skin, no difference was found (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- Role for fibroblasts, given the increased intralesional elastic fibers in generalized multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma, has been postulated (J Dermatol 2021;48:114)
- Role for estrogen receptor alpha overexpression has been proposed (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:655)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
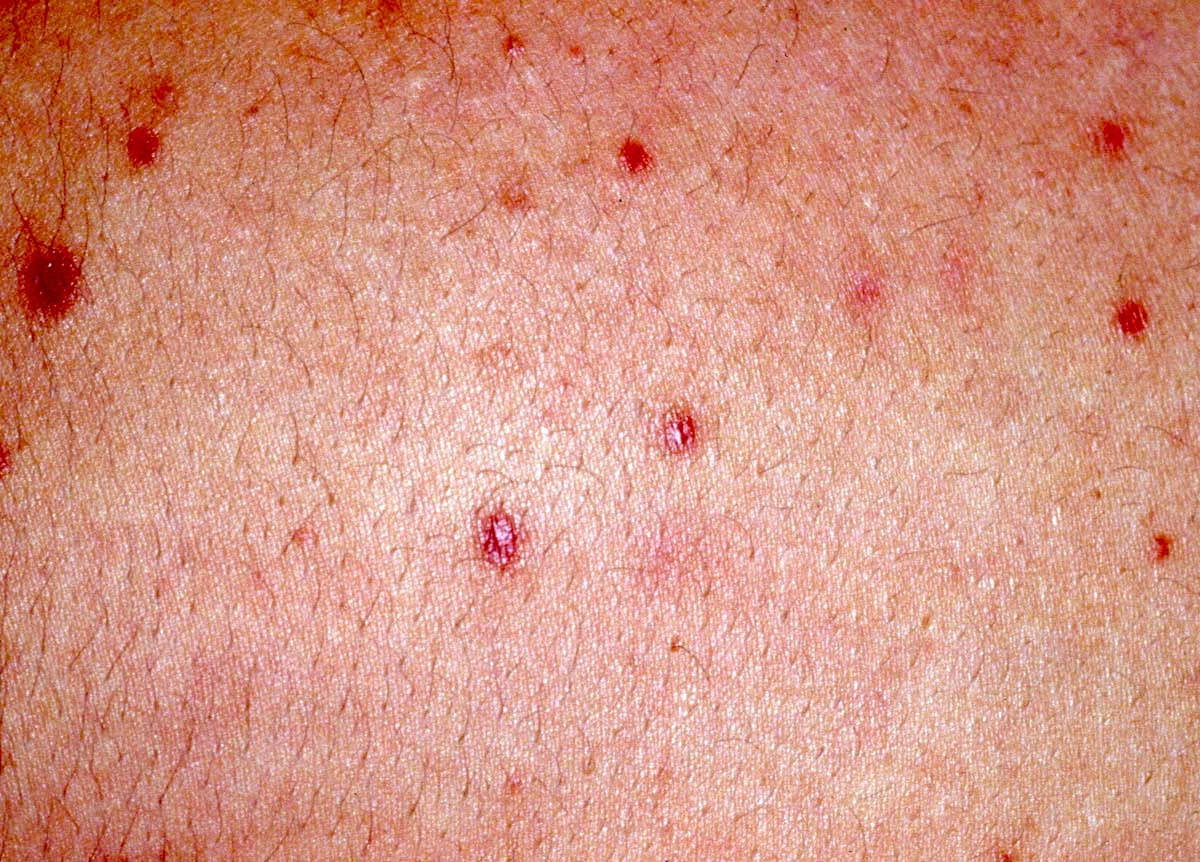
- Dull red papules and nodules
- Lesions may be single, multiple or generalized (rare)
- Reference: J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563
Diagnosis
- Made on H&E stain with light microscopy in conjunction with clinical findings
Prognostic factors
- Benign
- May recur (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:655)
Case reports
- 28 year old woman with congenital chronic hepatitis B with multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma and with cutaneous plasmacytosis (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:678)
- 42 year old woman with generalized multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:125)
- 42 year old man with generalized multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma with involvement of palms and soles (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2018;84:468)
- 42 year old man with Kaposi sarcoma-like multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma complicating an iatrogenic arteriovenous fistula (Eur J Dermatol 2010;20:642)
Treatment
- No standard first line therapy; without treatment, course is indolent and progressive and spontaneous remission is rare
- Numerous treatment modalities have shown success:
- Intralesional corticosteroids (An Bras Dermatol 2020;95:480)
- Surgical excision (An Bras Dermatol 2020;95:480)
- Potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser in combination with intralesional corticosteroids (JAAD Case Rep 2019;5:880)
- Fractionated ablative carbon dioxide (CO2) laser (JAAD Case Rep 2019;5:297)
- Pulsed dye laser (Clin Exp Dermatol 2016;41:312)
- Intense pulsed light (Dermatol Surg 2009;35:1141)
- Argon laser (Br J Dermatol 1995;133:308)
Clinical images
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
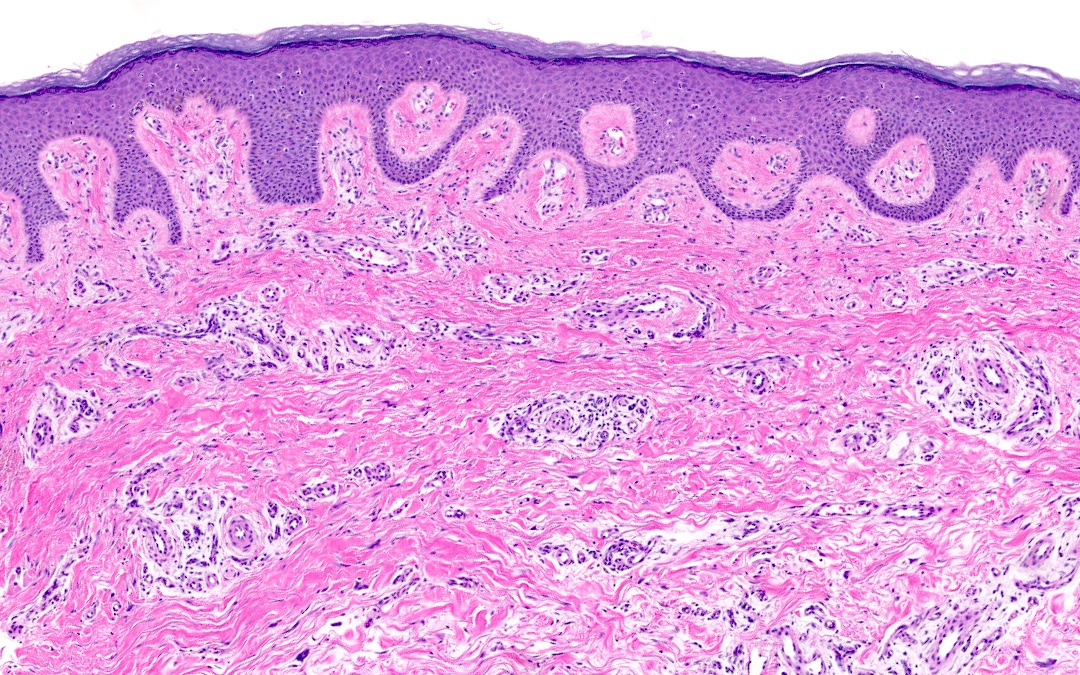
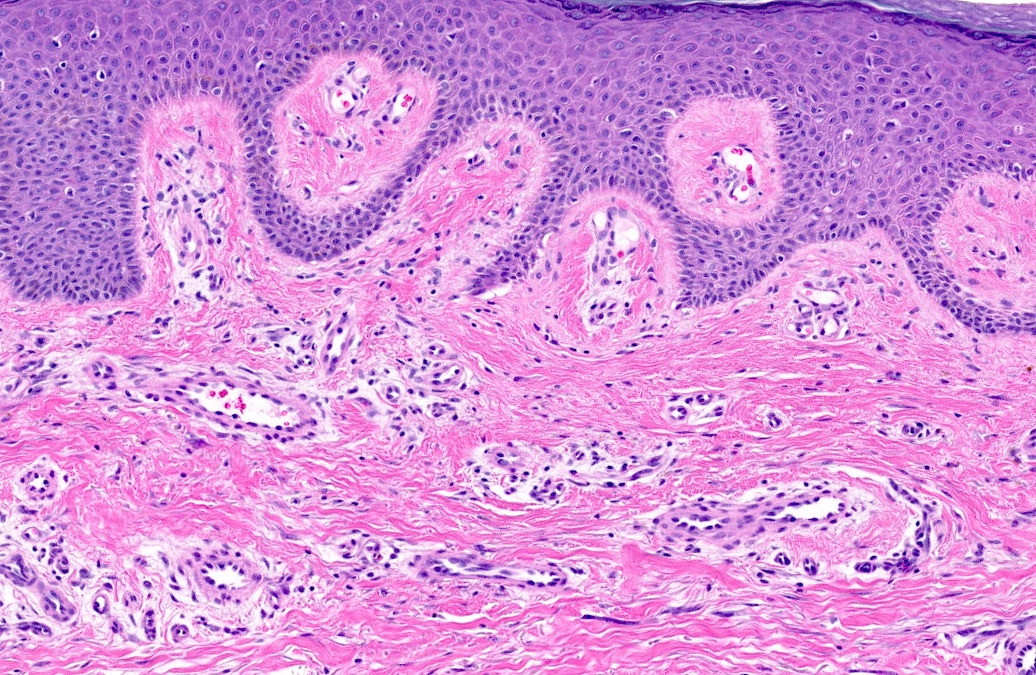
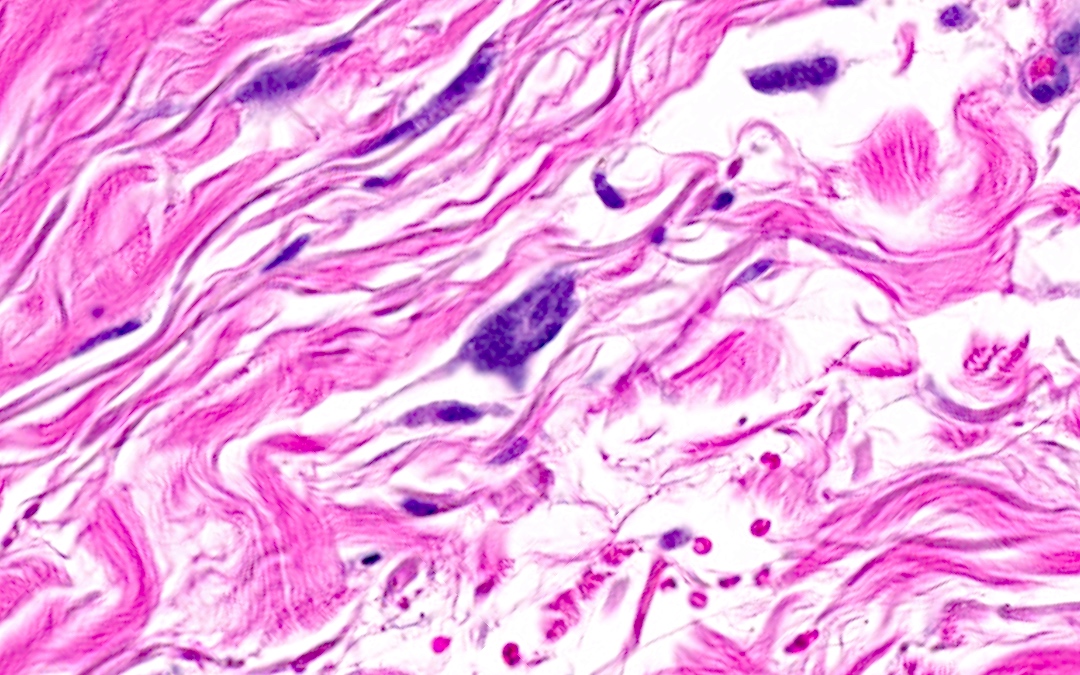
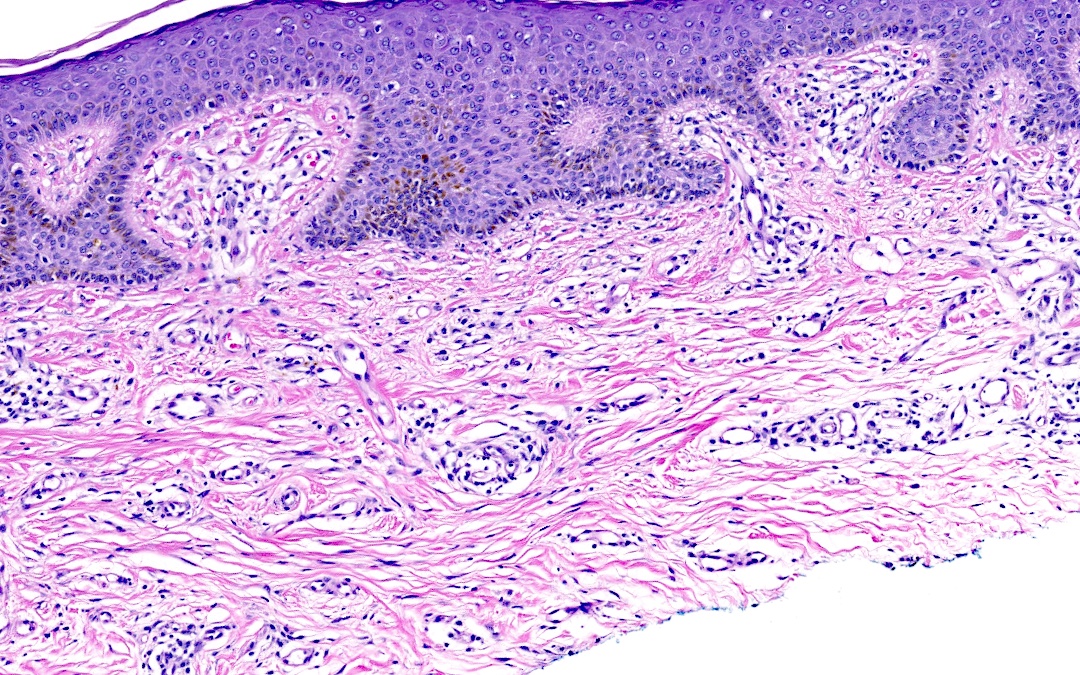
- Presence of odd multinucleated, stellate fibroblasts with stretched out cytoplasmic extensions; multinucleated cells may be scant and may require additional tissue levels (Dermatol Online J 2009;15:4)
- Presence of superficial parallel fibrosis (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- Presence and thickening of superficial papillary dermal vessels (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- May show moderately increased number of blood vessels
- Absence of perifollicular fibrosis (found in the fibrous papule of the nose) (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- May be acanthotic or flat architectural profile, with generally a normal basket woven stratum corneum (Dermatol Online J 2009;15:4)
- Eosinophils are very rarely encountered (Cutis 2017;100:429)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Immunohistochemistry is seldom contributory for the diagnosis (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- Multinucleated cells: variably CD68, vimentin and factor XIIIa positive (Dermatol Online J 2009;15:4)
- Mast cells, plasma cells and prominent vessels may be highlighted with their respective markers (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
Negative stains
- Multinucleated cells are generally CD163, CD34 and factor VIII negative (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left dorsal hand, punch biopsy:
- Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show superficial parallel fibrosis, thickened and abundant papillary dermal vessels and stellate multinucleated cells consistent with multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Fibrous papule of the nose:
- Can also show prominent superficial papillary dermal vessels and multinucleated cells but the fibrosis is not parallel to the epidermis
- Shows concentric perifollicular fibrosis in most instances, unlike multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
- Much more commonly seen on the face / nose (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- Dermatofibroma:
- More common on lower extremities
- Atrophic vascular variant of dermatofibroma may mimic multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
- Fibrosis in dermatofibroma is more storiform, rather than parallel to the epidermis
- May also show multinucleated cells and factor XIIIa positivity
- Follicular induction and beta catenin positivity in underlying dermal fibroblasts is frequent in dermatofibroma but absent in multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
- Telangiectasia macularis eruptive perstans:
- Eosinophils are frequent in the inflammatory infiltrate of telangiectasia macularis eruptive perstans but very rare in multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
- Multinucleated cells in telangiectasia macularis eruptive perstans are slightly different, showing < 3 nuclei, contrarily to multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
- Mast cell counts are elevated in telangiectasia macularis eruptive perstans compared with multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma or normal skin (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:563)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
There are multiple red papules on the dorsal hands with multinucleated stromal cells, thickened superficial papillary dermal vessels and superficial dermal fibrosis arrayed in parallel to the epidermis. What is the best diagnosis?
- Dermatofibroma
- Fibrous papule
- Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma (MCAH)
- Telangiectasia macularis eruptive perstans (TMEP)
Board review style answer #1
C. Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma (MCAH)
Comment Here
Reference: Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
A. Concentric perifollicular fibrosis. Concentric perifollicular fibrosis is rather a feature of fibrous papule of the nose and is the main histopathological criteria to distinguish these entities, along with knowledge of the anatomical site.
Comment Here
Reference: Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma