Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Warmke L, Meis J. Angiolipoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueadiposeangiolipoma.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign, soft tissue tumor consisting of mature adipose tissue and clusters of thin walled vessels, often containing intraluminal fibrin thrombi
- First described in 1912 by Bowen (Hum Pathol 1981;12:739)
- Established as a distinct entity in 1960 by Howard and Helwig (Arch Dermatol 1960;82:924)
Essential features
- Mature adipocytes
- Clusters of capillary sized vessels
- Fibrin thrombi in vessels
Terminology
- Cellular angiolipoma (morphologic variant)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8861/0 - angiolipoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2E80.0Y & XH3C77 - other specified lipoma & angiolipoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Relatively common in young adults (Arch Dermatol 1960;82:924)
- Usually appears in late second to early third decade of life
- Rare in children or adults > 50 years
- Male predominance
Sites
- Forearm, trunk and upper arm common sites
- Rare on scalp or face
- Intramuscular hemangiomas represent different lesions (Arch Surg 1980;115:281)
- So called angiolipomas of parenchymal organs and central nervous system represent different lesions containing larger vessels (World Neurosurg 2018;114:264)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
- Association between sporadic angiolipoma and overlying cutaneous capillary malformation has been reported (Am J Clin Dermatol 2008;9:389)
Etiology
- Majority are sporadic
- Rare familial predilection (5%) with autosomal dominant inheritance (Dermatol Online J 2007;13:3, Hum Pathol 1981;12:739)
Clinical features
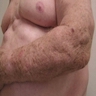
- Frequently present as multiple subcutaneous small nodules
- Nodules are usually tender or painful
- There is no correlation between degree of vascularity and intensity of pain (Hum Pathol 1981;12:739)
Diagnosis
- Tender, often multiple subcutaneous nodules (Arch Dermatol 1960;82:924)
- Mature adipocytes
- Clusters of capillary sized vessels
- Intraluminal fibrin microthrombi
Radiology description
- Ultrasound (Skeletal Radiol 2012;41:1055):
- Oval shaped
- Well defined margins
- Hyperechoic lesions compared to muscle
- Color Doppler flow present in < 25% of cases
- CT (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:862):
- Heterogeneous appearance
- Mixed fat and soft tissue density
- MRI (Skeletal Radiol 2018;47:859):
- Fatty component shows high signal intensity on T1 weighted images and signal suppression on fat suppressed images
- Vascular component shows areas of low signal intensity on T1 weighted images and high signal intensity on fat suppressed T2 weighted images
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion with excellent prognosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:862)
- Local recurrence very rare
- No risk of malignant transformation
Case reports
- 41 year old man with painful scrotal angiolipoma (Urol Case Rep 2020;32:101217)
- 60 year old man presents with 20 year history of angiolipoma on right index finger (Dermatol Online J 2019;25:13030)
- 68 year old man with bronchial angiolipoma (BMC Surg 2019;19:13)
Treatment
- Simple surgical excision
- Liposuction may reduce tumor burden in familial multiple angiolipomatosis (Dermatol Online J 2007;13:3)
Clinical images
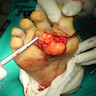
Gross description
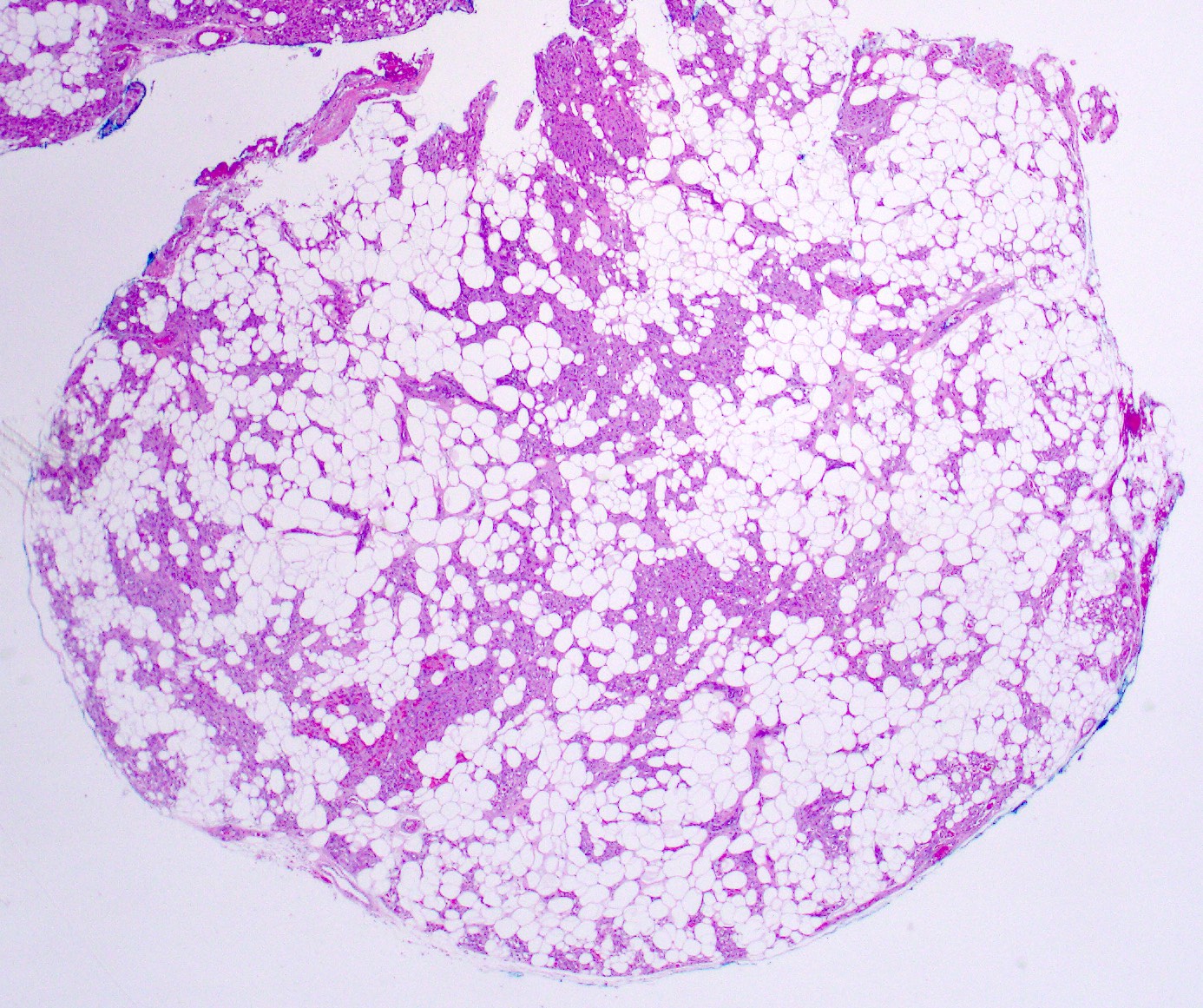
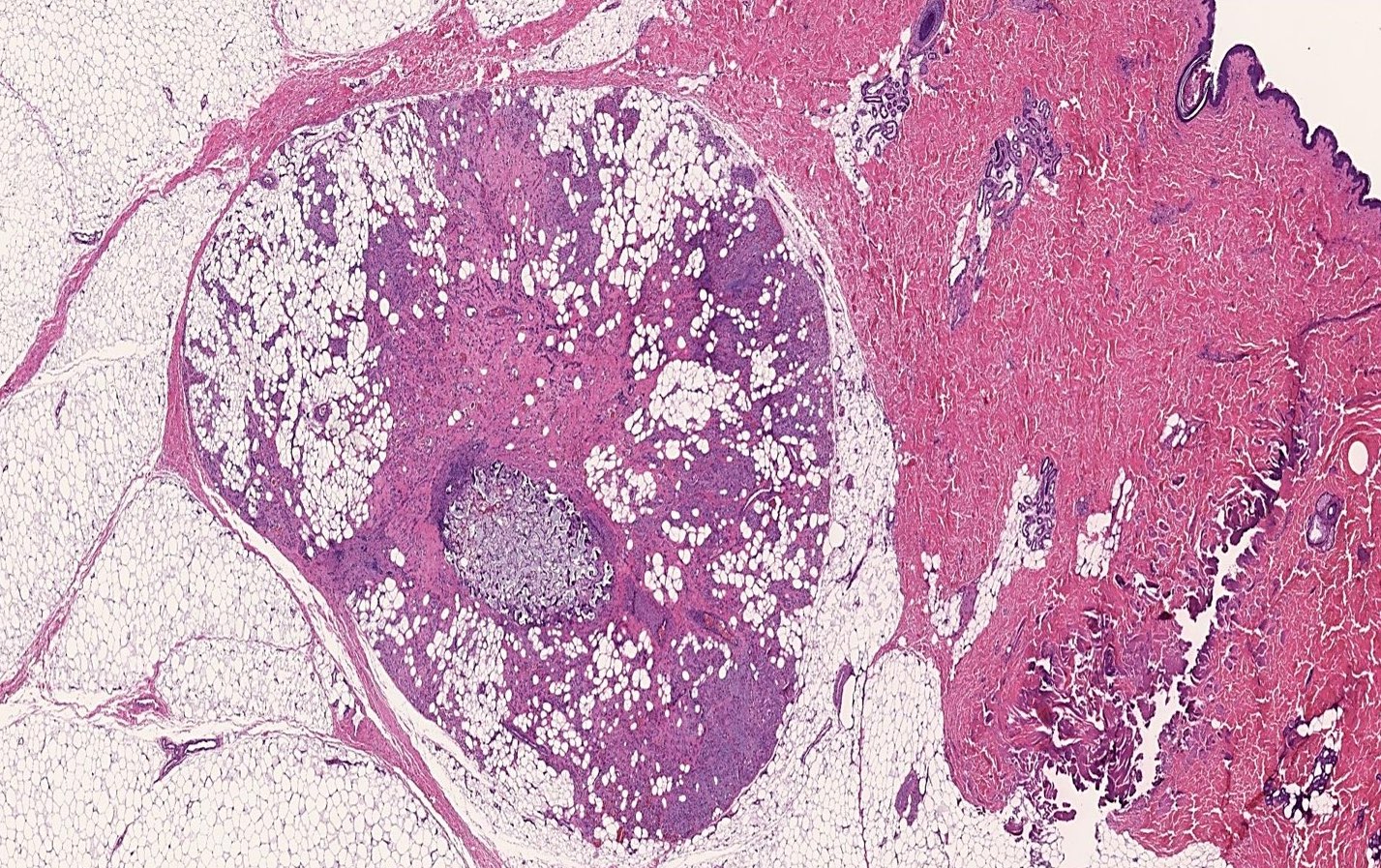
- Well circumscribed / encapsulated nodule
- Usually < 2 cm in size
- Denser consistency than lipoma (Arch Dermatol 1960;82:924)
- Vascular component evident with red-yellow color (Arch Dermatol 1960;82:924)
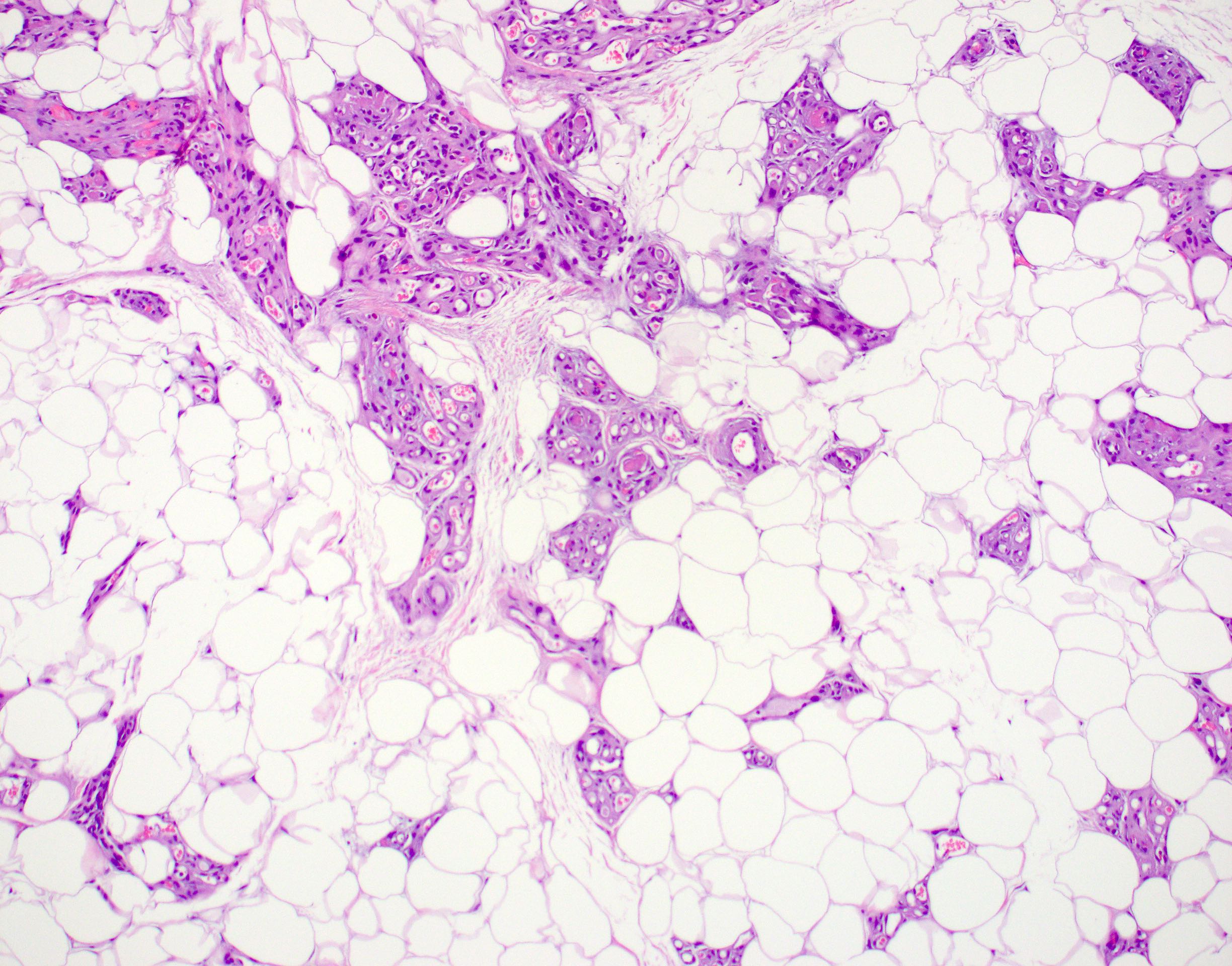
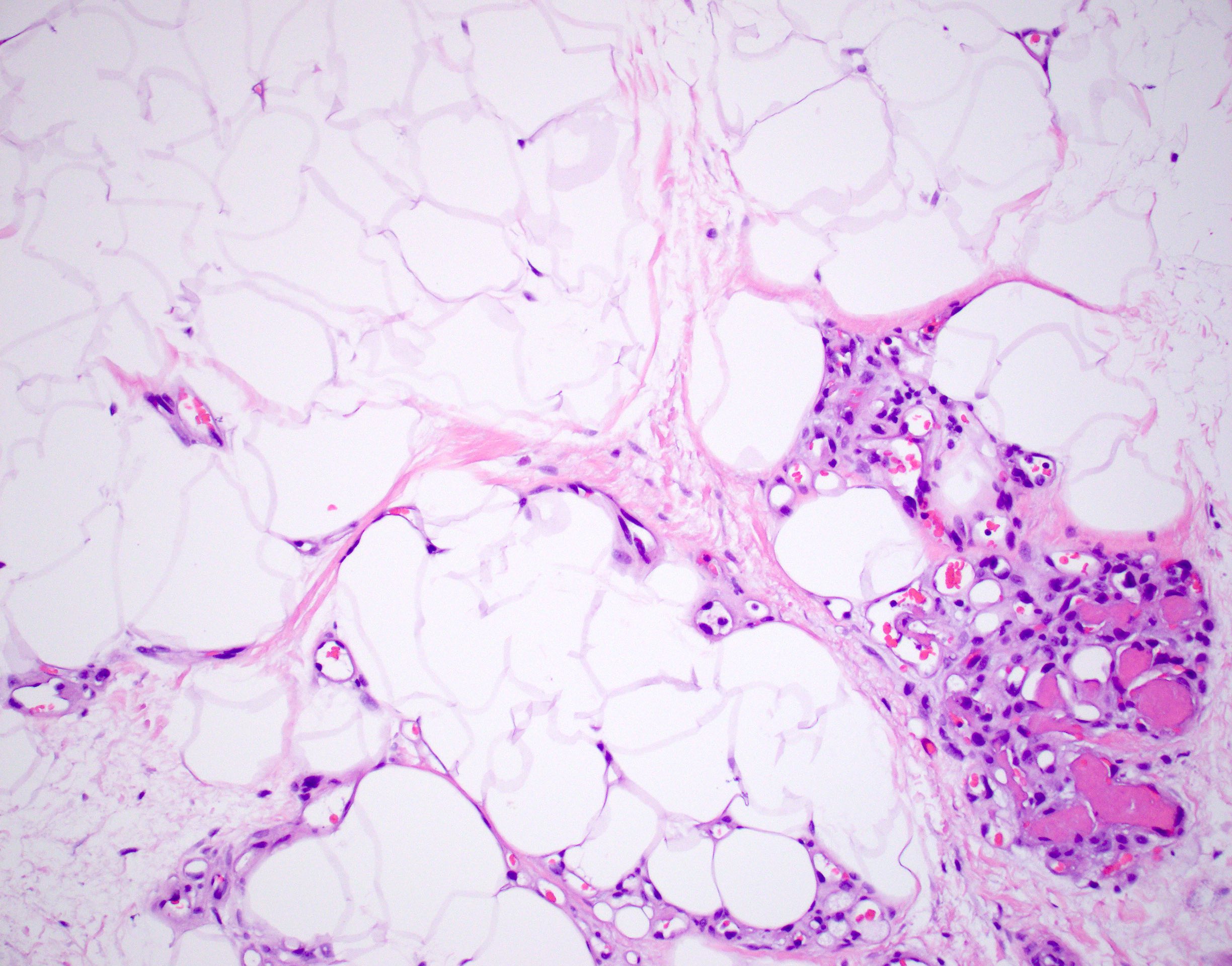
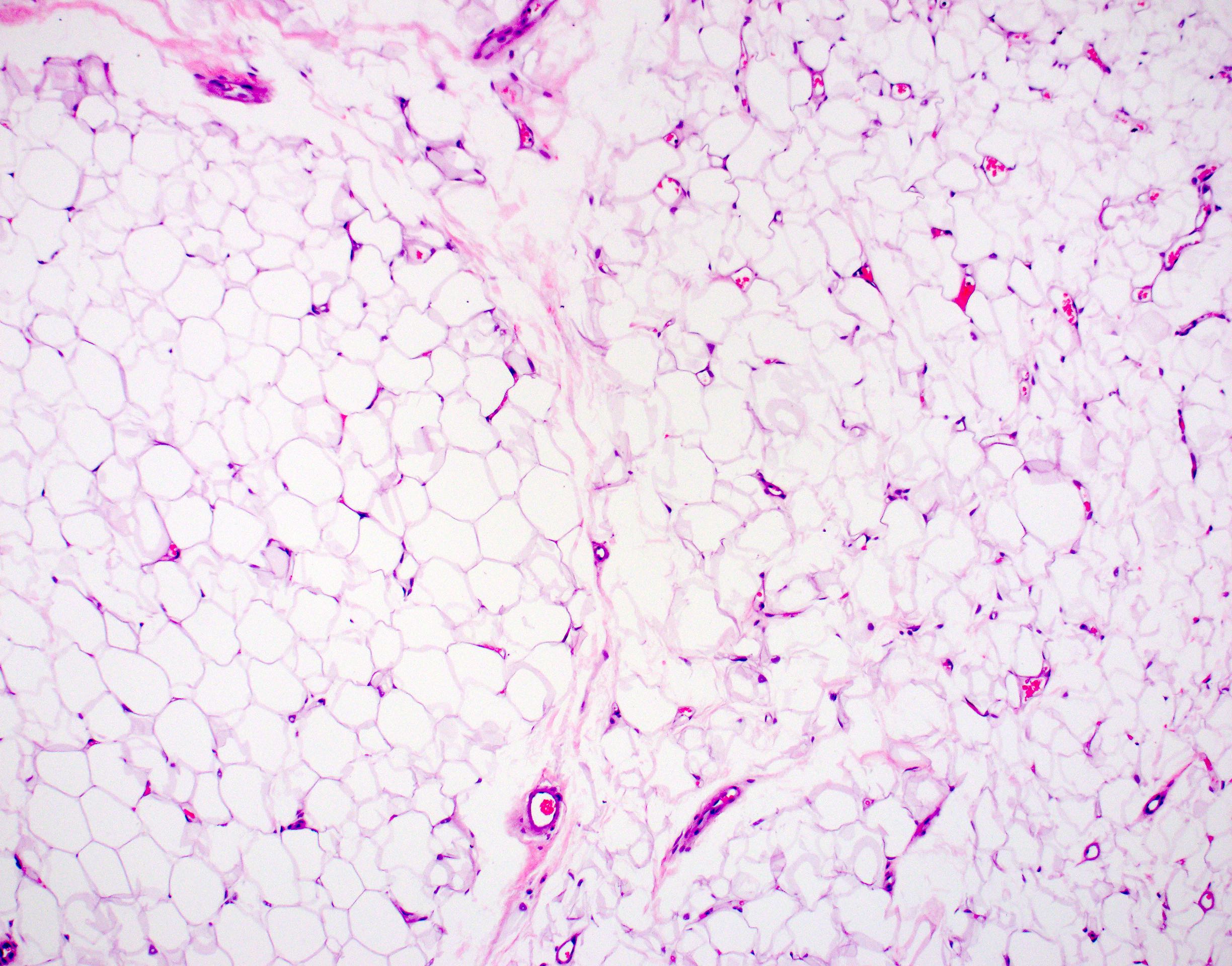
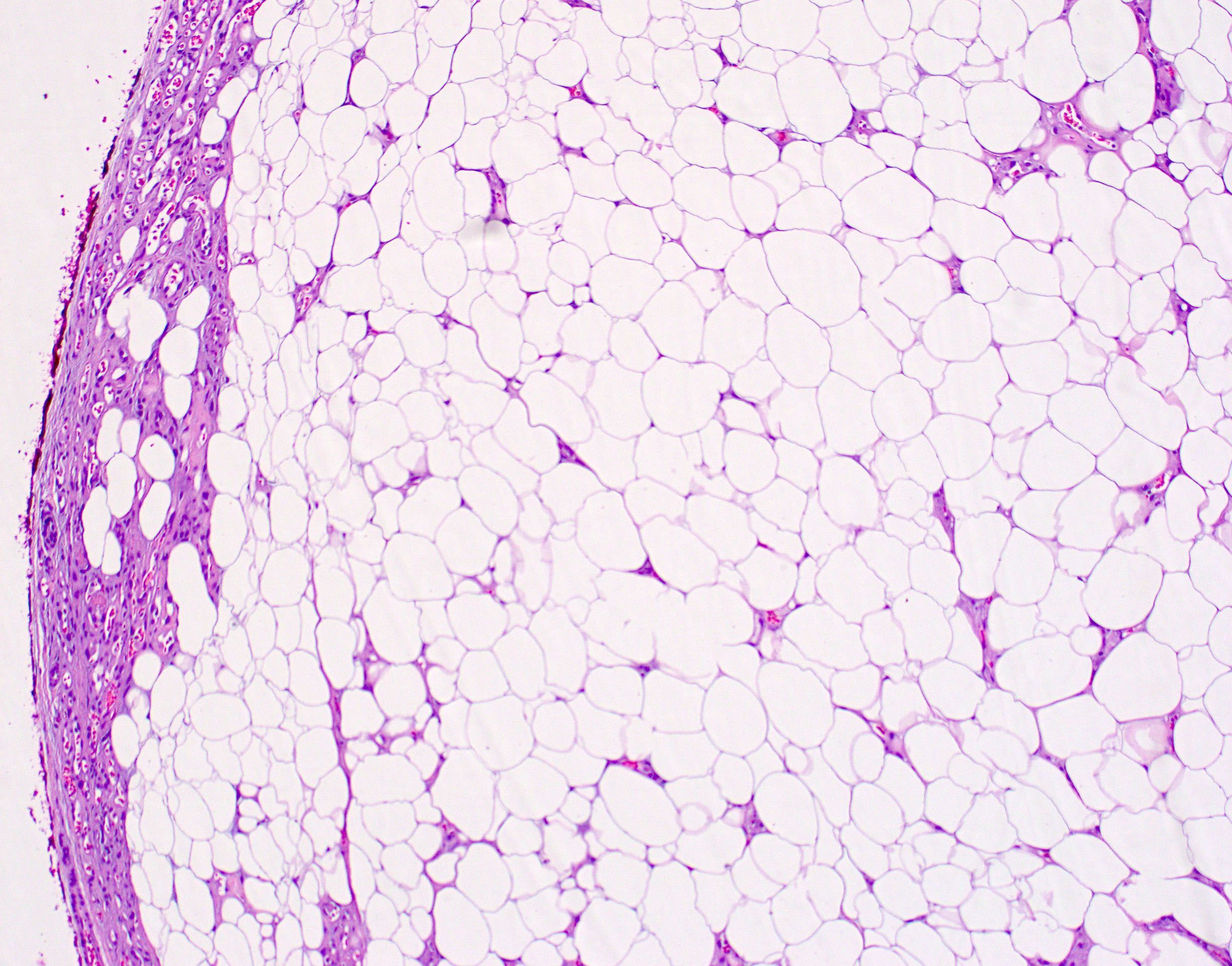
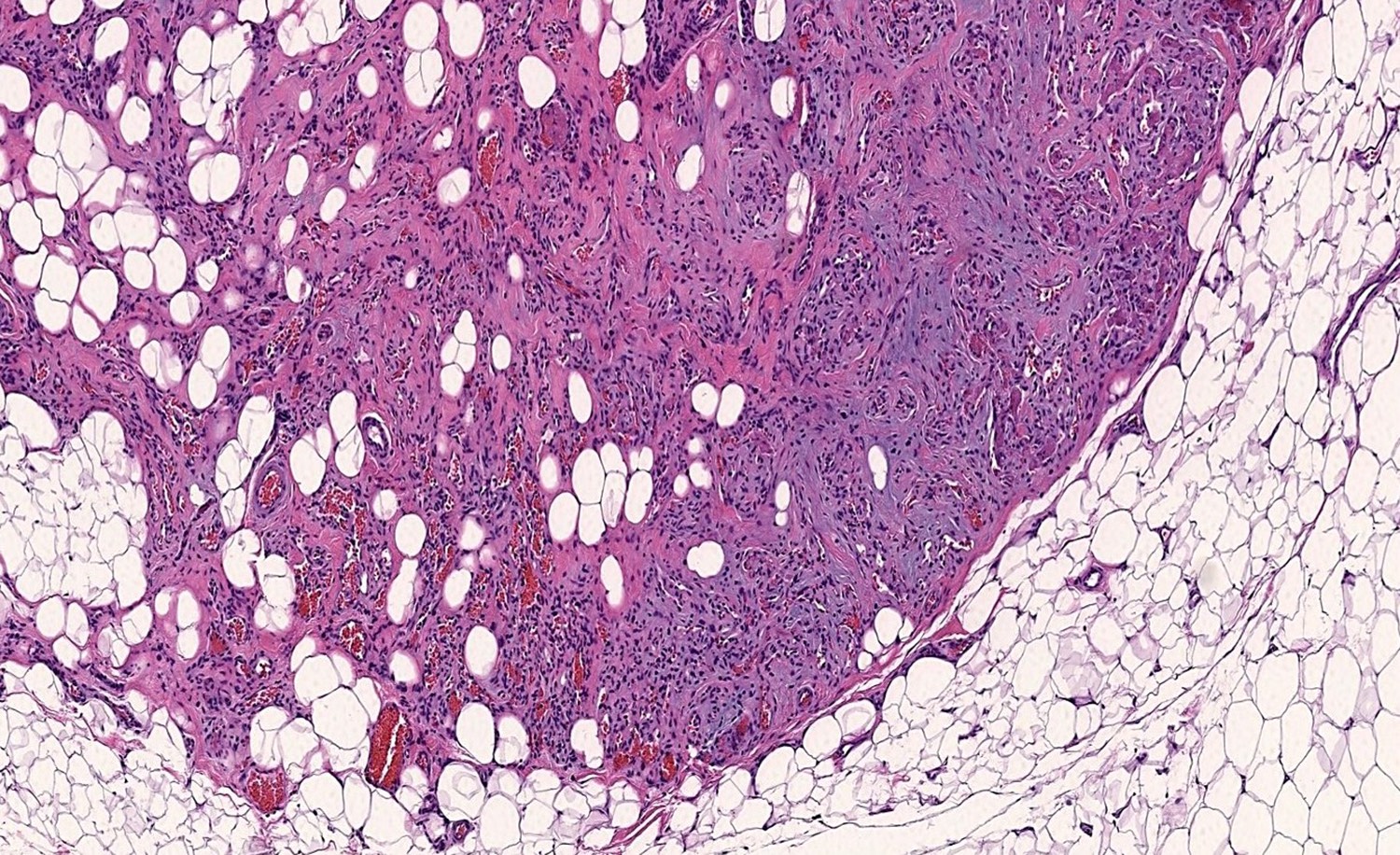
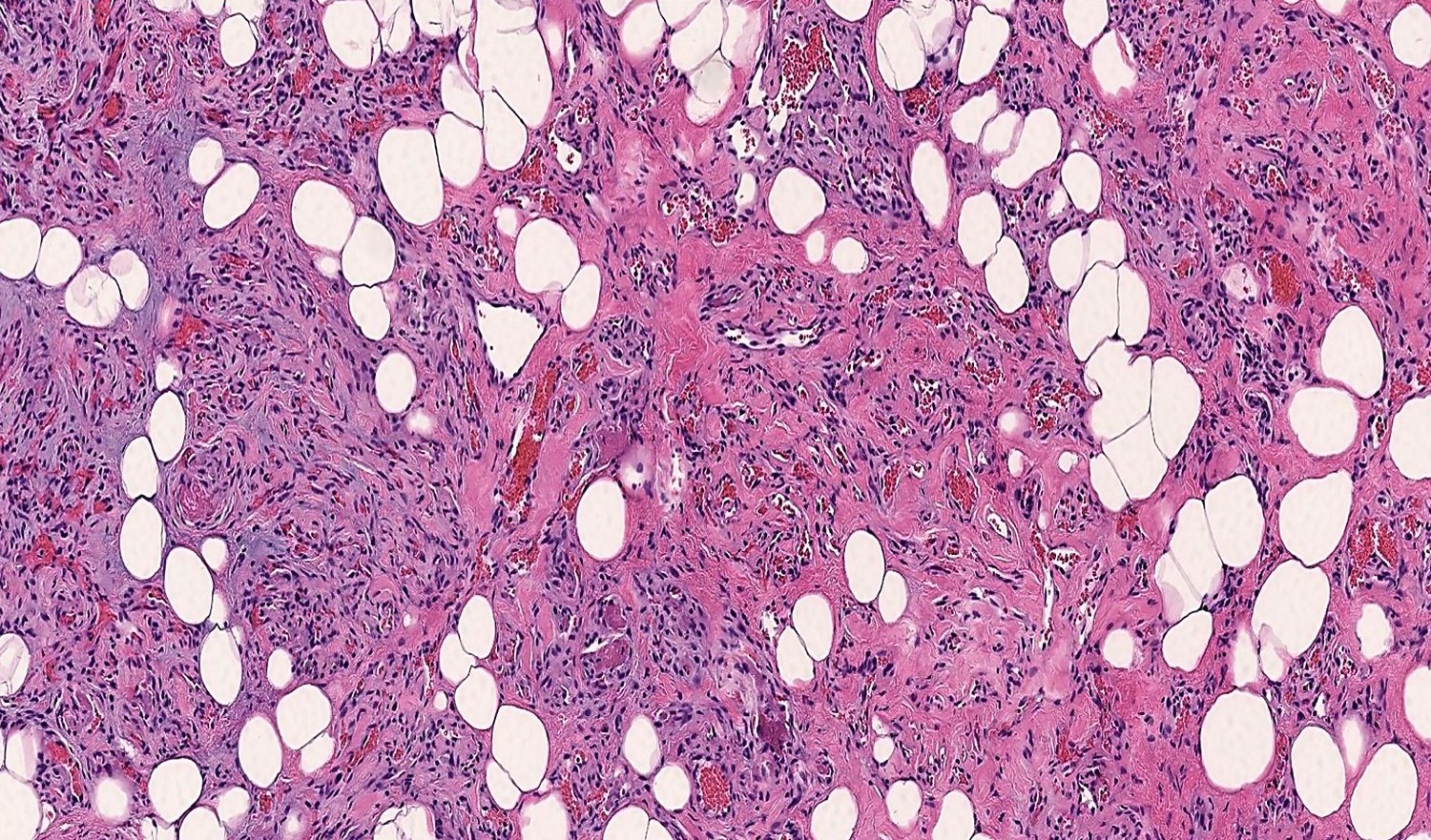
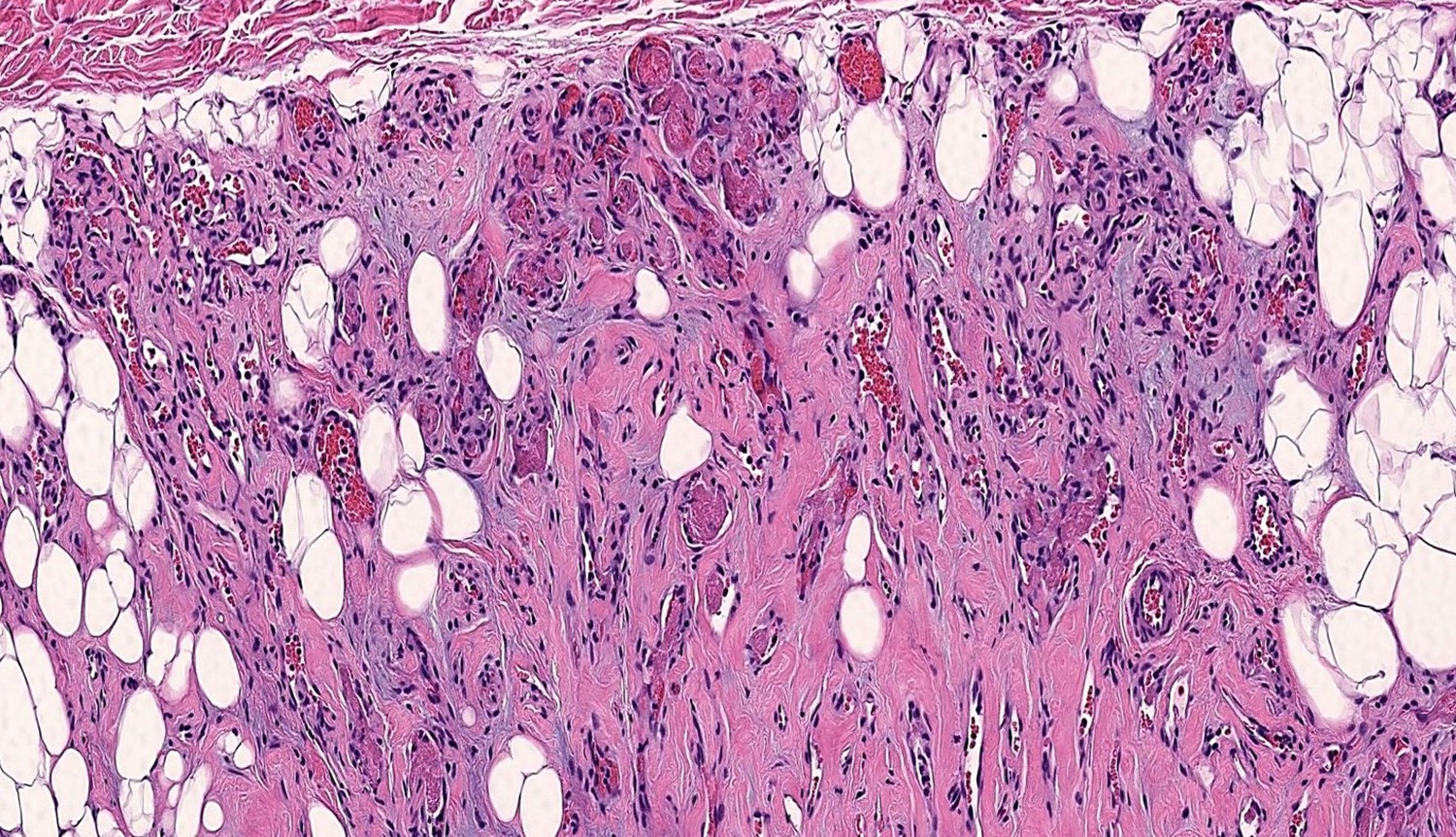
Microscopic (histologic) description
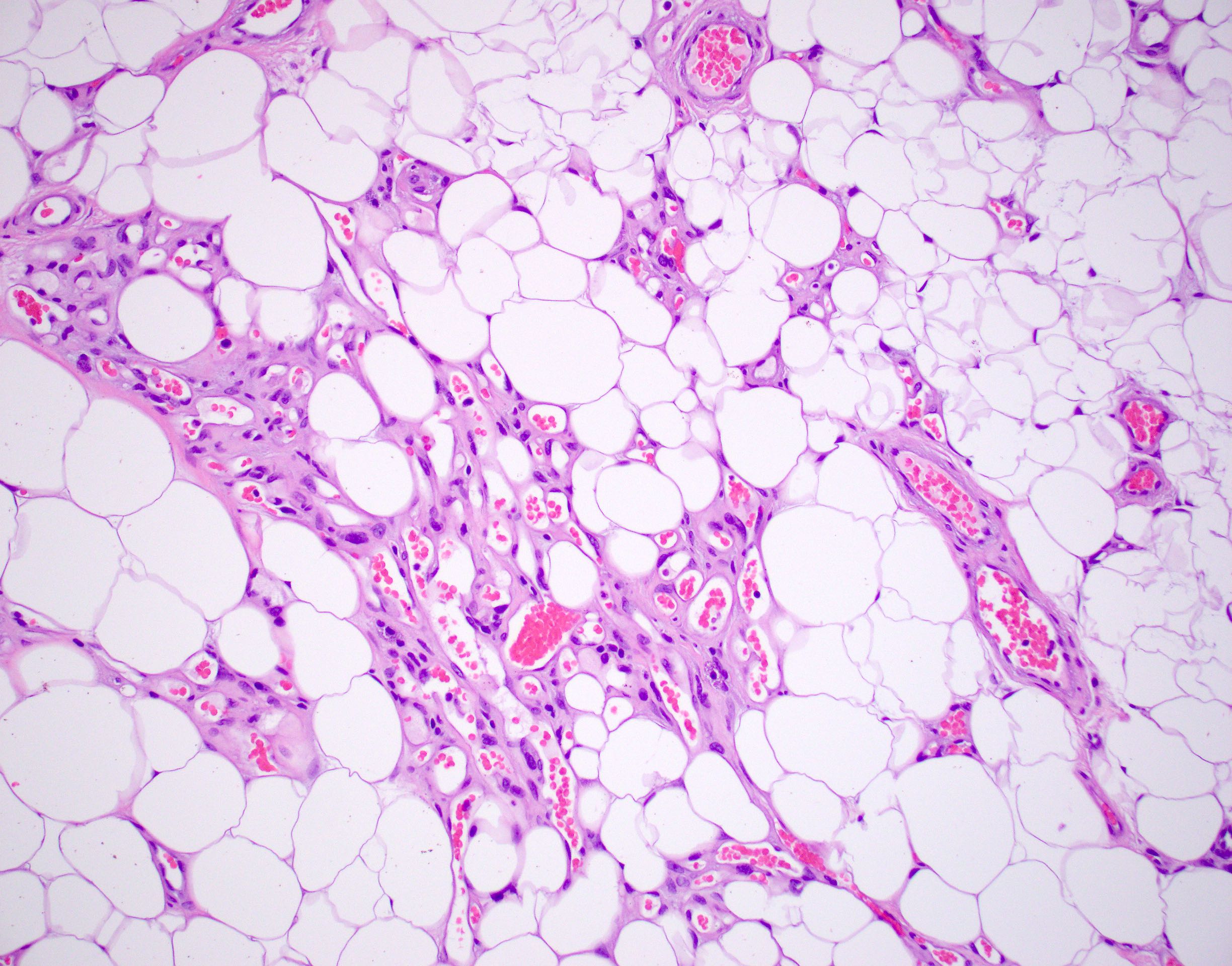
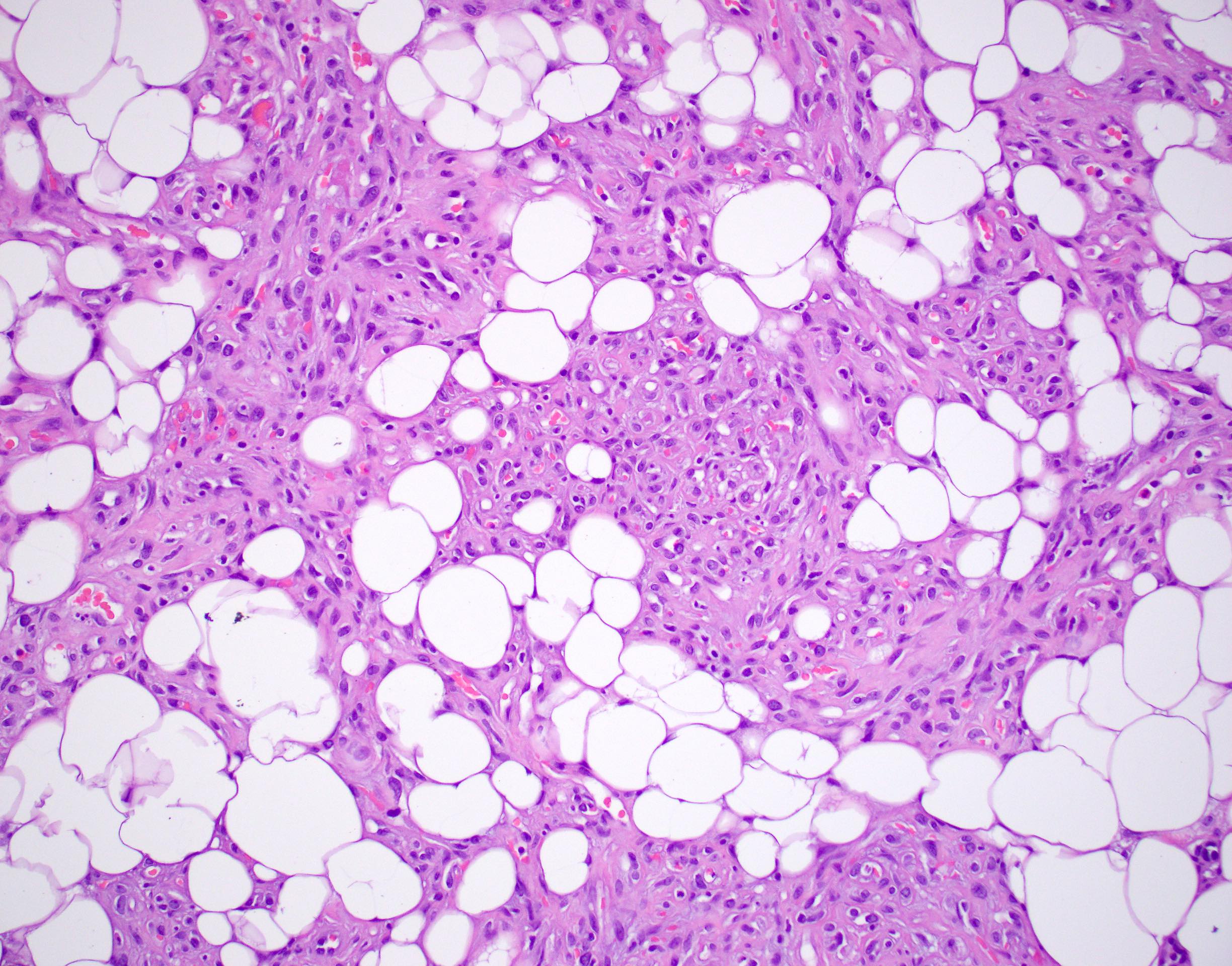
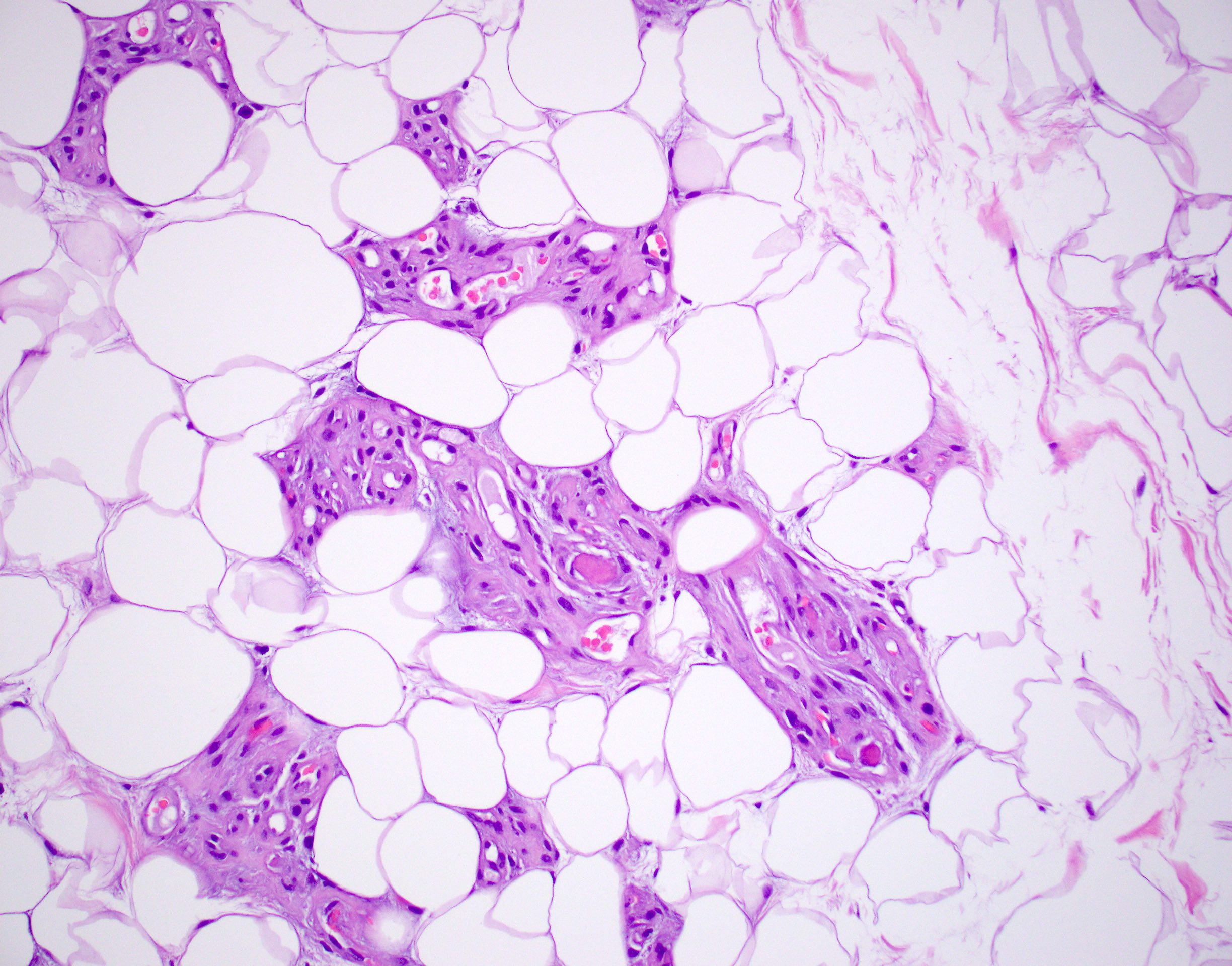
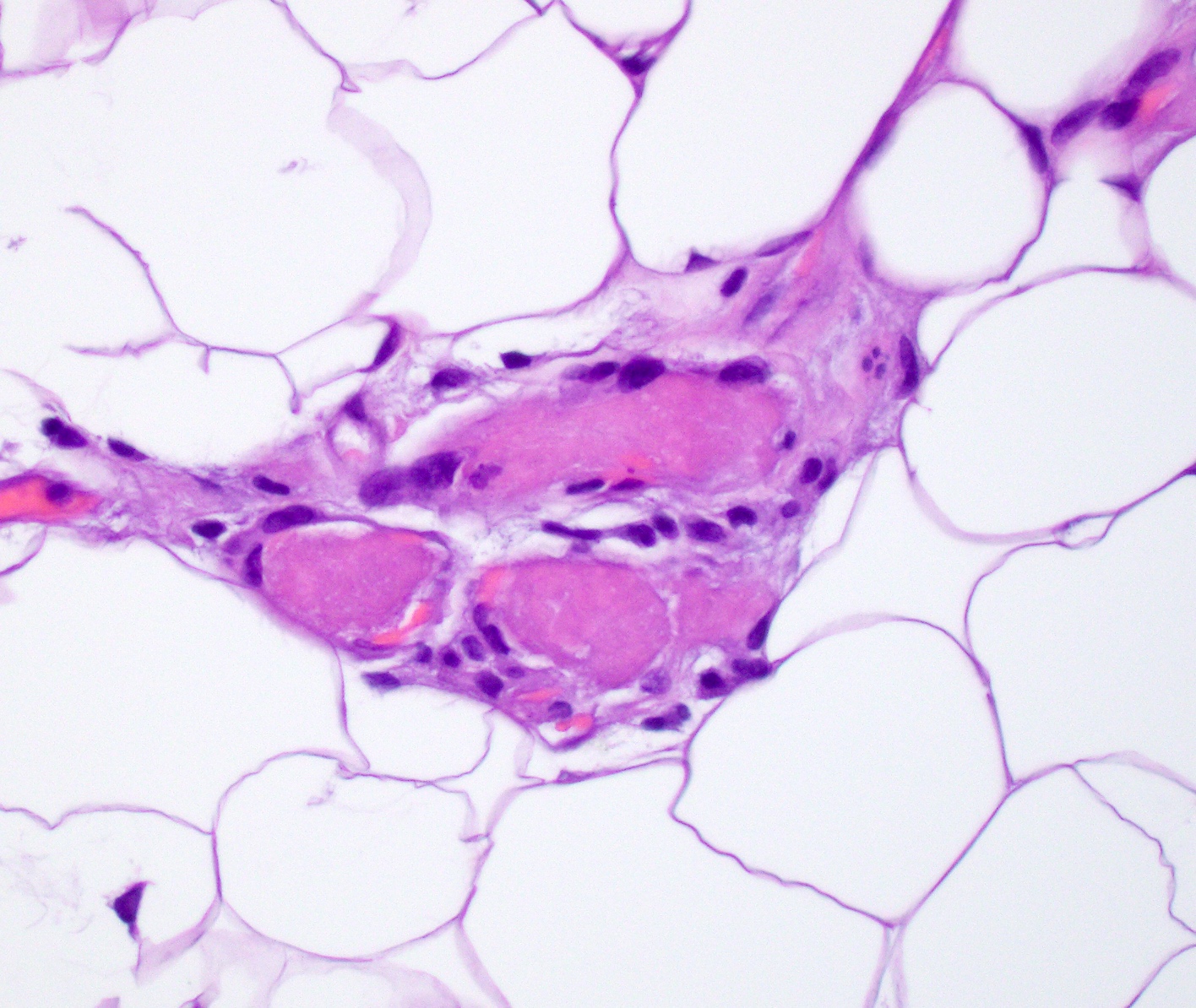
- Consists of mature adipose tissue and branching capillary sized vessels
- Thin walled vessels often contain bright pink fibrin thrombi
- Vascularity is more prominent in the periphery (Hum Pathol 1981;12:739)
- Well formed capillaries often have a lobular arrangement
- Occasionally, few thin fibrous septae present
- Proportion of adipocytes and vessels varies
- No nuclear atypia in the adipocytic or vascular component
- Endothelial cells are bland and uniform
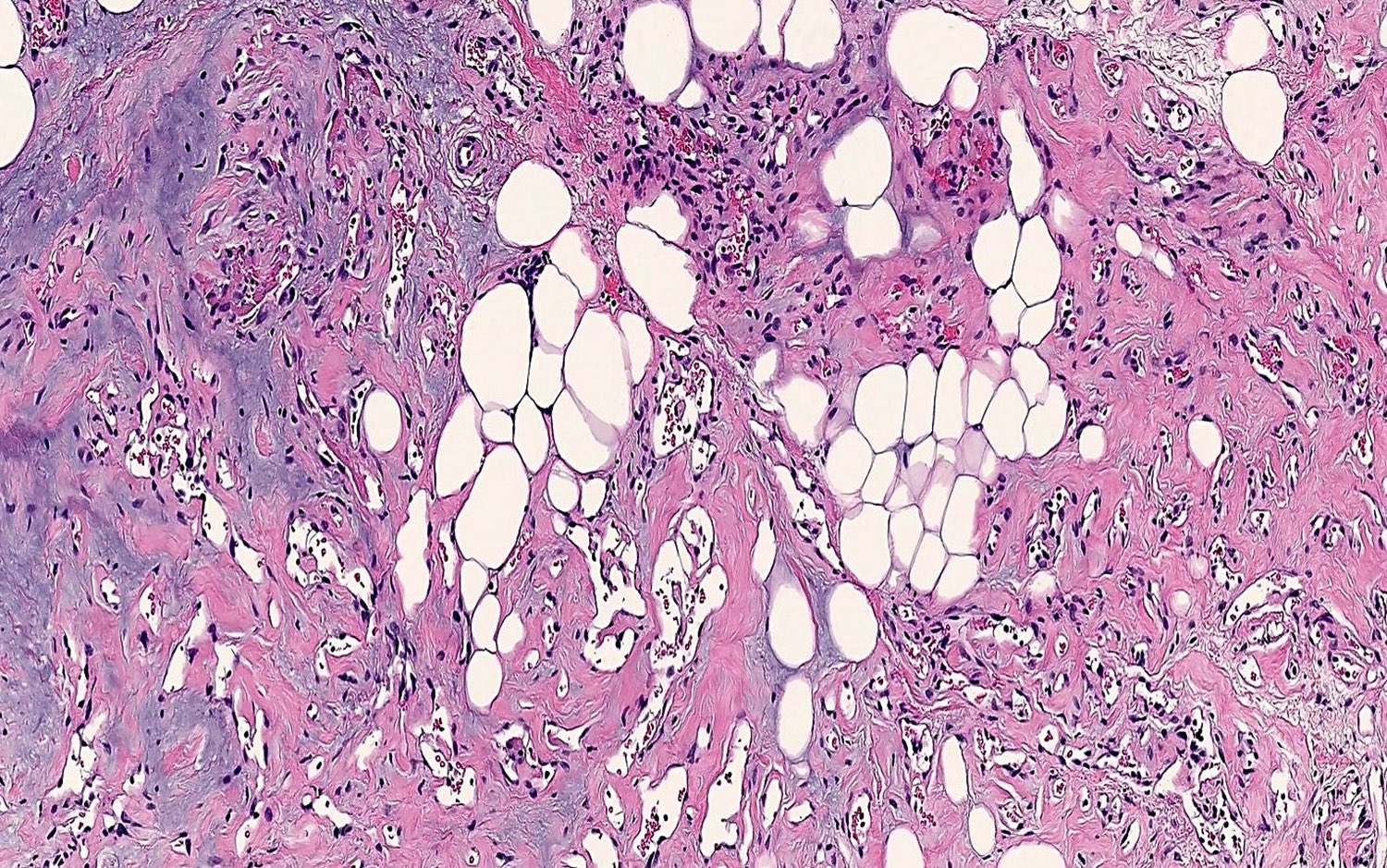
- Morphologic variant: cellular angiolipoma (vessels predominate)
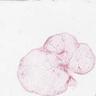
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Laura Warmke, M.D. and Jeanne Meis, M.D.
Cellular angiolipoma
Cytology description
- Not clinically relevant
Immunofluorescence description
- Fluorescein labeled antihuman fibrinogen demonstrates intense, irregularly homogeneous fluorescence of the fibrin thrombi (Hum Pathol 1981;12:739)
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Adipose tissue with central lipid droplet surrounded by thin rim of cytoplasm
- Capillaries lined by one or more endothelial cells
- Decreased number of Weibel-Palade bodies in endothelial cells (Hum Pathol 1981;12:739)
- Endothelial cells frequently surrounded by pericytes
- Variable numbers of fibrin thrombi within capillaries
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Most have a normal karyotype (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:441, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1994;9:207)
- Rare cases show rearrangements of chromosome 13 (Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2018;15:61)
- Majority (80%) have been reported to have low frequency PRKD2 mutations (J Pathol 2017;241:578)
- Activating PIK3CA mutations have been reported in sporadic angiolipoma (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:211)
Videos
Angiolipoma
Sample pathology report
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue, left forearm, excision:
- Angiolipoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show an oval, well circumscribed lesion composed of mature adipose tissue with clusters of capillary sized vessels. Multiple fibrin microthrombi are identified with the lumen of the vessels, supporting the above diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Lipoma:
- Mature adipose tissue
- Lacks vascular component and fibrin thrombi
- Various translocations of chromosome 12q or 6p
- May mimic fat predominant angiolipoma
- Intramuscular hemangioma:
- Previously known as infiltrating angiolipoma
- May have fatty overgrowth
- Large, infiltrative lesion
- Located deep in muscle (not subcutaneous tissue)
- Large thick walled vessels present
- Spindle cell hemangioma:
- Multiple painful subcutaneous nodules in extremities
- Cavernous vascular spaces
- Cellular zones of spindled and epithelioid endothelial cells
- Large calcified thrombi (phleboliths)
- Angiomyolipoma:
- Spindle cells that are HMB45+ smooth muscle cells
- Large caliber and thick walled vessels
- Rare in subcutaneous tissue
- Kaposi sarcoma (distinguish from cellular angiofibroma):
- Angiosarcoma (distinguish from cellular angiofibroma):
- Nuclear atypia in endothelial cells
- Aggressive, infiltrative growth
- Mitotic activity and necrosis frequent
- Loss of pericytic (perivascular smooth muscle) cells
- Lack of fibrin thrombi
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2