Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Stuart LN, Jimenez R, Gardner JM. Proliferative funiculitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuepf.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Pseudosarcomatous inflammatory lesion involving the spermatic cord (Pathol Int 2003;53:897)
- Lesion is composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:448)
Terminology
- Also known as pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferation of spermatic cord
- Some studies mention relationship to: inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, inflammatory pseudotumor, atypical myofibroblastic tumor, pseudosarcoma (Urology 2009;73:1423)
- These terms are often used inappropriately in literature and may not truly be related to proliferative funiculitis
Epidemiology
- Older men (ages 52 - 76 years)
Sites
- Spermatic cord
- Similar lesions in epididymis (Pathol Int 2003;53:897)
Etiology
- May be due to ischemia, torsion or extension of vasitis
Clinical features
- Swelling in inguinal area; usually found in association with inguinal hernia (Pathol Int 2003;53:897, Cheng Essentials of Anatomic Pathology 2011)
- Usually incidental at herniorrhaphy
Laboratory
- Normal levels of α-fetoprotein, β-human chorionic gonadotropin
Radiology description
- Multicystic mass (ultrasound, Tunis Med 2012;90:333)
Prognostic factors
- Can recur locally; excellent prognosis when resected with negative margins
Treatment
- Surgical resection
Gross description
- Ill-defined, firm or gelatinous mass with a gray-white cute surface
- Calcification, hemorrhage, and necrosis are uncommon (Int J Surg Case Rep 2012;3:618, Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:448)
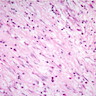
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Infiltrative spindle cell proliferation within a myxoid or loose collagenous stroma
- Nuclei are oval to fusiform
- Basophilic nucleoli may be present
- Mixed inflammatory infiltrate mainly composed of plasma cells and lymphocytes
- May contain malignant appearing glandular structures composed of keratin+ mesothelial cells (Int J Surg Pathol 2008;16:48), rarely has proliferation of mast cells (Pathol Int 2003;53:897)
Positive stains
- Vimentin, muscle specific actin, SMA, desmin (Urology 2009;73:1423)
- Entrapped mesothelial cells stain with keratins, mesothelial markers (D2-40, WT1)
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Dedifferentiated liposarcoma: much more atypical; adjacent well-differentiated adipocytic component (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:448)
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: younger population (children and adolescents); more cellular and atypical; (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:448) positive for desmin, myogenin, myoD1
- Myxoid leiomyosarcoma: intracytoplasmic glycogen; nuclear pleomorphism; necrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:448, Pathol Int 2006;56:625)