Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Michal M. ERG. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainserg.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Transcriptional regulator ERG is a protein encoded by ERG (ETS family transcription factor ERG), which is located at 21q22
- Anti-ERG monoclonal antibodies to the N or C terminus are available, with a slightly different specificity (the few differences marked throughout the text)
- Highly sensitive immunohistochemical marker for vascular differentiation, immature myeloid differentiation, cartilaginous differentiation (anti-N terminus antibody), expressed also in half of prostatic adenocarcinomas and in Ewing sarcomas with ERG rearrangement
Essential features
- ETS family transcription factor ERG has nuclear staining
- Highly sensitive and quite specific immunohistochemical marker for vascular differentiation, including benign and malignant vascular tumors
- Anti-N terminus ERG monoclonal antibody is a useful marker for certain chondrogenic tumors
- Also expressed in tumors harboring ERG rearrangements: 50% of prostatic adenocarcinomas and 5% of Ewing sarcomas
- Marker for immature myeloid differentiation including cases of acute myeloid leukemia / myeloid sarcoma
Terminology
- V-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog
- ERG3
- p55
- Transcriptional regulator ERG (transforming protein ERG)
Pathophysiology
- Ewing sarcoma with EWSR1-ERG fusion:
- ERG is a member of the ETS (E26) family, which contains a highly conserved 85 amino acid winged helix - loop - helix domain that mediates DNA binding to sequences containing a GGAA / T core motif
- Combination with EWSR1, which belongs to the TET protein family and contains domains resembling transcription activation domains, results in a strong aberrant transcriptional activator that is overexpressed
- Expression of this fusion protein is thought to have a critical role in both the development and maintenance of the Ewing sarcoma phenotype (Mod Pathol 2012;25:1378)
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma:
- Mechanism for ERG overexpression entails a recurring gene fusion involving the androgen responsive gene TMPRSS2 and the ERG gene following intrachromosomal rearrangement
- This leads to an overexpression of the ERG gene as a consequence of androgen dependant stimulation of the resulting fusion gene (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1014)
Clinical features
- TMPRSS2-ERG fusion may be an early event in prostate cancer, although marked intrafocal heterogeneity exists (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1033, Mod Pathol 2013;26:106)
- EWSR1-ERG or FUS-ERG rearrangements are together present in about 5% of Ewing sarcomas (Mod Pathol 2012;25:1378, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016;55:340)
- Hematopoietic oncogene that may play a direct role in myeloid leukemia pathogenesis FUS-ERG fusion is present in a subset of acute myeloid leukemias and ERG overexpression in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with poor prognosis (Cancer Res 2009;69:4665, Oncogene 2016;35:1965, J Clin Oncol 2009;27:5031)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining
Uses by pathologists
- Currently one of the best available markers of endothelial differentiation, including vascular neoplasms, such as hemangioma, hemangioendothelioma, angiosarcoma and Kaposi sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:432)
- Aids in confirming / ruling out lymphovascular invasion
- Anti-N terminus ERG monoclonal antibody is a useful marker for certain chondrogenic tumors (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:125, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:1043)
- Differentiating between prostatic small cell carcinoma (positive) and small cell carcinoma of lung or bladder (negative) (Hum Pathol 2011;42:11, Mod Pathol 2011;24:820)
- Nuclear expression can assess the presence of TMPRSS2-ERG or SLC45A3-ERG fusions in prostatic adenocarcinomas; however, since only about 40 - 50% of these tumors harbor ERG rearrangement and as high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or other mimics can also be positive, this marker is rarely used for the diagnosis of prostate adenocarcinoma in routine clinical practice, providing useful information (beyond other stains) in only 29% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1014, Adv Anat Pathol 2018;25:387, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1007)
- Useful marker in distinguishing between leukemia cutis (mainly acute myeloid leukemia) and reactive nonleukemic predominantly neutrophilic infiltrates in the skin (Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:672)
- ERG was shown to be positive in almost 70% of cases of acute myeloid leukemia / myeloid sarcoma, especially those with myeloid differentiation when compared with those of pure monocytic / monoblastic differentiation, which were ERG negative, while all blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms were negative (Hum Pathol 2022;124:1)
- ERG can serve as a reliable marker of immature myeloid cells in cases of extramedullary hematopoiesis, bone marrow trephine biopsies and in adrenal myelolipomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:432, Hum Pathol 2022;124:1)
- Reliably identifies the presence of ERG fusions in Ewing sarcomas (Mod Pathol 2012;25:1378, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016;55:340)
- Strong and diffuse nuclear expression is present in EWSR1-SMAD3 rearranged fibroblastic tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1325, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:522)
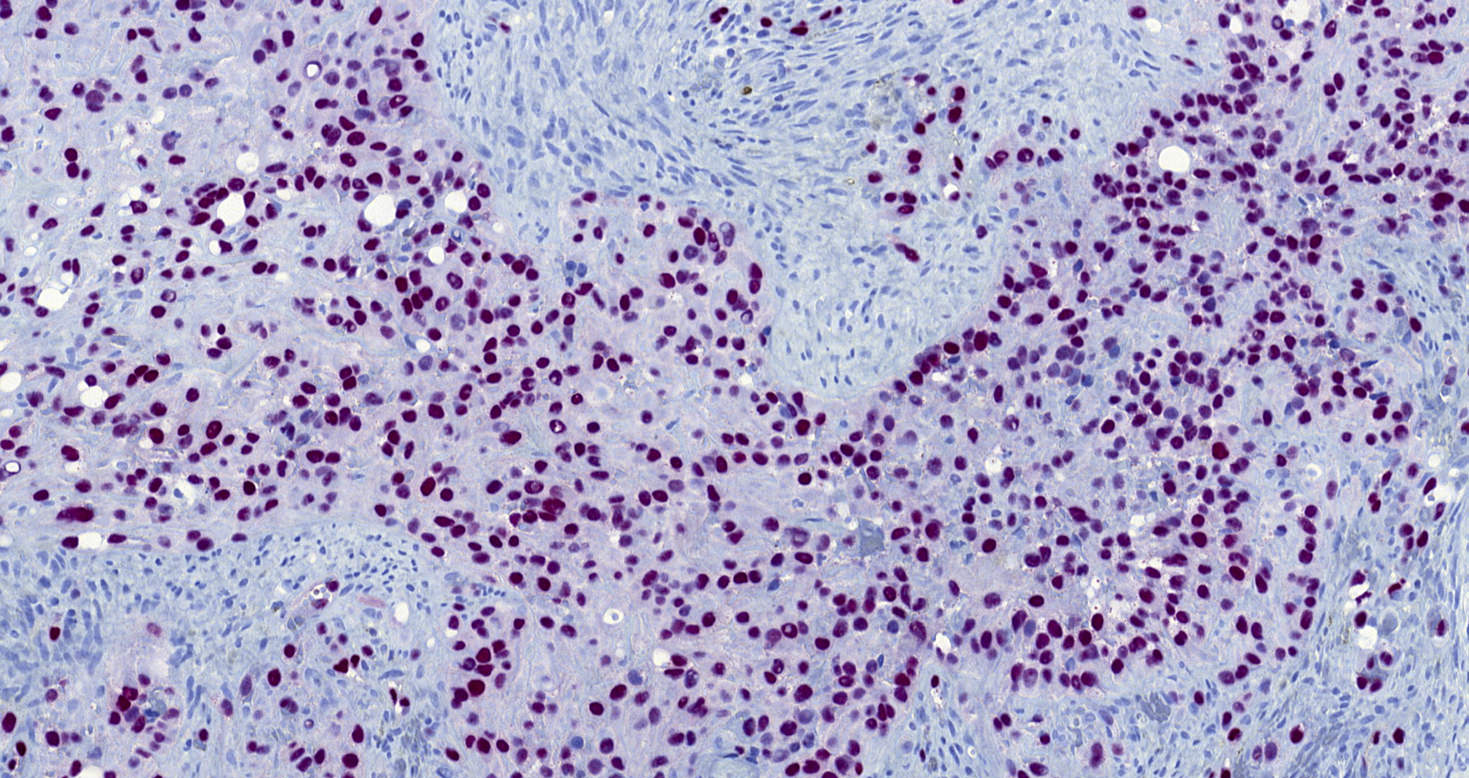
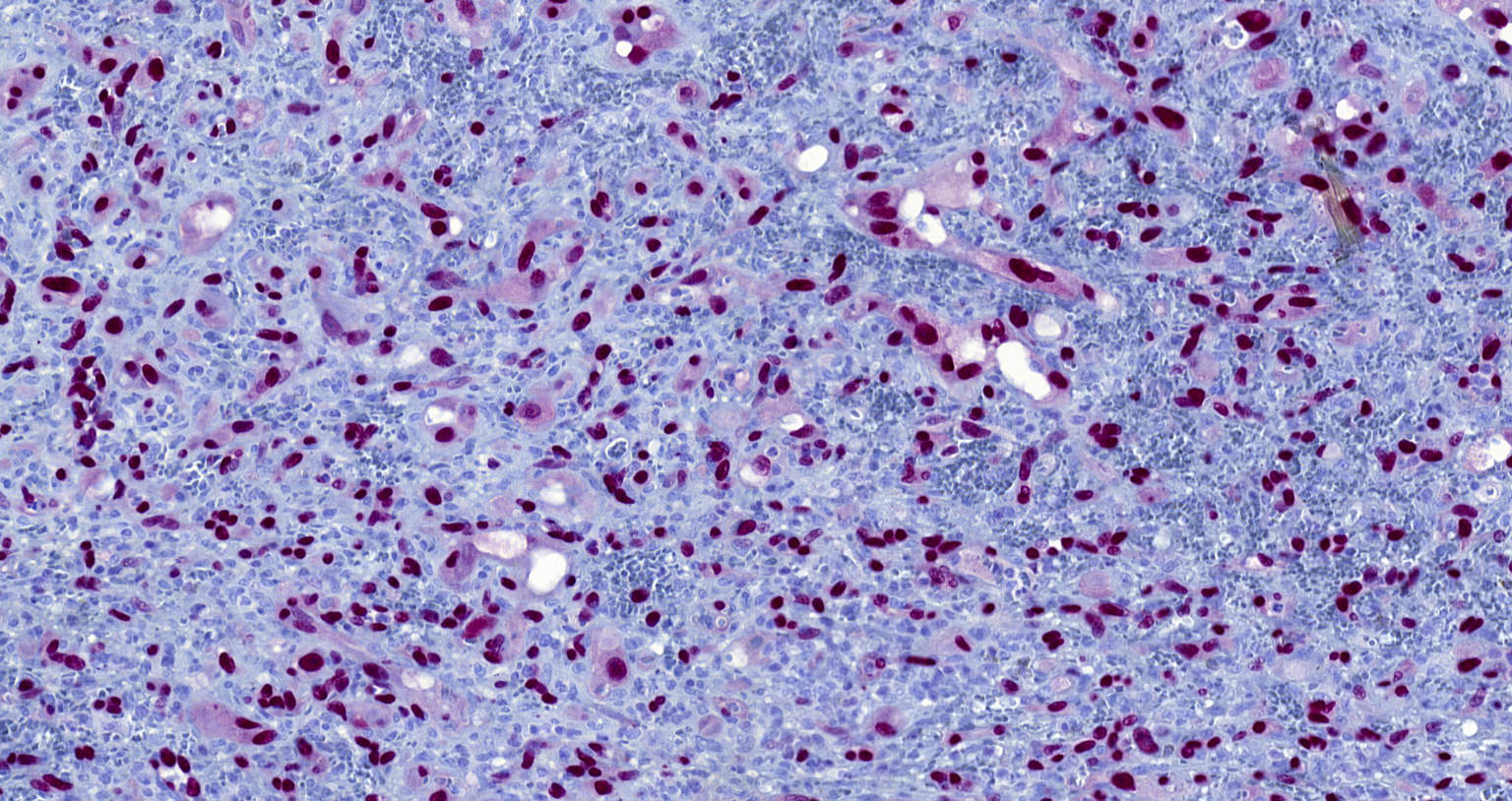
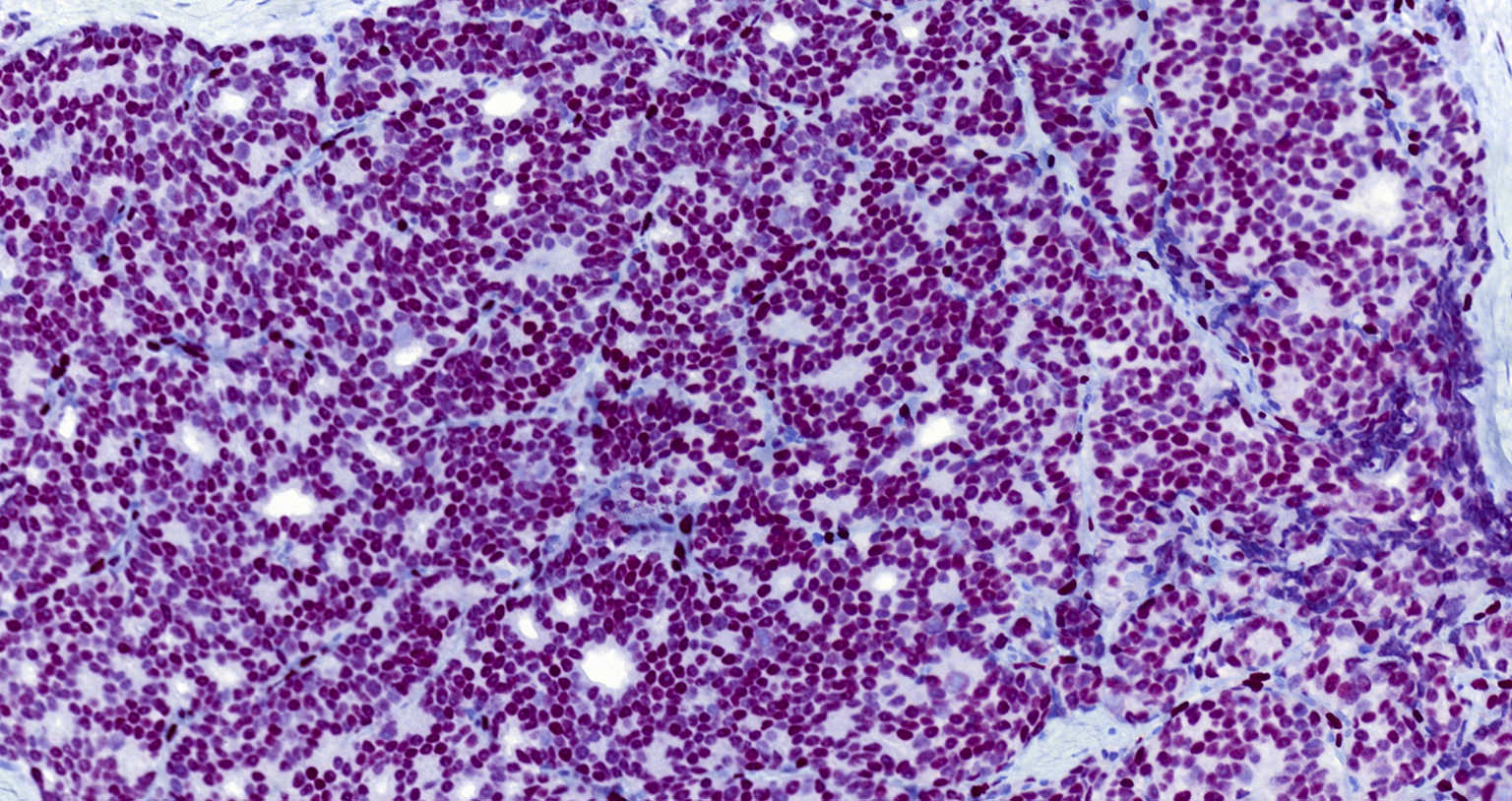
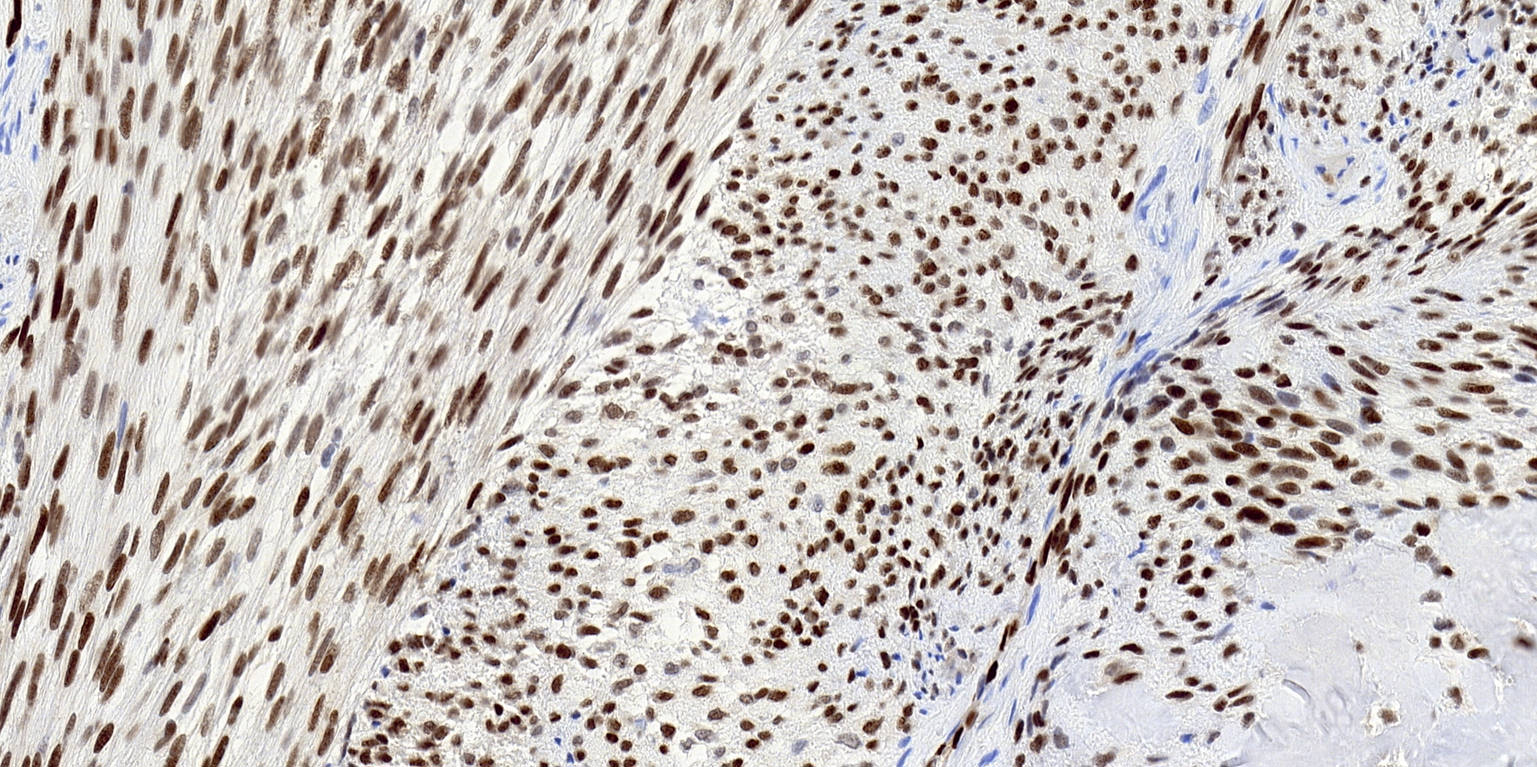
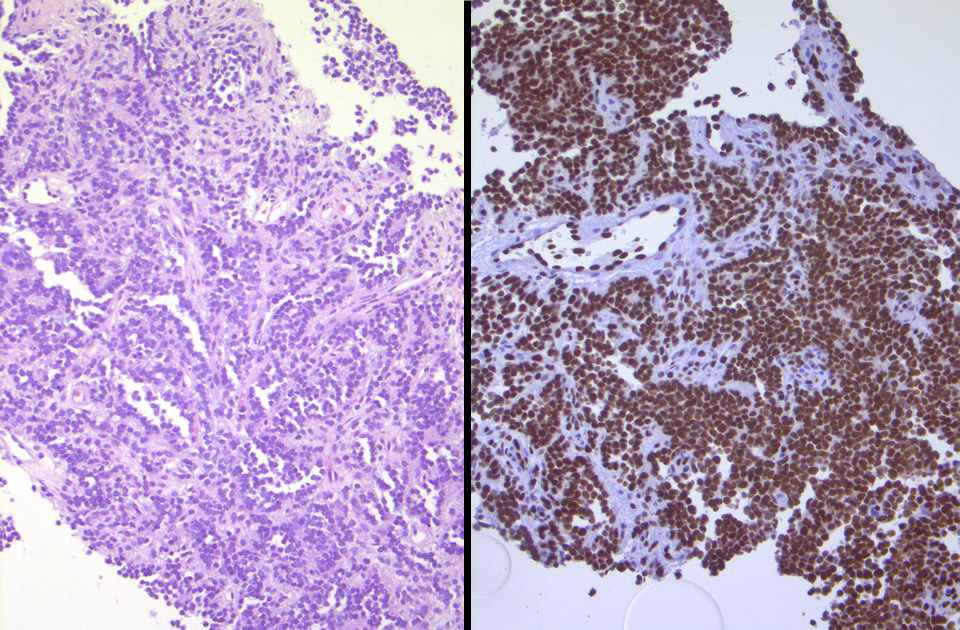
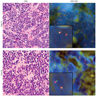
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Michael Michal, M.D., Ph.D., Brendan C. Dickson, M.D., M.Sc. and Debra Zynger, M.D.
Positive staining - normal
- Both blood vessel and lymphatic endothelial cells
- Subpopulation of immature myeloid cells in an adult bone marrow, extramedullary hematopoiesis and in adrenal myelolipomas (Hum Pathol 2022;124:1)
- Early embryonic subepidermal and paraspinal mesenchyme and periphery of cartilage (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:432)
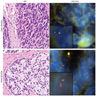
Positive staining - disease
- Highly sensitive and specific marker for benign and malignant vascular tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:432)
- Selected chondrogenic tumors (with anti-N terminus ERG monoclonal antibody only):
- Conventional chondrosarcoma
- Chondromyxoid fibroma
- Chondroblastic osteosarcoma
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:125, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:1043)
- EWSR1-SMAD3 rearranged fibroblastic tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1325)
- Fibrous histiocytomas, including cellular fibrous histiocytomas (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1003, Am J Clin Pathol 2015;144:A309)
- Weak to moderate expression in most calcifying aponeurotic fibromas (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:522)
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma (40 - 60%), high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (20 - 30%) or benign glands adjacent to prostatic adenocarcinoma and other high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or benign glands (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1062, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:608, Mod Pathol 2011;24:1128)
- Prostatic small cell carcinoma (but not small cell carcinoma from lung or bladder) (Hum Pathol 2011;42:11, Mod Pathol 2011;24:820)
- Nuclear staining for the antibody against N terminus of ERG is present in more than half of epithelioid sarcomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1007)
- Ewing sarcomas with EWSR1-ERG or FUS-ERG rearrangement (Mod Pathol 2012;25:1378, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016;55:340)
- Subset extramedullary myeloid tumors and acute myeloid leukemias / myeloid sarcomas (Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:672, Hum Pathol 2022;124:1)
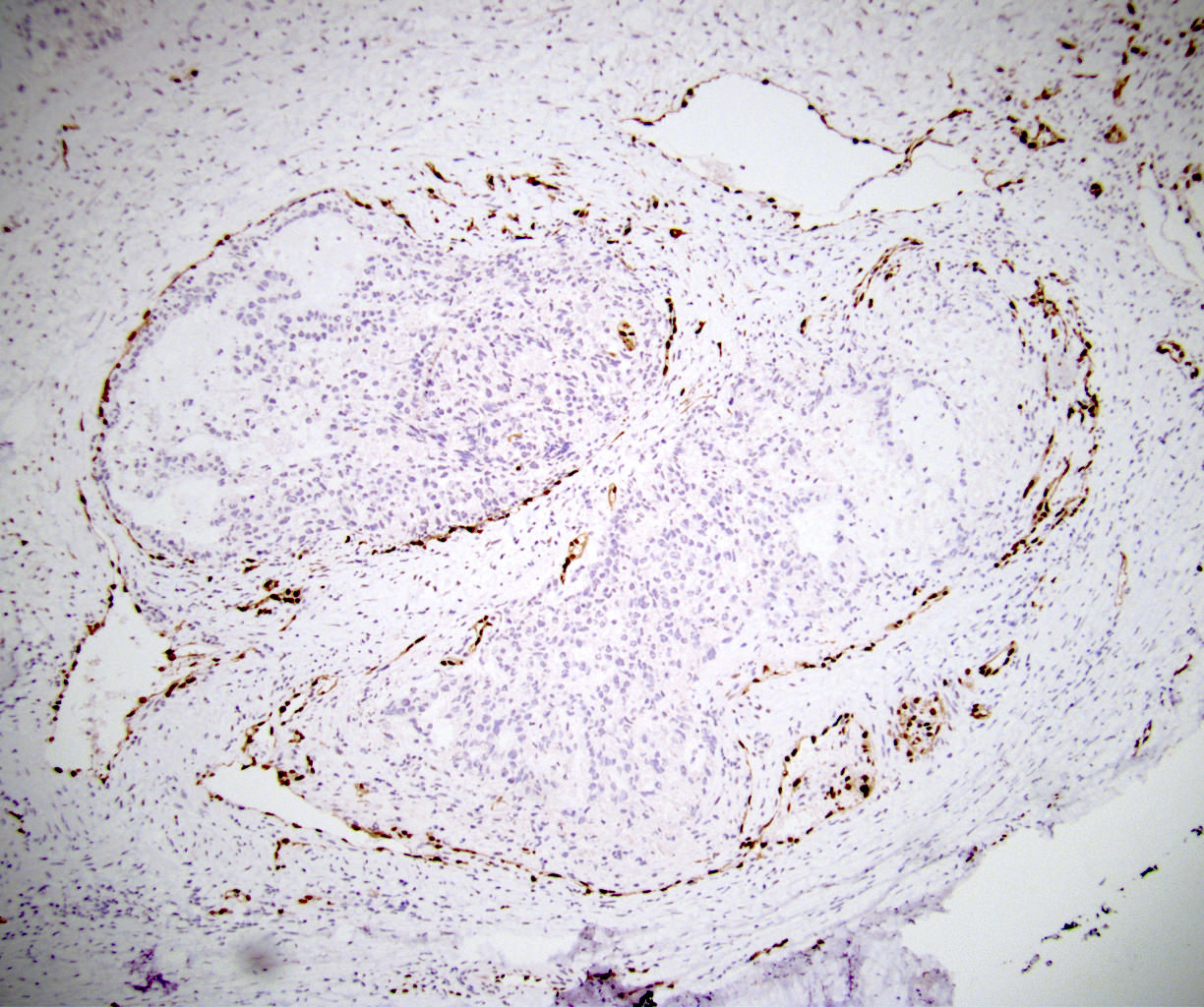
Negative staining
- Nuclear expression is absent in the vast majority of nonprostatic carcinomas and other mesenchymal, neuroectodermal and hematopoietic tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:432)
- All blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms are negative (Hum Pathol 2022;124:1)
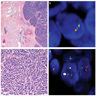
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Breast, excision:
- Postirradiation epithelioid angiosarcoma (see comment)
- Comment: There is an infiltrating tumor composed of malignant epithelioid cells, which focally form primitive vascular lumina, immunohistochemically show diffuse nuclear expression of ERG and are also positive with CD31 and CD34.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following neoplasms will most likely be ERG negative?
- Angiosarcoma
- Chondrosarcoma
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma
- Ewing sarcoma with EWSR1-ERG fusion
- Prostate adenocarcinoma with TMPRSS2-ERG fusion
Board review style answer #1