Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Stokes NL, Jimenez RE. Fibroma thecoma group. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisfibroma.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Sex cord stromal tumors composed of spindle, oval or round cells with varying amounts of collagen present
Essential features
- Hemorrhage and necrosis absent
- Variable cell density, variable collagen
- Usually no Sertoli or granulosa elements present but may have minor aggregates of other sex cord cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:391)
- Usually scanty mitoses (≤ 5 mitoses/10 high power fields), can be as high as 10 mitoses/10 high power fields
Terminology
- Synonyms:
- Fibrothecoma
- Thecofibroma
- Thecoma / fibroma group
- Testicular fibroma
ICD coding
- ICD-O:
- ICD-10: D29.20 - benign neoplasm of unspecified testis
- ICD-11: 2F34 & XH34A0 - benign neoplasm of skin of male genital organs & thecoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare tumor
- Age range: 16 - 69 years; mean age: 44 years (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1208)
- Often occurs in third or fourth decade of life
Sites
- Testis
- Paratestis
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
- May be associated with Gorlin syndrome (nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome), abnormalities of PTCH gene (J Pediatr Surg 2010;45:E1)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Commonly presents as slowly increasing unilateral testicular mass (Urol Ann 2021;13:308)
- Hormonal changes are extremely uncommon
- Clinically benign behavior with no reported recurrences or metastases (Urol Ann 2021;13:308)
Diagnosis
- Ultrasound
- Orchiectomy
Laboratory
- Hormone levels are typically within normal range
- Serum testosterone and estrogen may be elevated in some secreting tumors
- Tumor markers (beta human chorionic gonadotropin [hCG], alpha fetoprotein [AFP], lactate dehydrogenase [LDH]) are within normal range (Urol Case Rep 2020;33:101368, Urol Ann 2021;13:308)
Radiology description
- Well defined, hypoechoic, solid mass
- Can appear as a heterogeneous mass
Prognostic factors
- Benign behavior
- Even 10 mitoses per 10 high power fields show no adverse prognosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1208)
Case reports
- 31 year old man with a firm nodule in the right testis and a 14 year old boy with a nontender mass in the left testis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:391)
- 33 year old man with an incidental nodular mass in the left testis (Hum Pathol 2009;40:584)
- 37 year old man with a firm right testicular mass (Urol Case Rep 2020;33:101368)
- 51 year old man with a 2 year history of a small painless testicular mass, with recent size increase (Urol Ann 2021;13:308)
Treatment
- Diagnostic orchidectomy is curative; observation after orchidectomy is the only necessary treatment
Gross description
- Well defined, firm tumors ranging from 0.5 to 7.6 cm in greatest dimension (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1208)
- Cut surface is tan, yellow or white and solid to cystic; can have focally hemorrhagic areas
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Circumscribed but unencapsulated; encapsulated forms are rare
- Arranged in fascicles, storiform or a combination pattern in collagenized stroma with small blood vessels
- Herringbone pattern may be seen
- Variable cell density, variable collagen
- Usually scanty mitoses (≤ 5 mitoses/10 high power fields), can be as high as 10 mitoses/10 high power fields
- May be infiltrative and entrap seminiferous tubules; this feature has no impact on tumor behavior
- Usually no Sertoli or granulosa components are present but may have minor aggregates of other sex cord cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:391)
- If > 1 microscopic focus of other sex cord stromal cells, classify as mixed or unclassified since these tumors have metastatic potential unlike the classical fibroma
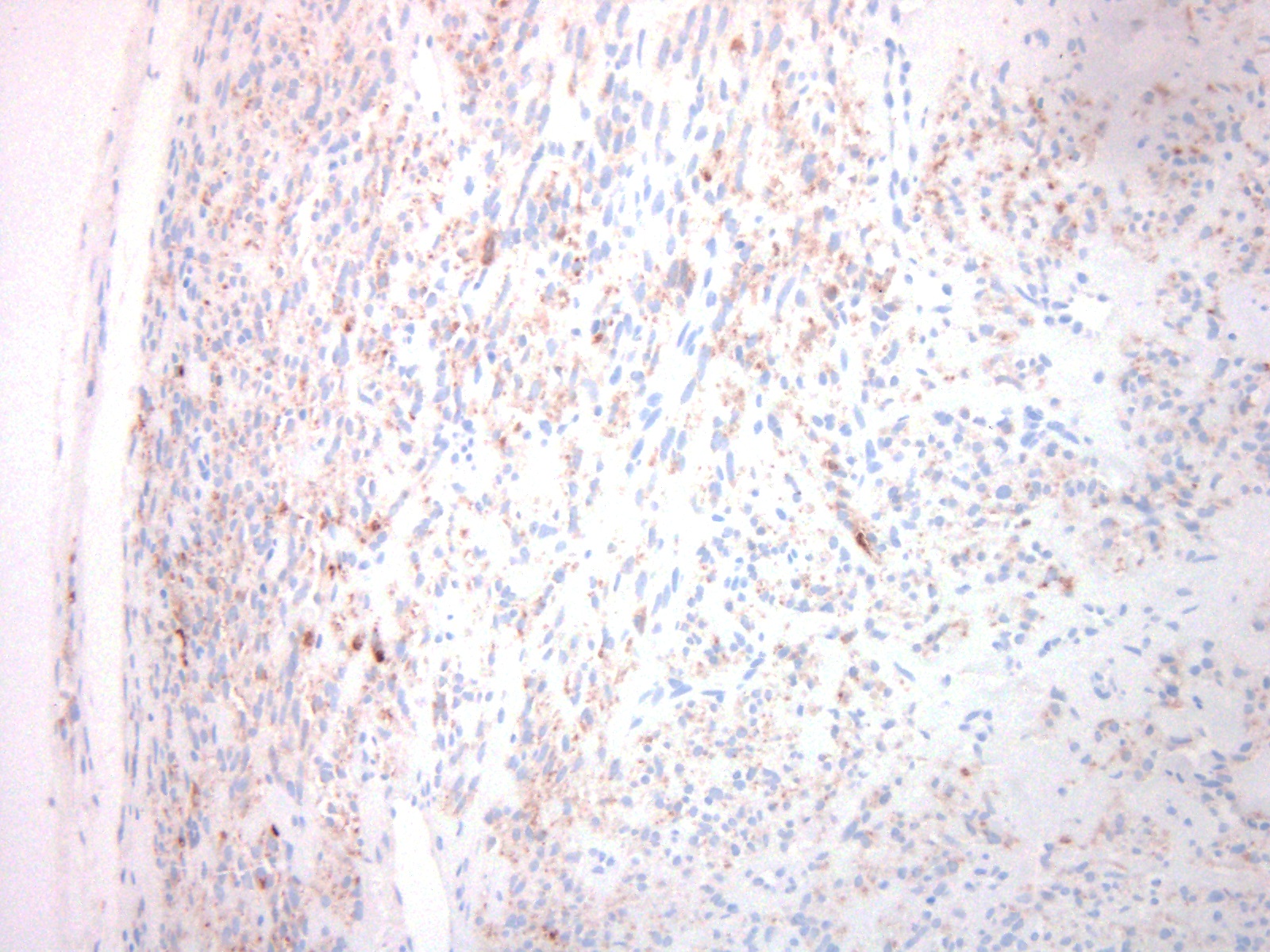
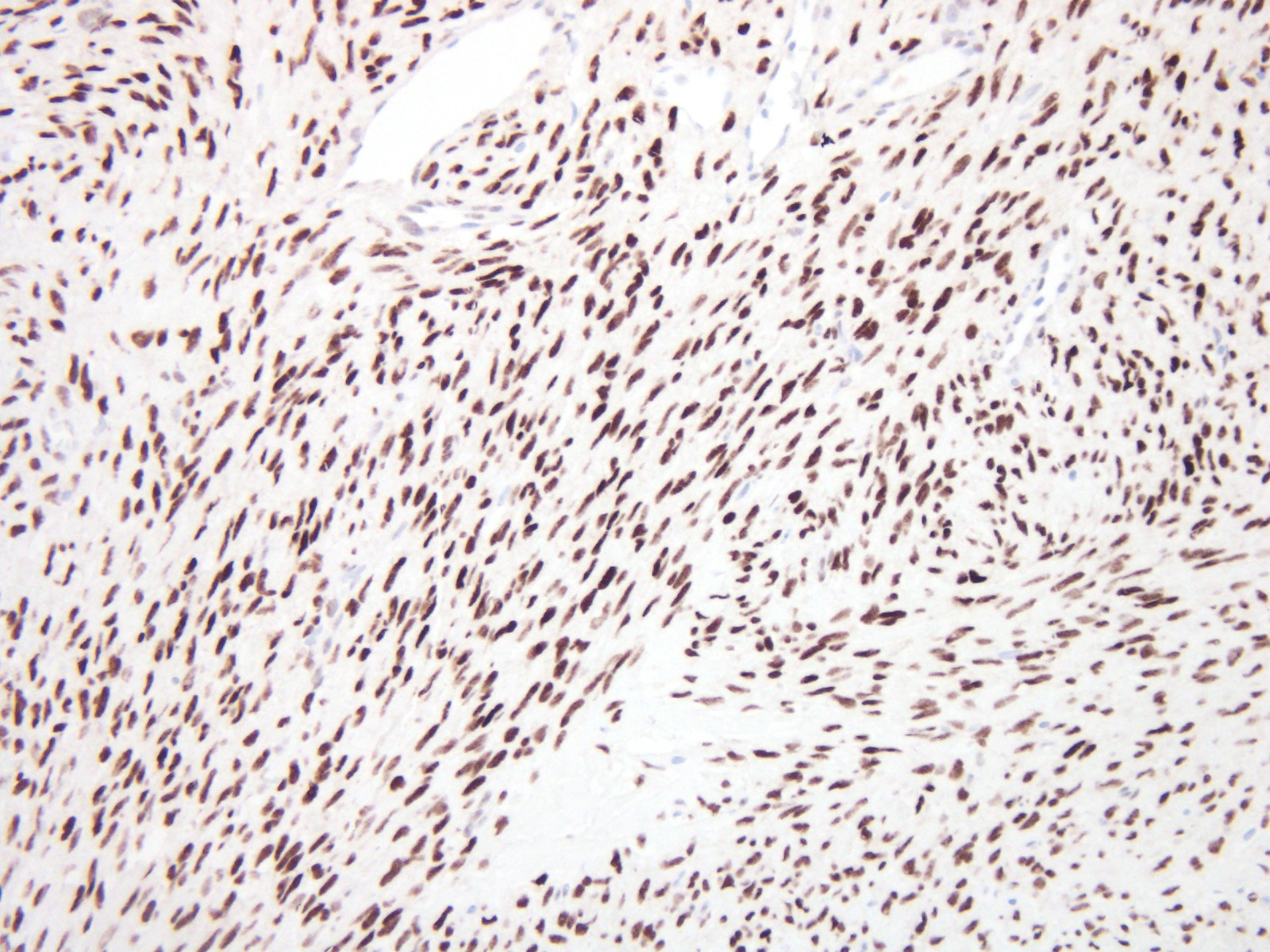
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Fibroma cells resemble both fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Although loss of heterozygosity at 9q22.3 (PTCH locus) is observed in 40% of sporadic ovarian thecoma fibromas, only one case in testis has been reported (J Pediatr Surg 2010;45:E1)
Sample pathology report
- Right testis, orchiectomy:
- Fibrothecoma (see comment)
- Comment: The neoplastic cells showed positivity for inhibin, smooth muscle actin and SOX9 while MelanA, KIT and desmin were negative. This is consistent with the diagnosis above.
Differential diagnosis
- Fibrosarcoma:
- Malignant tumor with infiltration, cytological atypia, frequent mitoses, necrosis
- Leiomyoma:
- Positive for muscle markers; negative for inhibin and other sex cord stromal markers
- Neurofibroma:
- Patchy S100 positive; negative for sex cord stromal markers
- Fibrous pseudotumors:
- Less cellular, more inflammatory cells
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- CD34 positive; tends to arise from extratesticular tissues like tunica albuginea, tunica vaginalis, gubernaculum, not testicular stromal cells
- Unclassified sex cord stromal tumors:
- Show more than focal incomplete Sertoli cell differentiation; strong positive S100 is useful stain
- Myoid gonadal stromal tumor:
- Granulosa cell tumor:
- Nodular growth pattern with cells showing nuclear grooves; luteinization of cells and mitotic figures are rare
- FOXL2 mutations can be seen
- Reticulin staining shows fibers surrounding aggregates of cells instead of individual cells as in fibrothecoma
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 65 year old man presented with a painless mass in his right testis. An ultrasound demonstrated a solid mass, measuring 5.4 cm in greatest dimension. He was scheduled for a radical orchiectomy. The resected tumor's histology is depicted in the image above. What is the best course of action after this diagnosis?
- Chemotherapy
- Observation
- Orchiectomy
- Radiation
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following immunohistochemical profiles best supports the diagnosis of a fibrothecoma of the testis?
- Calretinin positive, S100 negative, CD34 positive
- CD56 negative, inhibin negative, smooth muscle actin negative
- Inhibin positive, FOXL2 positive, MelanA negative
- MIC2 positive, FOXL2 negative, S100 negative
Board review style answer #2