Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Alhatem A, Heller D. S. Fibroepithelial (stromal) polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/vaginafibroepithelial.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign mesenchymal mass characterized by a polypoid proliferation of the stroma with overlying squamous epithelium
- Originally described by Norris and Taylor in 1966 (Cancer 1966;19:227)
Essential features
- Common benign polypoid proliferation of the stroma with overlying squamous epithelium
- Hormonally related and affects women, mostly of reproductive age
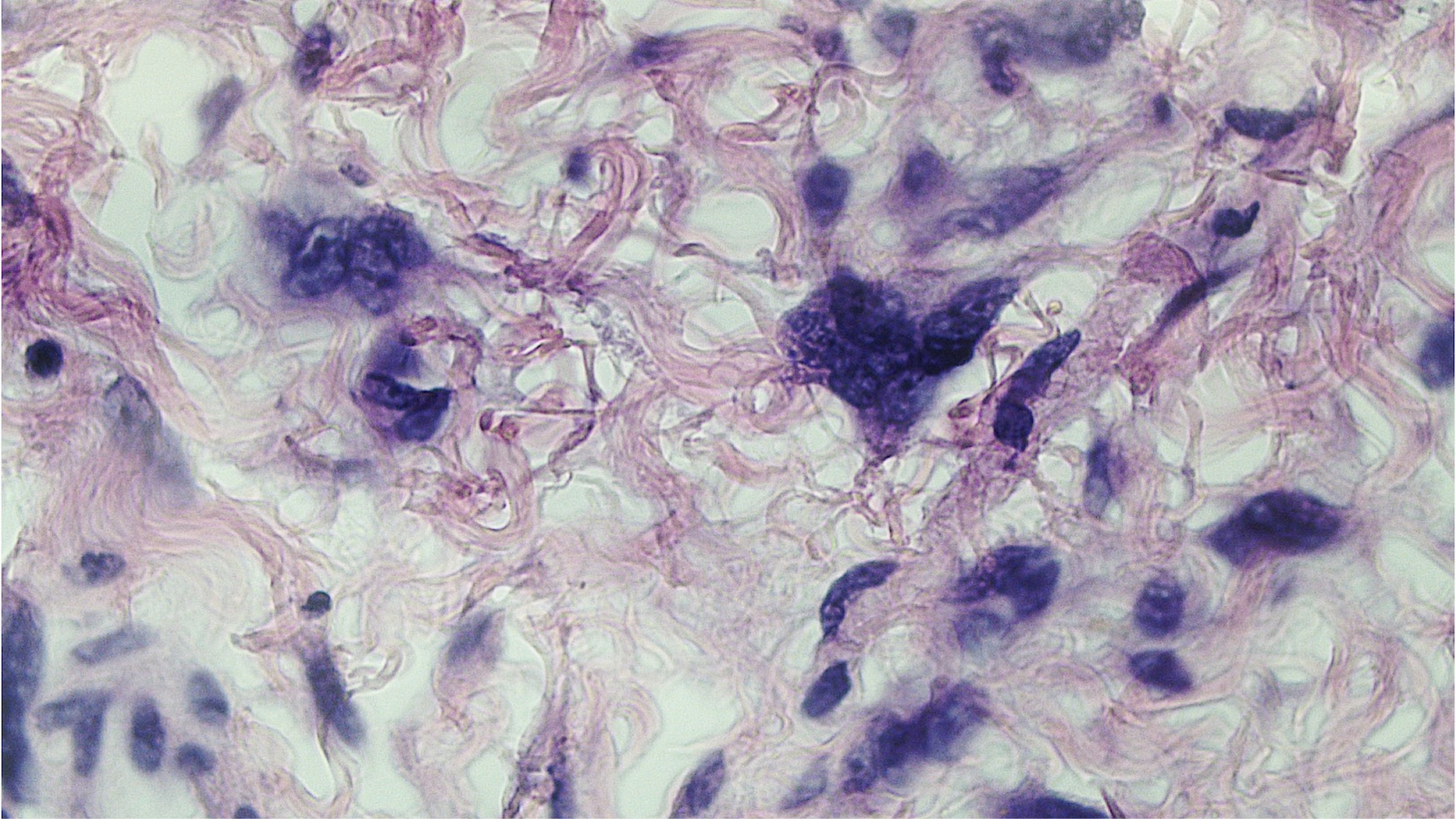
- The key to diagnosis is the characteristic stellate and multinucleated stromal cells
- May raise concern of a sarcoma due to the stromal cellularity
- Complete surgical resection is curative or otherwise it can recur
Terminology
- Formerly known as pseudosarcoma botryoides (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: N84.3 - polyp of vulva
Epidemiology
- Common
- Reproductive age women, often during pregnancy or in postmenopausal women taking hormone replacement therapy
Sites
- Most common in vagina
- Can also occur in the vulva or cervix (Gynecol Oncol 2005;98:168)
- Rarely extragenital sites (BMC Res Notes 2013;6:345)
Pathophysiology
- Reactive hyperplastic process arising from the distinctive specialized subepithelial stromal cells of the lower female genital tract (Histopathology 2000;36:97)
- Some of these stromal cells exhibit hormonal responsiveness and immunoreactivity to estrogen and progesterone receptors (Am J Perinatol 1991;8:236)
- Due to hormone induced hyperplasia of loose subepithelial connective tissue or end stage of granulation tissue (J Clin Pathol 1992;45:235)
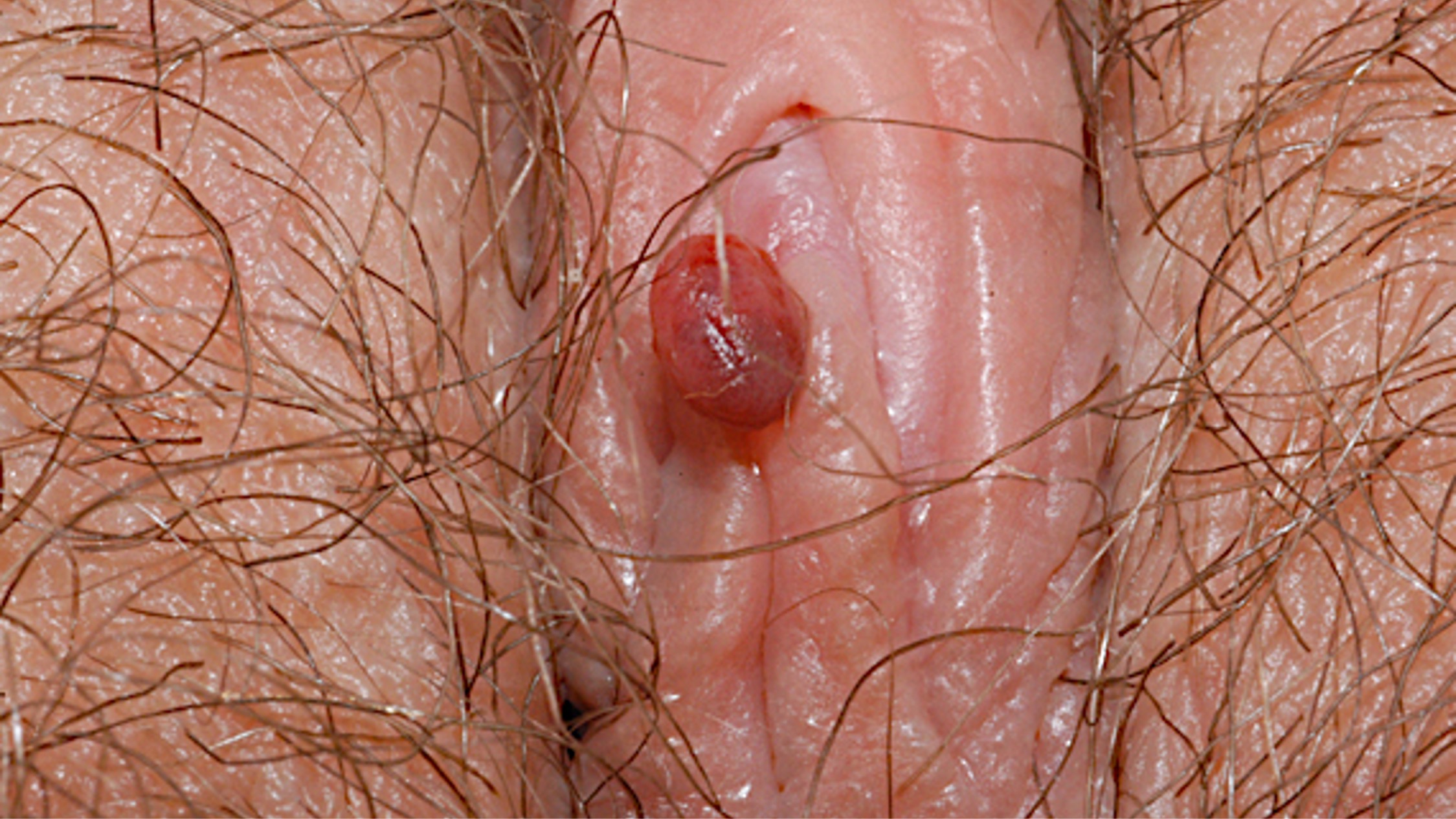
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic
- Occasionally can cause bleeding, discharge and general discomfort
Diagnosis
- Morphology is the key to diagnosis
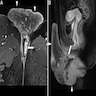
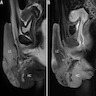
Radiology description
- Imaging is rarely done but the typical findings are (Jpn J Radiol 2010;28:609):
- Polypoid stromal proliferation
- Hyper and hypointense areas
- Covering surface epithelium
- Central fibrovascular core
- No focal or diffusion restriction
- No pelvic lymph node enlargement
Prognostic factors
- Benign, may recur during pregnancy, often regresses following delivery
Case reports
- 7 month old with a labial papule (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:465)
- 16 year old girl with large pedunculated mass (Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki) 2018;39:127)
- 16 year old girl with vulvar mass (Gynecol Oncol 2005;98:168)
- 21 year old woman with a giant mass (Ann Surg Innov Res 2013;7:8)
- 31 year old woman with labial mass (BMJ Case Rep 2018;2018:bcr2017222789)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is curative
- Recurrence is possible if incompletely excised (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1988;7:351)
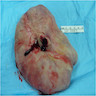
Gross description
- Polypoid, multilobulated or pedunculated mass usually < 5 cm
- Giant polyps (15 - 20 cm) are rare; likely arise from proliferation of mesenchymal cells within the hormonally sensitive subepithelial stromal layer and have been reported in association with chronic lymphedema (Gynecol Oncol 2005;98:168)
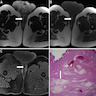
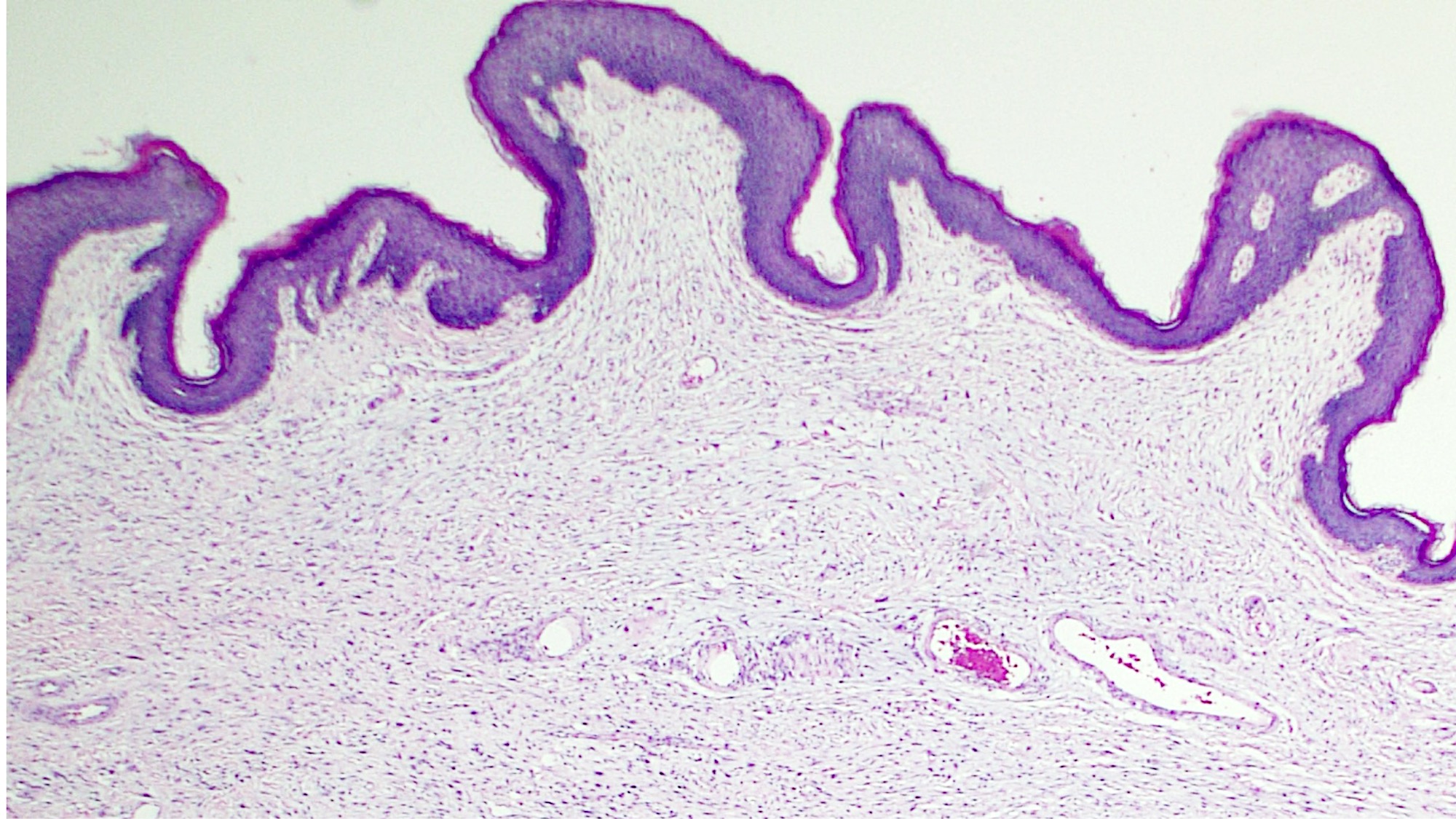
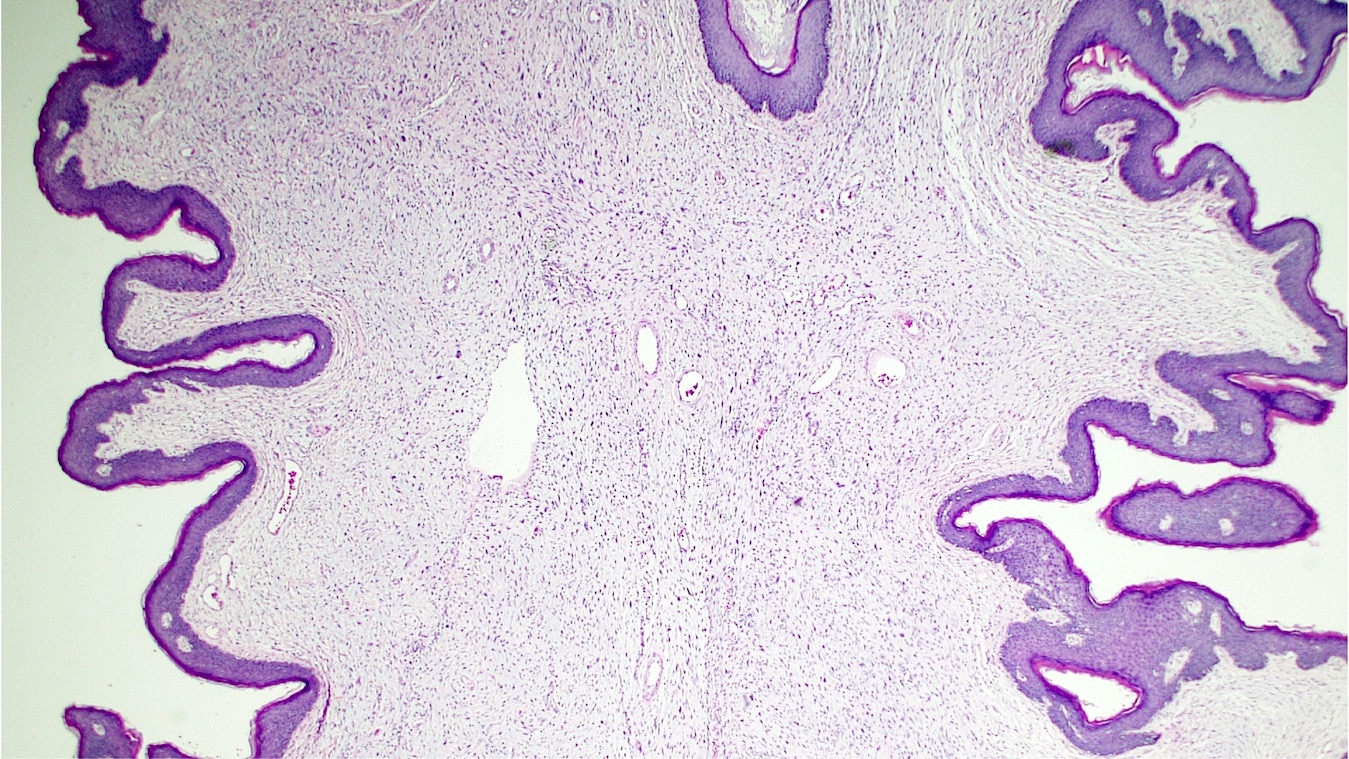
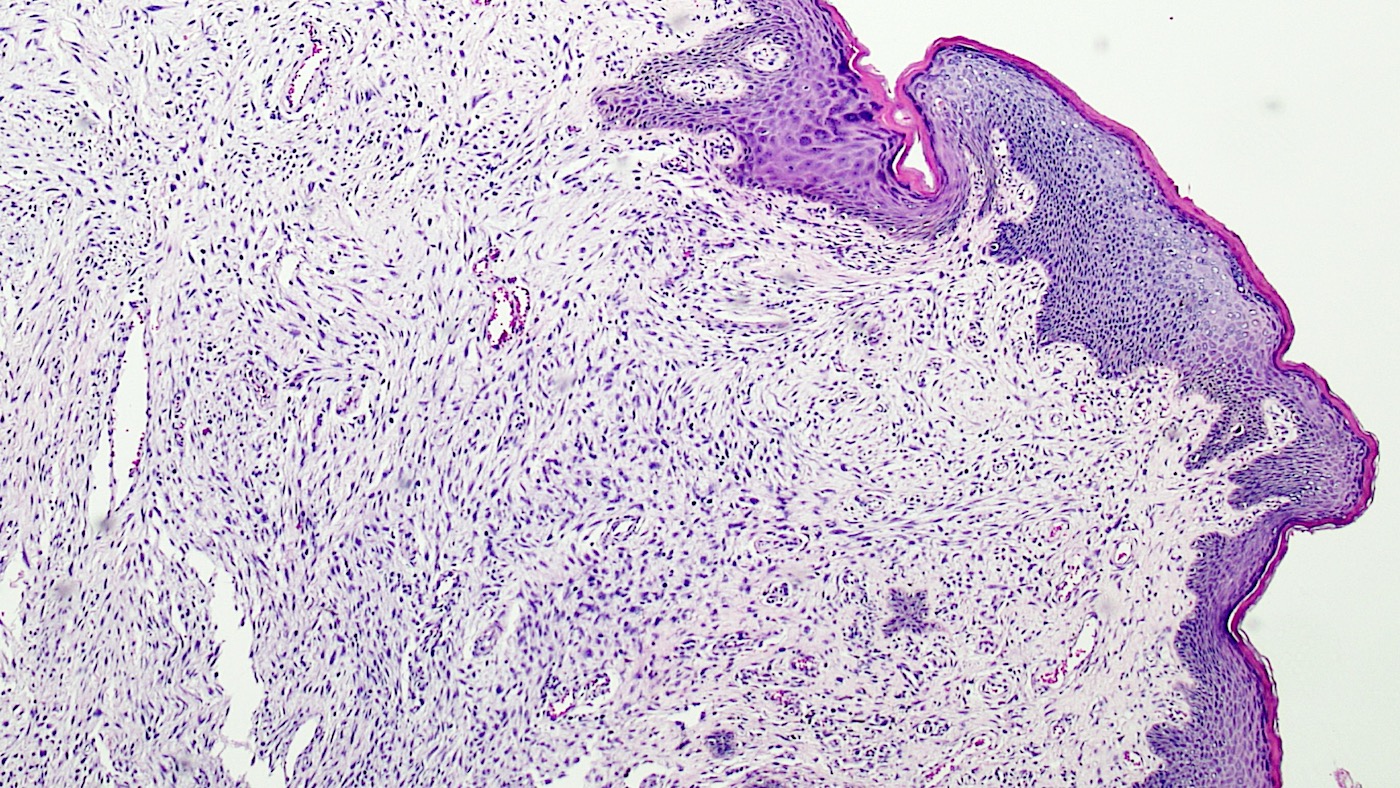
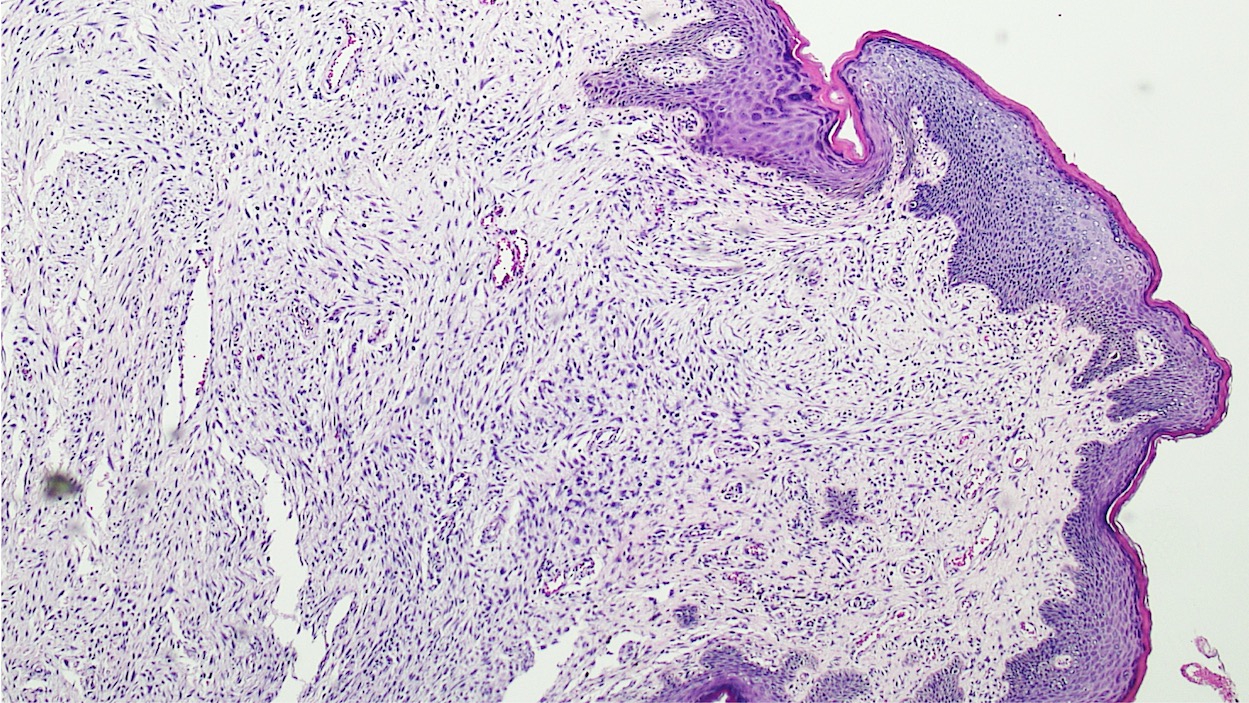
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Polypoid and noncircumscribed, extending to the epithelial / subepithelial interface (J Low Genit Tract Dis 2011;15:69, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:231)
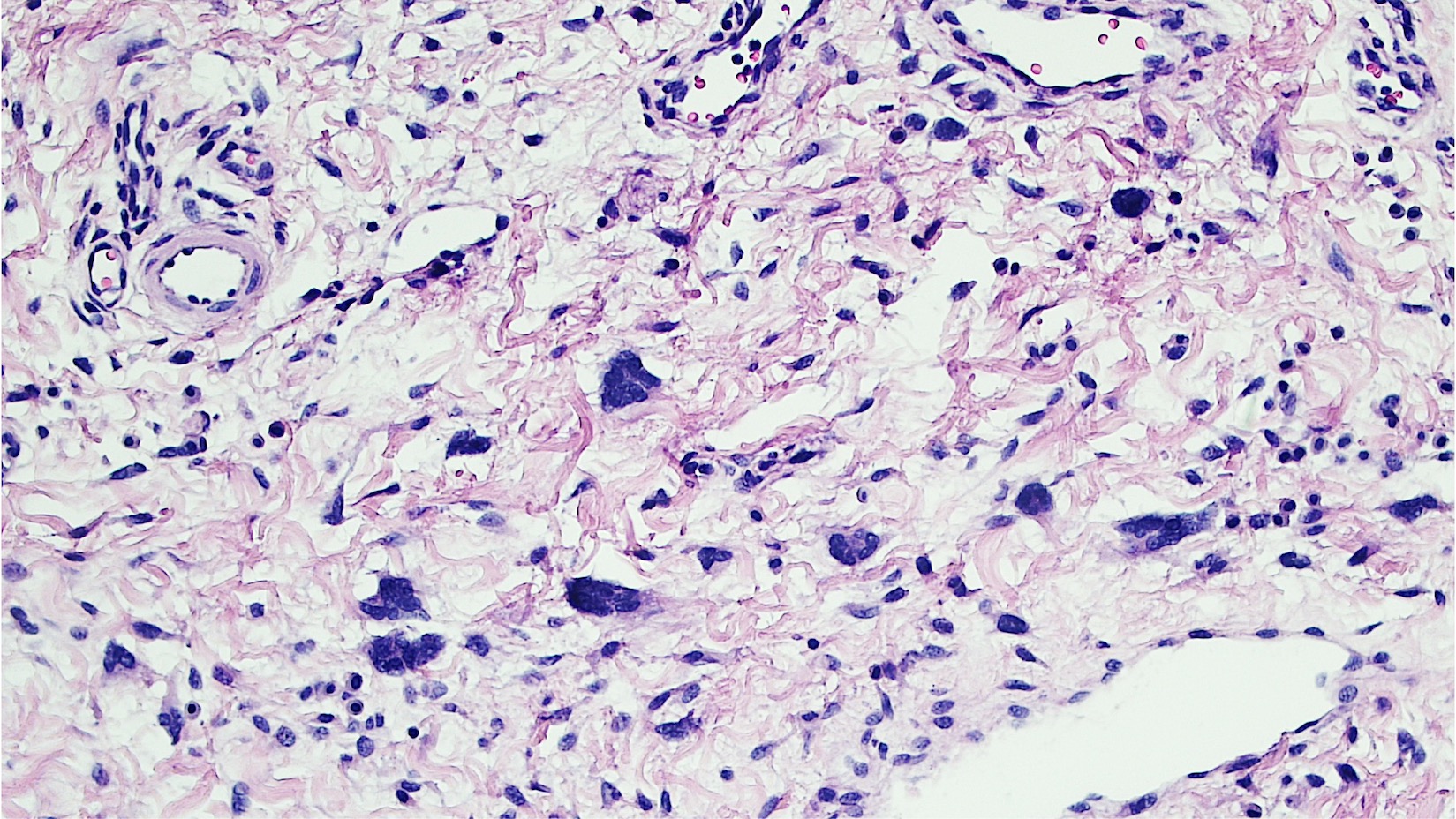
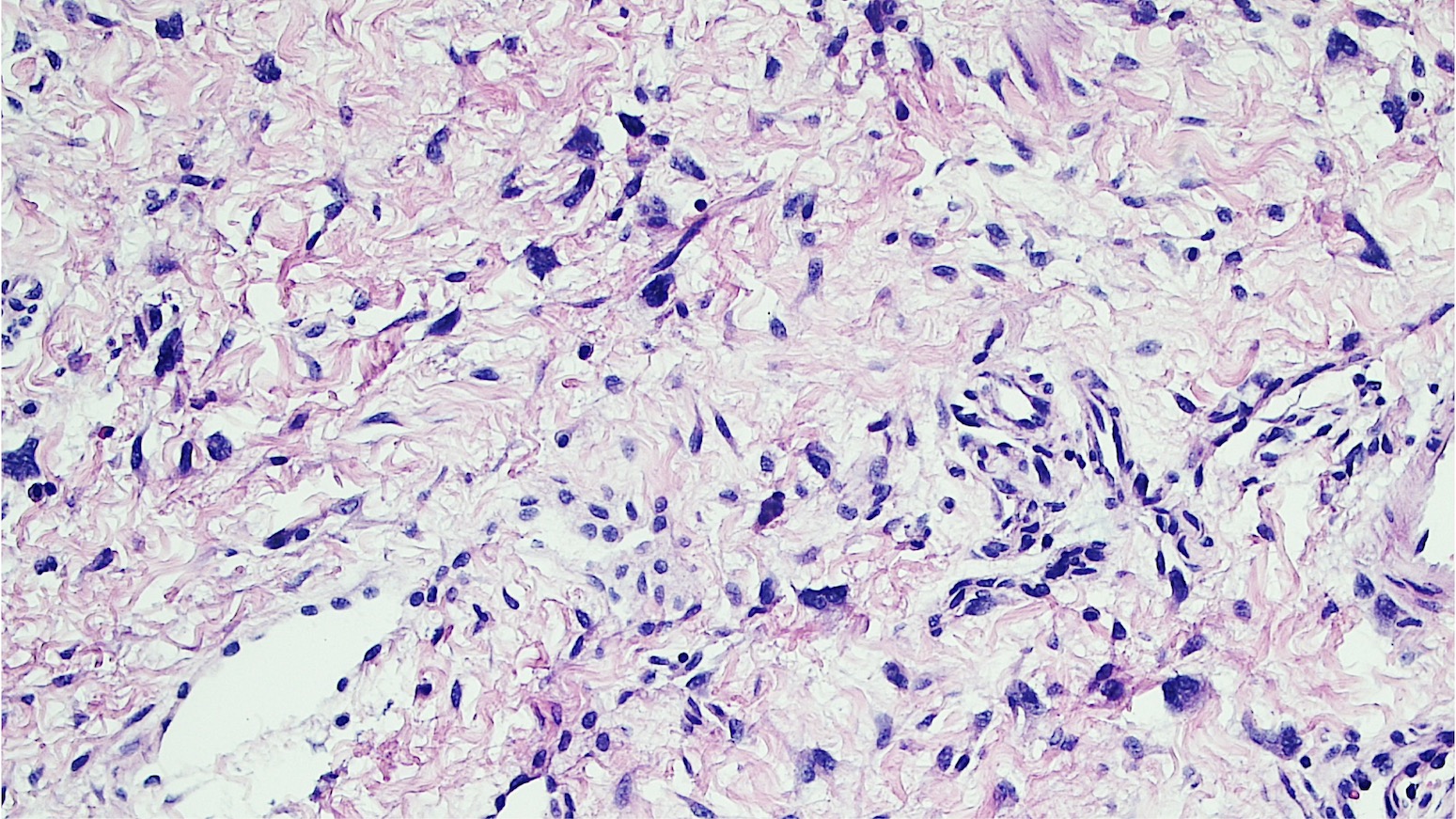
- 2 stromal cellularity variants: hypocellular form (spindle cells set within a loose collagenous myxoid-like stroma) or hypercellular variant (exhibits marked nuclear pleomorphism and frequent mitoses, including atypical forms), especially during pregnancy, therefore mimicking leiomyosarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:231)
- Overlying squamous epithelium may display reactive changes but without papillomatous architecture or koilocytosis, which distinguishes it from condyloma acuminatum (caused by human papillomavirus) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:460)
- Stellate cells should not be interpreted as sarcoma (J Low Genit Tract Dis 2011;15:134)
- Commonly found around blood vessels or near the epidermal stromal interface
- Acrochordon of vulva (skin tag) may be either predominantly epithelial (with papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis or attenuation of the epithelium) or primarily stromal (hypo or hypercellular with atypical cells) (Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki) 2018;39:127)
- Usually associated with systemic conditions: type 2 diabetes mellitus, genital psoriasis, congenital lymphedema, Crohn's disease or obesity
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Positive stains
- Desmin, ER, PR, vimentin variable, actin (occasional), MyoD1 (focal rarely) (Gynecol Oncol 2005;98:168, Hum Pathol 2020;99:75)
Negative stains
- SMA, HMGA2, S100, cytokeratin, myogenin (commonly) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1988;7:351)
Sample pathology report
- Vulva, lesion, excision:
- Fibroepithelial stromal polyp
Differential diagnosis
- Aggressive angiomyxoma:
- Deep location
- Large size (> 10 cm)
- Infiltrative borders
- Lack of hypercellular areas
- Presence of uniformly distributed blood vessels throughout the tumor
- Rearrangements of the high mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) gene (chromosome 12q15)
- Immunohistochemistry: strong nuclear reactivity for HMGA2
- Angiomyofibroblastoma:
- Subcutaneous rather than a polypoid mass
- Stromal cells are:
- Epithelioid with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Cluster around blood vessels
- Abundant thin walled blood vessels
- Mean age: fifth decade of life
- Mast cells within the stroma
- Epithelioid and spindle cells are myofibroblastic in origin
- Immunohistochemistry: positive for desmin with coexpression of BCL2 and CD99
- Cellular angiofibroma:
- Well circumscribed
- Moderately cellular stroma
- Intersecting short fascicles of bland spindle cells
- Numerous medium sized blood vessels often with thick hyalinized walls
- Immunohistochemistry: weak to absent staining with desmin and SMA and variably positive for CD34
- Loss of 13q14 (FOX1A1) (similar to spindle cell lipoma and extramammary myofibroblastoma)
- Superficial angiomyxoma:
- Superficial location
- Multinodular growth pattern in a myxoid stroma
- Thin blood vessels
- Neutrophils in the stroma
- Lack of stellate stromal cells
- Mostly found in the head and neck and rarely in the vulva
- Multiple extragenital superficial angiomyxomas are strongly associated with Carney complex
- Prepubertal vulvar fibroma:
- Botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Usually under 5 years of age
- Cambium layer
- Invasion
- Rapid growth
- Cross striations
Additional references
Board review style question #1
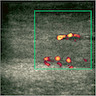
- A 25 year old woman presented with a vulvar mass, measuring 3.0 cm in diameter. The lesion was excised and the H&E image is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Superficial angiomyxoma
- Cellular angiofibroma
- Fibroepithelial stromal polyp
- Angiomyofibroblastoma
- Acrochordon of vulva
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
- Which of the following morphologic features is characteristic of fibroepithelial stromal polyps?
- Uniformly distributed blood vessels
- Thin blood vessels
- Thick walled blood vessels
- Stellate cells around the blood vessels
- Abundant thin walled blood vessels
Board review style answer #2