10 May 2006 - Case #45
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
This case was contributed by Dr. Ankur Sangoi, Stanford University Department of Pathology, Stanford, California, USA.
Case #45
Clinical history:
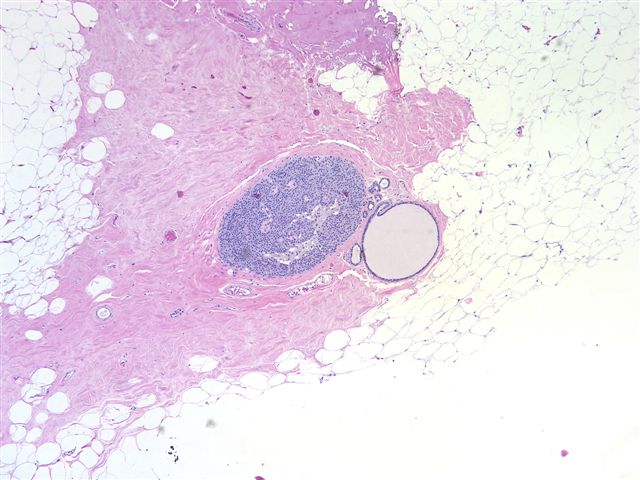
A 72 year old woman with no prior history underwent a lumpectomy for calcifications on her mammogram.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
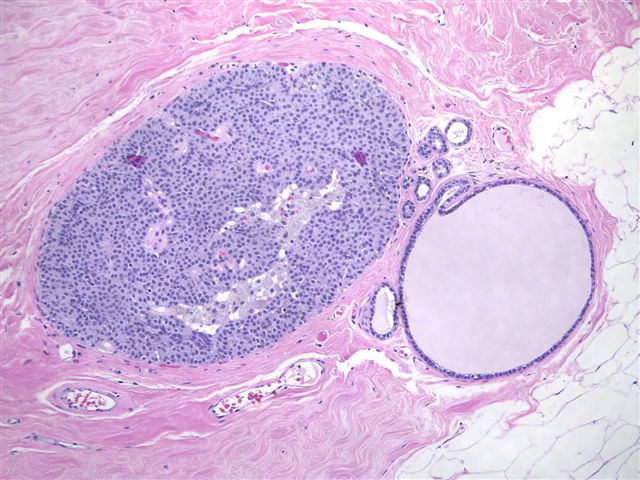
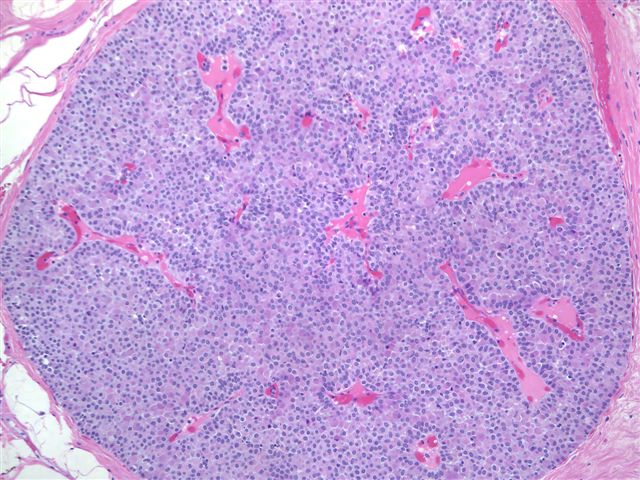
Diagnosis: Low grade DCIS with neuroendocrine features
Stain images:
Discussion:
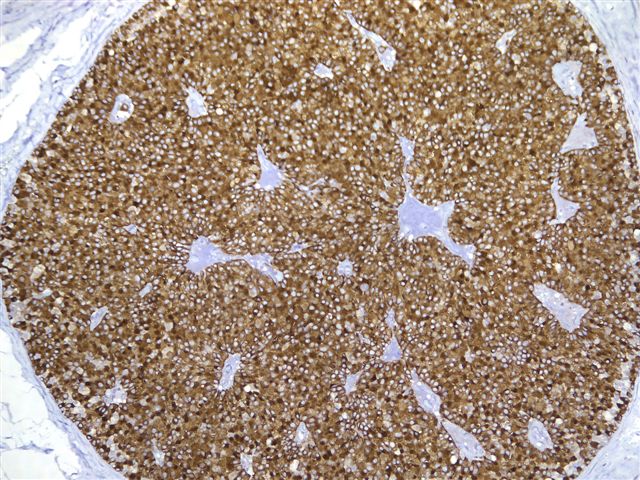
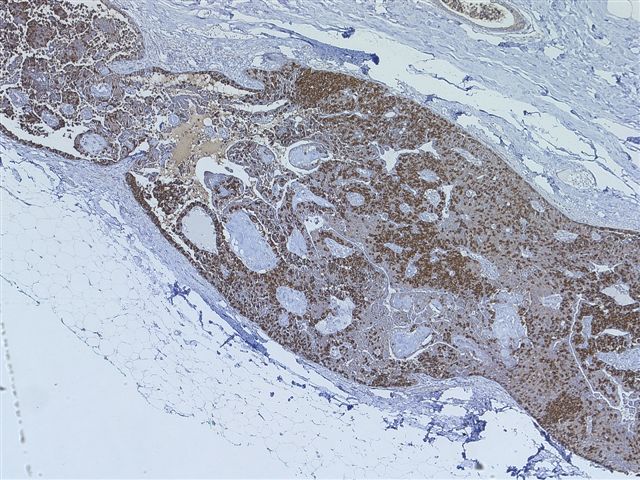
An immunostain for synaptophysin confirmed the neuroendocrine nature of the tumor cells (image 9, image 10).
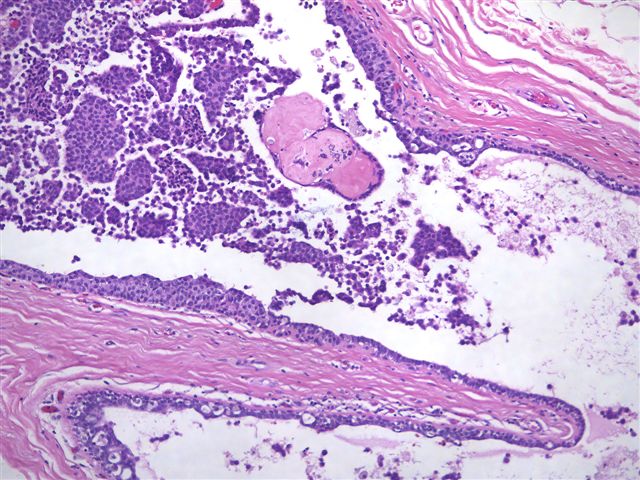
Neuroendocrine type DCIS is a rare variant that is also called intraductal papillary carcinoma. It typically occurs in women age 60 years or greater and is often accompanied by a breast mass or nipple discharge. It is frequently associated with intraductal papilloma with pagetoid involvement by the tumor cells and despite its low grade nature, may have an invasive component, which often has mucinous or endocrine features (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1237, Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:921).
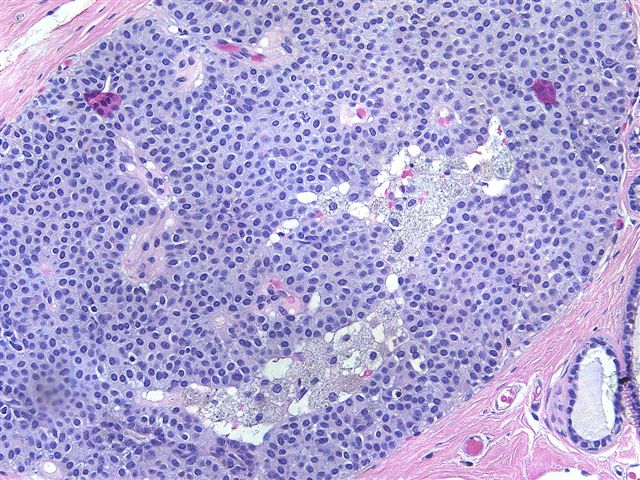
Microscopically, the tumor has a solid growth pattern or may have neuroendocrine-like festoons and rosettes and a prominent fibrovascular septa. The cells are polygonal, oval or spindled, with abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and bland, oval nuclei. There may be accumulation of basophilic intracellular mucin. Stromal fibrosis is variable. There is usually no necrosis.
Cytologic smears show plasmacytoid tumor cells and arborizing papillary fronds (Cancer 2000;90:286).
Tumor cells are immunoreactive for neuroendocrine markers chromogranin, synaptophysin and neuron specific enolase. They are usually ER+ and PR+ and negative for high molecular weight cytokeratin, p53, HER2 and Ki67 (Histopathology 2004;45:343). Ultrastructural examination shows dense core neurosecretory granules and larger mucigen granules.
The differential diagnosis includes florid epithelial hyperplasia and papilloma, which can be distinguished based on the monomorphic cell population associated with DCIS or the neuroendocrine immunostains.
References: Am Surg 2000;66:1163 (case report)
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
This case was contributed by Dr. Ankur Sangoi, Stanford University Department of Pathology, Stanford, California, USA.
Case #45
Clinical history:
A 72 year old woman with no prior history underwent a lumpectomy for calcifications on her mammogram.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Click here for diagnosis and discussion:
Diagnosis: Low grade DCIS with neuroendocrine features
Stain images:
Discussion:
An immunostain for synaptophysin confirmed the neuroendocrine nature of the tumor cells (image 9, image 10).
Neuroendocrine type DCIS is a rare variant that is also called intraductal papillary carcinoma. It typically occurs in women age 60 years or greater and is often accompanied by a breast mass or nipple discharge. It is frequently associated with intraductal papilloma with pagetoid involvement by the tumor cells and despite its low grade nature, may have an invasive component, which often has mucinous or endocrine features (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1237, Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:921).
Microscopically, the tumor has a solid growth pattern or may have neuroendocrine-like festoons and rosettes and a prominent fibrovascular septa. The cells are polygonal, oval or spindled, with abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and bland, oval nuclei. There may be accumulation of basophilic intracellular mucin. Stromal fibrosis is variable. There is usually no necrosis.
Cytologic smears show plasmacytoid tumor cells and arborizing papillary fronds (Cancer 2000;90:286).
Tumor cells are immunoreactive for neuroendocrine markers chromogranin, synaptophysin and neuron specific enolase. They are usually ER+ and PR+ and negative for high molecular weight cytokeratin, p53, HER2 and Ki67 (Histopathology 2004;45:343). Ultrastructural examination shows dense core neurosecretory granules and larger mucigen granules.
The differential diagnosis includes florid epithelial hyperplasia and papilloma, which can be distinguished based on the monomorphic cell population associated with DCIS or the neuroendocrine immunostains.
References: Am Surg 2000;66:1163 (case report)