19 December 2013 - Case #295
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. Ankur Sangoi, El Camino Hospital (California), for contributing this case. This case was reviewed in May 2020 by Dr. Jennifer Bennett, University of Chicago and Dr. Carlos Parra-Herran, University of Toronto.
Case #295
Clinical history:
A 50 year old woman presented with an ovarian mass, which was excised.
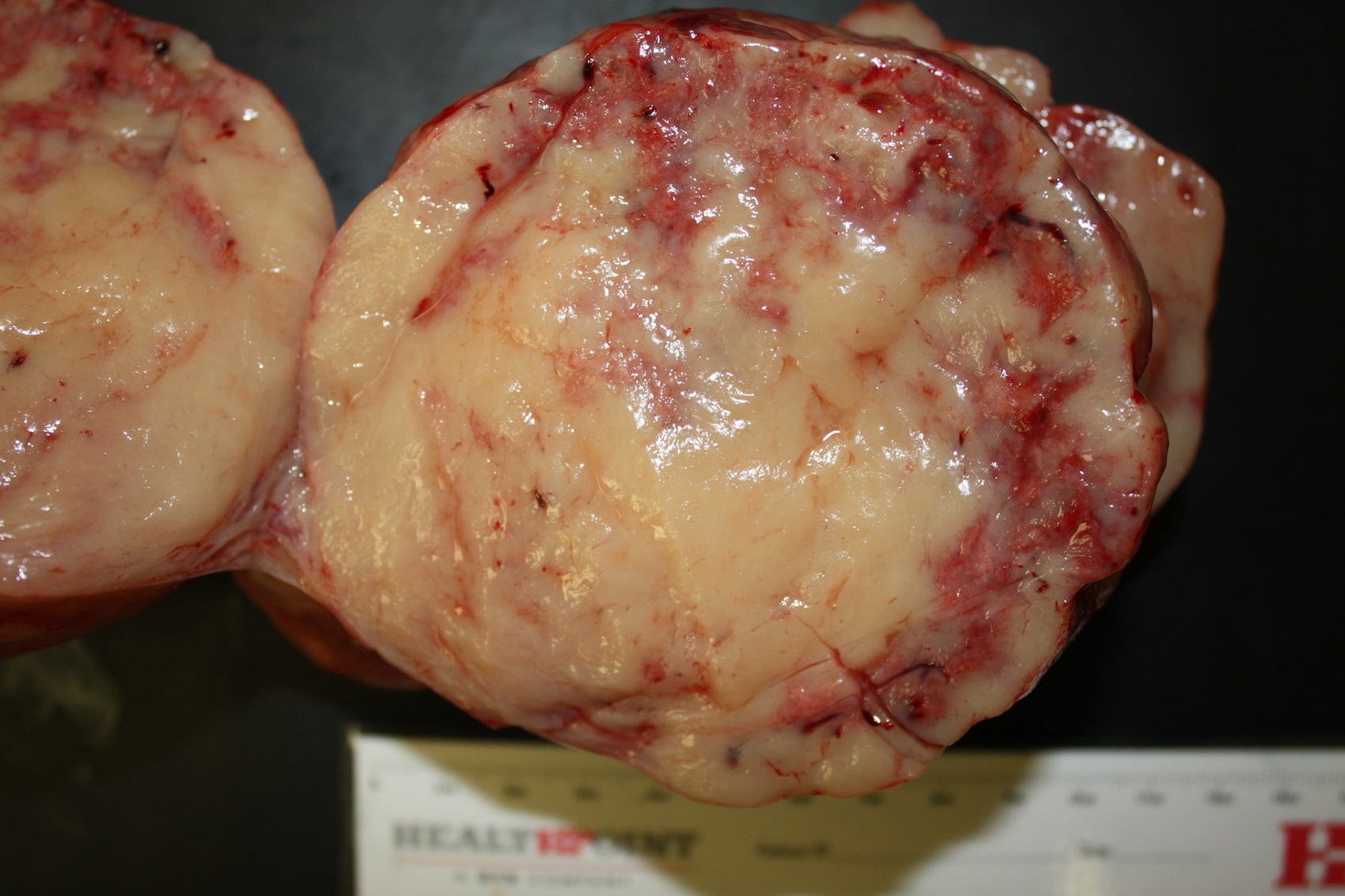
Gross images:
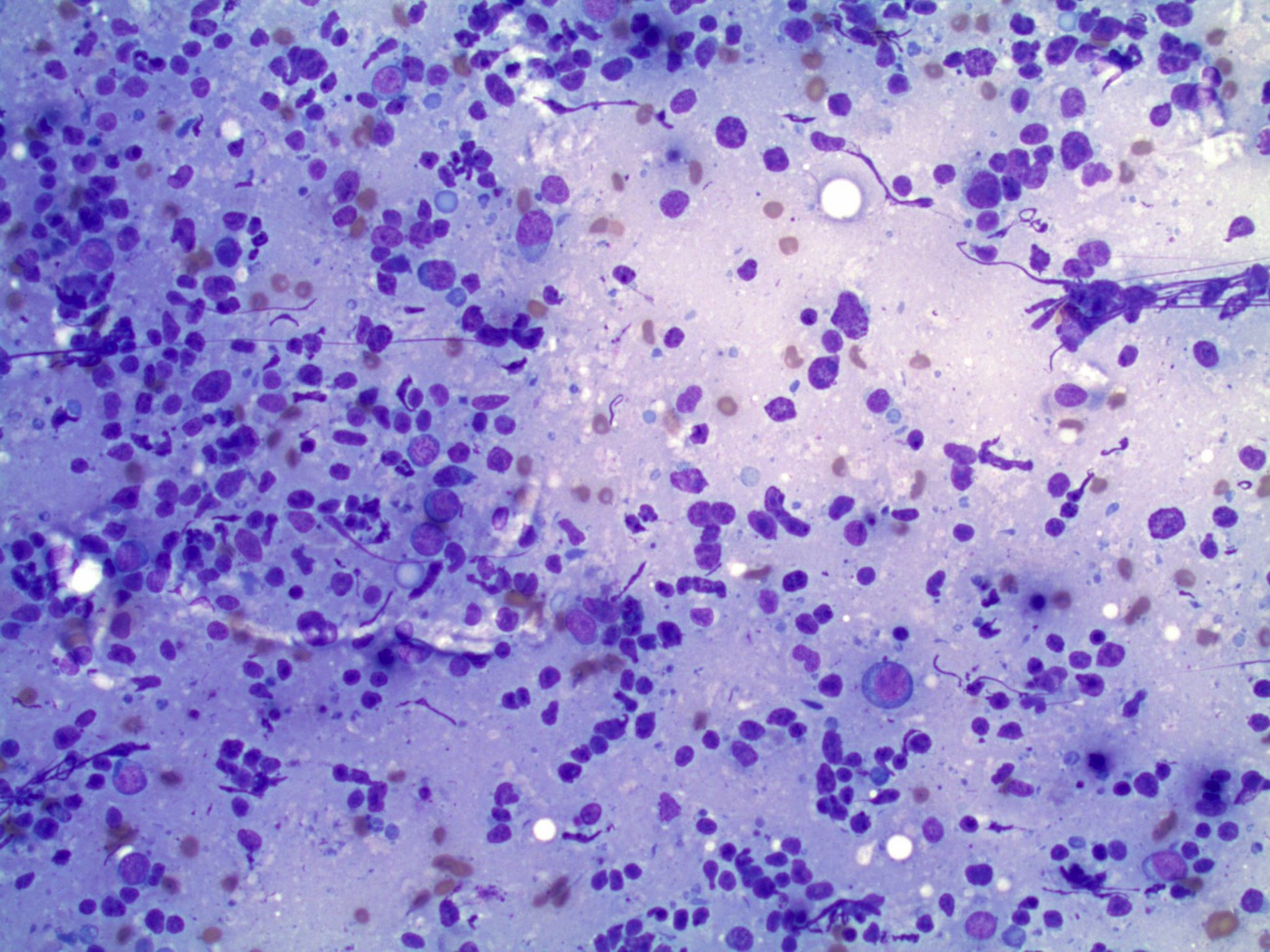
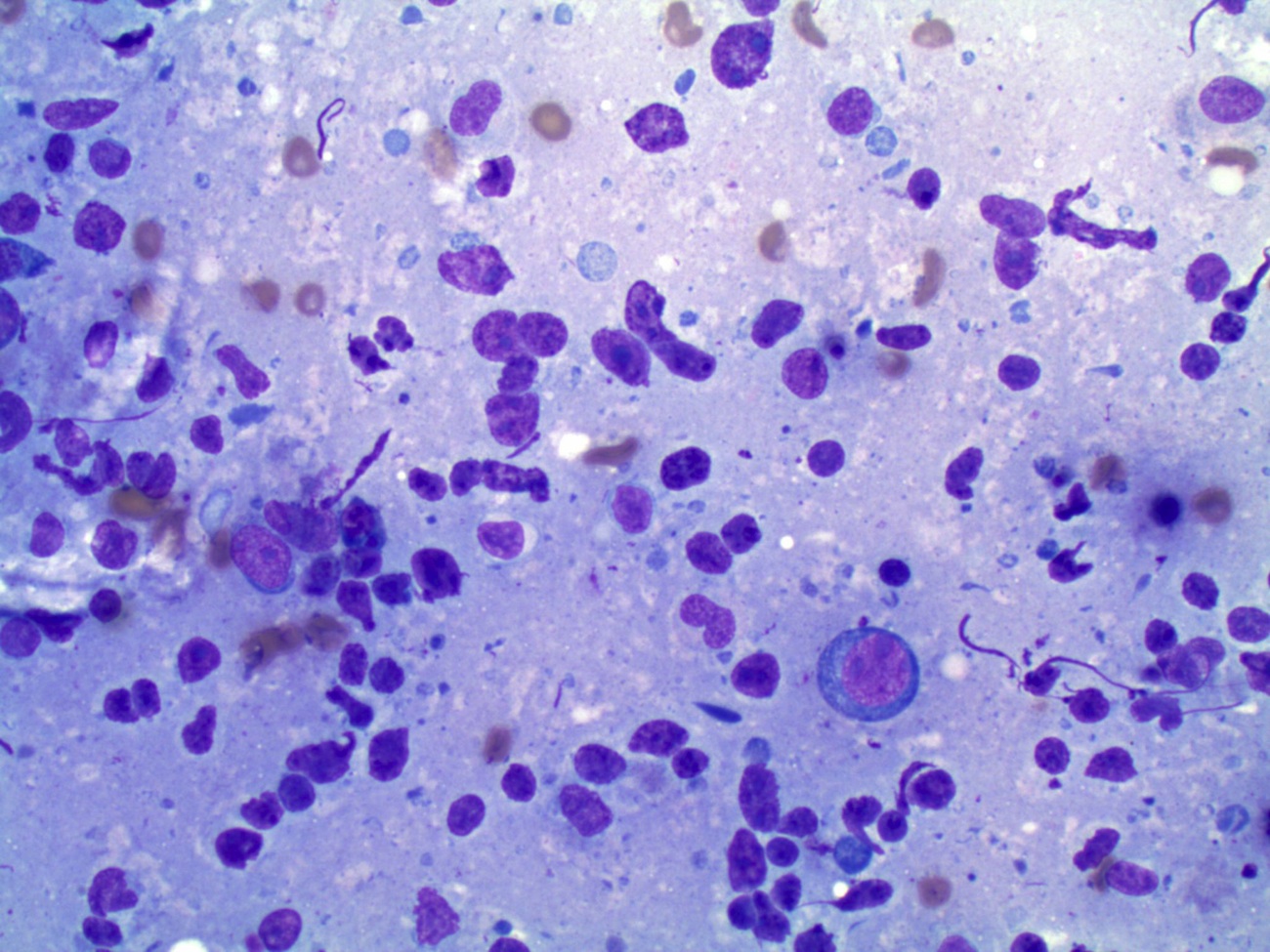
Cytology images:
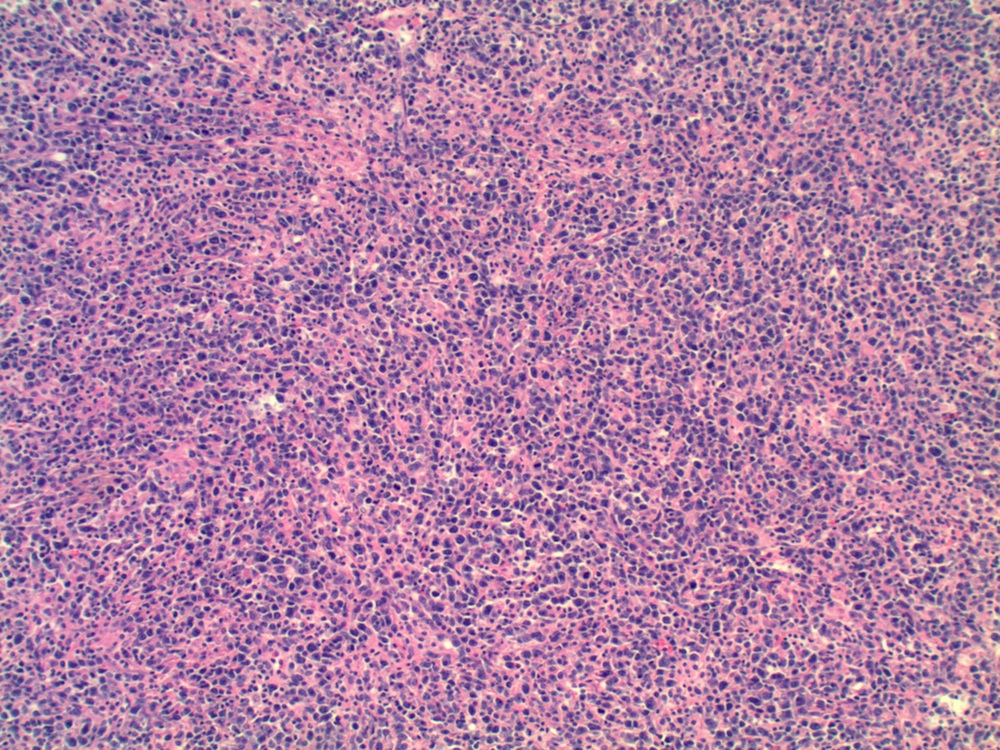
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
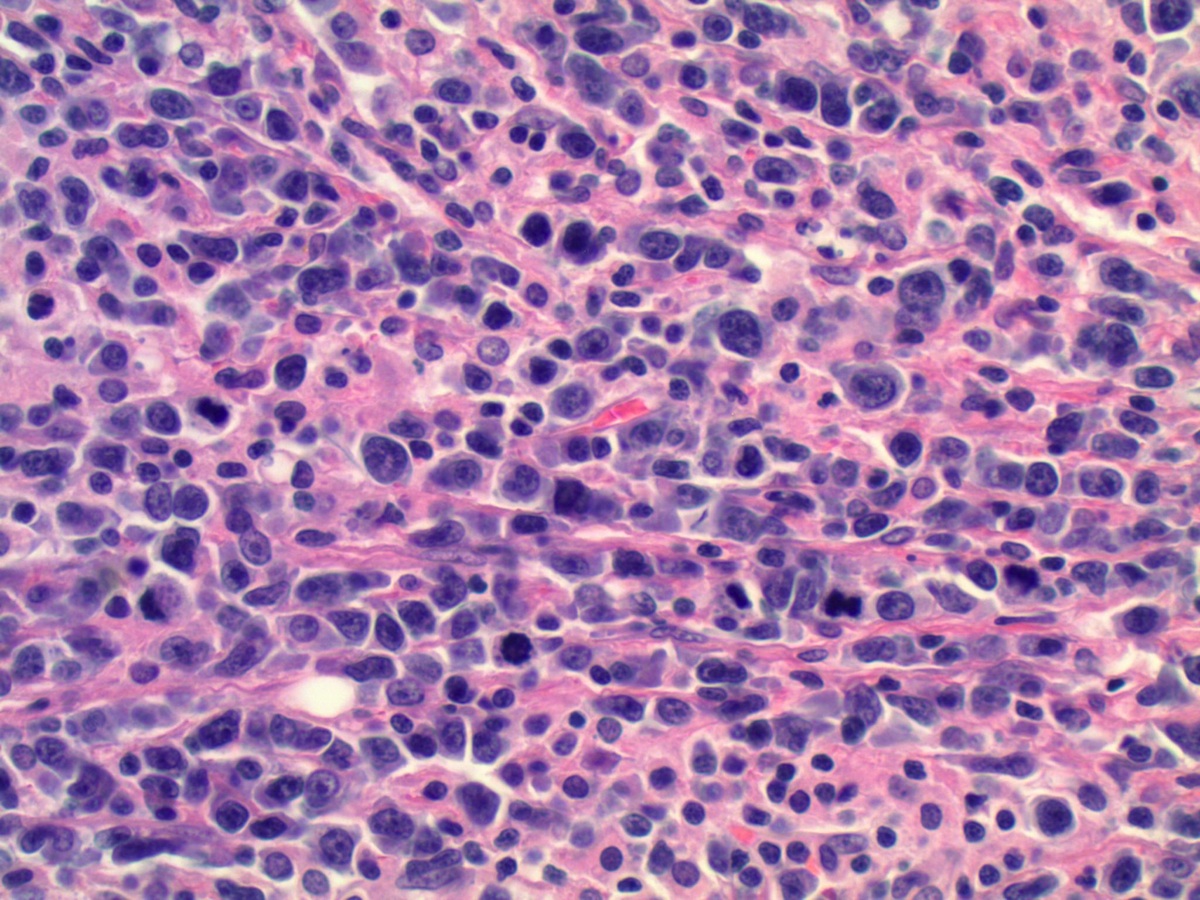
Diagnosis: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
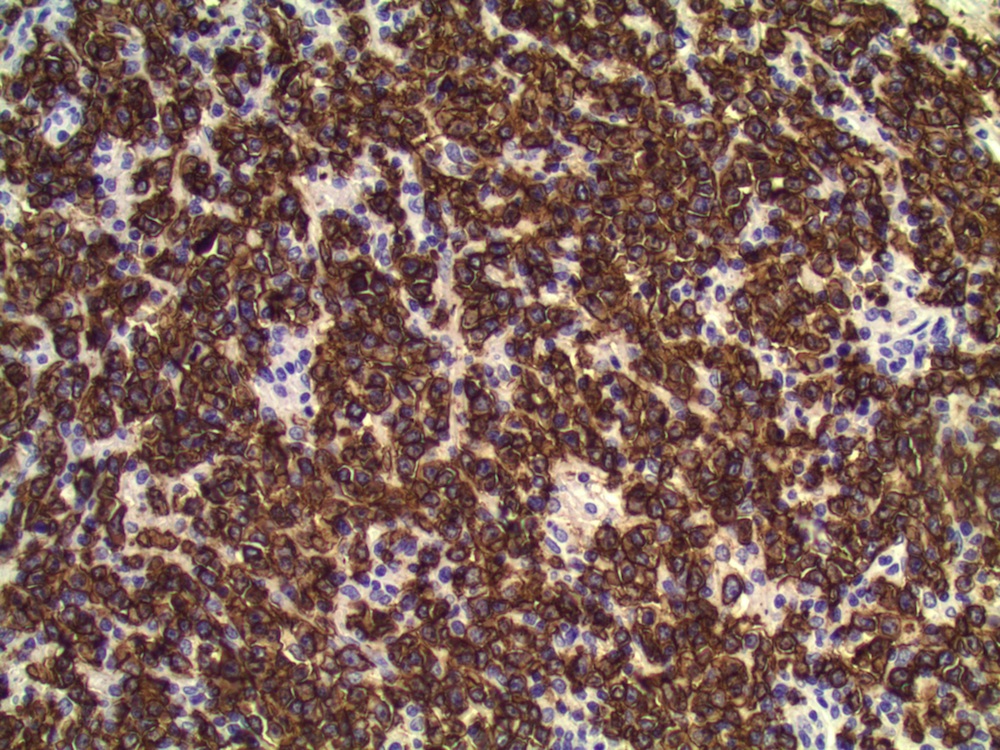
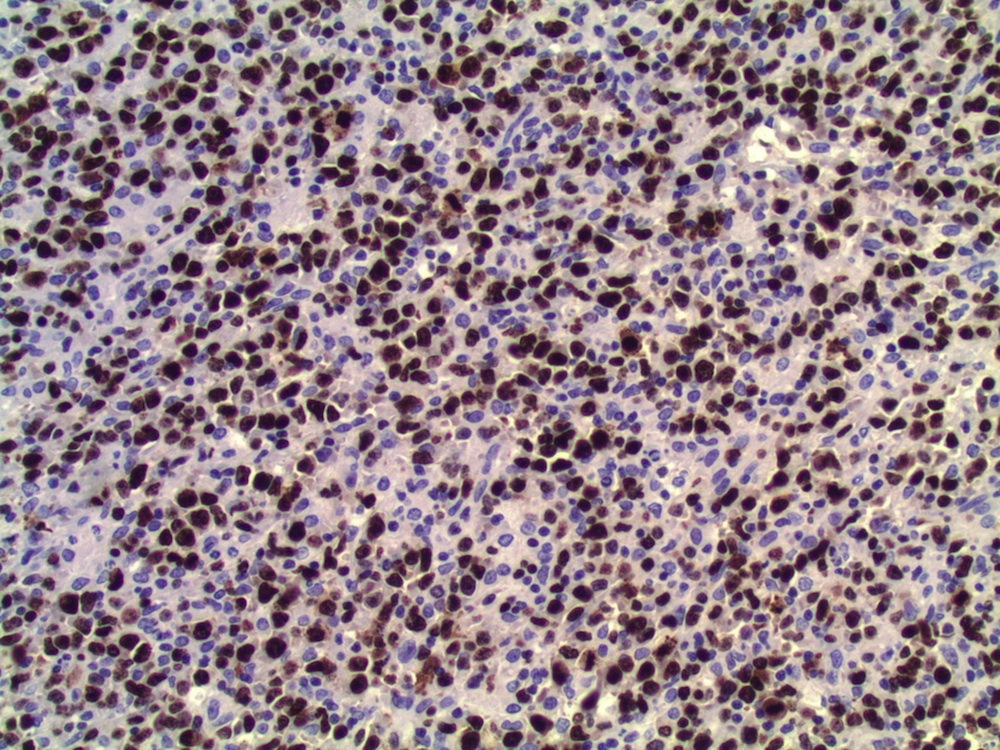
Immunostains:
Discussion:
Most ovarian lymphomas are B cell tumors, as in this case, which was strongly CD20+ and showed marked proliferative activity with Ki67 nuclear staining.
Primary ovarian lymphoma is rare (Am J Case Rep 2012;13:96). Most ovarian B cell lymphomas are diffuse large B cell lymphoma or follicular lymphoma. In the ovary, diffuse B large cell lymphoma may resemble a stromal tumor (particularly granulosa cell tumor the adult of and juvenile types) as well as germ cell tumors (mainly dysgerminoma). At all sites, diffuse large B cell lymphoma has a diffuse growth pattern of large CD20+ B cells (usually 5 times normal lymphocytes) resembling immunoblasts (amphophilic cytoplasm, eccentric nuclei with one central nucleoli) or centroblasts (pale or basophilic cytoplasm, vesicular chromatin due to chromatin margination, 2 - 3 nucleoli, often near membrane). Occasionally neutrophils, histocytes or infiltrating T cells are prominent. Touch preps show scattered large atypical cells in a background of small mature lymphocytes.
Double hit lymphoma has features intermediate between Burkitt lymphoma (with marked proliferative activity and a starry sky appearance) and diffuse large B cell lymphoma, including rearrangements of MYC, BCL6 and BCL2. In this case, molecular testing for these rearrangements were negative.
Treatment for low stage, primary ovarian disease is typically surgical and chemotherapy, with a good prognosis.
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. Ankur Sangoi, El Camino Hospital (California), for contributing this case. This case was reviewed in May 2020 by Dr. Jennifer Bennett, University of Chicago and Dr. Carlos Parra-Herran, University of Toronto.
Website news:
(1) We have added new Board Review questions, courtesy of BoardVitals, which are accessible via our CME page.
(2) Our Feature Page for December highlights Grossing Equipment / Workstations and includes EXAKT Technologies, Inc., Leica Biosystems, Milestone Medical, MOPEC, Photodyne Technologies and Sakura Finetek USA. We also have a new Mystery Case on the right side of the Home Page.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
(1) We have added new Board Review questions, courtesy of BoardVitals, which are accessible via our CME page.
(2) Our Feature Page for December highlights Grossing Equipment / Workstations and includes EXAKT Technologies, Inc., Leica Biosystems, Milestone Medical, MOPEC, Photodyne Technologies and Sakura Finetek USA. We also have a new Mystery Case on the right side of the Home Page.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
Case #295
Clinical history:
A 50 year old woman presented with an ovarian mass, which was excised.
Gross images:
Cytology images:
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Click here for diagnosis and discussion:
Diagnosis: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Immunostains:
Discussion:
Most ovarian lymphomas are B cell tumors, as in this case, which was strongly CD20+ and showed marked proliferative activity with Ki67 nuclear staining.
Primary ovarian lymphoma is rare (Am J Case Rep 2012;13:96). Most ovarian B cell lymphomas are diffuse large B cell lymphoma or follicular lymphoma. In the ovary, diffuse B large cell lymphoma may resemble a stromal tumor (particularly granulosa cell tumor the adult of and juvenile types) as well as germ cell tumors (mainly dysgerminoma). At all sites, diffuse large B cell lymphoma has a diffuse growth pattern of large CD20+ B cells (usually 5 times normal lymphocytes) resembling immunoblasts (amphophilic cytoplasm, eccentric nuclei with one central nucleoli) or centroblasts (pale or basophilic cytoplasm, vesicular chromatin due to chromatin margination, 2 - 3 nucleoli, often near membrane). Occasionally neutrophils, histocytes or infiltrating T cells are prominent. Touch preps show scattered large atypical cells in a background of small mature lymphocytes.
Double hit lymphoma has features intermediate between Burkitt lymphoma (with marked proliferative activity and a starry sky appearance) and diffuse large B cell lymphoma, including rearrangements of MYC, BCL6 and BCL2. In this case, molecular testing for these rearrangements were negative.
Treatment for low stage, primary ovarian disease is typically surgical and chemotherapy, with a good prognosis.