Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Nguyen NNJ, Downes MR. Interstitial cystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderinterstitial.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Bladder syndrome of unknown etiology that clinically presents as chronic pelvic pain with lower urinary tract symptoms (Int J Urol 2020;27:578)
- Clinical diagnosis of exclusion
Essential features
- Idiopathic, debilitating syndrome that presents as chronic pelvic pain accompanied by lower urinary tract symptoms, diagnosed clinically after confusable diseases are ruled out
- Conservative, multimodal approach recommended as initial treatment
- Can be classified into non-Hunner lesion subtype (most common) and Hunner lesion subtype via cystoscopy with or without histopathology
- Non-Hunner lesion subtype has a strong association with nonbladder pain syndromes and worse / unchanged therapeutic outcomes; bladder with no diagnostic pathology
- Hunner lesion subtype has a strong association with more severe bladder symptoms and better outcomes from intravesical therapy; nonspecific histopathological features including but not limited to pancystitis with suburothelial lymphoplasmacytic inflammation and urothelial denudement
Terminology
- Commonly referred to as bladder pain syndrome
- Also called painful bladder syndrome and chronic interstitial cystitis
- Subtypes: interstitial cystitis / bladder pain syndrome with Hunner lesions, interstitial cystitis / bladder pain syndrome without Hunner lesions
ICD coding
- ICD-9: 595.1 - chronic interstitial cystitis
Epidemiology
- Up to 7% of women and 4% of men (J Urol 2011;186:540, J Urol 2013;189:141)
- Wide age range with a peak prevalence in the fourth and fifth decades
- Older age at diagnosis in Hunner lesion subtype cases (Urology 2011;78:301)
- No significant difference in race / ethnicity
Sites
- Bladder
Pathophysiology
- Poorly understood pathophysiology
- Chondroitin sulfate, a glycosaminoglycan on the urothelial luminal surface that plays an important role in urothelial barrier function, is deficient, which leads to increased urothelial permeability (J Urol 2013;189:336)
- Antiproliferative factor (APF), a sensitive and specific urinary biomarker of interstitial cystitis, plays a role in the inhibition of urothelial cell proliferation and in the alteration of urothelial cell adhesion (Urology 2001;57:104, J Urol 1996;156:2073, Mol Cell Proteomics 2011;10:M110.007492)
- Upregulation of genes involved in pronociceptive inflammatory reactions and nociceptive pathways in the brain and spinal cord leads to pelvic pain (J Urol 2013;190:1925, Nat Rev Urol 2019;16:187)
- Pelvic visceral organ cross sensitization theory: nonpelvic organs sharing sensory pathways with the bladder can undergo persistent physiologic changes induced by interstitial cystitis, which explains the high prevalence of extravesical pain in patients with interstitial cystitis
Etiology
- No clear etiology for the onset of interstitial cystitis
- Acidic food, caffeine and alcohol were found to be associated with acute exacerbation of interstitial cystitis (BJU Int 2012;109:1584)
Clinical features
- Persistent or recurrent pelvic discomfort / pain with bladder filling, relieved by voiding (J Urol 2015;193:1545, Eur Urol 2010;57:35)
- Pain is usually suprapubic but can radiate to the groin, vagina, rectum and sacrum
- Accompanied by urinary frequency, urgency or nocturia
- Often associated with extrapelvic pain, other systemic pain syndromes, somatic disorders and psychosocial difficulties / dysfunction (Nat Rev Urol 2019;16:187)
- Interstitial cystitis with Hunner lesions are associated with more severe bladder symptoms (smaller bladder capacity and higher bladder pain), whereas the non-Hunner lesion subtype correlates with nonbladder syndromes (J Urol 2021;205:226, Urology 2011;78:301)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis of exclusion without any invasive investigation required
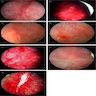
- Cystoscopy with or without cytology and biopsy / resection can be performed as clinically warranted to rule out other underlying pathology, especially in older patients and to subtype interstitial cystitis in the context of persistent, debilitating bladder pain syndrome (Neurourol Urodyn 2017;36:984, Can Urol Assoc J 2016;10:E136)
Laboratory
- Basic laboratory investigations, including urine analysis and culture, are negative for confusable diseases
- Many patients have hematuria (J Psychosom Res 2014;77:510)
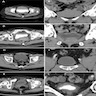
Radiology description
- Pelvic imaging is unnecessary for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis (BJU Int 2018;122:729)
- Diffuse and focal bladder thickening on CT is significantly more frequent in patients with Hunner lesion subtype than in patients with non-Hunner lesion subtype (Biomedicines 2021;9:1306)
Prognostic factors
- Patterns described: complete resolution, relapsing remitting, intermittent disease flares, chronic progression (Transl Androl Urol 2015;4:629)
- Patients with no positive histopathological finding (non-Hunner lesion subtype) have worse or unchanged outcomes from intravesical therapy compared with those who have at least one histopathological finding consistent with Hunner lesion subtype (J Urol 2021;205:226)
- No association between individual histopathological findings and treatment outcomes in the Hunner lesion subtype
- No impact on survival
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with ulcerative interstitial cystitis treated with complete transurethral ulcer resection (IJU Case Rep 2018;2:51)
- 35 year old woman with interstitial cystitis and persistent arousal treated with combined site specific sacral neuromodulation and pudendal nerve release surgery (BMJ Case Rep 2016;2016:bcr2015213513)
- 67 year old woman with bladder pain syndrome caused by iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerve injuries following a laparoscopic pyeloplasty (Urol Case Rep 2019;28:101056)
Treatment
- Initial treatment for the non-Hunner lesion subtype should be conservative; however, cystoscopic techniques represent the first line treatment in the Hunner lesion subtype (J Urol 2022;208:34, Int J Urol 2016;23:542)
- Conservative: multimodal therapy (pain management, behavioral, psychological, educational), stress management, dietary advice, physiotherapy
- Oral therapies: amitriptyline, cimetidine, hydroxyzine, oral pentosan polysulphate
- Intravesical therapies: dimethylsulfoxide, heparin, lignocaine
- Cystoscopic techniques: fulguration of ulcers, injection of triamcinolone to ulcers, hydrodistension
- Other treatments: botulinum toxin A, sacral neuromodulation, cyclosporin A
- Major surgery (option of last resort): urinary diversion or substitution cystoplasty with or without cystectomy
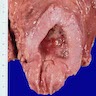
Gross description
- Bladder mucosa is unremarkable or with Hunner lesions or glomerulations (Eur Urol 2008;53:60)
- Hunner lesion (5 - 57% of cases): reddened mucosal area with small vessels that radiate towards a central scar, with fibrin deposition or an attached blood clot; can present as a denuded urothelium with oozing blood due to rupture and bladder distension (Int J Urol 2019;26:26)
- Glomerulations (nonspecific): petechial mucosal hemorrhages (J Urol 2016;195:19)
- Bladder wall is smooth or with focal to diffuse thickening
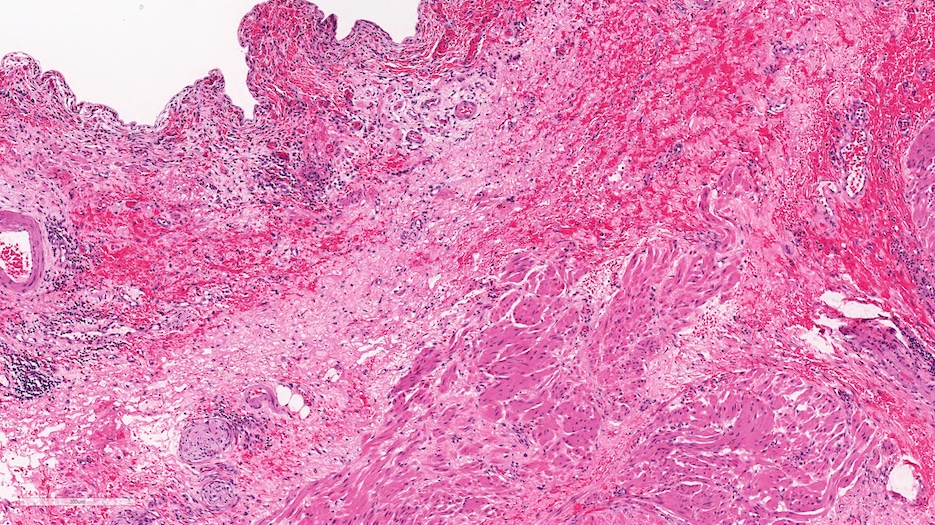
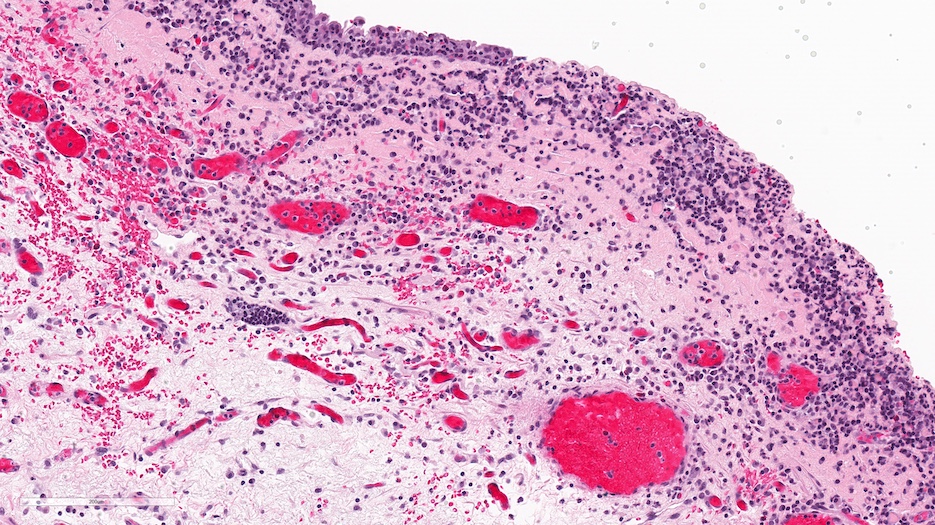
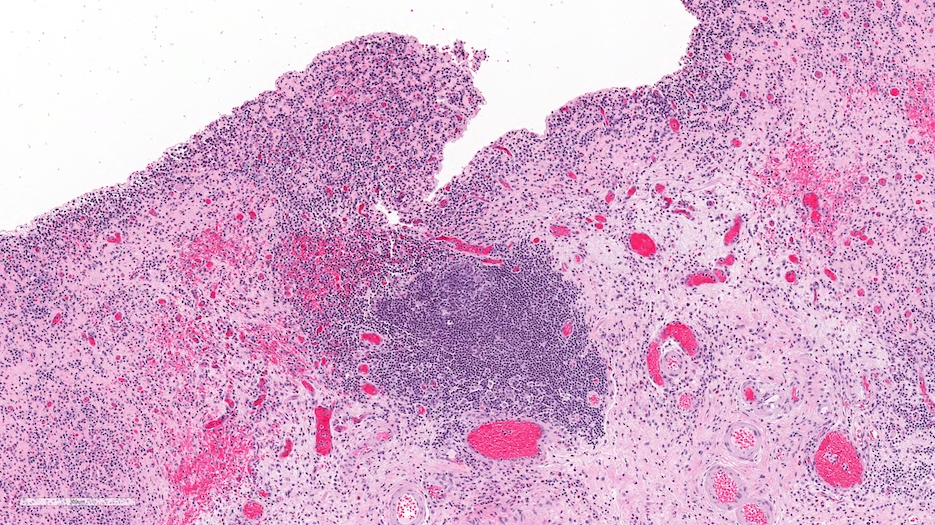
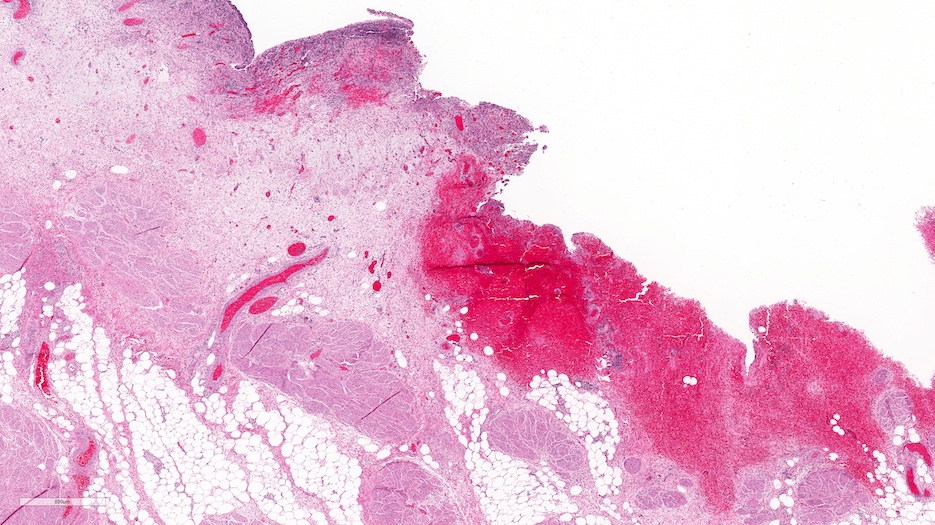
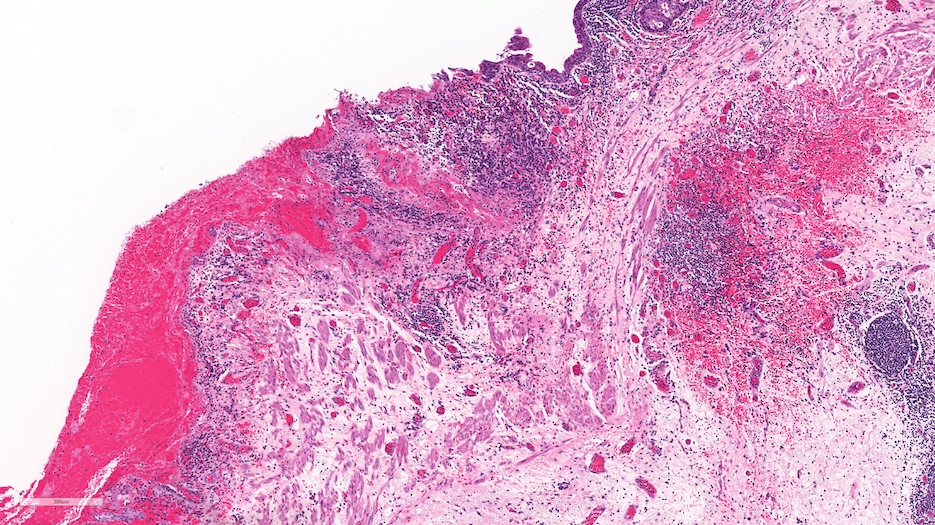
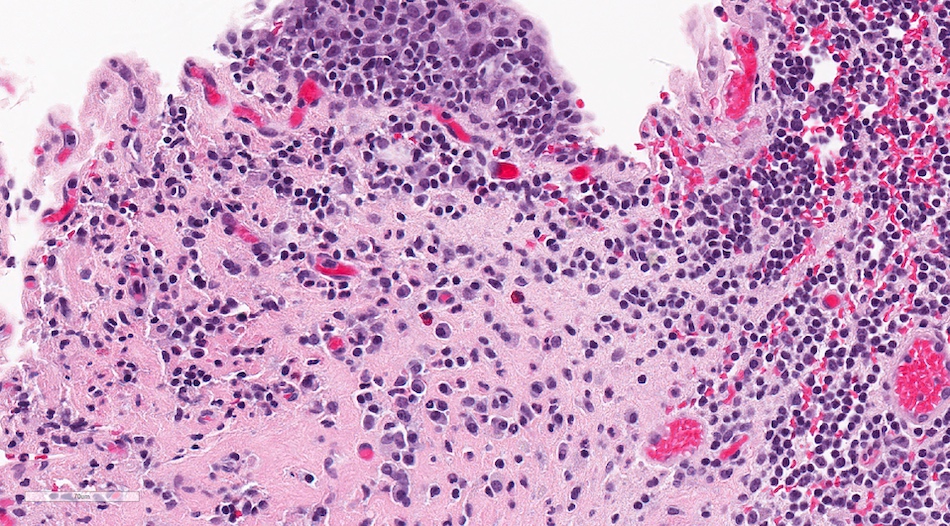
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Histologic features are nonspecific
- Features suggestive of the Hunner lesion subtype (at least one positive histological finding) (Int J Urol 2020;27:491, J Transl Med 2022;20:97, PLoS One 2015;10:e0143316, Scand J Urol 2020;54:91, Biomedicines 2021;9:1306)
- Pancystitis with subepithelial lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate with frequent lymphoid aggregates (B cell clonal expansion) with or without monocytes / macrophages or granulocytes
- Urothelial detachment / denudation with or without fibrin deposition with or without granulation tissue
- Lamina propria with hemorrhage, neovascularization, fibrosis or edema
- Detrusor mastocytosis or fibrosis
- Non-Hunner lesion subtype
- No or scarce histopathological changes
- Noninflammatory with preserved urothelium
- Patients with diffuse bladder wall thickening on CT correlates with greatest inflammatory cell infiltration, urothelial denudation and granulation tissue, as well as obvious fibrosis in both superficial and deep lamina propria
- Patients with focal bladder wall thickening have fewer inflammatory and reactive changes and typically demonstrate obvious fibrosis only in the deep lamina propria (Biomedicines 2021;9:1306)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Masson trichrome can be used to highlight fibrosis in the lamina propria in the Hunner lesion subtype (Biomedicines 2021;9:1306)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No clinically approved diagnostic molecular / cytogenetic testing
- Overexpression of genes related to immune and inflammatory responses: CXCR3, TNFSF14, NOS, IL6, IL8, IL10, IL17A, NGF, CCL21, IL4, iNOS (J Urol 2010;183:1206, Ther Adv Urol 2011;3:19, Eur Urol 2016;70:283, J Urol 2014;192:1564)
- Increased expression of genes involved in pronociceptive inflammatory reactions: TRPV1, TRPV2 and TRPV4, ASIC1, NGF and CXCL9 (J Urol 2013;190:1925)
- WNT11 decreased in non-Hunner lesion subtype compared with Hunner lesion subtype (Sci Rep 2018;8:9782)
- Overexpression of VEGF and BAFF correlates with symptom severity in Hunner lesion subtype (J Urol 2019;202:290)
Sample pathology report
- Bladder, biopsy:
- Urothelial denudation with lamina propria edema, congestion and inflammation (lymphoid aggregates, plasma cells and granulocytes) (see comment)
- Muscularis propria sampled
- Comment: The histological features are not specific but would be in keeping with interstitial cystitis in the appropriate clinical context.
- Bladder, cystectomy:
- Inflammatory process with features in keeping with the clinical impression of interstitial cystitis (see comment and microscopic description)
- Negative for malignancy
- Comment: The histological features in this condition can be nonspecific but the findings in the current specimen would be in keeping with the clinical impression of interstitial cystitis.
- Microscopic description: Bladder with marked urothelial denudation, vascular congestion and red cell extravasation. The lamina propria is markedly edematous and in areas polypoid, with focal surface fibrin deposition in keeping with ulceration. There is marked inflammation, predominantly chronic (lymphocytes and plasma cells) with neutrophils and some mast cells within the lamina propria. The muscularis propria is uninvolved by either inflammation or fibrosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Includes other types of cystitis with nonspecific histopathological findings, such as
- Drug or radiation mediated cystitis:
- Urothelium with cellular enlargement, multinucleation, nuclear hyperchromasia and cytoplasmic vacuolation
- Other classic findings include hemorrhage, fibrin deposition, fibrin thrombi, fibrosis, acute and chronic inflammation, edema, vascular congestion and thickened vessels
- Infectious cystitis:
- Neutrophilic inflammation
- Follicular cystitis:
- Lymphoid follicles within the urothelium and lamina propria
- Granulomatous cystitis:
- Granulomas in the lamina propria
- Can have surface ulceration and chronic inflammation
- Eosinophilic cystitis:
- Prominent eosinophilic infiltrate in the acute phase
- Fewer eosinophils but more prominent mast cells, plasma cells and muscle fibrosis in the chronic phase
- Polypoid / papillary cystitis:
- Exophytic bullous, polypoid or papillary structures covered by benign urothelium and composed of stromal cores
- Varying degree of edema, vascular ectasia, congestion, inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis
- Drug or radiation mediated cystitis:
- Clinical correlation is required
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 50 year old woman, known for fibromyalgia with otherwise unremarkable past medical history, has been having chronic pelvic pain with urinary frequency for 6 months. Recently, she has been having intermittent, mild hematuria. Physical examination and laboratory investigations, including urine analysis and culture, as well as abdominal / pelvic ultrasound, are negative. A cystoscopy was performed and showed reddened mucosal areas with small vessels radiating towards a central scar, which were biopsied. No mass or lesion suspicious for malignancy was seen on cystoscopy and urine cytology was negative. Bladder biopsies showed the histology above. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Bladder stones
- Infectious cystitis
- Interstitial cystitis
- Lymphoma
- Papillary urothelial neoplasm
Board review style answer #1
C. Interstitial cystitis. Chronic pelvic pain with urinary frequency as well as intermittent mild hematuria can be seen in the Hunner lesion subtype of interstitial cystitis. Confusable diseases such as infectious cystitis and malignancy are ruled out, with negative urine analysis and culture as well as the absence of cytologic atypia and architectural disorder on pathology. Lesions characteristic of Hunner lesion (reddened mucosal areas with small vessels radiating towards a central scar) visualized on cystoscopy. Histopathology showing urothelial denudation and lamina propria inflammation are suggestive of the Hunner lesion subtype of interstitial cystitis.
Answer A is incorrect because no stones were detected on ultrasound and on cystoscopy, which cannot explain the persistent pelvic pain with urinary frequency. Answer B is incorrect because urine analysis and culture are negative. Answer D is incorrect because there is no diffuse infiltrate of atypical lymphoid cells seen on pathology. Answer E is incorrect because pathology shows no cytologic atypia and architectural disorder.
Comment Here
Reference: Interstitial cystitis
Answer A is incorrect because no stones were detected on ultrasound and on cystoscopy, which cannot explain the persistent pelvic pain with urinary frequency. Answer B is incorrect because urine analysis and culture are negative. Answer D is incorrect because there is no diffuse infiltrate of atypical lymphoid cells seen on pathology. Answer E is incorrect because pathology shows no cytologic atypia and architectural disorder.
Comment Here
Reference: Interstitial cystitis
Board review style question #2
Pathological subtyping of interstitial cystitis is nonessential for diagnostic purposes but can guide treatment and aid in prognostication. What are the 2 subtypes of interstitial cystitis?
- With / without atypia
- With / without fibrosis
- With / without glomerulation
- With / without Hunner lesion
- With / without ulceration
Board review style answer #2
D. With / without Hunner lesion. Interstitial cystitis with Hunner lesions shows nonspecific histopathological features including but not limited to pancystitis with suburothelial lymphoplasmacytic inflammation and urothelial denudement. The non-Hunner lesion subtype shows no diagnostic pathology. The Hunner lesion subtype is associated with more severe bladder symptoms and better outcomes from intravesical therapy compared with the the non-Hunner lesion subtype.
Answer A is incorrect because no atypia is seen in interstitial cystitis. Answer B is incorrect because fibrosis can be seen in both the Hunner lesion subtype and non-Hunner lesion subtype of interstitial cystitis, although it is usually absent or scarce in the non-Hunner lesion subtype. Fibrosis is a nonspecific finding in interstitial cystitis and has no predictive or prognostic value. Answer C is incorrect because glomerulations are nonspecific findings in interstitial cystitis and have no predictive or prognostic value. Answer E is incorrect because ulceration can be found in some cases of the Hunner lesion subtype of interstitial subtype. It is a nonspecific finding.
Comment Here
Reference: Interstitial cystitis
Answer A is incorrect because no atypia is seen in interstitial cystitis. Answer B is incorrect because fibrosis can be seen in both the Hunner lesion subtype and non-Hunner lesion subtype of interstitial cystitis, although it is usually absent or scarce in the non-Hunner lesion subtype. Fibrosis is a nonspecific finding in interstitial cystitis and has no predictive or prognostic value. Answer C is incorrect because glomerulations are nonspecific findings in interstitial cystitis and have no predictive or prognostic value. Answer E is incorrect because ulceration can be found in some cases of the Hunner lesion subtype of interstitial subtype. It is a nonspecific finding.
Comment Here
Reference: Interstitial cystitis