Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Lee J, Yeh YA. Radiation cystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderradiationcystitis.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Radiation cystitis: inflammation of the urinary bladder caused by radiation therapy for pelvic malignancies
- Radiation induced pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia: florid nonneoplastic urothelial proliferation with pseudoinfiltrative features (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:909)
Essential features
- Classic findings of hemorrhage, fibrin deposition, fibrin thrombi, fibrosis, acute and chronic inflammation, edema, vascular congestion and thickened vessels (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:909)
- May have variable sized urothelial nests and cords with rounded or irregular edges present in the lamina propria, mimicking carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:92)
Terminology
- Radiation induced hemorrhagic cystitis (Urology 2019;131:190)
- Radiation induced cystitis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Incidence of acute radiation cystitis and urethritis: 50% of irradiated patients
- Incidence of severe chronic cystitis and urethritis: 5 - 10% of irradiated patients
- Age range: 40 - 85 years, average 69 years
- M > F, 2.8:1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:92)
Sites
- Urinary bladder and urethra
Pathophysiology
- Acute phase: lasting for several weeks postradiation therapy (Urology 2016;88:14)
- Urothelial cell damage
- Damage to glycosaminoglycan layer
- Irritability from urine leakage
- Inflammation of the bladder wall
- Pseudocarcinomatous epithelial hyperplasia
- Edema of lamina propria
- Telengiectasia
- Stromal cell atypia
- Latent phase: symptom free phase lasting for months to years (Rev Urol 2016;18:57)
- Obliterative endarteritis
- Urothelial proliferation
- Chronic phase: irreversible, late response (Rev Urol 2016;18:57)
- Loss of smooth muscle cells
- Fibroblast proliferation, collagen deposition (fibrosis), atrophy
- Telengiectasia
- Edema
- Hemorrhage
Etiology
- High energy radiation separates water molecule to free oxygen radicals - radiolysis (Urology 2016;88:14)
- Free oxygen radicals cause injury to cell membrane by lipid peroxidation, leading to immediate cell death and cause genetic damage by reacting with DNA
- High energy radiation directly absorbed by DNA, resulting in genetic damage including mutation or replication failure and cell death (Rev Urol 2016;18:57)
Clinical features
- Past medical history of radiation therapy for pelvic malignancies
- Acute radiation cystitis (Nat Rev Urol 2010;7:206)
- Complications occur during or soon after therapeutic irradiation
- Irritative voiding symptoms include dysuria, frequency, urgency, cystalgia with bladder spasms, usually no hematuria (Cells 2020;10:21)
- Chronic radiation cystitis (Urol Int 2022;106:63)
- > 3 months after radiotherapy and a clinical event free interval
- 6.5 - 9% postradiotherapy, more frequently hematuria
- 3 different types (Urol Int 2022;106:63)
- Inflammation predominant
- Bleeding predominant
- Combination of inflammation and bleeding radiation cystitis and urethritis
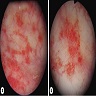
- Cystoscopy: irritated mucosa with edema, erythema, papillary, polypoid or atrophic lesions with congestion, telangiectasia, ulceration, stricture, necrosis or hemorrhage (J Urol 2013;189:2083)
Diagnosis
- Previous clinical history of pelvic irradiation
- Hematuria, dysuria, urgency
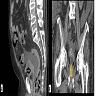
- Ultrasound, CT, MRI (Urol Int 2022;106:63)
- Cystoscopic evaluation and biopsies of lesions
Laboratory
- Complete blood count, coagulation studies, serum creatinine, urinalyses, urine culture and cytology (Can Urol Assoc J 2019;13:15)
Radiology description
- Asymmetrical bladder wall thickening (Cureus 2022;14:e25774)
Prognostic factors
- Acute radiation cystitis: self limiting, favorable outcome
- Chronic radiation cystitis: life threatening hemorrhage may occur (Nat Rev Urol 2010;7:206)
Case reports
- 22 year old woman presented with gross and painless hematuria (J Cancer Res Ther 2021;17:580)
- 65 year old woman presented with hematuria and dysuria (Indian J Palliat Care 2019;25:471)
- 71 year old man presented with a bladder mass (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1067)
- 82 year old man with gross hematuria and hemorrhagic shock (Cureus 2022;14:e25774)
- 86 year old man presented with hematuria and clot retention (Case Rep Nephrol Urol 2014;4:53)
Treatment
- Discontinue insulting agents or aggravating factors, proper hydration and symptomatic treatment
- Radiation cystitis with predominant hemorrhage:
- Hydration, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (Nat Rev Urol 2010;7:206)
- Oral drugs (sodium pentosan polysulfate, aminocaproic acid, immunokine WF10, conjugated estrogen or pentoxifylline plus vitamin E) if hyperbaric oxygen therapy is not available
- Laser or electrocoagulation of bleeding vessels (Urol Int 2022;106:63)
Gross description
- Thickened bladder mucosal wall in acute phase and atrophy in chronic phase
- Bladder mucosa with marked congestion, hemorrhage, telangiectasia, ulceration, stricture and necrosis (Urol Int 2022;106:63)
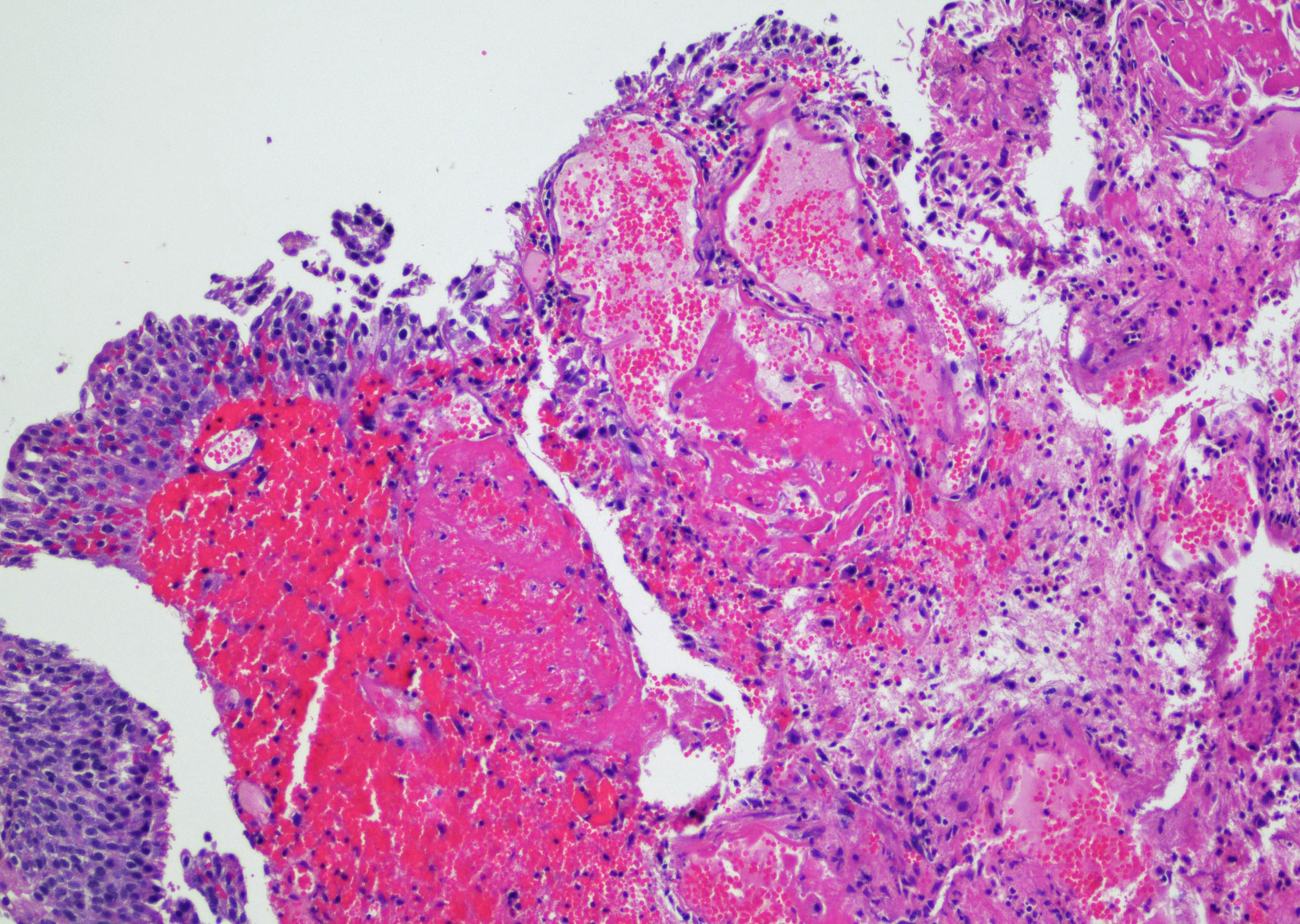
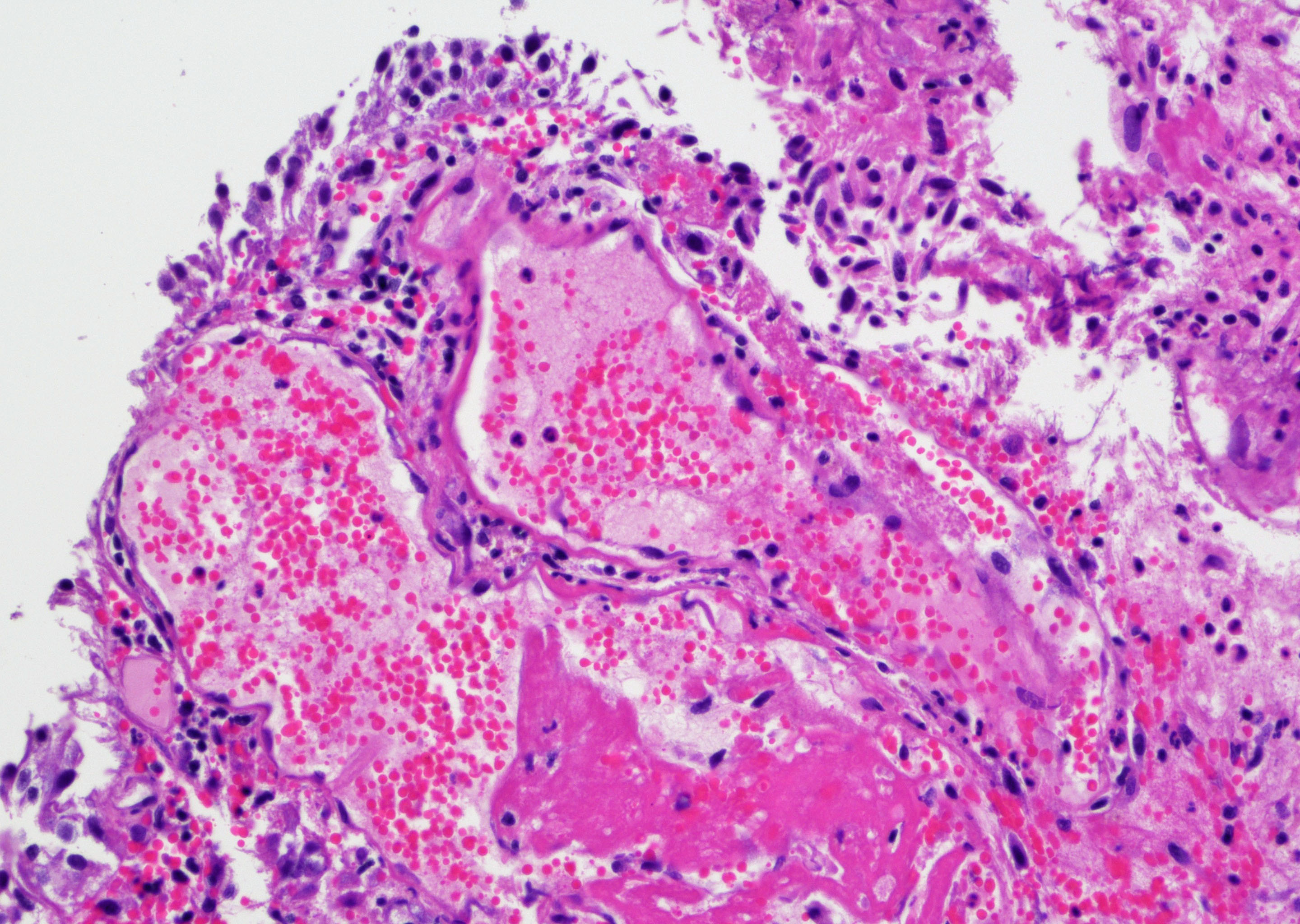
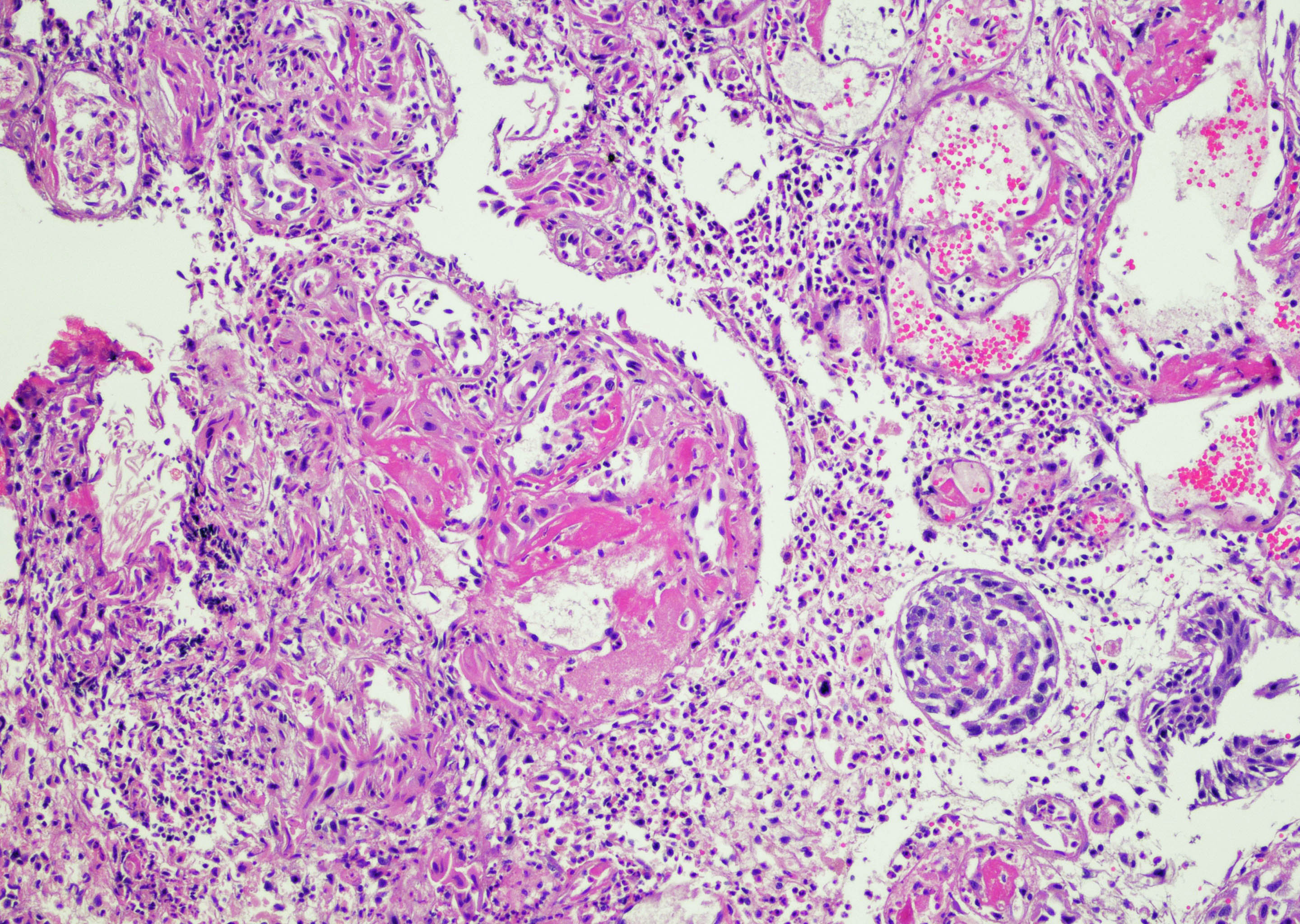
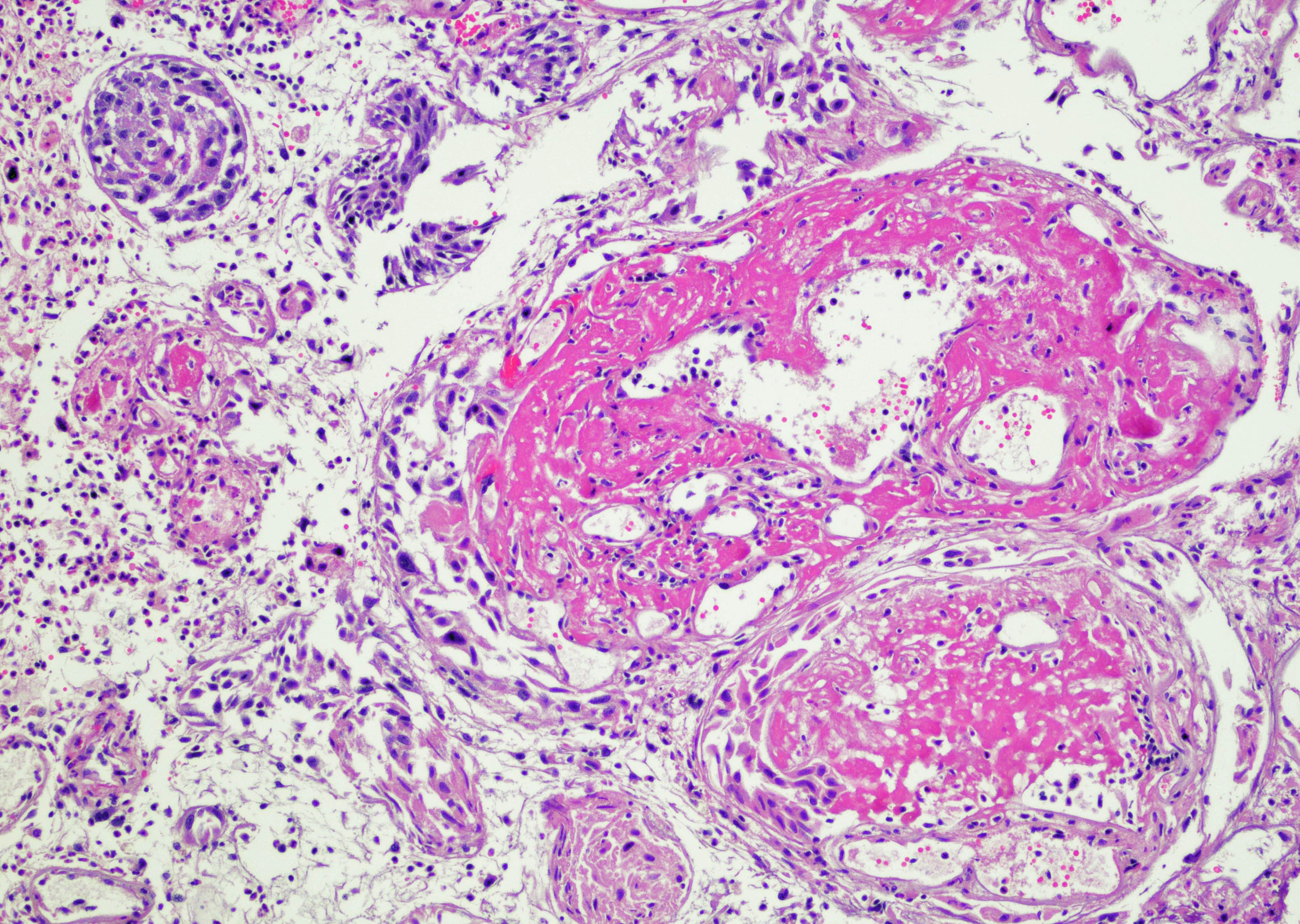
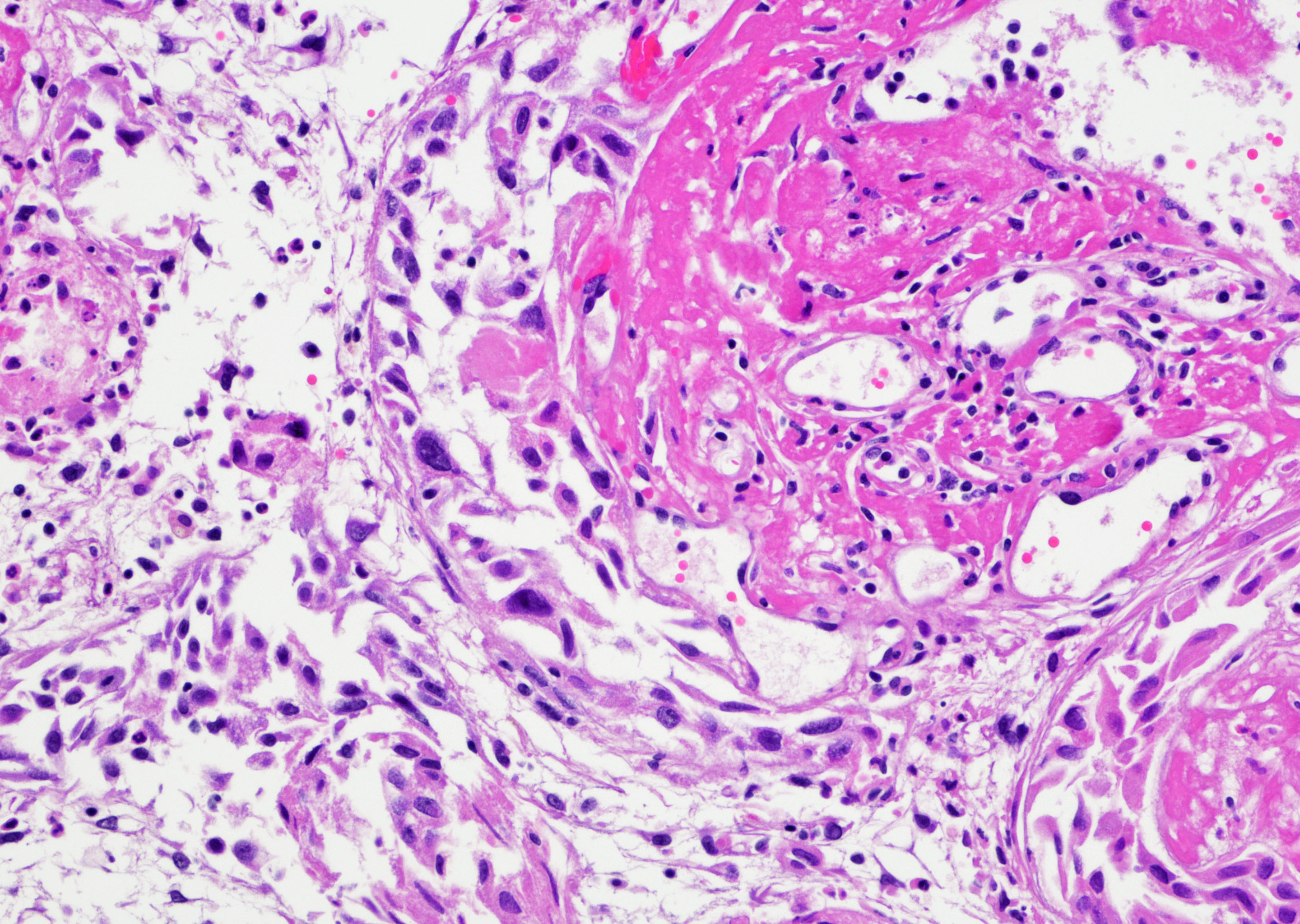
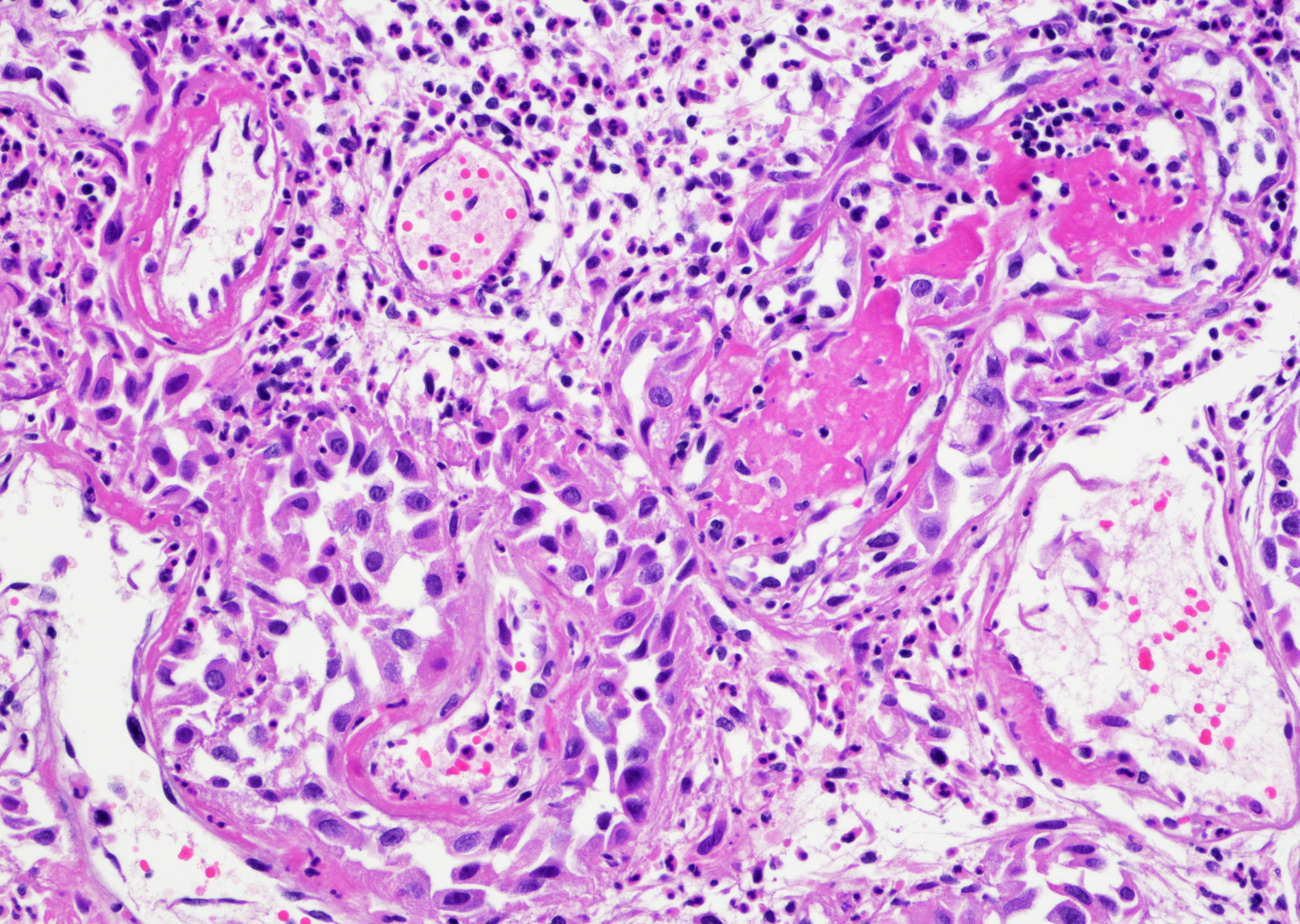
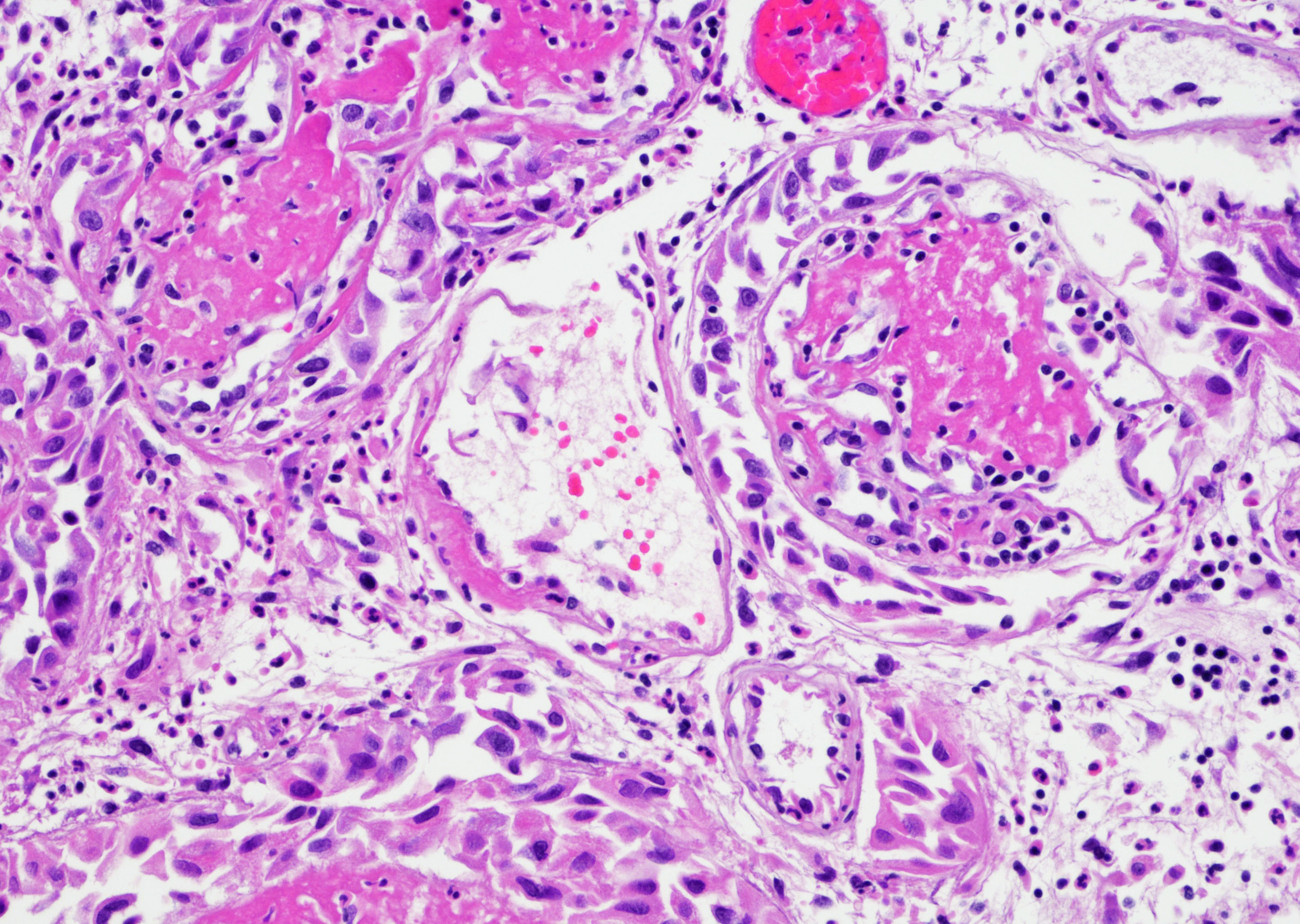
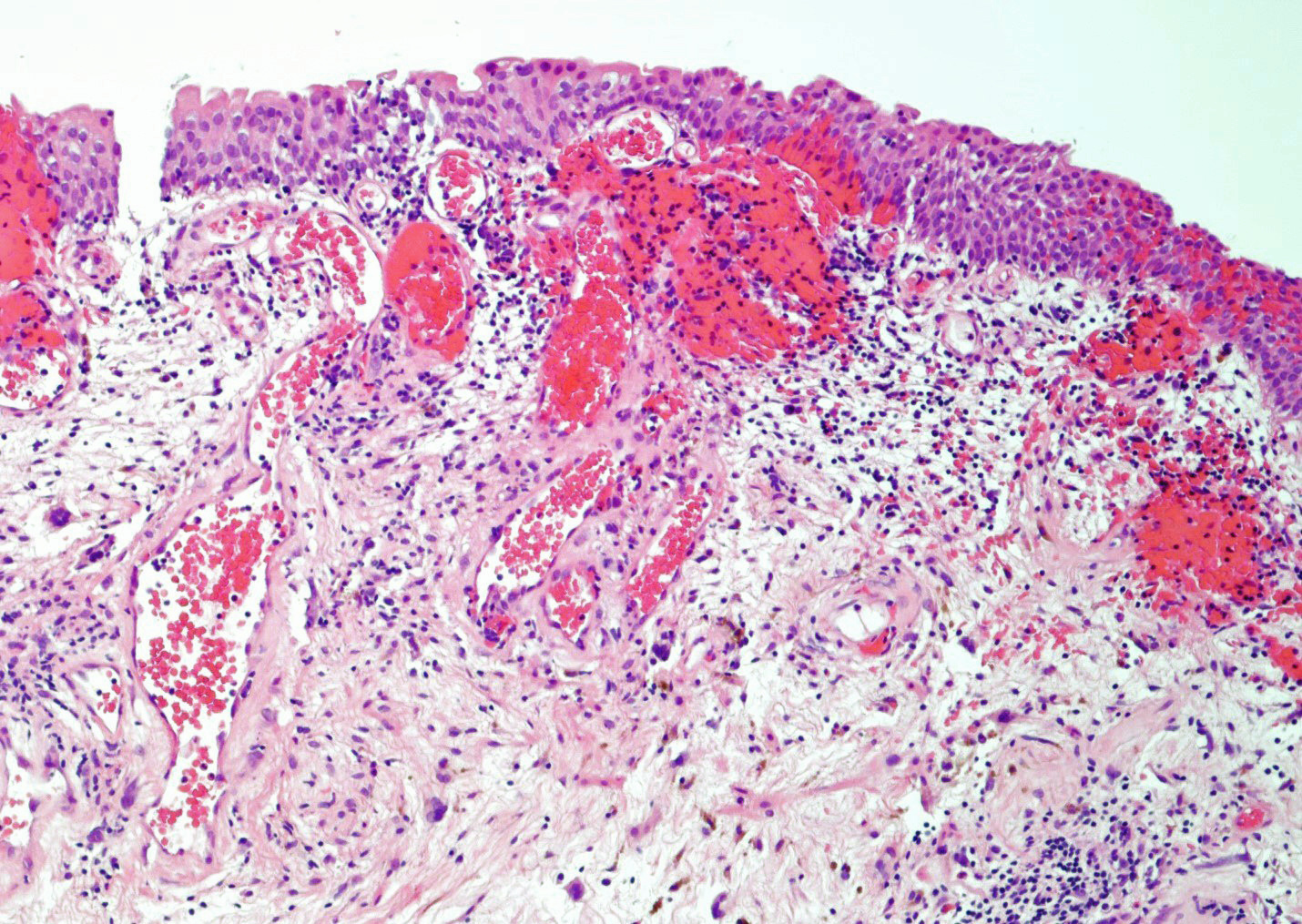
Microscopic (histologic) description
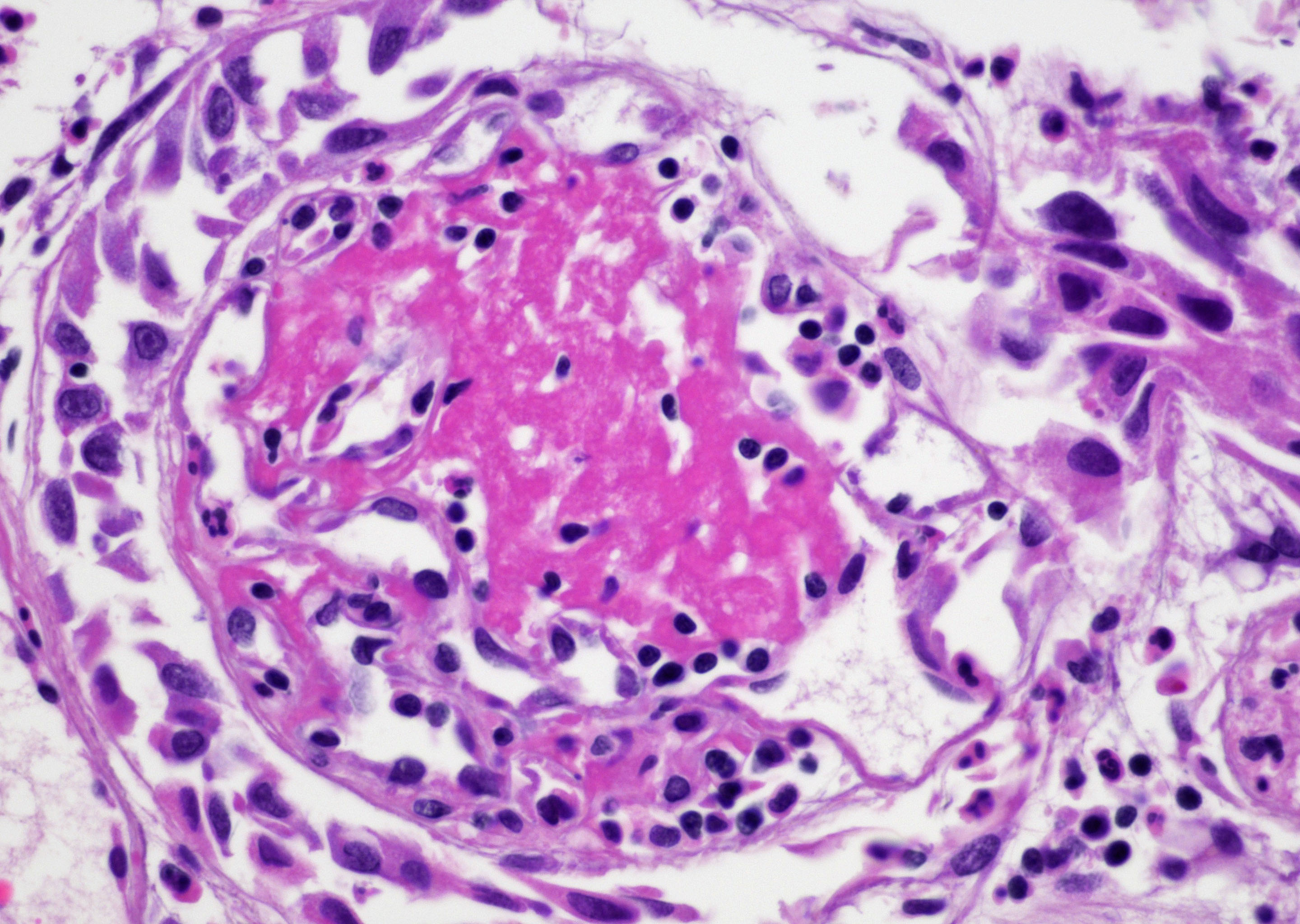
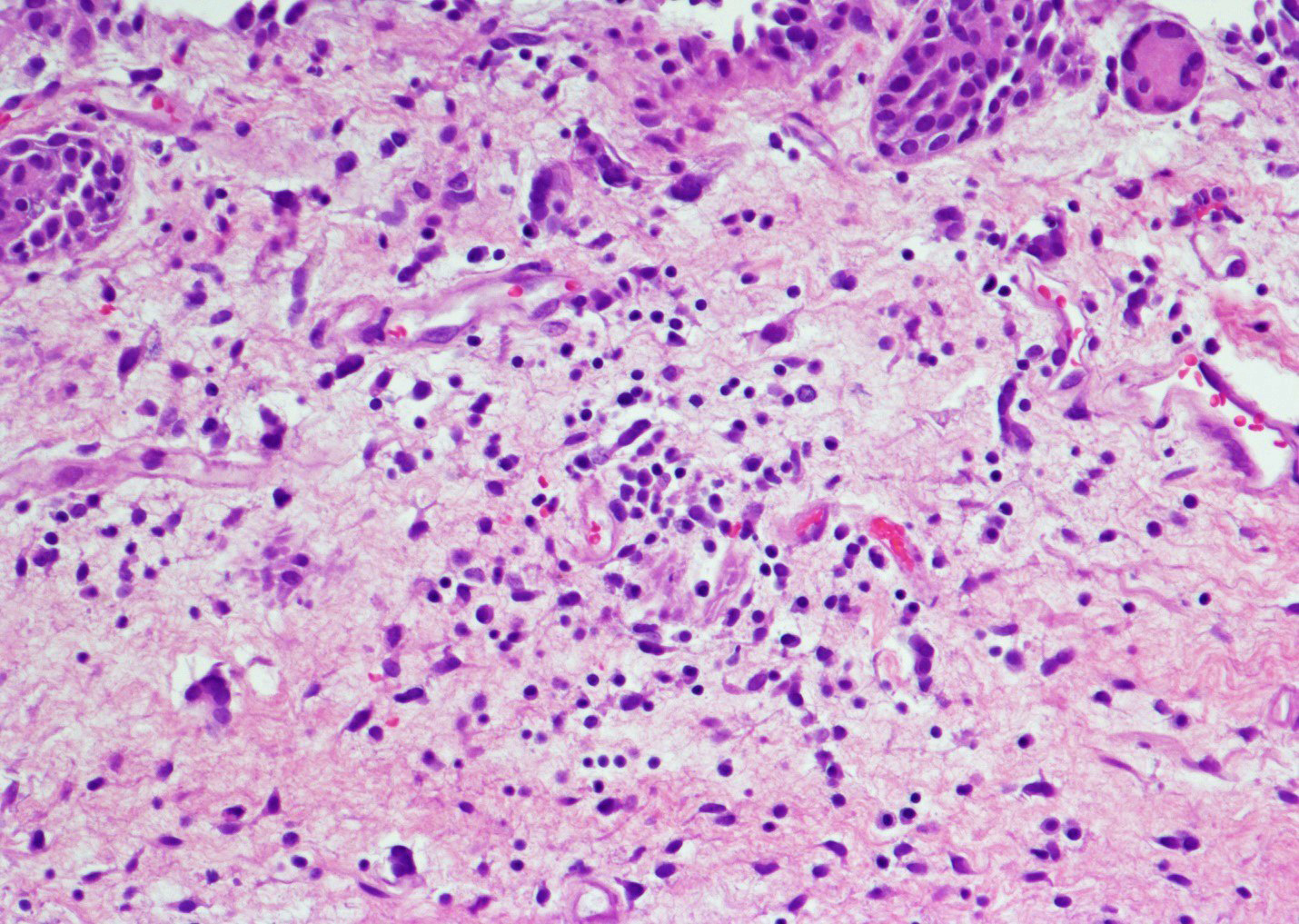
- Vessels with fibrin thrombi, fibrinoid vascular necrosis, vascular congestion, thickened walls, endothelial proliferation and telangiectasia
- Acute and chronic inflammation
- Reactive multinucleated stromal fibroblasts with smudgy nuclei
- Fibrosis and edema
- Hemorrhage and hemosiderin
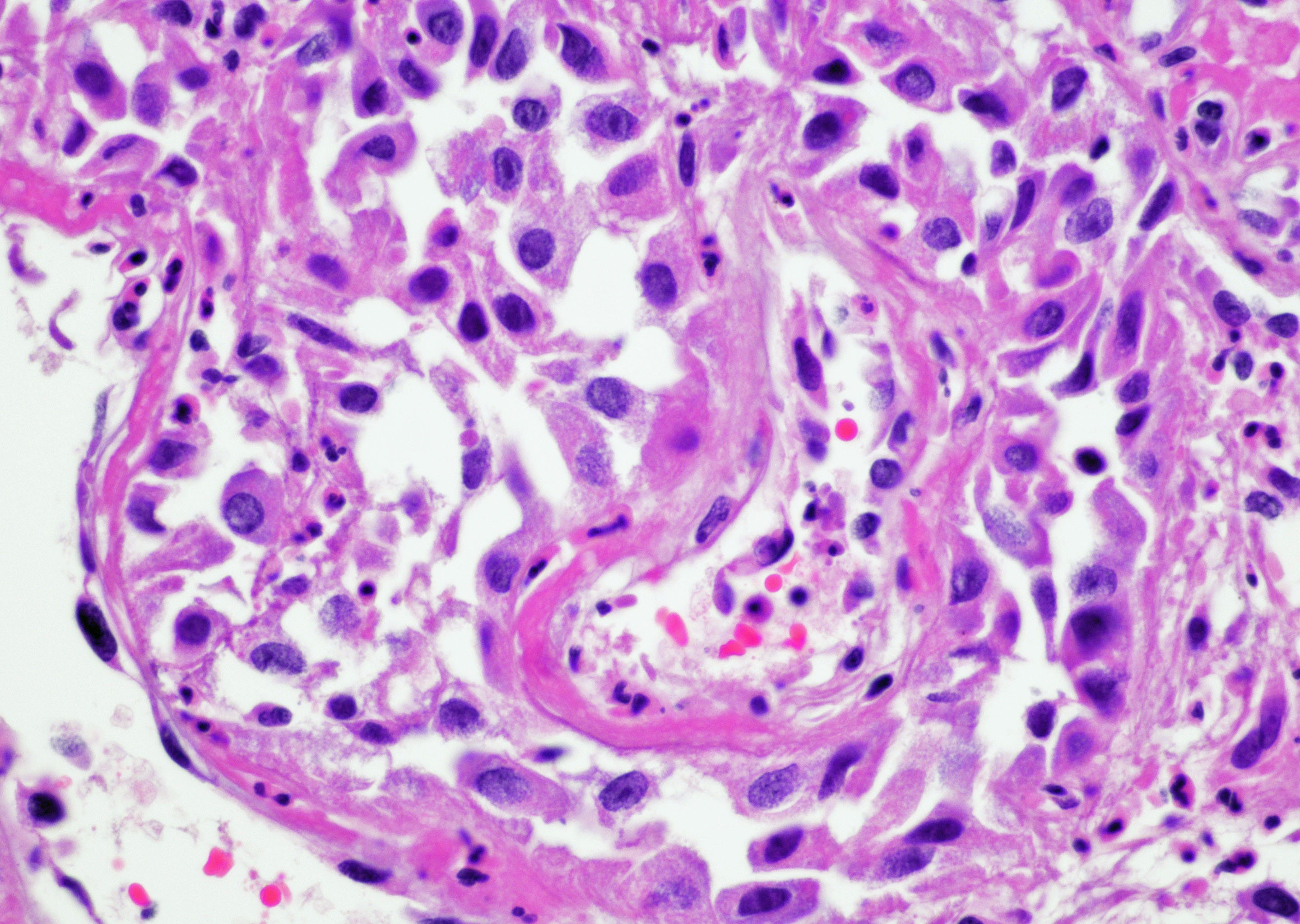
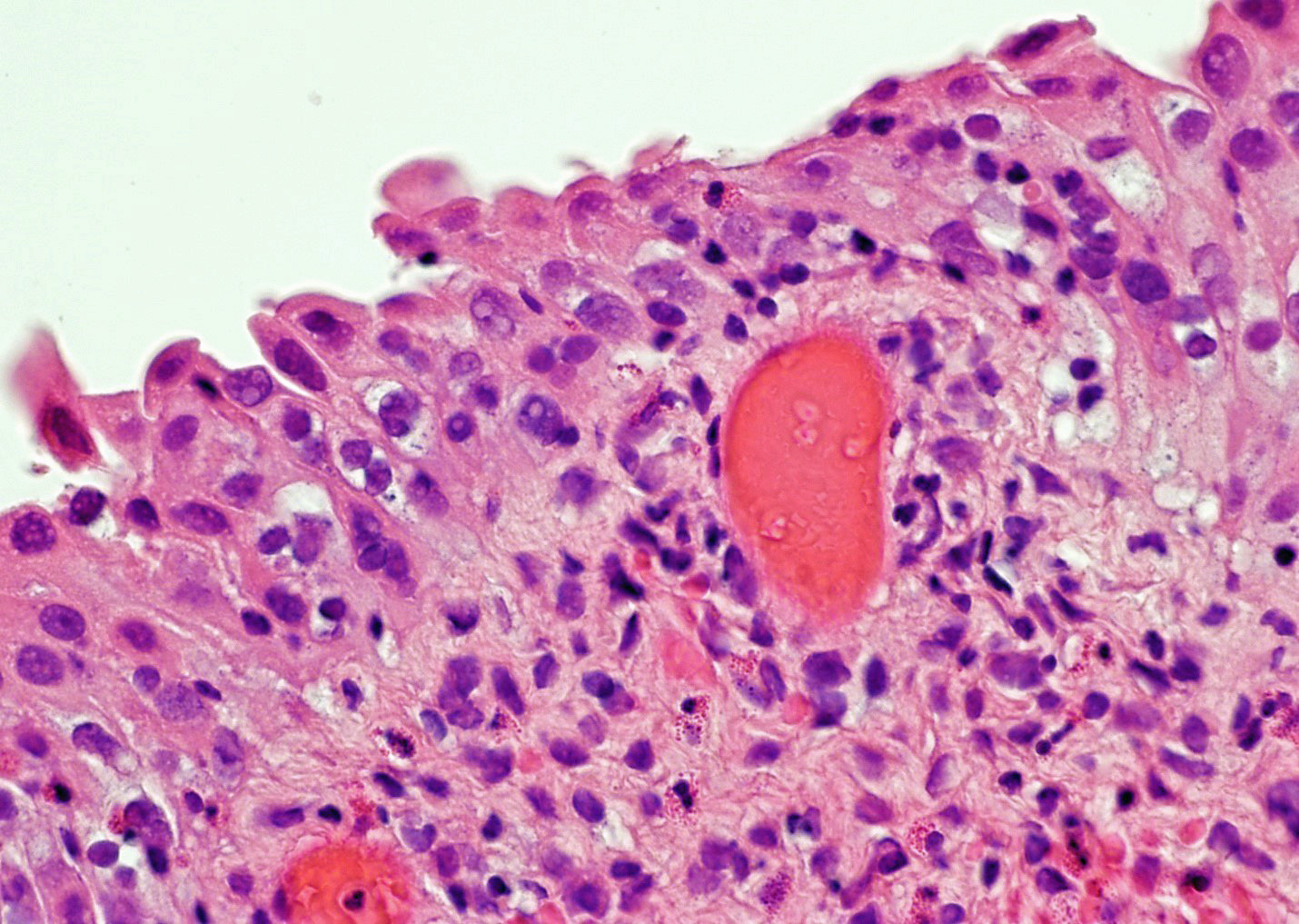
- Urothelium can show
- Nuclei with variation in nuclear size and shape, hyperchromasia, vesicular or smudgy chromatin
- Eosinophilic or amphophilic cytoplasm, cytoplasmic vacuoles
- Multinucleated giant cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:92)
- Usually no mitotic figures
- Surface erosion, ulceration
- Squamous metaplasia
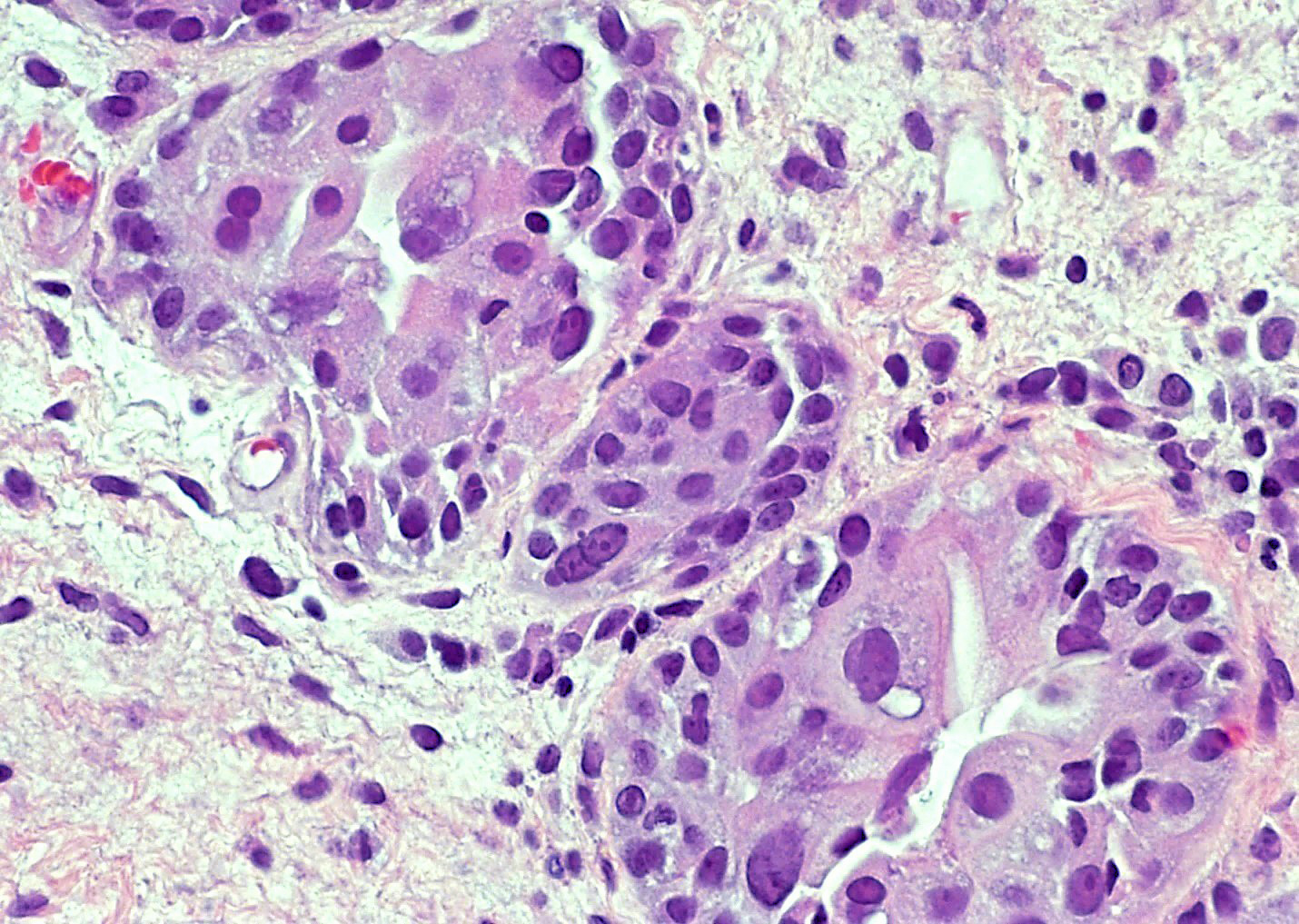
- Pseudocarcinomatous urothelial hyperplasia: variable sized urothelial cords and nests with rounded or irregular edges present in the lamina propria and enclose dilated blood vessels with fibrin deposition (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:92)
- Acute phase: edematous, congested and telangiectatic vessels, acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrate, atypical stromal cells with multinucleated forms
- Chronic phase: atrophic urothelium, atrophic smooth muscle layer, collagen deposition (fibrosis) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:909)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Y. Albert Yeh, M.D., Ph.D. and Jennifer Lee, M.D.
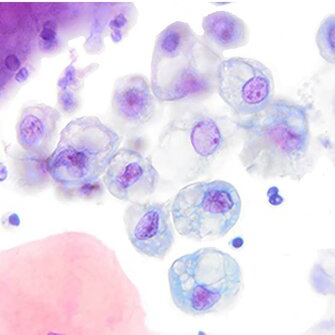
Cytology description
- Cohesive groups and dispersed urothelial cells with cellular and nuclear enlargement and maintained N:C ratio (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2023;147:1148)
- Variable combinations of the following features: dense to vacuolated cytoplasm, nucleomegaly with increased N:C ratio (> 0.5), nuclear vacuolization, vesicular to finely granular chromatin, prominent nucleoli, nuclear hyperchromasia, smudgy / glassy nuclei, smooth to irregular membrane, nuclear grooves
Cytology images
Positive stains
- CK20: positive staining in umbrella cells only
- p53: patchy and weak staining (wild type pattern)
- CD44: positive staining in full thickness or nearly full thickness of urothelium
- Reference: Zhou: Uropathology, 2nd Edition, 2022
Negative stains
- CK20 could be negative
- p53 could be negative
- Reference: Zhou: Uropathology, 2nd Edition, 2022
Electron microscopy description
- Increased stromal cellularity with enlarged fibroblast
- Dilatation of rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Prominent nucleoli
- Enlargement of endothelial cells
- Multiplication of vascular basal lamina around capillaries
- Reference: Korean J Urol 1993;34:969
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- UroVysion® multiprobe FISH testing: tetraploidy with a balanced duplication of the whole genome or polyploidy in benign bladder lesions including radiation induced cystitis (Ann Pathol 2012;32:e52)
Sample pathology report
- Urinary bladder, right wall polypoid lesion, transurethral resection:
- Radiation cystitis with pseudocarcinomatous urothelial hyperplasia (see comment)
- Muscularis propria not identified
- Comment: There is a history of radiation therapy per the medical record. The transurethral resection of the bladder lesion shows fragments of urothelial mucosa with total and partial denudation of urothelium. The urothelial lining cells show reactive changes. There is marked edema, hemorrhage and mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed predominantly of neutrophils and lymphocytes in the lamina propria. Reactive multinucleated stromal fibroblasts are seen. Telangiectatic vessels with fibrinoid necrosis and intravascular fibrin deposition are seen. Anastomosing cords and nests of urothelial cells encircling the vessels with fibrin deposition is evident. Urothelial cells with hyperchromatic nuclei, increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio and prominent nucleoli are seen. These features are consistent with radiation cystitis with pseudocarcinomatous urothelial hyperplasia. Muscularis propria is not identified in this specimen.
Differential diagnosis
- Invasive urothelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:909):
- Absence of urothelial nests surrounding ectatic vessels with intravascular and stromal fibrin deposition
- More prominent urothelial atypia
- Usually without pronounced acute and chronic inflammation
- Invasion of muscularis propria (if present) is most diagnostic
- Florid proliferation of von Brunn nests (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;38:11):
- Absence of urothelial nests surrounding ectatic vessels with intravascular and stromal fibrin deposition
- Nests of benign urothelial cells with uniformly round and lobular configuration
- Well demarcated from underlying lamina propria
- Inverted urothelial papilloma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;38:11):
- No history of radiation therapy
- Absence of urothelial nests surrounding ectatic vessels with intravascular and stromal fibrin deposition
- Thin anastomosing cords or trabeculae with bland urothelial cells invaginate into lamina propria
- Periphery of trabeculae show palisading of cellular nuclei and central areas show cellular spindling (streaming)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 68 year old man presented with hematuria and dysuria. He has a medical history of prostate cancer that was treated with radiation therapy. Cystoscopy revealed hemorrhage in the right bladder wall. A transurethral resection of the lesion was performed. A photomicrograph is shown above. What is the diagnosis?
- Cystitis cystica
- Invasive urothelial carcinoma, nested variant
- Radiation cystitis with pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia
- Urothelial carcinoma in situ
Board review style answer #1
C. Radiation cystitis with pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because anastomosing cords and nests of urothelial cells encircling ectatic vessels with intravascular and stromal fibrin deposition in a background of mixed inflammation are not present in these entities.
Comment Here
Reference: Radiation cystitis
Comment Here
Reference: Radiation cystitis