Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Treatment effect. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladdertreatmenteffect.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Histologic changes associated with chemotherapy (systemic or topical), radiation therapy or surgery (J Clin Pathol 2002;55:641)
Terminology
- See also granulomatis cystitis, radiation cystitis
Clinical features
- Cyclophosphamide causes hemorrhagic cystitis, and is associated with high grade bladder carcinoma and sarcoma
Case reports
- 71 year old man with bladder mass 6 years postradiation therapy for prostate cancer (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1067)
Gross description
- Chemotherapy may destroy tips of papillae in papillary tumors
Microscopic (histologic) description
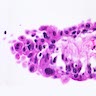
- General characteristics include pseudoinvasive urothelial nests wrapping around vessels associated with fibrin deposition; also hemorrhage, fibrin thrombi, fibrosis, acute and chronic inflammation; usually edema and vascular congestion; occasionally ulceration; no mitotic figures (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:909)
- Radiation therapy: causes endothelial swelling and necrosis, mural thickening and hyalinization with late luminal narrowing; also pseudoinfiltrative epithelial cords and nests extending into lamina propria and wrapping around dilated blood vessels containing fibrin; radiation fibroblasts with cytoplasmic or nuclear vacuoles and prominent nucleoli, stromal edema, extravasated red blood cells, destruction of bladder tumor papillae (Hum Pathol 2000;31:678)
- Surgery: associated with granulomatous reaction, postoperative spindle cell nodules, trapping of epithelial cells by inflammatory reaction resembling invasive disease, regenerative atypia resembling carcinoma in situ, reactive bone / osteoid
- Systemic chemotherapy: nuclear atypia, hemorrhagic cystitis, polyoma virus related changes
- Topical (intravesicular) Mitomycin C / ThioTEPA: may cause exfoliation of normal and abnormal urothelial cells, degeneration, multinucleation and bizarre reactive nuclear changes
- Topical bCG (immunotherapy): causes focal epithelial denudation with granulomatous inflammation of lamina propria
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Pseudocarcinomatous epithelial hyperplasia:
- Similar changes may occur due to ischemia and chronic irritation, not treatment (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:92)
- Urothelial carcinoma:
- Usually no history of treatment; definite invasive changes, mitotic figures present