Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Renal osteodystrophy | Osteitis fibrosa cystica | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ahmed R, Anjum S, Ud Din N. Brown tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonehyperarathyroidism.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Metabolic bone disease
- Manifestation of hyperparathyroidism
- Caused by increased osteoclastic activity and fibroblastic proliferation
- The term brown tumor derives from the color, which is caused by the vascularity, hemorrhage and deposits of hemosiderin
Essential features
- Elevated blood calcium or parathyroid hormone levels
- Radiologically osteolytic lesion
- Histologically giant cell rich lesion
Terminology
- Osteitis fibrosa
- Cystica generalisata
- Von Recklinghausen disease of bone
ICD coding
- ICD-10: E21.3 - hyperparathyroidism, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Prevalence 0.1% (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;23:477)
- More common in persons older than 50 years of age
- M:F = 1:3
- Associated with primary, secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Incidence is about 2 - 3% in primary hyperparathyroidism and up to 13% in secondary hyperparathyroidism (Int J Surg Case Rep 2021;79:375)
Sites
- Any part of the skeleton
- Most frequently encountered in the ribs, clavicles, long bones, pelvic girdle, craniofacial bones (Case Rep Nephrol Dial 2016;6:46)
- Rare in spine
Pathophysiology
- Primary, secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Increased serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) concentrations
- Detected by receptors on osteoblasts, which then release factors that stimulate osteoclast activity
- Skeletal manifestations of hyperparathyroidism are caused by unabated osteoclastic bone resorption leading to mobilization of skeletal calcium
- Rapid osteoclastic turnover of bone maintains normal serum calcium levels
- In localized regions, bone loss is particularly rapid; hemorrhage and reparative granulation tissue with active, vascular, proliferating fibrous tissue may replace the normal marrow contents, resulting in a brown tumor
- Hemosiderin imparts the brown color (hence the name of the lesions) (Kumar: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 10th Edition, 2020)
Etiology
- Primary hyperparathyroidism: adenoma (80 - 85%), hyperplasia (10 - 15%), carcinoma (1 - 5%) (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:176)
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism: chronic renal disease, continual and excessive urinary calcium excretion (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:176)
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism: prolonged parathyroid stimulation from a secondary cause (e.g. paraneoplastic syndrome) (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:176)
Clinical features
- Solitary or multiple lesions (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2021;22:443)
- Symptoms related to sites of involvement
- Pain, pathological fractures, disfigurement (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:176)
Renal osteodystrophy
- Collectively describes all the skeletal changes of chronic renal disease, including those associated with dialysis; the manifestations include:
- Osteopenia / osteoporosis
- Osteomalacia
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Growth retardation
- Various histologic bone changes in individuals with end stage renal failure can be divided into 3 major types of disorders:
- High turnover osteodystrophy characterized by increased bone resorption and bone formation, with the former predominating
- Low turnover or aplastic disease manifested by adynamic bone (little osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity) and less commonly, osteomalacia
- Mixed pattern of disease
- Pathophysiology:
- Kidney disease causes skeletal abnormalities through 3 mechanisms:
- Tubular dysfunction leading to renal tubular acidosis: the associated systemic acidosis dissolves hydroxyapatitie, resulting in matrix demineralization and osteomalacia
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism due to reduced phosphate excretion, chronic hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia
- Decreased production of vitamin D3 from damaged kidneys and reduced intestinal absorption of calcium because of low levels of vitamin D3
- Resultant secondary hyperparathyroidism produces increased osteoclast activity
- Other factors that are important in the genesis of adynamic renal osteodystrophy are diabetes mellitus, high dietary calcium ingestion, increasing age and iron accumulation in bone and aluminum deposition at the site of mineralization
- Kidney disease causes skeletal abnormalities through 3 mechanisms:
- Reference: Kumar: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 10th Edition, 2020
Osteitis fibrosa cystica
- Also called von Recklinghausen disease of bone
- Rare nowadays because hyperparathyroidism is diagnosed and treated at an early stage
- Increased number of osteoclasts erode bone matrix and mobilize calcium salts, particularly in the metaphysis of long tubular bones
- Bone resorption is accompanied by increased osteoblastic activity and the formation of new bony trabeculae
- Gross description: the cortex is thinned and the marrow contains increased amounts of fibrous tissue accompanied by foci of hemorrhage and cyst formation
- Microscopic (histologic) description: increased bone cell activity, peritrabecular fibrosis, cystic brown tumors (Kumar: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 10th Edition, 2020)
Diagnosis
- Requires integration of laboratory investigations, radiological and histopathological findings
Laboratory
- Elevated serum parathyroid hormone, calcium and alkaline phosphatase levels (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e11877)
- Elevated urinary calcium level
- Low serum phosphorus level (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e11877)
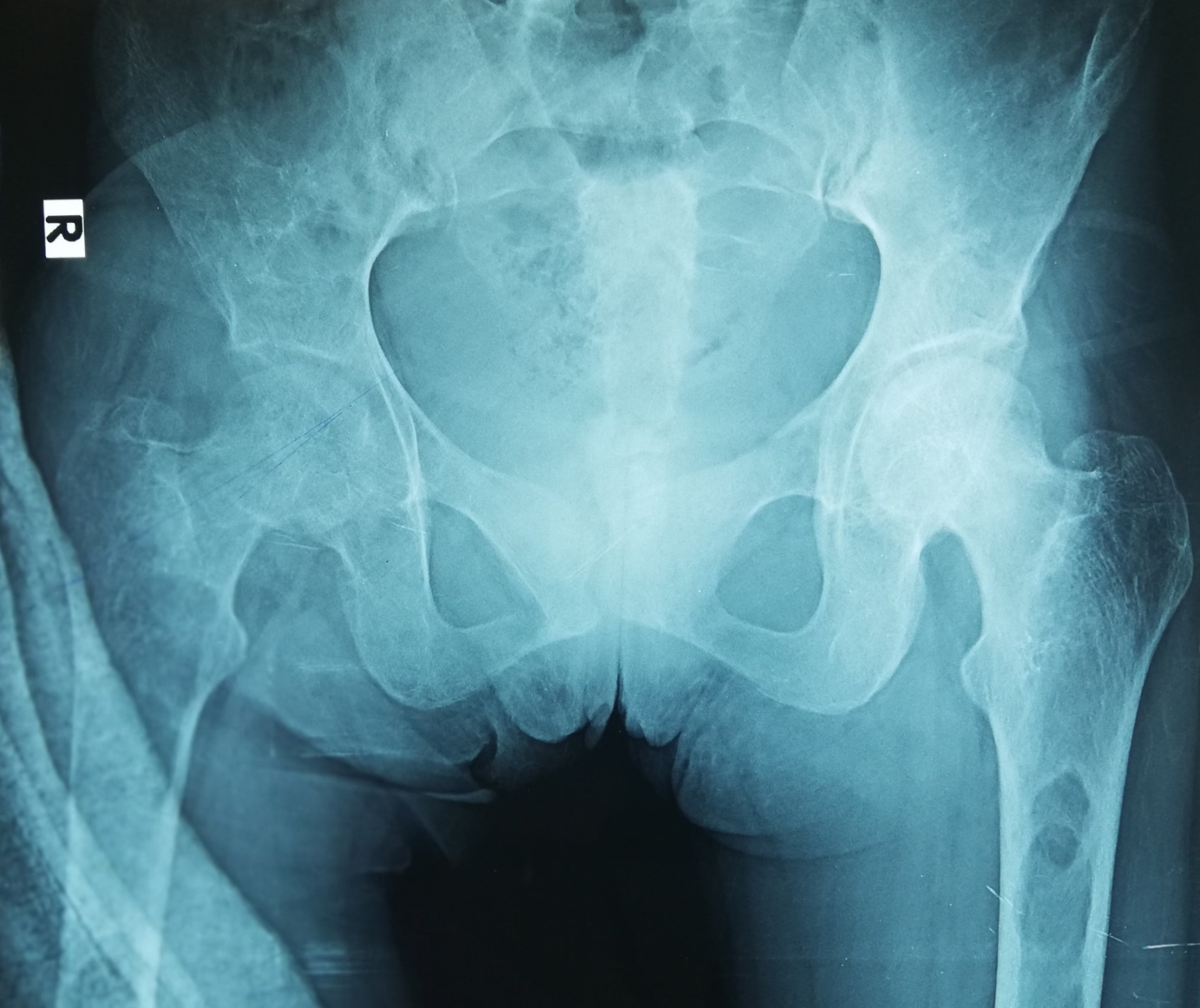
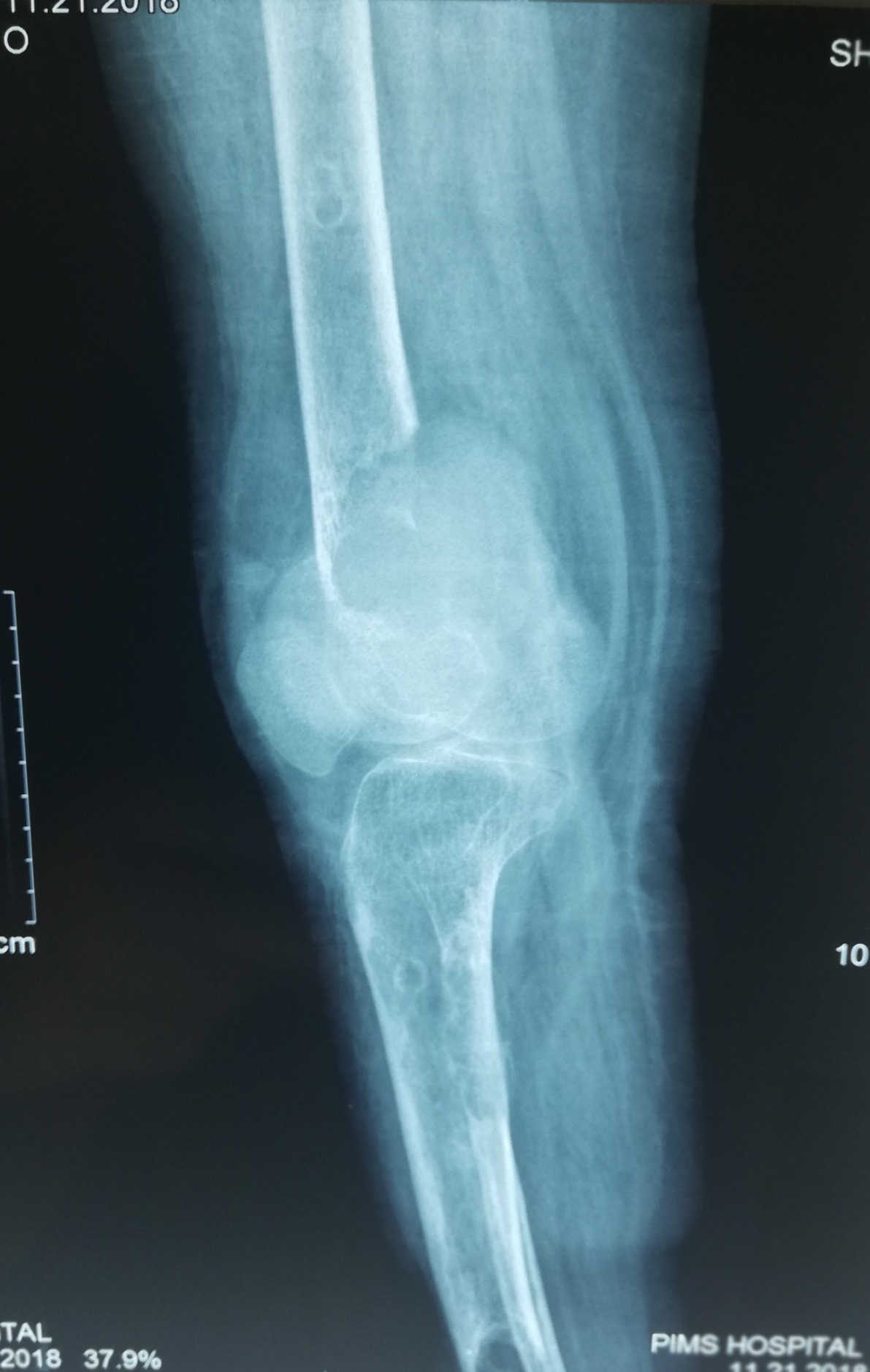
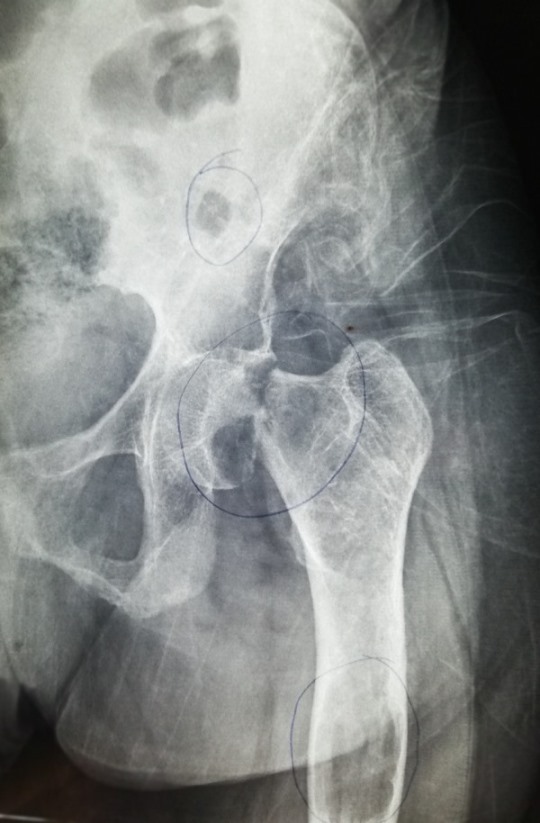
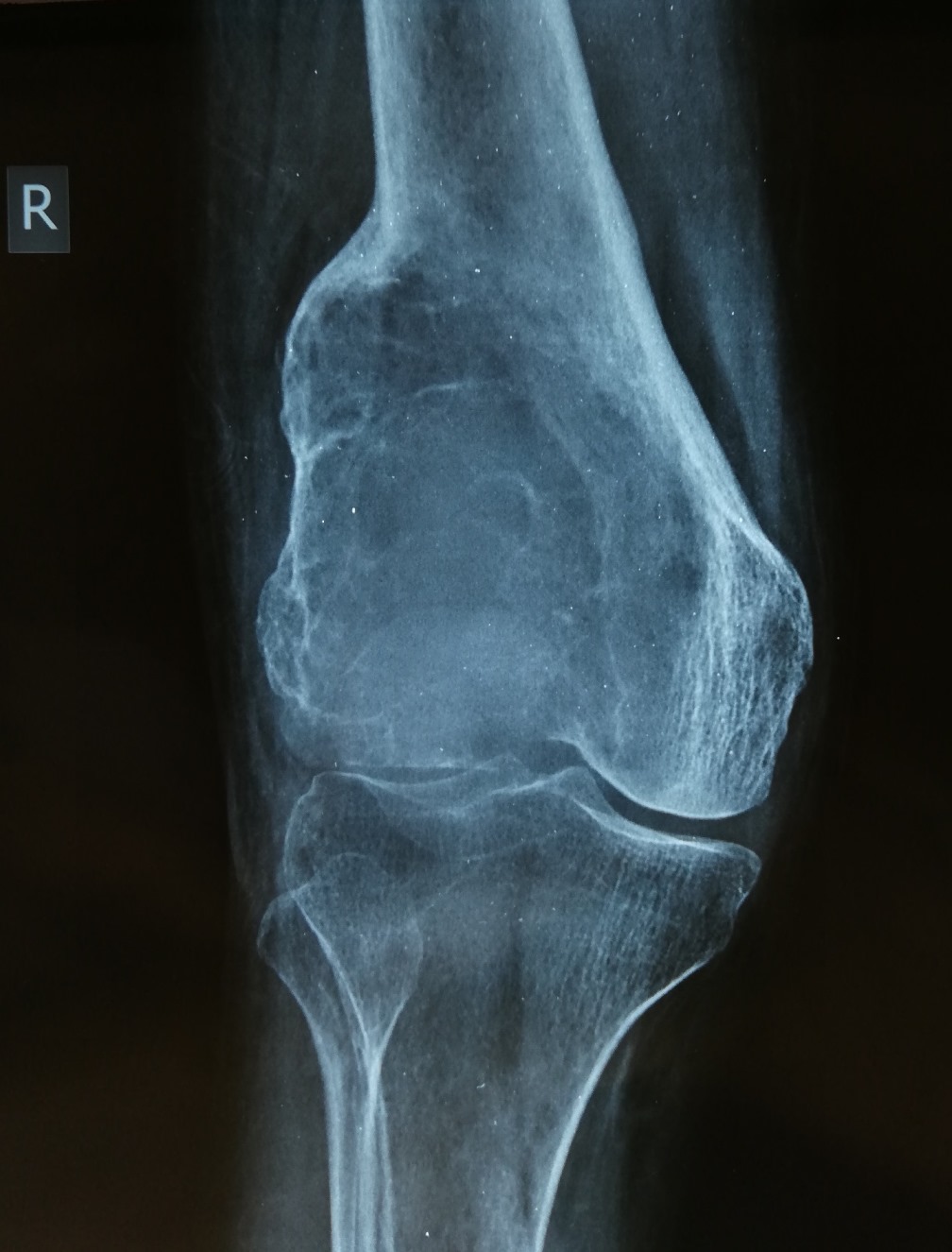
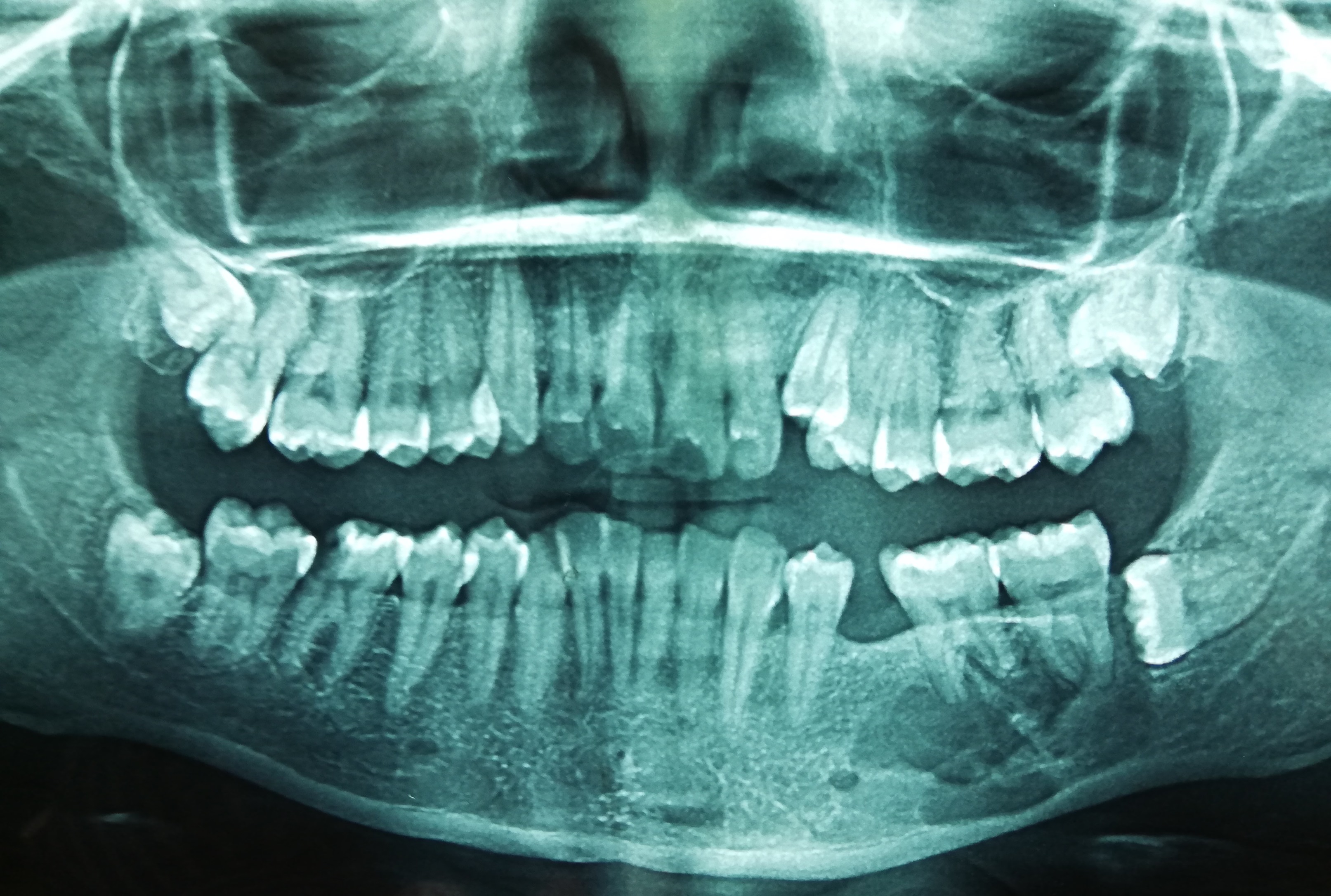
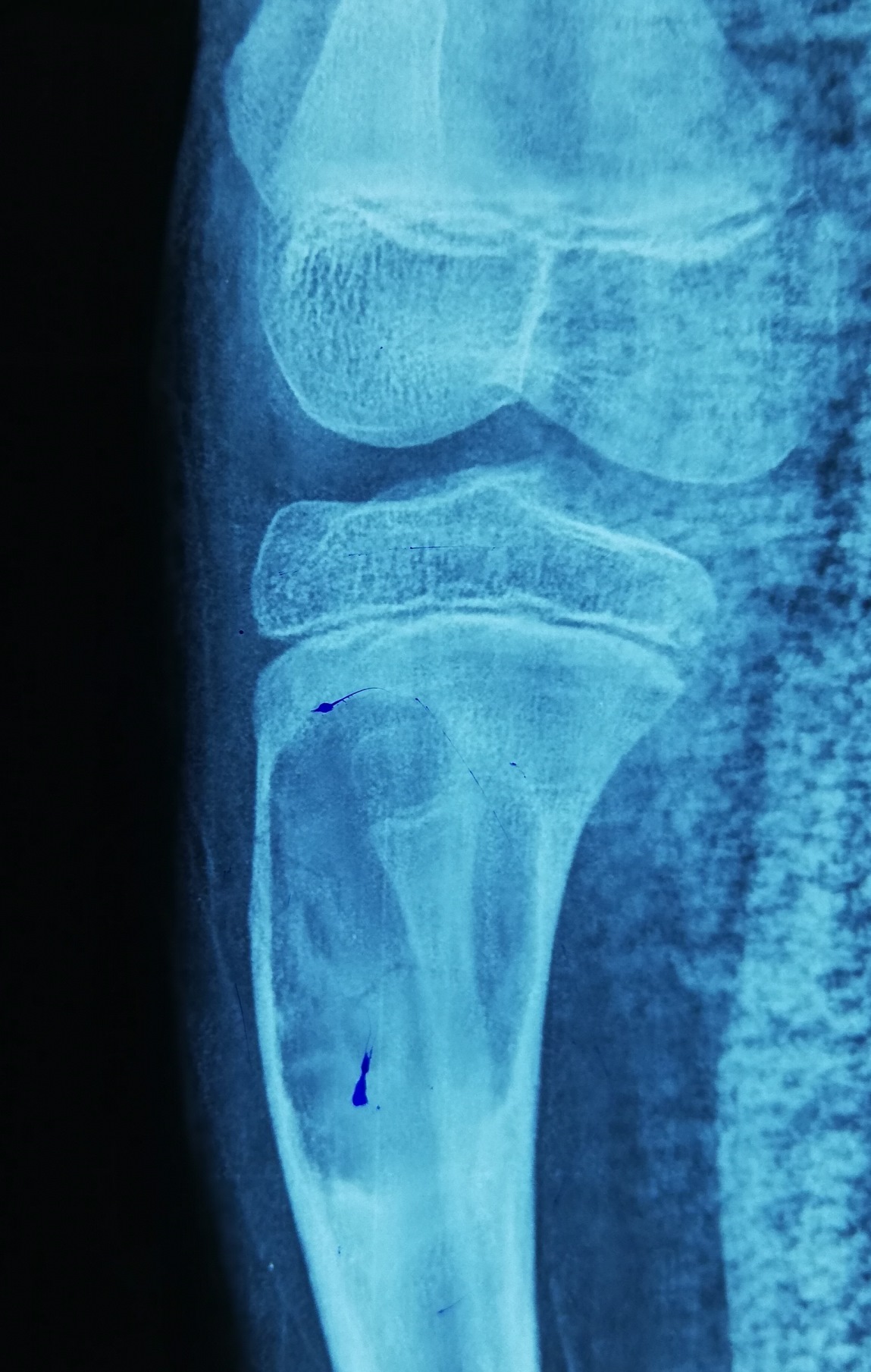
Radiology description
- Plain radiograph: well defined, purely lytic lesions that provoke little reactive bone; the cortex may be thinned and expanded but will not be penetrated (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1993;160:752)
- CT: attenuation values will be in the range of blood and fibrous tissue (Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:2482)
- Angiography (DSA): lesions are usually hypervascular (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1993;160:752)
- MRI: appearance depends on the relative proportion of its components; the lesions, therefore, may be solid, cystic or mixed (Skeletal Radiol 2011;40:205)
- Solid components are intermediate to low intensity on T1 and T2 weighted images, while the cystic components are hyperintense on T2 weighted images and may have fluid-fluid levels
- T1 C+ (Gd): there can be enhancement of the solid component and septa
- Nuclear medicine: bone scan often shows intense uptake (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1993;160:752)
Prognostic factors
- Brown tumors regress when the cause of hyperparathyroidism is removed
Case reports
- 21 year old woman with facial pain (J Med Case Rep 2016;10:166)
- 26 year old woman with neck pain (Asian Spine J 2015;9:110)
- 30 year old woman with back, lower limb and shoulder pain (Gland Surg 2019;8:810)
- 30 year old woman with chronic renal insufficiency (Case Rep Nephrol Dial 2016;6:46)
- 50 year old woman with thoracodorsal pain (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e15007)
- 53 year old man with osteolytic lesions of radius and ulna (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:176)
Treatment
- Normalizing PTH level with drugs, dialysis, parathyroidectomy or kidney transplantation will often cause the tumor to regress or resolve
- Surgical resection of a brown tumor is generally not recommended and should only be considered if the patient wants quick resolution, if the lesion is compromising body functions or promoting facial deformation or if the lesion fails to regress after 1 - 2 years of follow up (Case Rep Nephrol Dial 2016;6:46)
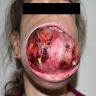
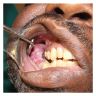
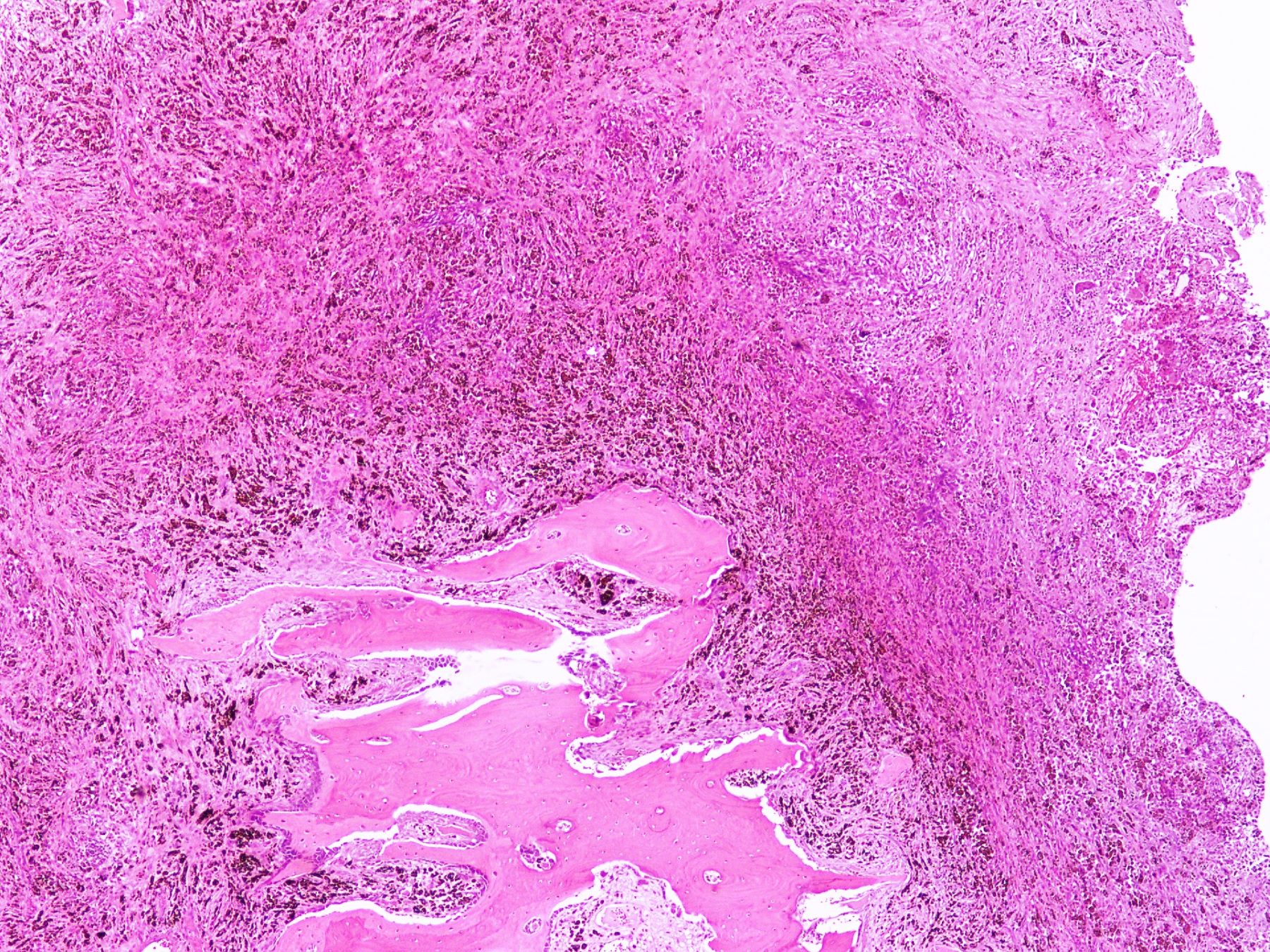
Gross description
- Spongy brown cystic hemorrhagic lesion
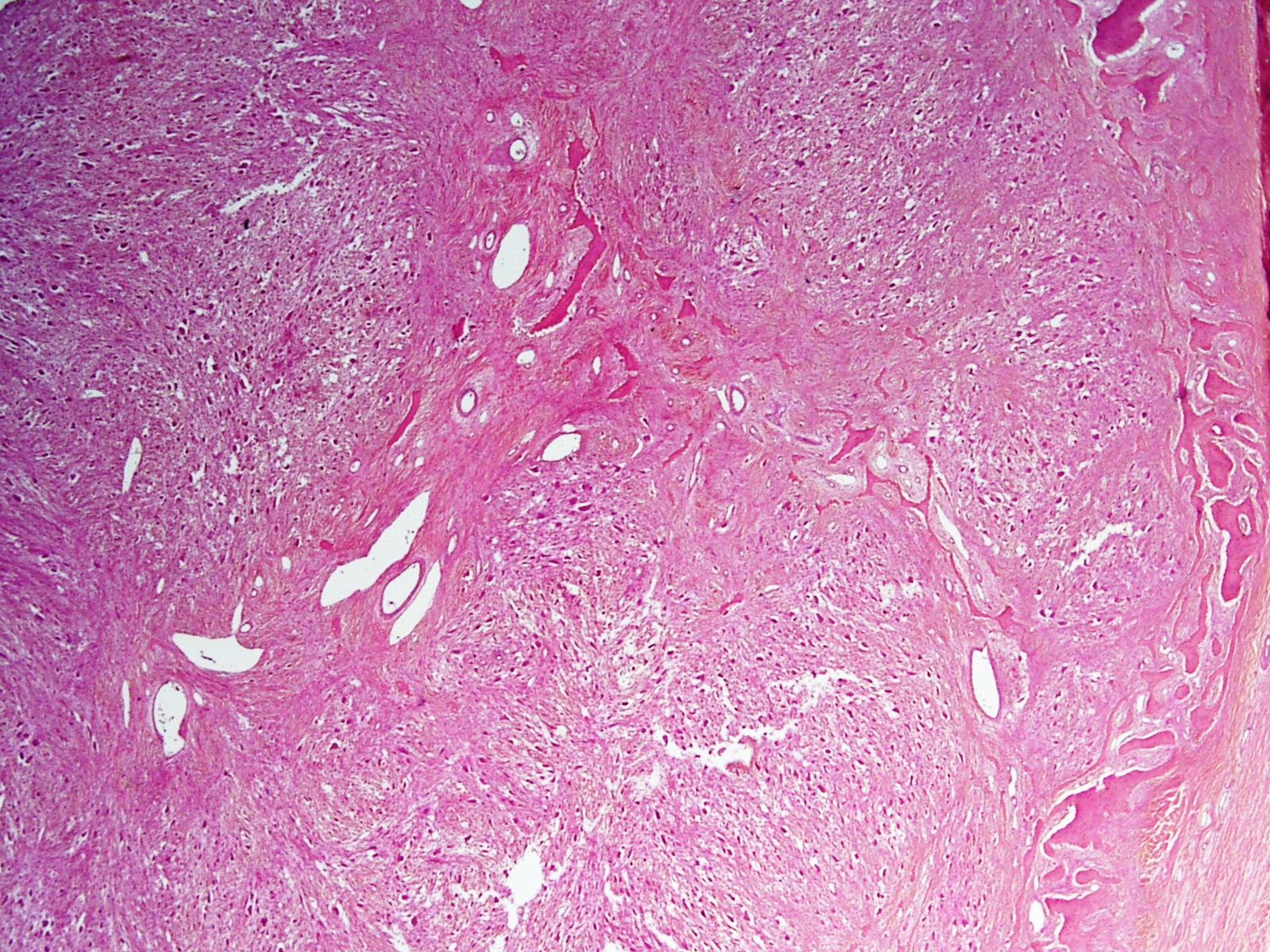
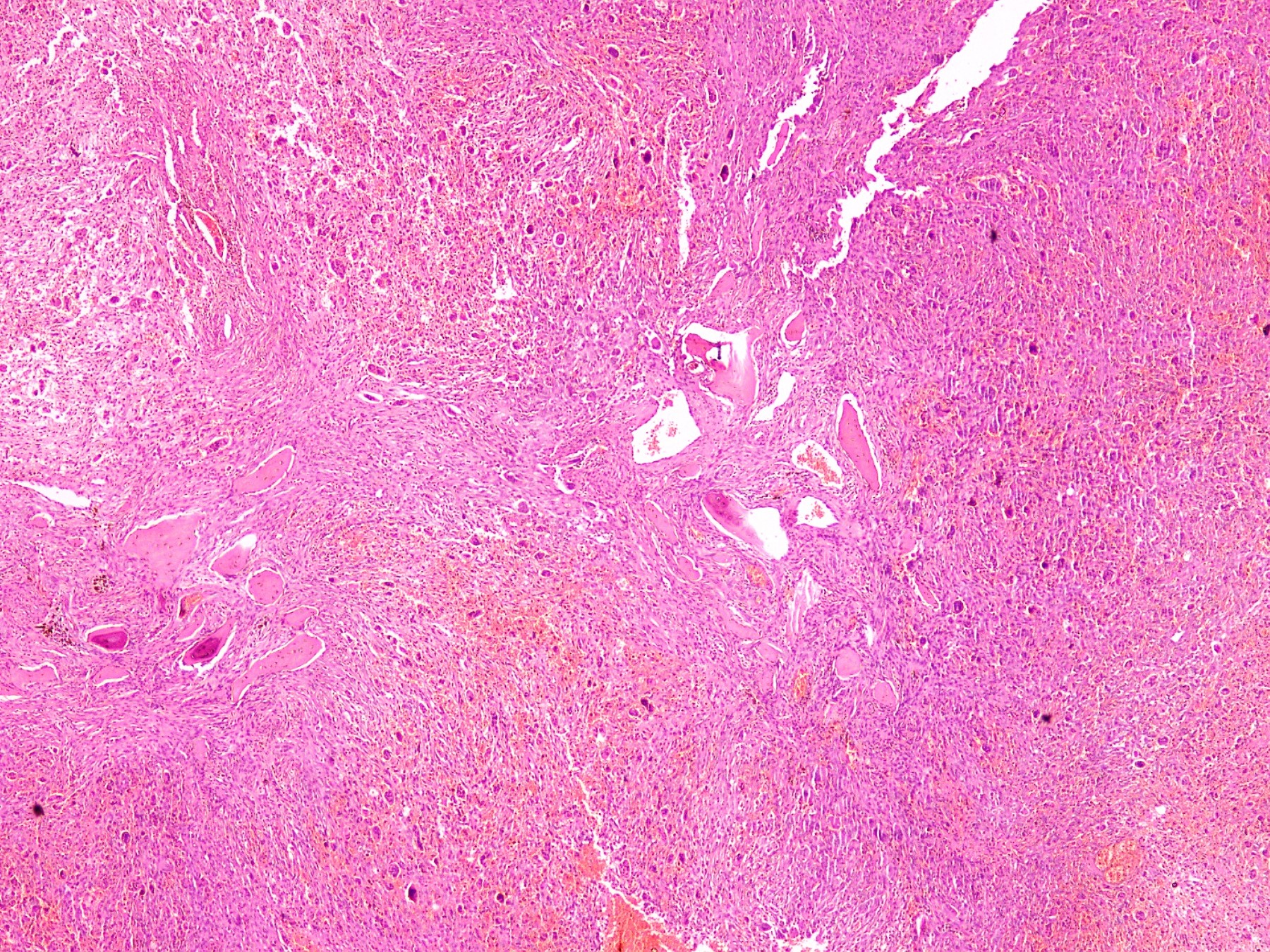
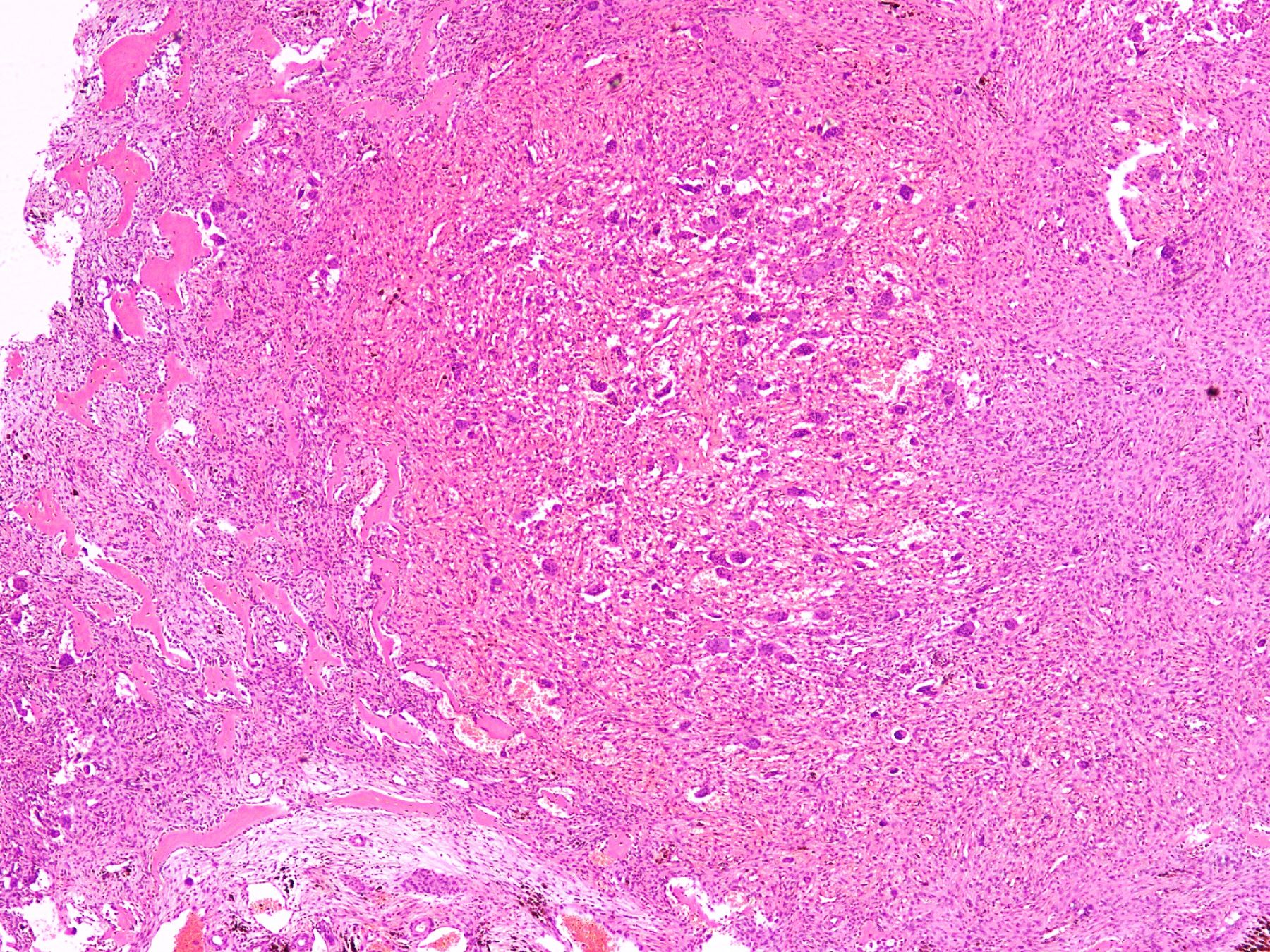
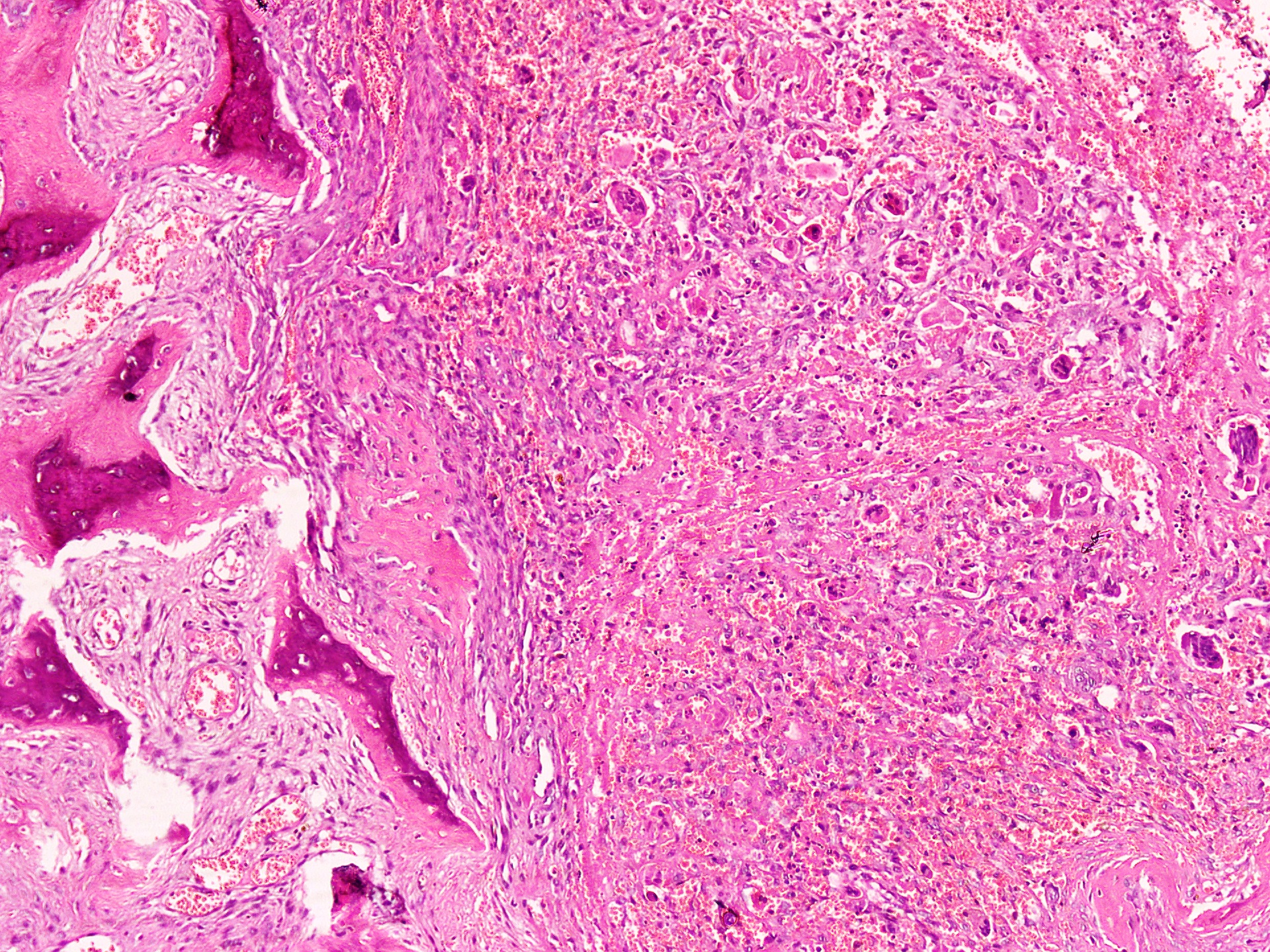
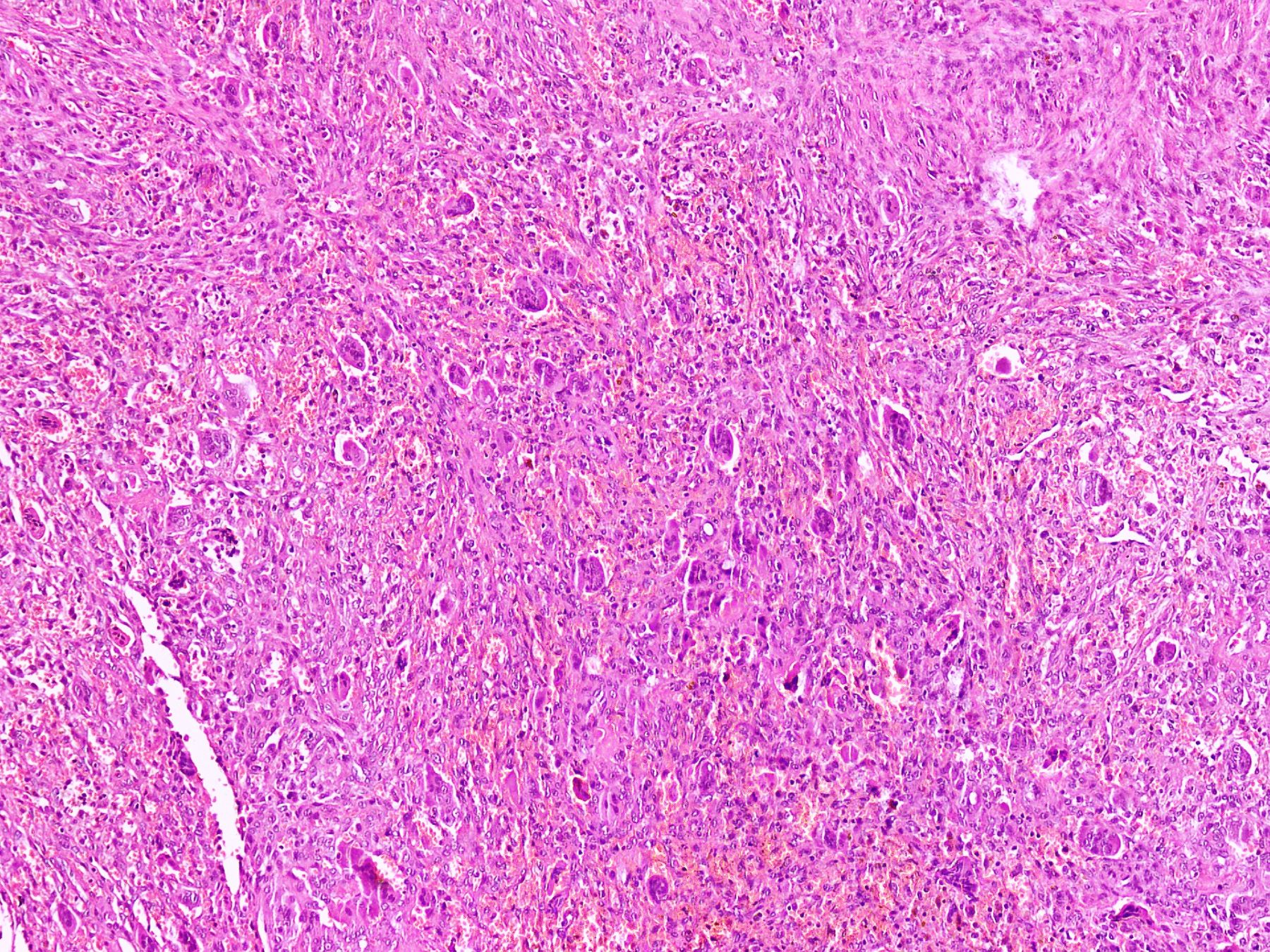
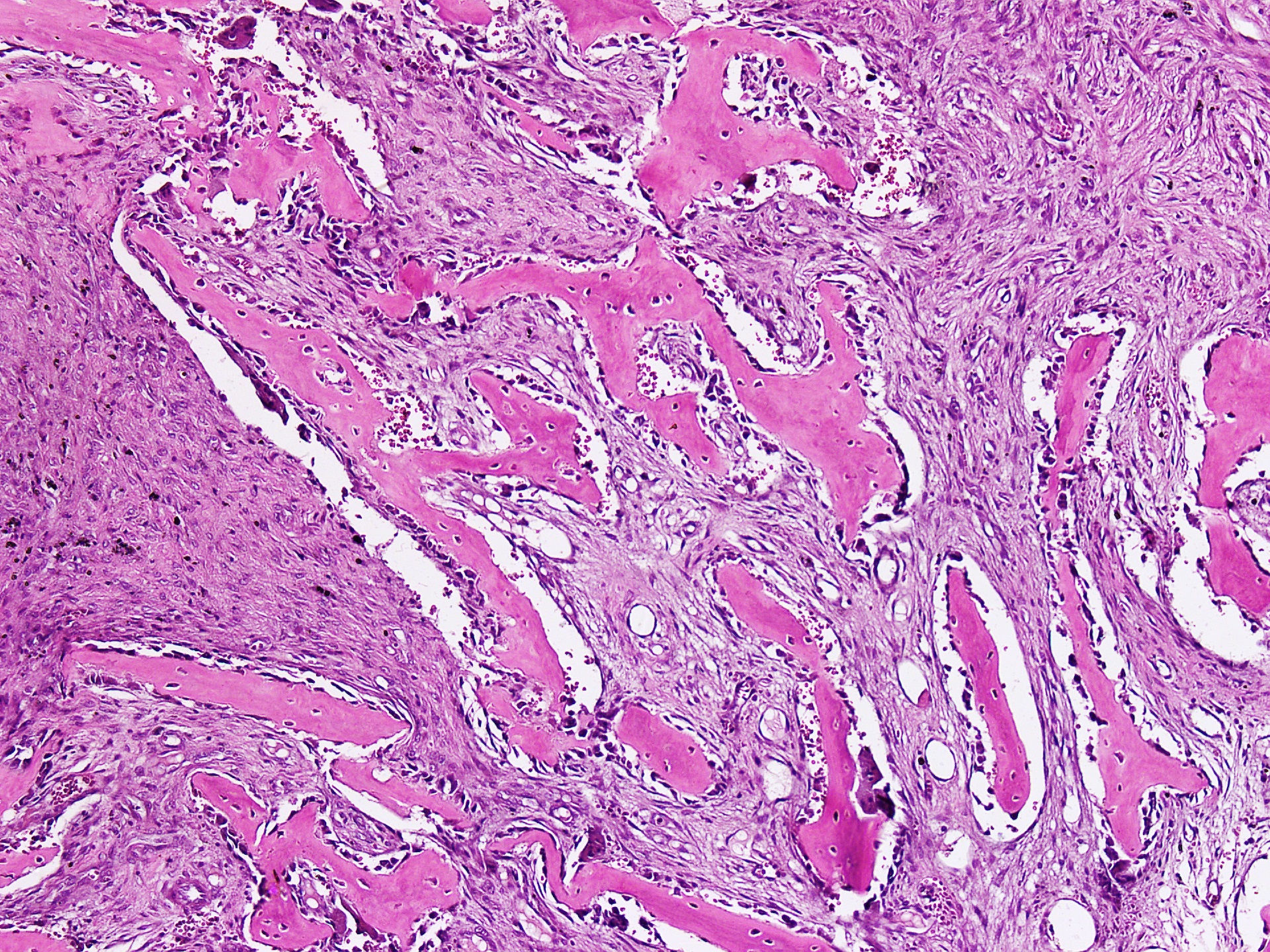
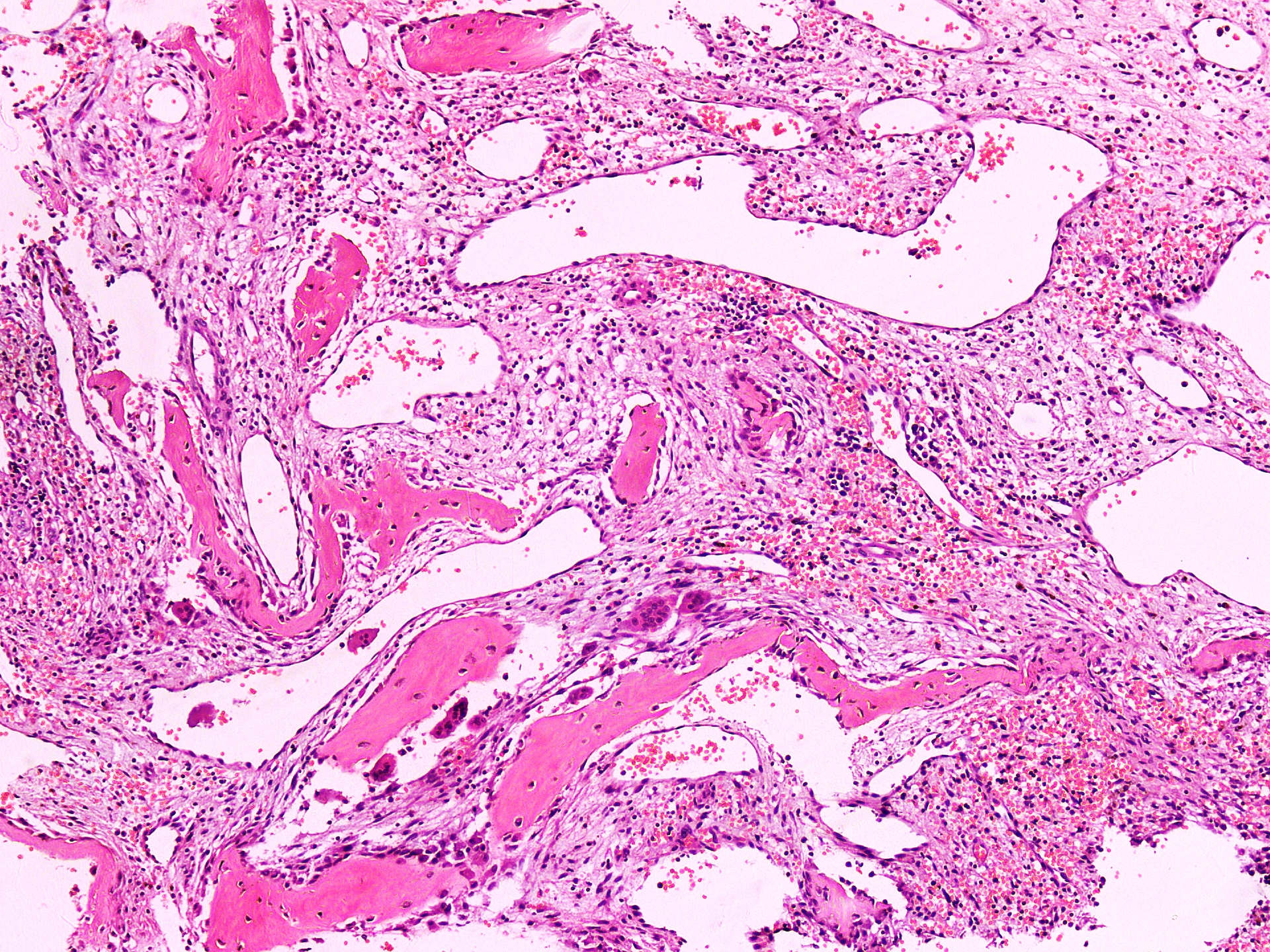
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Lobular pattern composed of groups and clusters of osteoclast-like multinucleated giant cells
- Vascular fibroblastic stroma
- Hemorrhage and hemosiderin deposits
- Tunneling resorption of adjacent uninvolved bone (J Int Oral Health 2015;7:50)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Videos
Bone changes in hyperparathyroidism
Sample pathology report
- Left femur lytic lesion, curettage:
- Giant cell rich lesion (see comment)
- Comment: The lesion is composed of clusters of giant cells in a hemorrhagic fibroblastic stroma. Focal tunneling bone resorption is seen. This feature, along with multiple lytic lesions on radiology, strongly favor brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism. Correlation with clinical history, radiological findings and serum PTH and calcium levels is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Giant cell tumor:
- Arises in epiphysis of long bones in adults
- Uniform distribution of osteoclast type giant cells among mononuclear cells
- Mononuclear cells are not as spindled as fibroblasts in brown tumor
- Nuclei of mononuclear cells of giant cell tumor are similar to those of osteoclasts
- Mononuclear cells are positive for H3G34W, p63 and CD68
- Harbor H3F3A (G34W/V) mutations
- Serum calcium and PTH levels are normal (Nielsen: Diagnostic Pathology - Bone, 3rd Edition, 2021)
- Giant cell reparative granuloma:
- Arises primarily in jaw, other craniofacial bones
- Can have very similar morphologic features and may be impossible to distinguish from brown tumor by H&E alone
- Brown tumor has much more lobulated growth pattern
- Features of hyperparathyroidism in surrounding bone are not present
- Nonuniform distribution of osteoclast type giant cells, mononuclear cells in a vascularized stroma
- Serum calcium and PTH levels are normal (Nielsen: Diagnostic Pathology - Bone, 3rd Edition, 2021)
- Solid aneurysmal bone cyst:
- Most common during first 2 decades of life
- Arises in the metaphysis of long bones
- Does not demonstrate lobular growth pattern seen in brown tumor
- Contains blood filled cystic spaces separated by fibrous septa
- Fibrous septa are composed of a moderately dense cellular proliferation of bland fibroblasts, with scattered multinucleated, osteoclast type giant cells and reactive woven bone rimmed by osteoblasts
- Solid subtype of aneurysmal bone cyst has the same components
- USP6 gene rearrangement (Nielsen: Diagnostic Pathology - Bone, 3rd Edition, 2021)
Board review style question #1
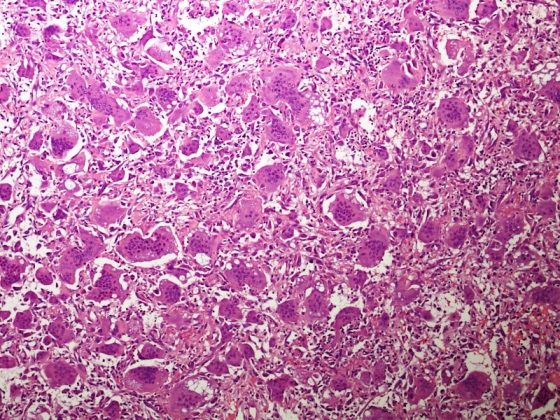
A 50 year old woman presented with a swelling on the right side of her face that gradually increased in size over last 3 years. It was associated with pain, trismus and inability to open her right eye. She also had history of frequent headaches, abdominal pain and renal stones. Xray revealed a lytic lesion within the right mandible. Incisional biopsy was performed and microscopic examination revealed a lesion (shown above). The most likely diagnosis is
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
- Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism
- Central giant cell granuloma
- Cherubism
- Giant cell tumor
Board review style answer #1
B. Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism. The photomicrograph shows a lesion composed of bony trabeculae showing resorption along with scattered osteoclast-like giant cells in a vascularized spindled stroma. These microscopic findings with above mentioned clinical and radiological features are characteristic of brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism. Aneurysmal bone cyst affects young adults and shows large blood filled spaces with intervening septae containing fibroblasts and giant cells. Central giant cell granuloma produces radiolucent lesions in children and young women and shows osteoclast-like giant cells near hemorrhagic areas, cellular vascular and fibrous stroma and new bone formation at edge of lesion. Cherubism shows bilateral involvement of mandible and maxilla in young individuals and histology is similar to central giant cell granuloma. Giant cell tumor rarely affects mandible and shows uniform distribution of osteoclast type giant cells among mononuclear cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism
Comment Here
Reference: Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism
Board review style question #2
A 49 year old hypertensive and diabetic man presents with a complaint of right mandibular pain, swelling and intraoral bleeding for a period of 12 months. There was a gradual increase in size and pain. Xray revealed a well defined multilocular lesion within the right mandible. Incisional biopsy was performed and microscopic examination revealed a lesion in the given photomicrograph. What is the most likely underlying etiology?
- Chronic adrenal insufficiency
- Chronic liver disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- End stage renal disease
- Ischemic heart disease
Board review style answer #2
D. End stage renal disease. The photomicrograph shows a lesion composed of scattered osteoclast-like giant cells in a vascularized spindled stroma characteristic of brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism. End stage renal disease causes decreased glomerular filtration due to reduced nephron function, which results in decreased synthesis of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 by the kidney. This leads to decreased absorption of calcium by the gut. Consequently, there is an increased level of serum phosphate. Increased serum phosphate causes serum calcium to be deposited in bone, also leading to a decreased serum calcium. In response to low serum calcium levels, the parathyroid glands secrete increased parathyroid hormone, which results in secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Comment Here
Reference: Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism
Comment Here
Reference: Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism