Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Burkett A, Farr GA, Leal SM. Cryptococcus neoformans & gattii. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/microbiologycneoformans.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Taxonomy: phylum Basidiomycetes (similar to mushrooms); order Tremellales; family Tremellaceae
- 7 species total:
- C. neoformans (formerly C. neoformans var grubiii)
- C. deoneoformans (formerly C. neoformans var neoformans)
- C. gattii species complex (formerly C. neoformans var gattii)
- C. gattii sensu stricto (ss; formerly molecular type VGI)
- C. deuterogattii (formerly molecular type VGII)
- C. bacillisporus (formerly molecular type VGIII)
- C. tetragattii (formerly molecular type VGIV)
- C. decagattii (formerly recognized as VGIII / VGIV)
- References: Mycoses 2019;62:1029, Emerg Infect Dis 2018;24:2095
Essential features
- Variably sized yeasts with thin walls and narrow based budding
- Encapsulated by thick sugar capsule composed of glucuronoxylomannan (GXM)
- Histopathology: methenamine silver+, mucicarmine+, Fontana-Masson+, India ink+
- Diseases range from cutaneous to severe pulmonary and central nervous system disease
Epidemiology
- C. neoformans: immunocompromised; bird droppings, soil, widespread distribution (UpToDate: Microbiology and epidemiology of Cryptococcus neoformans infection [Accessed 05 August 2020])
- C. gattii: immunocompetent; tropical / subtropical distribution; eucalyptus trees; Vancouver Island, BC; endemic in the Southeastern U.S.; South America, parts of Africa and Southeast Asia (UpToDate: Cryptococcus gattii infection - Microbiology, epidemiology, and pathogenesis [Accessed 05 August 2020])
Sites
- Immunocompromised host
- Lung / pneumonia
- CNS infection / meningitis / meningoencephalitis
- Cutaneous manifestation: pustules, papules, superficial granulomas, cellulitis (UpToDate: Cryptococcus neoformans infection outside the central nervous system [Accessed 05 August 2020])
- Can resemble molluscum contagiosum
- Disseminated infection
- Immunocompetent host
Pathophysiology
- Antiphagocytic and poorly immunogenic sugar capsule composed mainly of glucuronoxylomannan (GXM), which is a major virulence factor
- Phenol oxidase production of the antioxidant melanin
- Reference: Emerg Infect Dis 1998;4:71
Clinical features
- Opportunistic infection
- C. neoformans infection in immunocompetent individuals, however, C. gattii infects immunocompetent individuals
- Major illness in patients with HIV / AIDS with an estimated 220,000 annual cases of cryptococcal meningitis worldwide (Lancet Infect Dis 2017;17:873)
- Pulmonary disease can be subacute and indolent
- Cough and dyspnea with or without constitutional symptoms
- Pulmonary nodules; old cryptococcomas
- CNS disease presents with increased intracranial pressure, seizures and focal neurologic deficits
- Spectrum of diffuse meningeal disease and focal lesions including soap bubble lesions
- Not a known zoonotic disease
Diagnosis
- CrAg Lateral Flow Assay: Dipstick sandwich immunochromatographic assay: qualitative or semiquantitative detection of the capsular polysaccharide antigens of Cryptococcus species complex
- If CrAg is present in the specimen, then it binds to the gold conjugated, antiCrAg antibodies; gold labeled antibody antigen complex forms a sandwich at the test line causing a visible line to form
- Positive test results create 2 lines (test and control); negative test results form only 1 line (control); if a control line fails to develop, then the test is not valid
- Testing on BAL / pleural fluid is limited to large reference labs that have validated these sample types
- Unchanged or increased titer of antigen in CSF is correlated with clinical and microbiological failure to respond to treatment
- Titer >1:8
- Rise in CSF antigen titer during suppressive therapy is associated with relapse of cryptococcal meningitis (Clin Infect Dis . 1994;18:789)
Laboratory
- Gram stain shows variably sized yeasts with narrow based budding
- India ink highlights organisms (rarely used in clinical practice)
- Grows well on sheep blood, chocolate agar and fungal media, including sabouraud dextrose agar
- Rapid growth within 24 hours at 37 °C
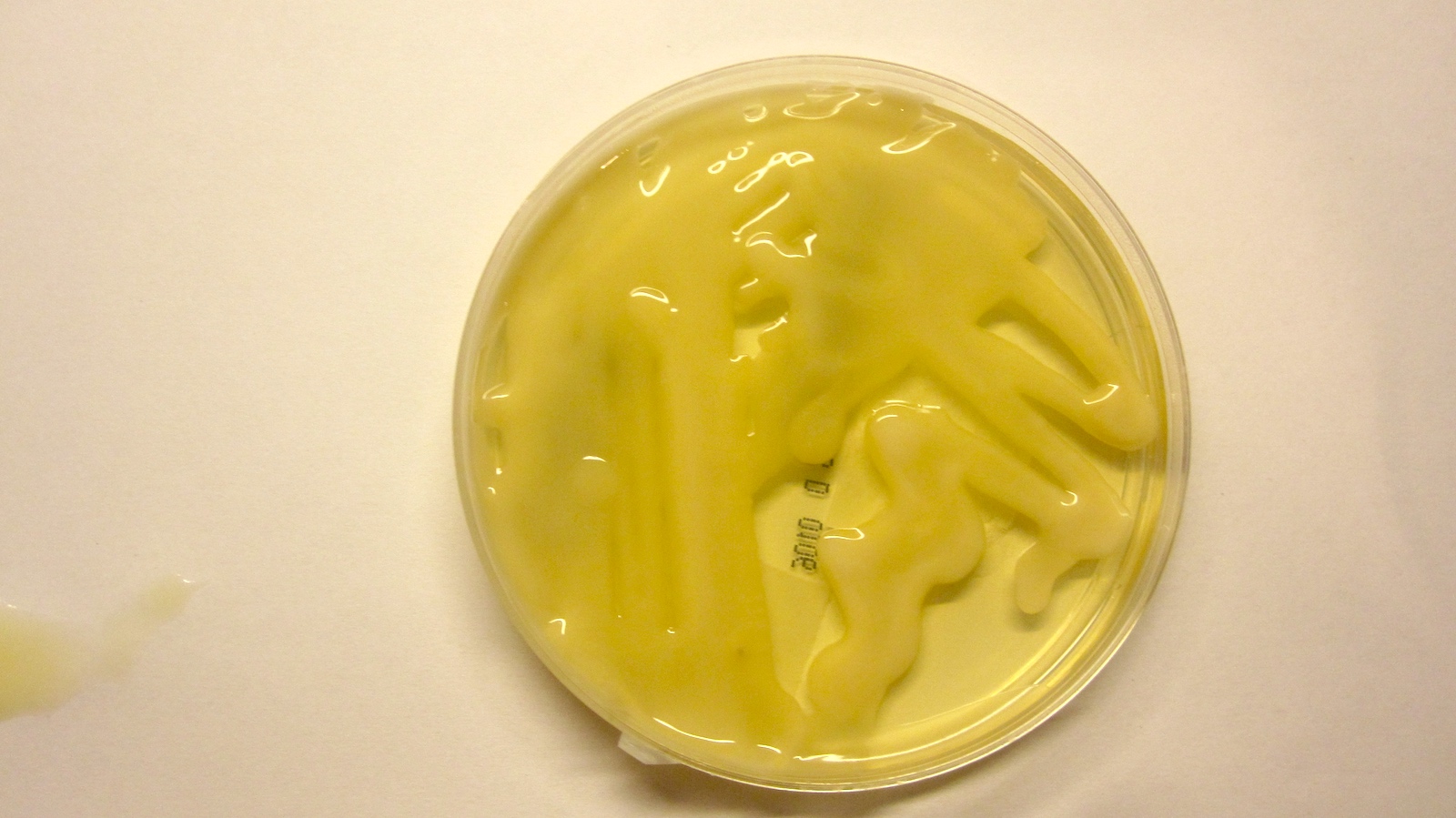
- Creamy, butyrous, mucoid colonies (due to sugar capsule)
- Rapid urease positive
- Brown colonies on birdseed agar due to melanin production
- Matrix assisted laser desorption / ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) can distinguish C. neoformans from C. gattii
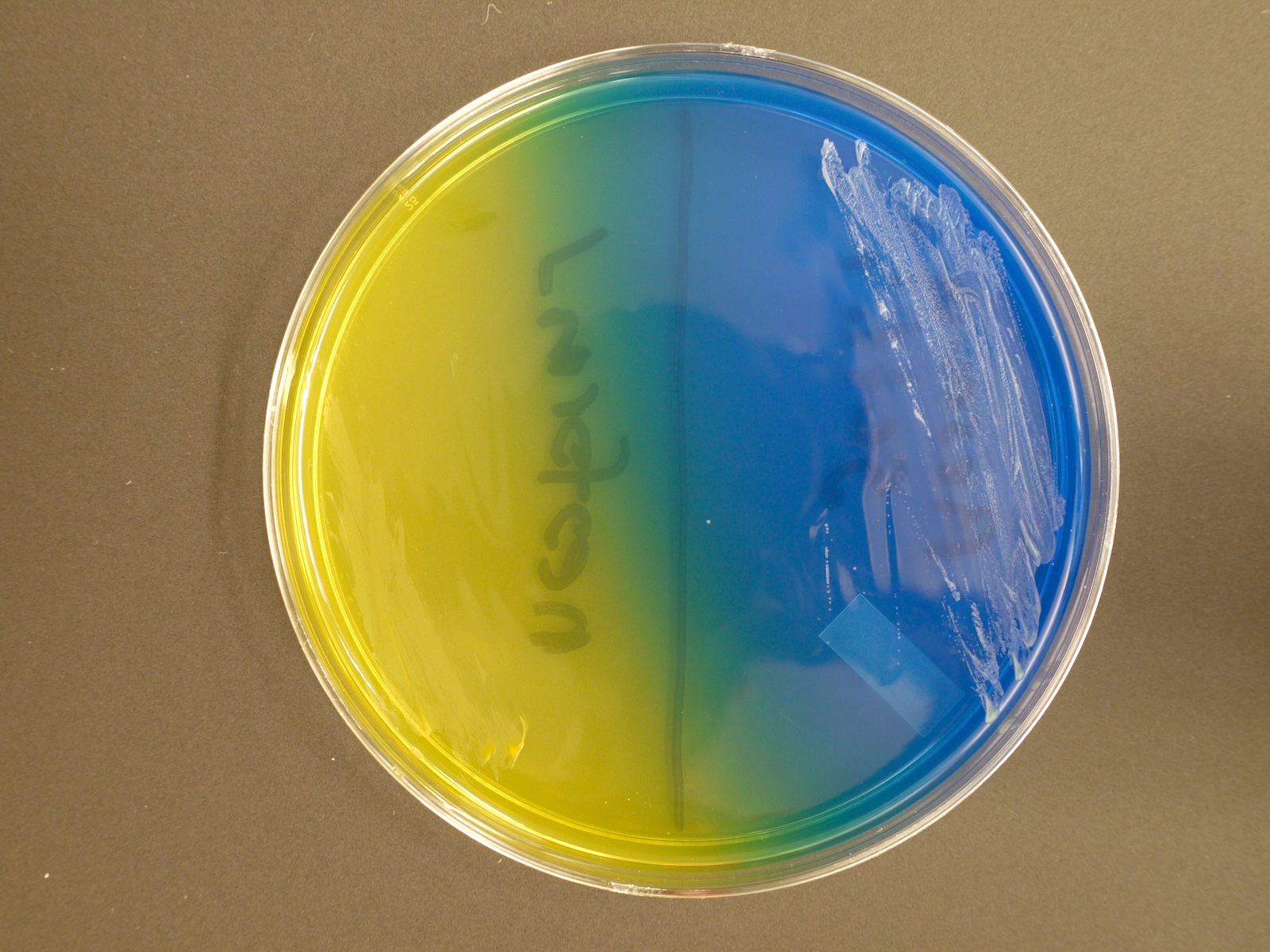
- Can distinguish C. gattii by deep blue colonies on canavanine glycine bromothymol blue (CGB) media
Case reports
- 28 year old woman from rural India admitted for an abrupt deterioration of mental status, behavioral changes and hallucinations (Cases J 2009;2:9084)
- 56 year old man presents for evaluation of a progressively worsening headache (PLoS One 2011;6:e28625)
- 68 year old man presents for outpatient evaluation of dyspnea and new onset atrial fibrillation 9 months after undergoing bilateral lung transplantation (Transpl Infect Dis 2019;21:e13137)
- 76 year old asymptomatic woman with incidental pulmonary nodule (Med Mycol Case Rep 2018;21:23)
Treatment
- Intrinsic resistance to echinocandins
- Induction therapy with liposomal amphotericin B and flucytosine for 14 days
- Consolidation with high dose fluconazole for 8 weeks
- Maintenance with lower dose fluconazole for 6 - 12 months
- C. gattii treatment regimens are similar but more intense
- Reference: J Fungi (Basel) 2018;4:79
Clinical images
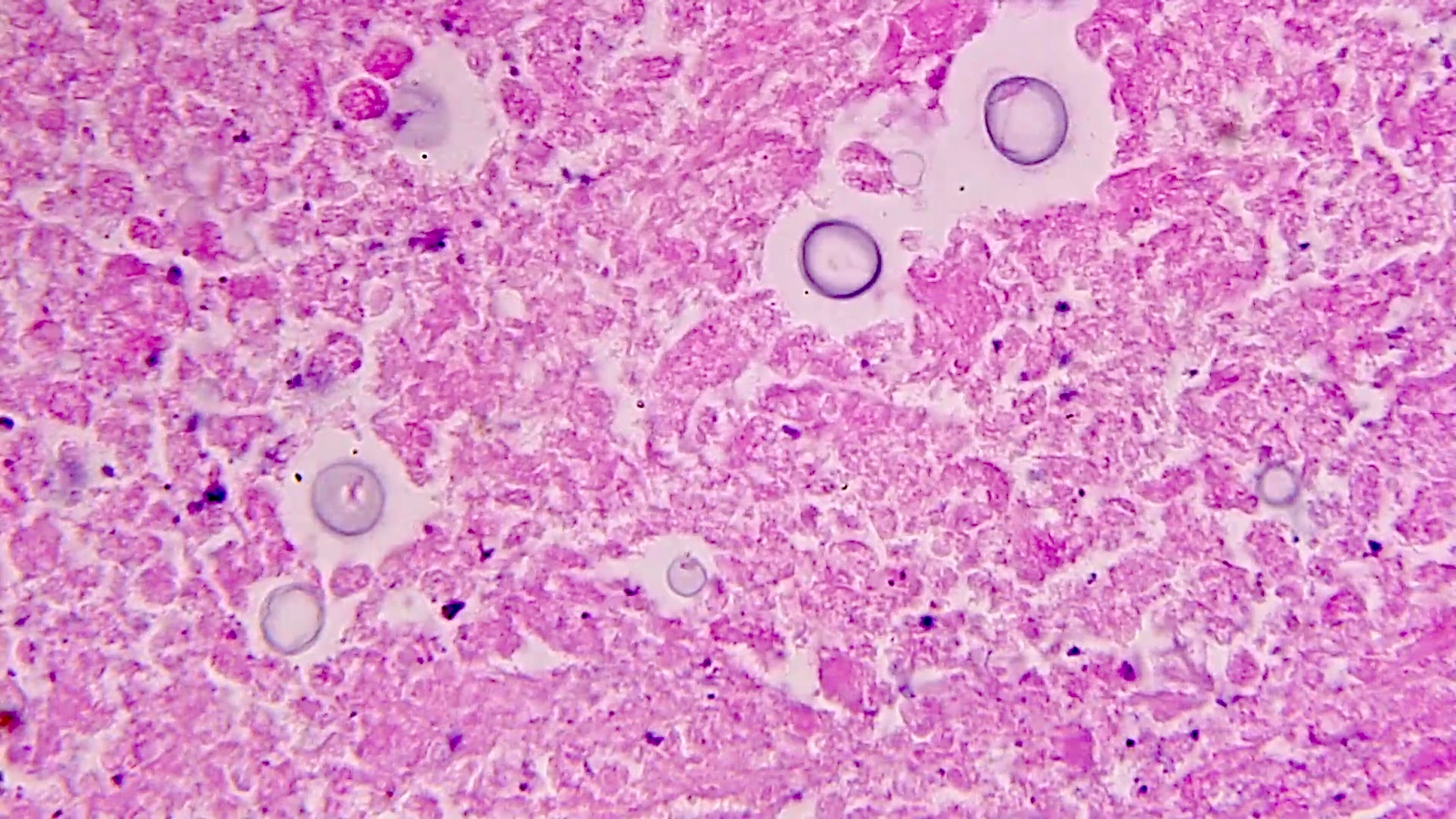
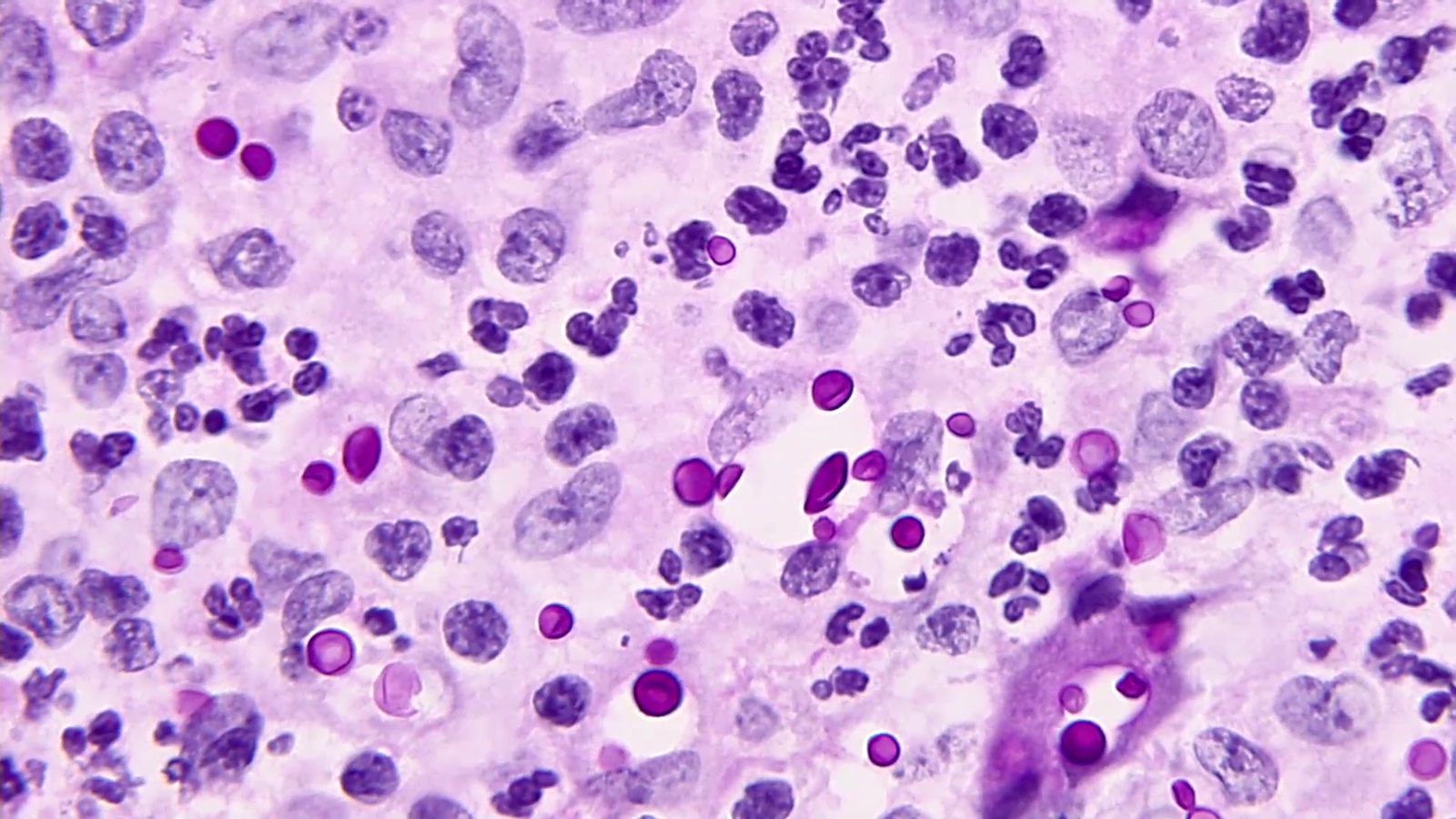
Microscopic (histologic) description
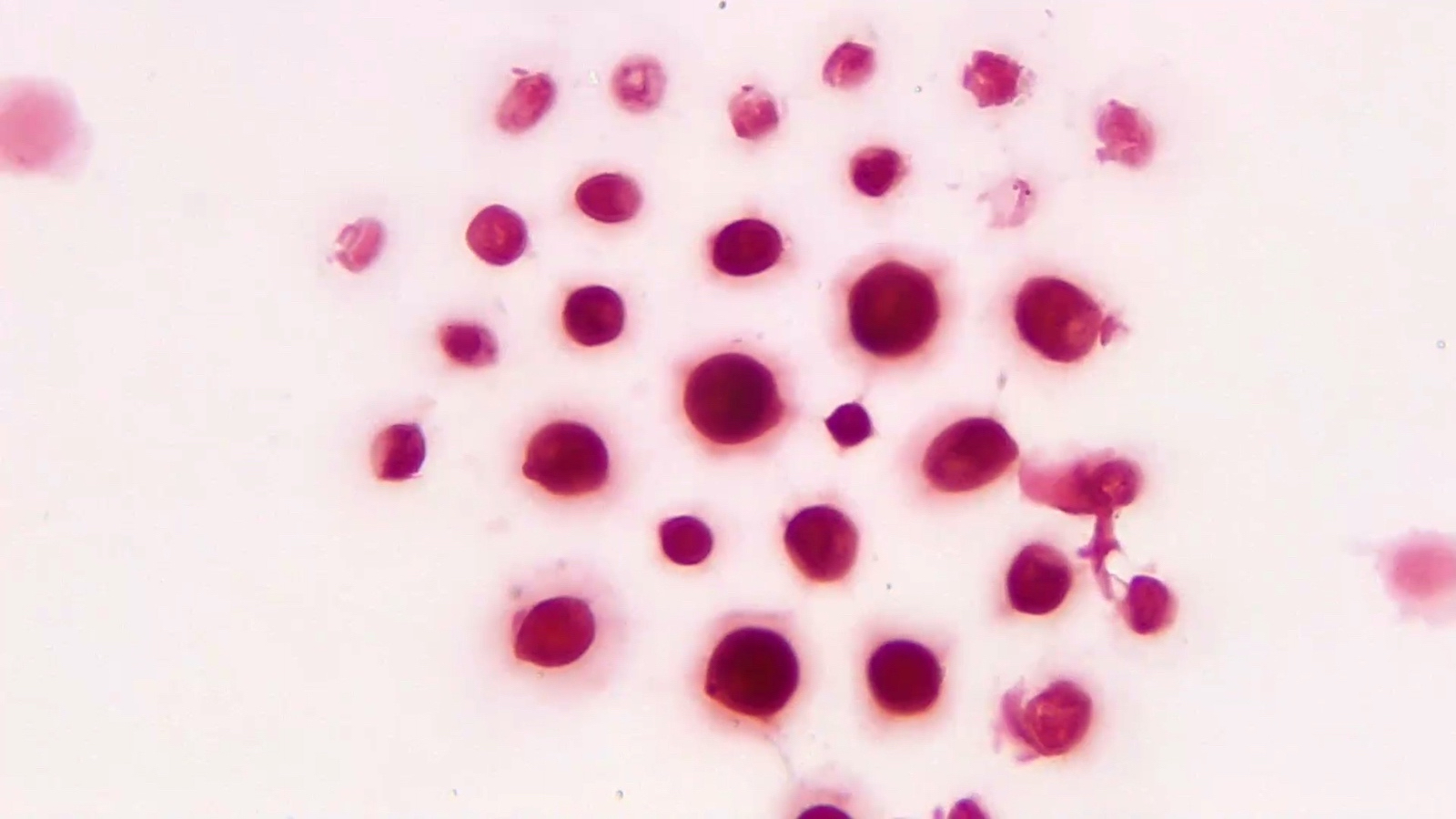
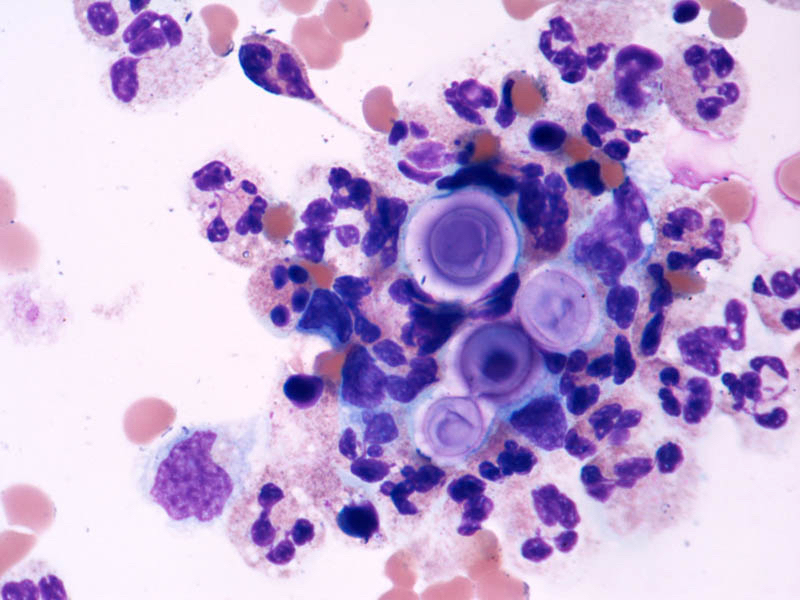
- Variably sized (3.5 - 8 μm in diameter)
- Round to oval encapsulated yeasts with thin cell walls
- Narrow based budding
- Chronic lesions with unencapsulated forms mimic Blastomyces
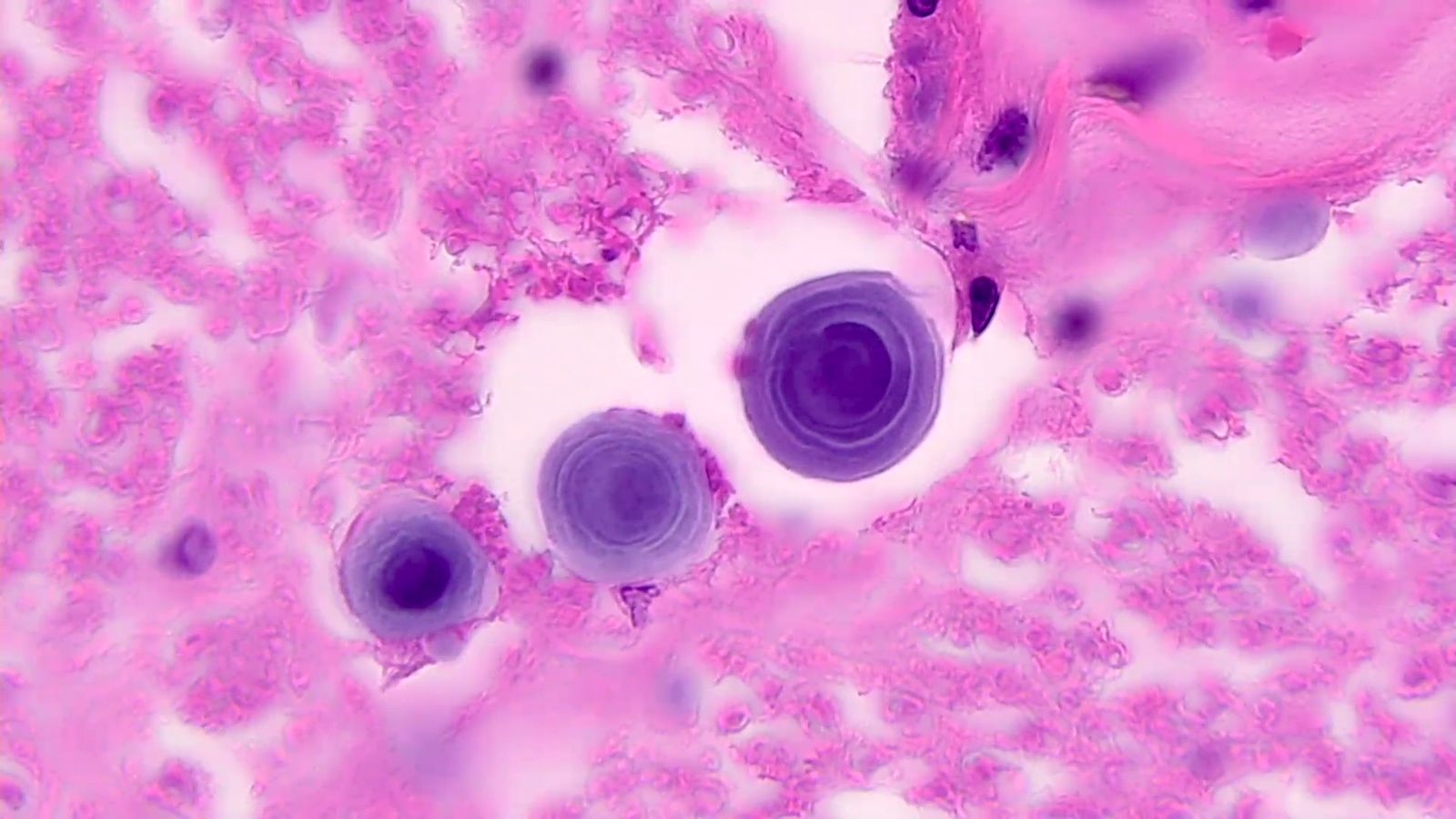
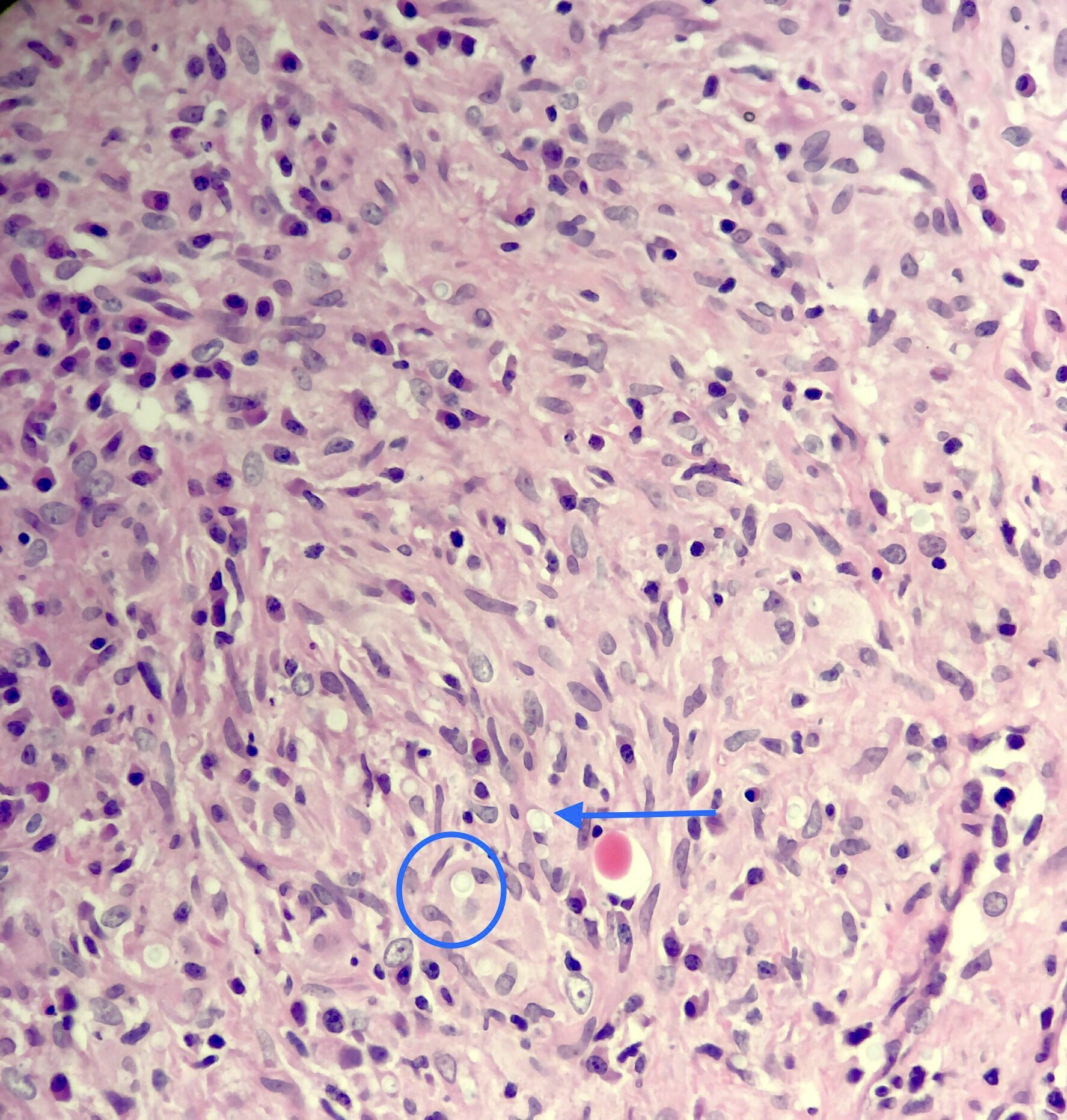
- Corpora amylacea with retraction artifact (neural tissues) mimics Cryptococcus species
- Predominantly chronic inflammation; pyogranulomatous not infrequent
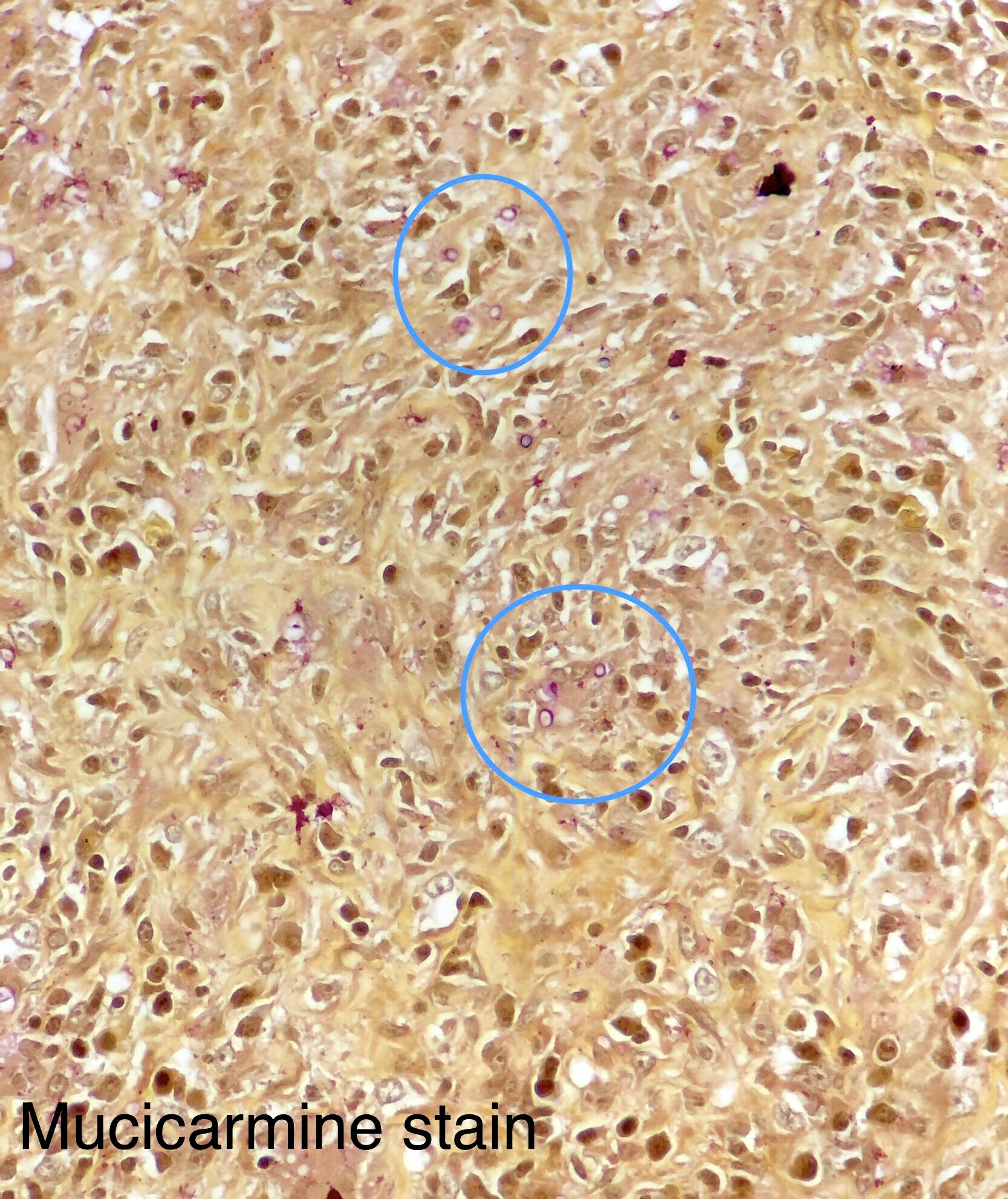
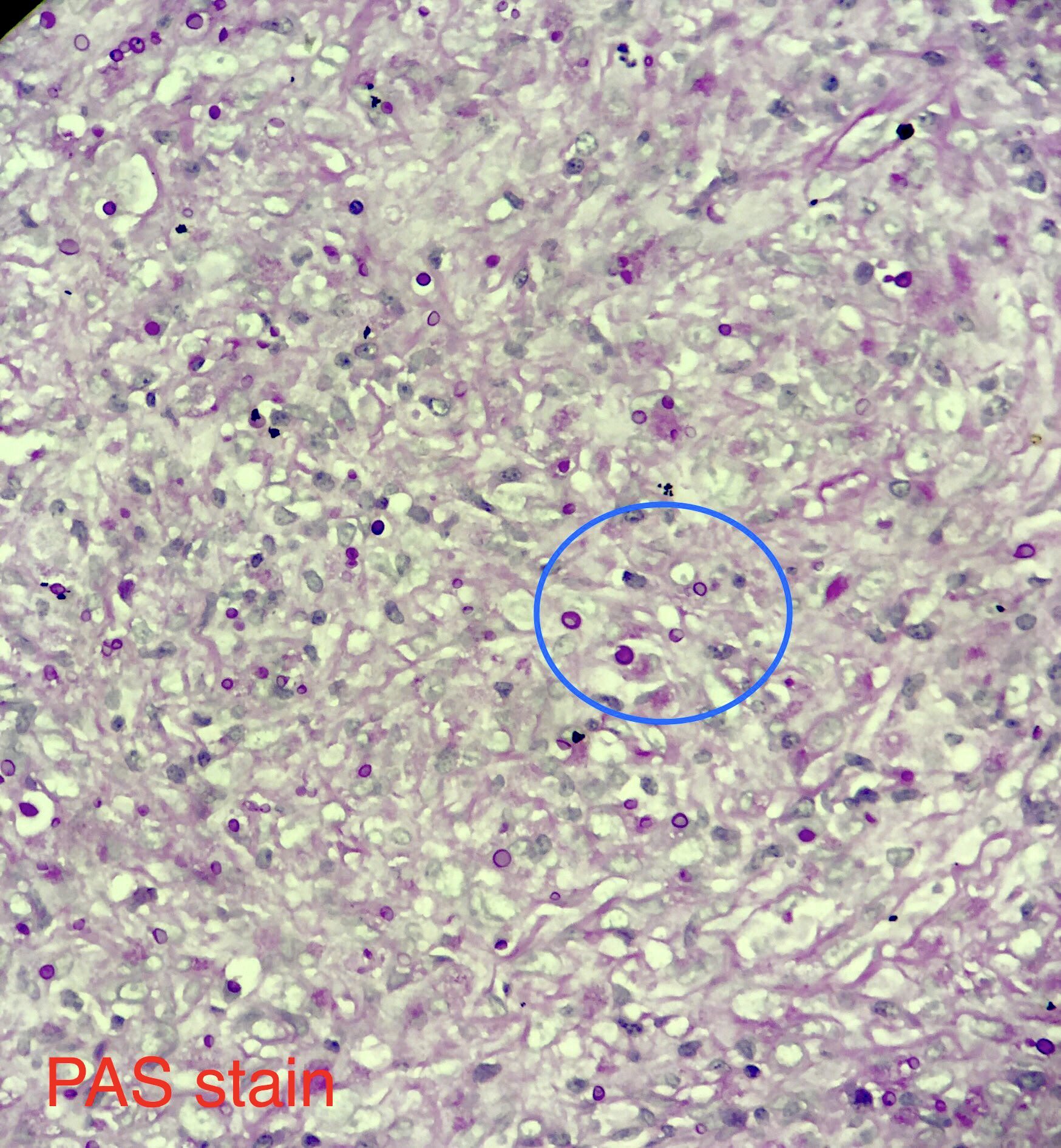
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Methenamine silver, mucicarmine and Fontana-Masson
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Detected on some meningitis molecular panels; relatively high false positive rate
- 28S rDNA sequencing
Differential diagnosis
- Unencapsulated strains mimic Blastomyces and Candida species:
- Fontana-Masson positivity is helpful
- Corpora amylacea in neural tissue:
- Concentric lamellations are helpful
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old previously healthy man is brought to the emergency department with fever, malaise and altered mental status. MRI reveals dilated perivascular spaces with soap bubble-like lesions in the basal ganglia. CSF analysis shows variably sized encapsulated yeasts with narrow based budding. Which culture media is useful in distinguishing C. neoformans from C. gattii?
- Sabouraud dextrose agar
- Birdseed agar
- Canavanine glycine bromothymol blue agar
- Sheep blood agar
Board review style answer #1
C. Canavanine glycine bromothymol blue agar. Both species produce the same features on all listed media except canavanine glycine bromothymol blue agar. Only C. gattii produces deep blue colonies on CGB agar.
Comment Here
Reference: Cryptococcus neoformans and gattii
Comment Here
Reference: Cryptococcus neoformans and gattii
Board review style question #2
A 67 year old woman presented with a solitary lung nodule. Biopsy showed variably sized yeast with no discernible capsule. The organism stained positive for mucicarmine and Fontana-Masson but serum cryptococcal antigen was negative. Two 10 μm formalin fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) scrolls were sent for sequencing and high confidence BLASTs resulted Cryptococcus neoformans. What is the most likely explanation for the negative antigen test?
- Cryptococcal antigen test is less sensitive than nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT)
- Too much antigen was present resulting in hook effect
- Unencapsulated Cryptococcus isolates produce significantly less capsule resulting in less antigen shedding
- Cryptococcus antigen test was negative because the organism is actually Blastomyces dermatitidis
Board review style answer #2
C. Unencapsulated Cryptococcus isolates produce significantly less capsule resulting in less antigen shedding. The Cryptococcus antigen test is more sensitive than nucleic acid amplification tests; however, unencapsulated Cryptococcus isolates produce minimal amounts of GXM antigen and are not readily detected by antigen assays and lack discernible capsule on H&E. Unencapsulated Cryptococcus still retains some mucicarmine and Fontana-Masson staining. Hook effect occurs with too much antigen. Blastomyces has a thick refractile cell wall that is characteristic on H&E and should be mucicarmine and Fontana-Masson negative (occasionally faint positive). 28S rRNA sequencing is the definitive gold standard.
Comment Here
Reference: Cryptococcus neoformans and gattii
Comment Here
Reference: Cryptococcus neoformans and gattii