Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Hamnvåg HM, Borys D. Bacterial osteomyelitis (acute). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonebacterialosteomyelitis.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Infection involving bone
- Rare due to use of antibiotics
- Usually pyogenic
- Classified based on:
- Mechanism of infection (hematogenous versus nonhematogenous)
- Duration of illness (acute, subacute or chronic) (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198, Infect Dis Clin North Am 2017;31:325, Clin Infect Dis 1997;25:1303, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999)
Essential features
- Classified on the basis of duration of illness and mechanism of infection (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2017;31:325, N Engl J Med 1970;282:198, Clin Infect Dis 1997;25:1303, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999)
- Due to proliferation of bacteria in bone, causing inflammation and necrosis
- Most common infectious agents
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Coagulase negative staphylococci
- Aerobic gram negative bacilli (Clin Infect Dis 2006;42:57)
- Diagnosis is established via culture obtained from biopsy of bone, histopathological findings and clinical / radiographic features (Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:885)
Terminology
- Osteomyelitis is infection of bone and bone marrow
- Synonym: osteitis
- Different classifications are based on:
- Duration of the illness
- Acute osteomyelitis: present with a symptom duration of a few days or weeks
- Sequestra are absent
- Chronic osteomyelitis: longstanding infection over months or years
- Sequestra are usually present (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198, Clin Infect Dis 1997;25:1303, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999)
- Mechanism of infection
- Hematogenous
- Direct extension from contiguous site
- Direct contamination (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198, Clin Infect Dis 1997;25:1303, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999)
- Duration of the illness
ICD coding
- ICD-10: M86.9 - osteomyelitis, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Hematogenous osteomyelitis
- Occurs most commonly in children
- More than half occurs in children younger than 5 years and one quarter in children younger than 2 years
- M > F
- Among adults:
- Most occur in patients > 50 years (BMC Infect Dis 2010;10:158)
- M > F
- Occurs most commonly in children
- Nonhematogenous osteomyelitis
- Among younger adults: occurs most frequently in the setting of trauma and related surgery
- Among older adults: occurs most frequently as a result of contiguous spread of infection to bone from adjacent soft tissues and joints (diabetic foot wounds or decubitus ulcers) (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198)
Sites
- Most common sites in children
- Areas of rapid growth or increased risk of trauma
- Distal and proximal femur
- Proximal tibia and humerus
- Distal radius (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2005;19:787, Adolesc Med State Art Rev 2007;18:79, J Med Assoc Thai 2011;94:S209)
- Areas of rapid growth or increased risk of trauma
- Most common sites for hematogenous osteomyelitis in adults
- Vertebrae (Clin Infect Dis 2015;61:e26)
- Flat bones of the axial skeleton (sternoclavicular and pelvic bones)
- Contiguous osteomyelitis
- Occurs in sites predisposed to pressure related skin ulcerations
- Sacrum
- Buttock
- Hips
- Heels (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198)
- Occurs in sites predisposed to pressure related skin ulcerations
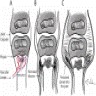
Pathophysiology
- Bacteria proliferate in bone, cause inflammation and necrosis
- Spread along haversian system or medullary cavity within shaft and to periosteum
- Subperiosteal abscesses impair blood supply, which causes more necrosis and often draining sinuses
- Sequestrum:
- Dead piece of bone
- Gradually separated from living bone by granulation tissue
- May pass through sinus tract
- Avascular and dense on Xray
- Involucrum: sleeve of living tissue created by periosteum, which is deposited around sequestrum (Infect Immun 2016;84:2586)
- Hematogenous spread:
- Most common cause
- Usually metaphyseal in children and adults
- Usually long tubular bones of children; involvement of flat bones is more common in adults (Lancet 2004;364:369, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999, N Engl J Med 1970;282:198)
- Direct extension:
- Less common
- May be associated with trauma or rarely iatrogenic implantation of infectious material
- In elderly, may affect vertebral column
- May be associated with systemic urinary tract infection, diabetes (affects small bones in feet)
- In younger adults, associated with immunodeficiency or intravenous drug abuse (Lancet 2004;364:369, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999, N Engl J Med 1970;282:198)
- Type of bacteria:
- 50% of cases are due to unknown bacteria
- 80% of known cases are due to Staphylococcus aureus, which produces receptors to bone matrix components
- Hematogenous osteomyelitis
- Usually monomicrobial
- Staphylococcus aureus is the most common isolated organism (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198, Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1996;13:701, N Engl J Med 1970;282:260, N Engl J Med 1970;282:316)
- All pediatric age groups
- Most common: Staphylococcus aureus
- Next most common: group A streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Kingella kingae (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2005;19:787)
- Neonatal age groups
- Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Escherichia coli (Pediatr Infect Dis J 1995;14:1047, J Bone Joint Surg Br 1990;72:846)
- Sickle cell patients
- Salmonella choleraesuis, Salmonella paratyphi B and Salmonella typhimurium (Blood 1995;86:776, J Pediatr Orthop 1992;12:534, Pediatrics 1998;101:296, Int Surg 1998;83:84)
- Intravenous drug addicts (affecting clavicle, sternoclavicular joint, spine or pelvis)
- Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010;468:2107)
- Posttraumatic cases: Pseudomonas and mixed bacteria
- Other known organisms are Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas and Klebsiella
- Rarely associated with malakoplaia
Etiology
- Hematogenous spread of infectious agents:
- Risk factors
- Endocarditis
- Indwelling catheters (vascular catheters, cardiovascular devices)
- Orthopedic hardware
- Injection drug use
- Hemodialysis
- Sickle cell disease (BMC Infect Dis 2010;10:158, Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2017;88:75)
- Risk factors
- Nonhematogenous spread:
- Direct inoculation
- Trauma, bite wound, surgery
- Contiguous spread
- Infection to bone from adjacent soft tissues and joints (diabetic foot wounds, vascular disease, decubitus ulcer) (Lancet 2004;364:369, N Engl J Med 1997;336:999, N Engl J Med 1970;282:198)
- Direct inoculation
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Signs and symptoms:
- Gradual onset of symptoms over several days
- Dull pain at the involved site
- Tenderness, warmth, erythema and swelling
- Fever and rigors may also be present (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of osteomyelitis is established via culture obtained from biopsy of the involved bone
- Histopathology consistent with osteomyelitis in the absence of positive culture data
- Typical clinical and radiographic findings together with persistently elevated inflammatory markers in the absence of positive culture and no biopsy interpretation (Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:885)
Laboratory
- Leukocytosis on complete blood count
- Elevated inflammatory markers: erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C reactive protein (CRP)
- Blood cultures are positive in 50 - 60% of cases
- Bone aspirate cultures may be positive when blood cultures are negative (N Engl J Med 1970;282:198, Semin Arthritis Rheum 2002;31:271, Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991;264:178)
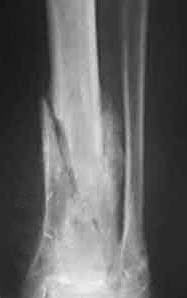
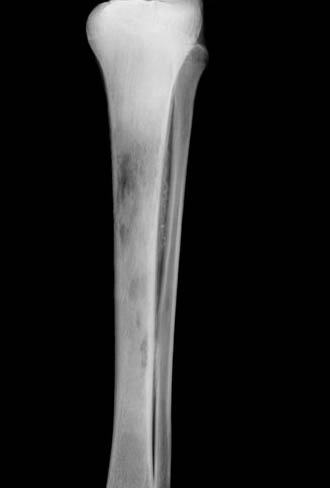
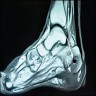
Radiology description
- Conventional radiography:
- Not for early detection of osteomyelitis
- Reasonable initial imaging modality with ≥ 2 weeks of clinical symptoms
- Soft tissue swelling
- Osteopenia
- Cortical loss
- Bony destruction
- Periosteal reaction (Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:885, Arch Intern Med 1994;154:753, AJR Am J Roentgenol 1991;157:365)
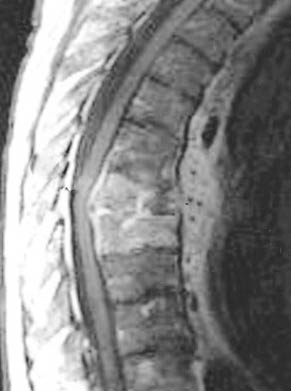
- Magnetic resonance imaging:
- High sensitivity and negative predictive value
- MRI with no evidence of osteomyelitis after 1 week of clinical signs or symptoms is sufficient for exclusion of osteomyelitis (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2006;20:789)
- Late images show prominent periosteal reaction resembling neoplasm (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2006;20:789)
- Sclerosing osteomyelitis of Garré:
- Lytic bone destruction surrounded by sclerosis
- Chronic disease may resemble malignant bone tumor due to destructive and regenerative bone changes (J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2019;27:2309499019874704)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Chronic osteomyelitis develops in a subset of acute osteomyelitis due to:
- Delayed treatment
- Inadequate antibiotics
- Incomplete surgical debridement of necrotic bone
- Weakened host defenses (EFORT Open Rev 2017;1:128)
Case reports
- 28 day old boy with Salmonella osteomyelitis (Ital J Pediatr 2018;44:28)
- 6 week old girl with brachial plexus palsy with history of osteomyelitis (Pediatr Infect Dis J 2017;36:1219)
- 37 year old man with Salmonella osteomyelitis (Ulster Med J 2015;84:171)
Treatment
- Antibiotic therapy
- Surgical debridement
- References: Diabetes Care 2015;38:302, Diabetologia 2008;51:962, Infect Dis Clin North Am 2017;31:325
Gross description
- Varies with patient age:
- Infants under age 1 year often have permanent joint and epiphyseal damage sparing metaphysis and diaphysis (Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1995;149:537)
- Children 1 year and older have opposite changes (sparing of joint, damage to metaphysis) (J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20:40, J Bone Joint Surg Br 2012;94:584)
- Adults have joint infection and extensive bone involvement
- Acute disease has pus tracking through bone, periosteal elevation and shell of reactive periosteal bone around necrotic center
- Neonates may have considerable subperiosteal spread
- Chronic disease is accompanied by prominent periosteal bone formation
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Histopathological Osteomyelitis diagnostics (GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW 2014;3:Doc08)
-
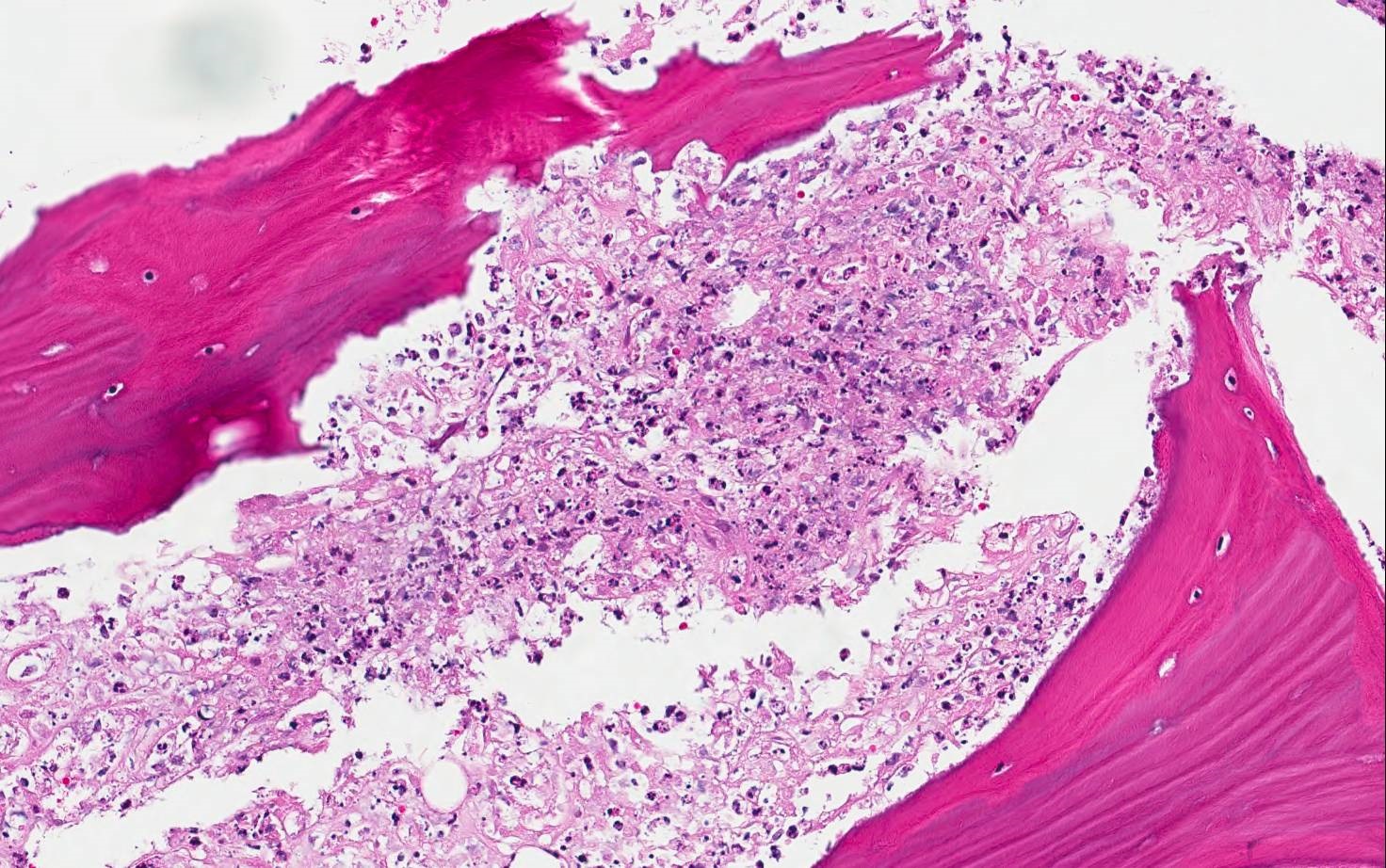
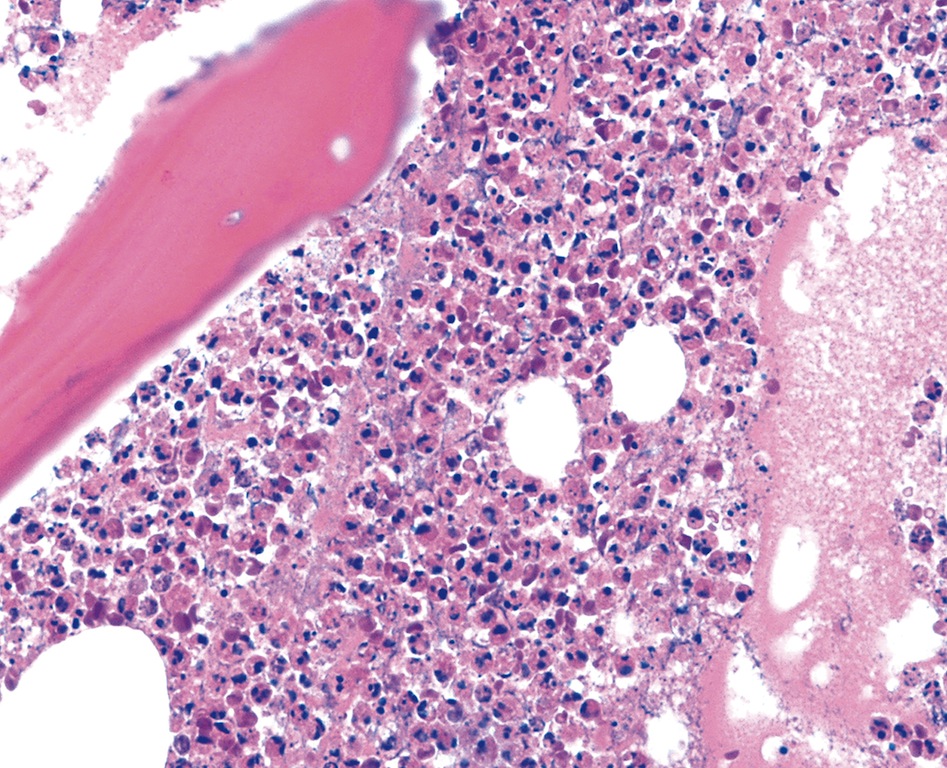
Patterns of acute osteomyelitis
- Osseous changes:
- Osteonecrosis: bone trabeculae with visually empty osteocyte cavities are detectable as a criterion for necrotic bone tissue especially with EDTA decalcification
- The bone trabeculae have irregular contours and are fragmented
- They may be fractured and completely necrotic (so called bone sequester)
- There are intramedullary granulocyte infiltrates and fibrin exudates
- In bone tissue with a haemopoietic function (e.g. axial skeleton) there is a reduced or complete lack of haemopoiesis
- Soft tissue changes:
- Soft tissue necrosis: criteria for soft tissue necrosis are apoptoses, a tissue eosinophilia, fibrin exudations and a confining texture of the tissue
- Inflammatory infiltrate pattern:
- Neutrophilic granulocyte infiltrate: diffuse and grouped deposits (so called microabscesses, ≥ 5 granulocytes) of segmented neutrophilic granulocytes in the usually highly oedematous medullary spaces
- The neutrophilic granulocytes are PAS cytoplasmic, coarsely granular positive and display a plumped, pyknotic chromatin texture (granulocyte apoptosis with pathogen phagocytosis and NETosis)
- Immunohistochemically there is a specific intensive, coarsely granular, predominantly cytoplasmic CD15 positivity
- Osteoclasts are also detectable alongside neutrophilic granulocytes on the irregular trabecular surface
-
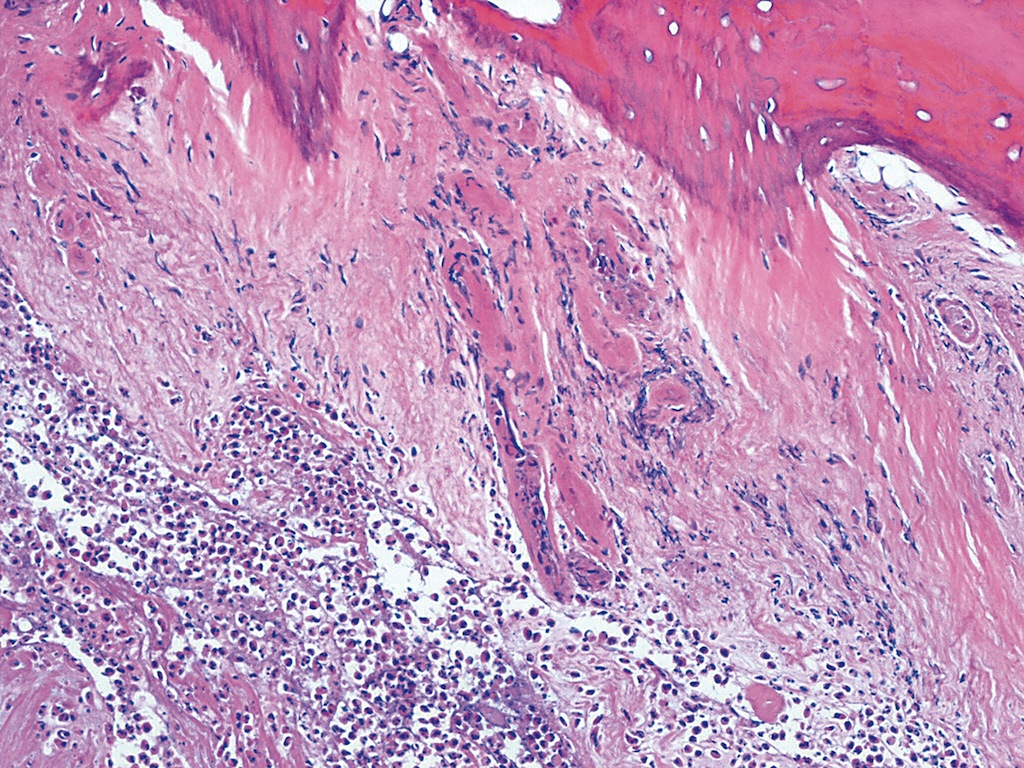
Patterns of chronic osteomyelitis
- Osseous changes:
- Bone neogenesis: spongy osseous tissue with reactive network bone neogenesis (POL detection of irregularly running fibrils), the bone surface is bordered by osteoblasts
- Medullary space fibrosis with ectatic sinus
- The medullary space tissue shows fibrosing with granulation tissue formation
- The infiltrate consists of macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells and a few neutrophilic granulocytes
- Soft tissue changes: there is fibrosing with granulation tissue formation, the infiltrate consists of macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells and a few neutrophilic granulocytes
- Inflammatory infiltrate pattern:
- Lymphocyte / macrophage / plasma cell infiltrate: in the highly fibrosed medullary spaces there is a lymphocyte and macrophage rich, sometimes also plasma cell rich, sometimes focal, sometimes inflammatory infiltration with a few neutrophilic granulocytes
- Neutrophils (may persist for weeks), lymphocytes and plasma cells with bone necrosis and reactive new bone formation
- Capillary proliferation and fibrosis
- Subtypes include plasma cell osteomyelitis and xanthogranulomatous osteomyelitis (abundant foamy macrophages)
- Bone marrow replaced by inflammatory tissue
- Salmonella infection may produce tuberculoid granules with variable central necrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1985;9:531)
- Osteoblastic bone resorption
- Bitten bone (chewed, scalloped bone)
- Bone necrosis
- Vessel damage
- Vascular thrombosis
- Marrow infarction
- Dirty marrow (J Foot Ankle Surg 2020;59:75, GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW 2014;3:Doc08)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Sample pathology report
- Femur, debridement (partial excision):
- Fragments of scalloped viable and non-viable bone with surrounding acute inflammatory infiltrate, consistent with acute osteomyelitis
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphoma:
- Monotonous lymphoid infiltrate
- Evidence of monoclonality by immunohistochemistry / molecular findings
- Sarcoidosis:
- Noncaseating granulomas
- Disease elsewhere in the body (mediastinum, lung, etc.)
- Inflammatory reaction:
- Response to fracture repair with history of trauma
- Not as prominent acute inflammatory infiltrate or dead bone
- Osteonecrosis:
- Often chronic process with known history of radiation or medication (bisphosphonate)
- Necrosis with subsequent remodeling of bone (Deyrup: Practical Orthopedic Pathology - A Diagnostic Approach, 1st Edition, 2015)
Board review style question #1
Hematogenous osteomyelitis is usually
- Monomicrobial and most common organism involved is Staphylococcus aureus
- Monomicrobial and most common organism involved is Streptococcus pyogenes
- Polymicrobial and most common organism involved is Staphylococcus aureus
- Polymicrobial and most common organism involved is Streptococcus agalactiae
- Polymicrobial and most common organism involved is Streptococcus pyogenes
Board review style answer #1
B. Monomicrobial and most common organism involved is Streptococcus pyogenes
Comment Here
Reference: Bacterial osteomyelitis (acute)
Comment Here
Reference: Bacterial osteomyelitis (acute)
Board review style question #2
Most common microbial etiology of bacterial osteomyelitis in neonatal age group is
- Salmonella typhi, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae
- Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli
- Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Escherichia coli
Board review style answer #2
D. Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Escherichia coli
Comment Here
Reference: Bacterial osteomyelitis (acute)
Comment Here
Reference: Bacterial osteomyelitis (acute)