Table of Contents
Terminology | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology descriptionCite this page: Warzecha H. Tuberculosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastTB.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Terminology
- Also called tuberculous mastitis
Epidemiology
- Rare in Western countries but more common in India (The Internet Journal of Tropical Medicine 2004;2(2))
Clinical features
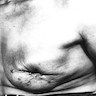
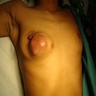
- May present with abscess, fistula or mass (Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2009;103:559)
- Usually unilateral without pulmonary involvement (ANZ J Surg 2006;76:234, Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2009;64:607)
- Acid fast bacilli are usually not identified
- For breast cancer patients with granulomatous axillary lymphadenitis, PCR may be required to rule out TB in endemic regions (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:699)
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with breast lump, a rare presentation of costochondral junction tuberculosis (Cases J 2009;2:7039)
- 47 year old woman with coexistence of carcinoma and tuberculosis in one breast (World J Surg Oncol 2008;6:29)
- 54 year old woman with tuberculosis of the breast (J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2010;63:e397)
- 73 year old woman with mammary tuberculosis mimicking breast cancer (J Med Case Rep 2008;2:34)
Treatment
- Antibiotics (eMedicine: Tuberculosis Treatment & Management); excision of mass may also be necessary (J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2009;19:158)
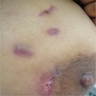
Clinical images
Gross description
- Multiple sinuses or fistulas; may have focal discoloration or mass
Microscopic (histologic) description
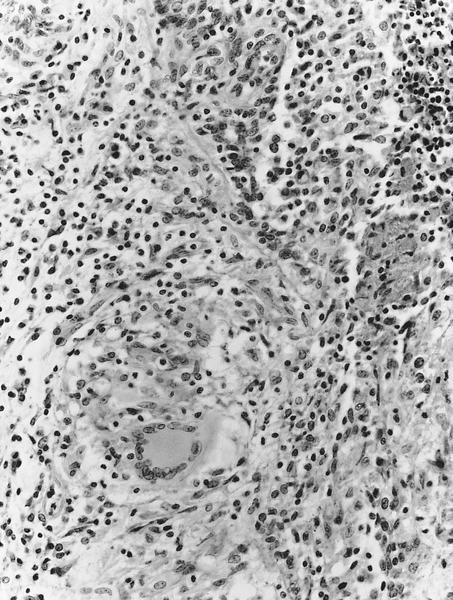
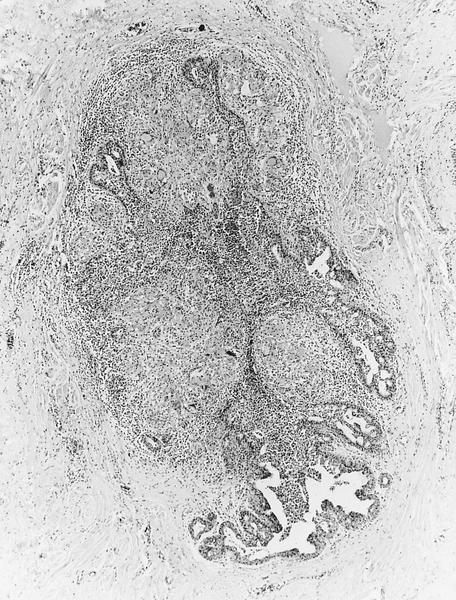
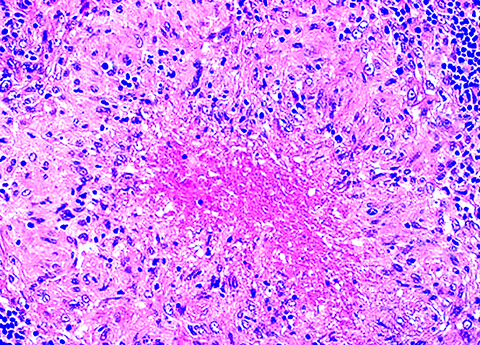
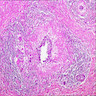
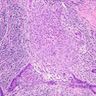
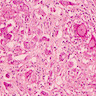
- Granulomas with Langhans giant cells and caseous necrosis (often)
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
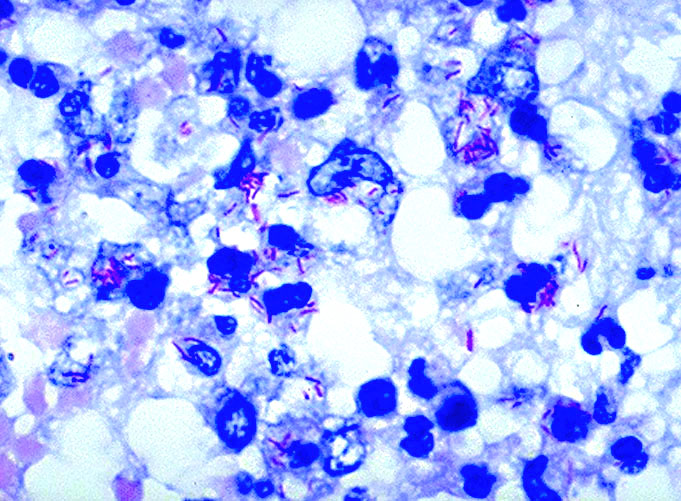
Cytology description
- Foamy histiocytes, neutrophils, necrotic debris