Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Clinical features | Radiology images | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Reisenbichler ES. Biopsy marking devices. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastbiopsymarkingdevices.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Clip placement, indicating the location of a percutaneous breast core biopsy, is utilized in many settings:
- Correlate lesion location across different imaging modalities (i.e. ultrasound, mammogram, tomosynthesis, MRI)
- Follow up progression of benign lesions over time
- Indicate tumor location in patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- Assist surgeons in localizing lesions or extent of disease in nonpalpable lesions, confirming excision of the appropriate region
- Guide the pathologist to identify the area of interest on gross specimen examination
- Different clips help distinguish separate lesions
- Markers are most commonly metallic, in various shapes, generally 2 - 3 mm in size, placed with or without accompanying packing / embedding material such as collagen, hydrogel or starch
Essential features
- Biopsy marker placement is an important step in any breast biopsy procedure
- Clips of varying material and shapes are placed to help distinguish different biopsied sites / lesions
- Clips may migrate away from the biopsy site or be incorrectly positioned; microscopic features of biopsy site changes must therefore still be identified in excision specimens
- Accompanying packing material placed with marker clips may make biopsy sites more readily detectable radiographically and often increase homeostasis immediately following the biopsy procedure
Clinical features
- Routine biopsy clip placement is associated with a higher rate of negative margins for wire localization excisions (Am J Surg 2005;190:618)
- Advantages to packing material with marker placement include decreased clip displacement, increased homeostasis, better identification of clip site soon after biopsy procedure
- Depending on clip design, some markers are delivered into the biopsy cavity through the biopsy probe while others are delivered manually by image guidance
- Clip migration away from the biopsied site is a well recognized complication and occurs for various reasons (Radiographics 2004;24:147), including breast decompression (aka the accordion effect, J Radiol 2009;90:31) or displacement due to hematoma formation following the biopsy procedure; migration may be reduced in clips placed with an embedding material (Eur Radiol 2016;26:866)
- FDA reports of allergic reactions to metallic biopsy markers have been reported (FDA: Johnson and Johnson, Ethicon Division Titanium Breast Clip [Accessed 14 December 2017]) but are rare
- Although markers with collagen embedding material are not placed in people with allergies to beef products, collagen or collagen products, there are no reports of allergic reactions in the current literature
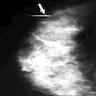
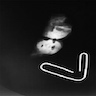
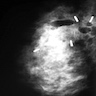
Radiology images
Case reports
- 37 year old woman with complete disappearance of biopsy marking clip following MRI guided breast biopsy (BMJ Case Rep 2014 Aug 19;2014)
- 39 year old woman undergoing excision for a biopsy marker and associated collagen plug mistaken for a mass lesion (Breast J 2005;11:504)
- Report of atopic dermatitis in relation with a surgical titanium clip in the breast (J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 2011;40:174)
Gross images
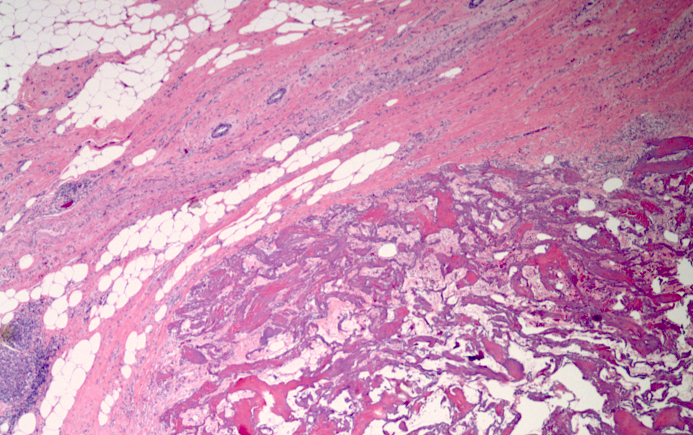
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Gel / polymer pellets:
- Initially hypocellular fibrotic reaction around empty spaces (processing dissolves the polymer), then multinucleated giant cell reaction with eosinophilic material in marker core (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:814)
- May also retain blue / grey material, resembling suture with multinucleated giant cell reaction to material (see microscopic images)
- Collagen plugs:
- Eosinophilic, hyalinized and acellular material with lymphocytic and eosinophilic infiltrate that gradually penetrates into the core
- No prominent multinucleated giant cell reaction
- May resemble amyloidosis (see microscopic images)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Calcifications may be mistaken for clips radiographically
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is not a use for biopsy marker placement?
- Assist the pathologist in gross identification of the targeted lesion in the surgical excision specimen
- Identification of a nonpalpable breast lesion (such as calcifications, asymmetry or distortion) for excision
- Identification of a palpable lesion in a patient with a metal allergy
- To follow the appearance and possible progression of a benign biopsied lesion over time
- Tumor localization in a patient undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to surgery
Board review style answer #1
C.
Although there are almost no contraindications for placing a biopsy marker, there are rare reports of allergic reaction to metallic clips. Forgoing clip placement in this situation may be considered, particularly if the lesion is palpable and has not been entirely removed by the biopsy procedure. For most cases, a marker clip is necessary and helpful to surgeons, oncologist and pathologists.
Comment Here
Reference: Breast biopsy marking devices
Comment Here
Reference: Breast biopsy marking devices