Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Warzecha H. Cystic hypersecretory hyperplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastcystichypersecretoryhyperplasia.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Cystically dilated ducts of various sizes with colloid-like material
- Ducts are lined by flat, orderly, bland columnar epithelial cells
- Not included in WHO classification of breast lesions
Terminology
- Cystic hypersecretory carcinoma: lesions that resemble cystic hypersecretory hyperplasia but with proliferative atypical epithelium
Epidemiology
- Rare
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Palpable mass or occasionally asymptomatic with mammographic abnormality
- Benign lesion with good prognosis when not associated with atypia or carcinoma
Case reports
- 48 year old woman with mass exhibiting atypia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e389)
Treatment
- Wide excision (Cancer 1988;61:1611)
- If atypia present at core biopsy, excise entire lesion because DCIS can be present (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:789)
Gross description
- Resembles juvenile papillomatosis
- Large, ill defined, firm to rubbery, spongy mass of fibrous tissue containing multiple small cysts
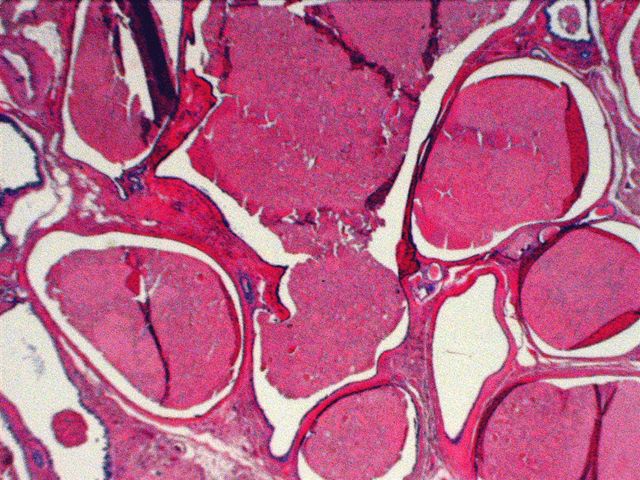
- Also abundant thick, sticky mucin within the cysts; resembles thyroid colloid
- May coexist with atypia or DCIS of cystic hypersecretory type, so sample generously
Microscopic (histologic) description
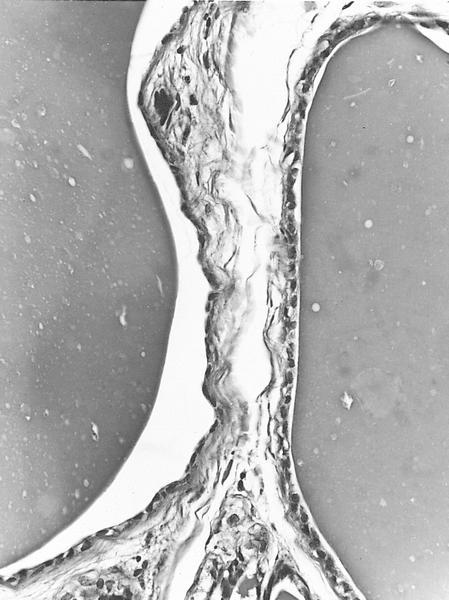
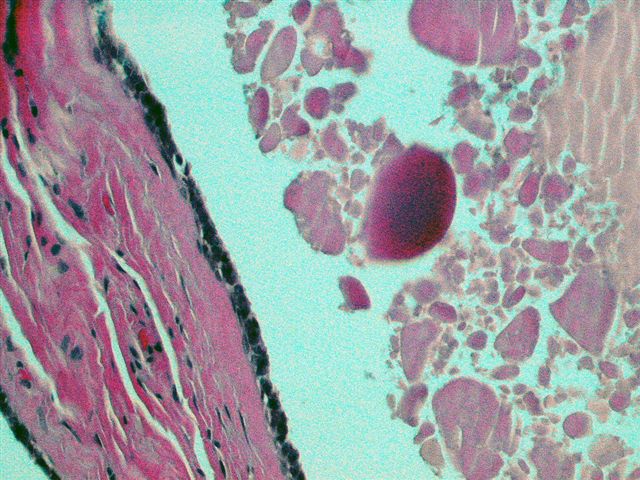
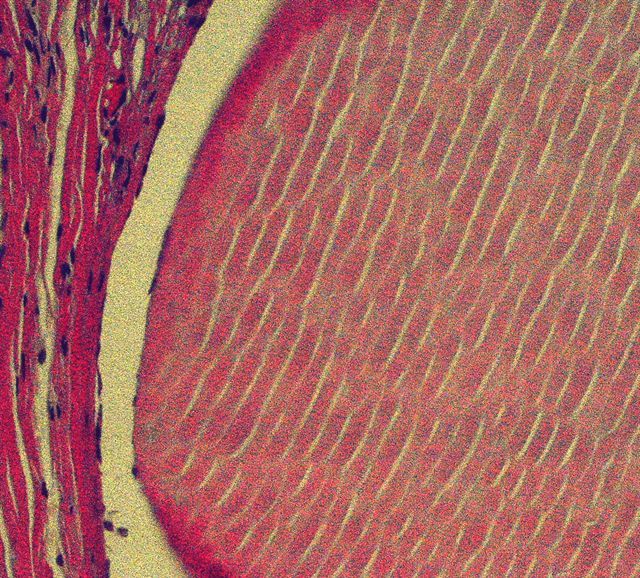
- Cystically dilated ducts of various sizes with colloid-like material, often with parallel fracture lines, retraction halo and overlapping due to processing
- Ducts are lined by flat, orderly, columnar epithelial cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm; nuclei are round / oval, vesicular, bland
- Atypical features are epithelial crowding, enlarged nuclei lacking normal polarization, hyperchromasia and rare mitotic figures
- Can be associated with pregnancy-like (pseudolactational) hyperplasia (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1670)
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Cytology description
- Secretory material (same as histology) with isolated or clusters of epithelial cells
Positive stains
- PR in a small subset
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Cystic hypersecretory DCIS