Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Cystic hypersecretory carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantcystichypersecretoryinvasive.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Not part of WHO breast classification
- First described in 1984 (Am J Surg Pathol 1984;8:31)
- Very rare (< 100 cases reported)
- DCIS or hyperplasia is more common
Clinical features
- Usually low grade for several years but may metastasize
Case reports
- 40 year old woman with painful breast mass (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:e79)
- 43 year old woman (Jpn J Radiol 2011;29:660)
- 45 year old woman (J Korean Med Sci 2004;19:149)
- 48 year old woman with Paget’s disease of nipple (Int J Surg Pathol 2008;16:208)
- 49 year old woman with invasive lobular carcinoma in opposite breast 10 years after diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:1108, free full text)
Gross description
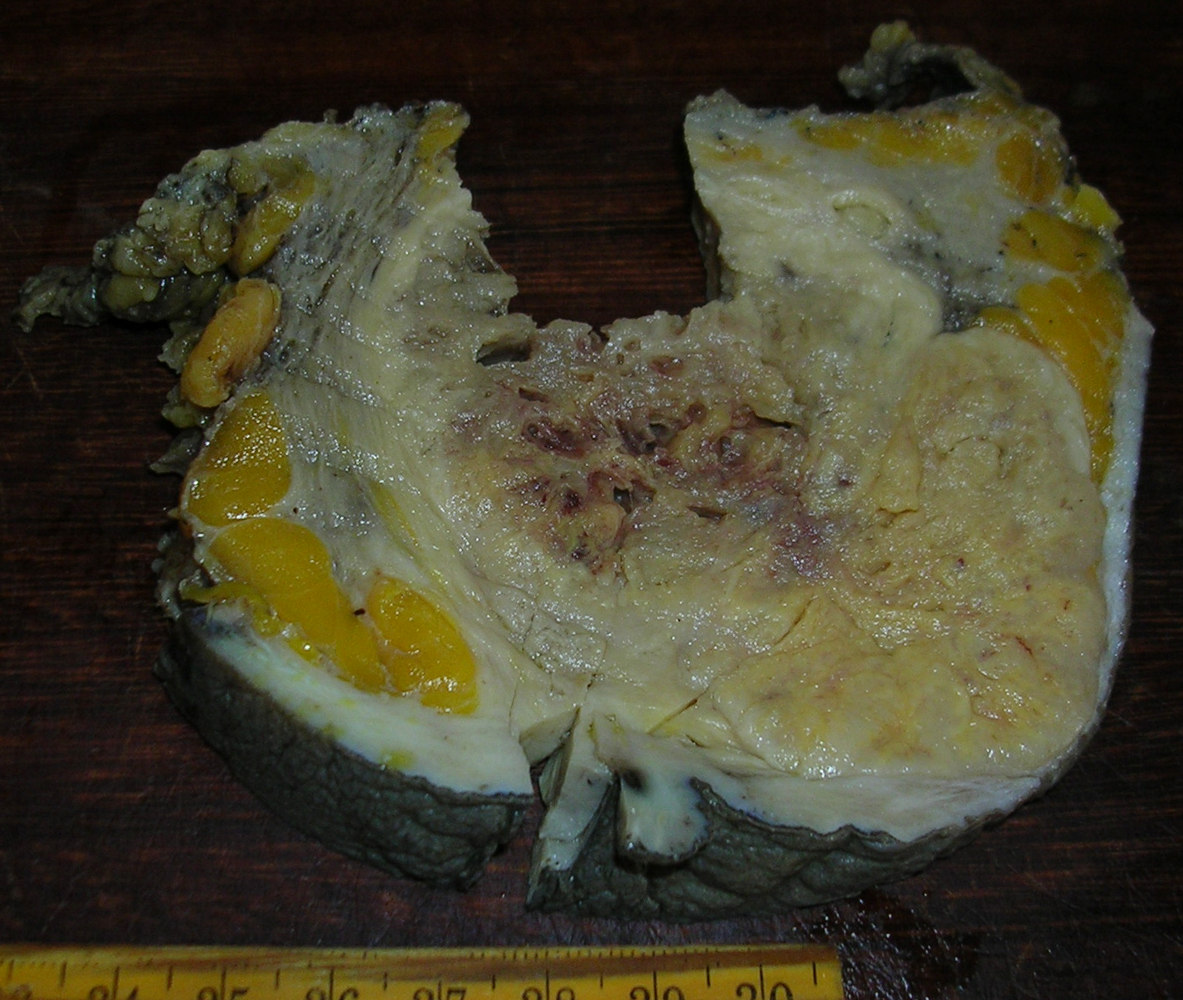
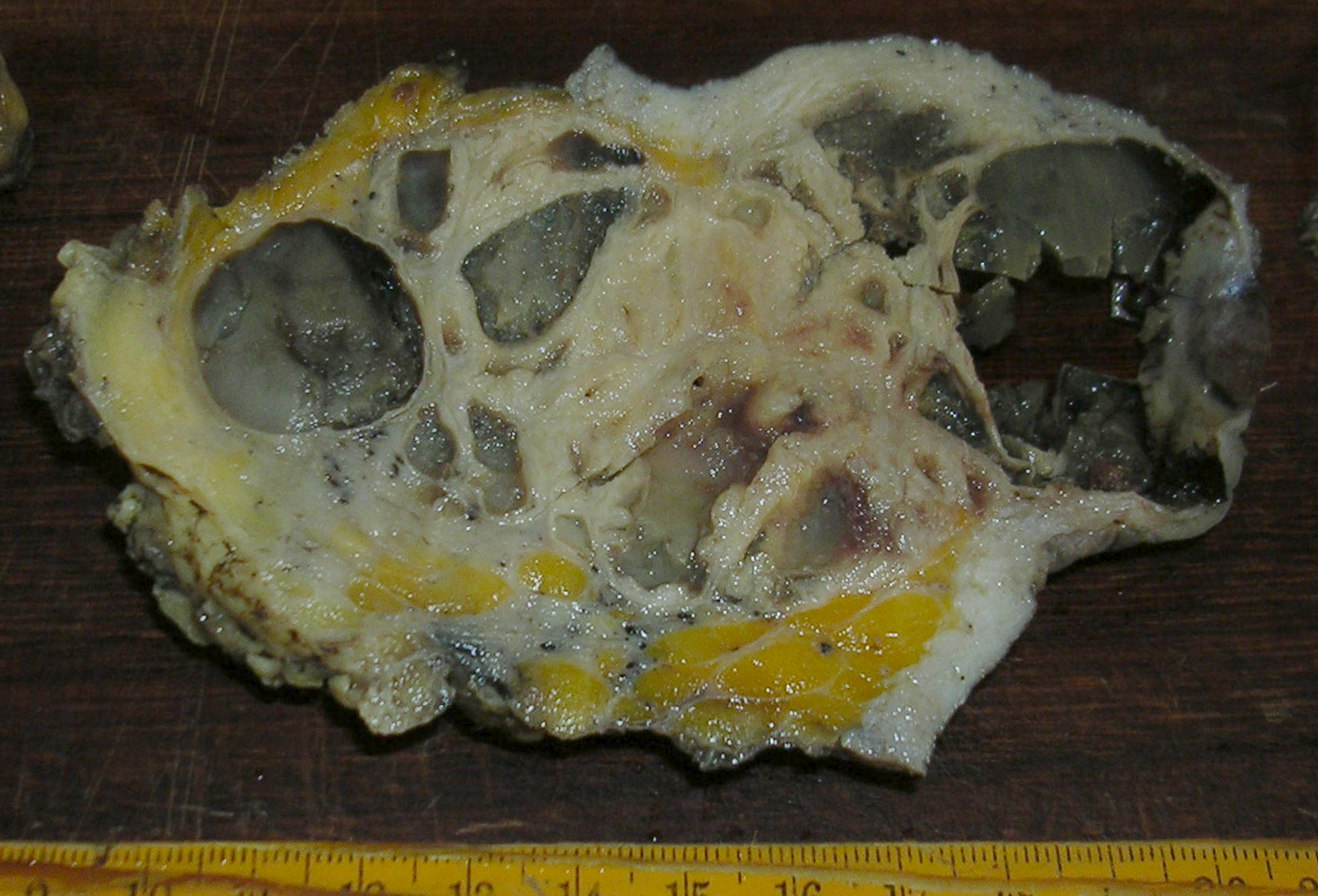
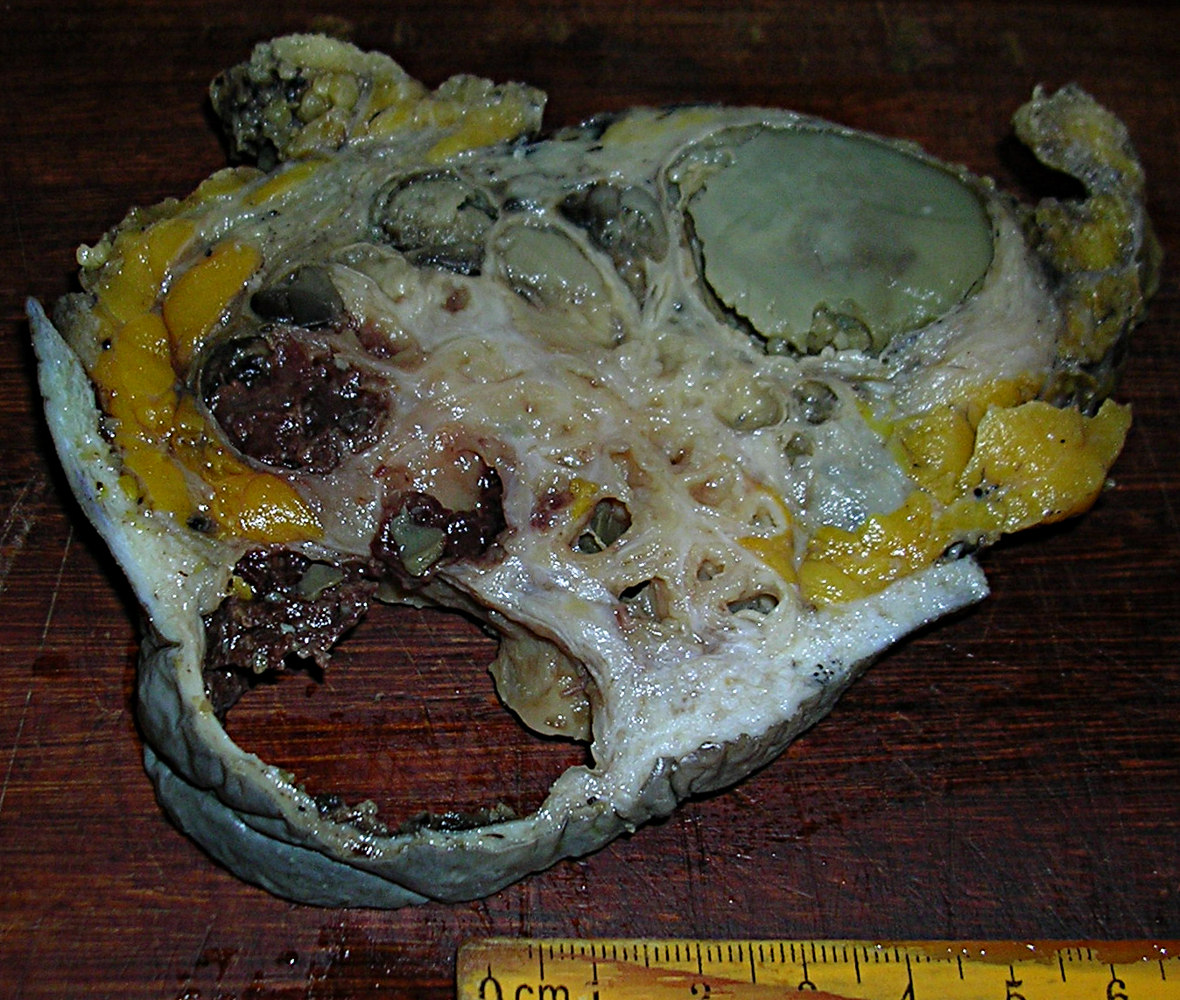
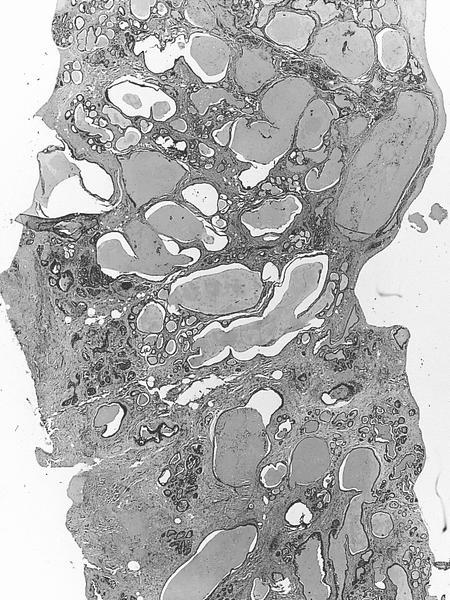
- Numerous cysts with mucoid or gelatinous secretions
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
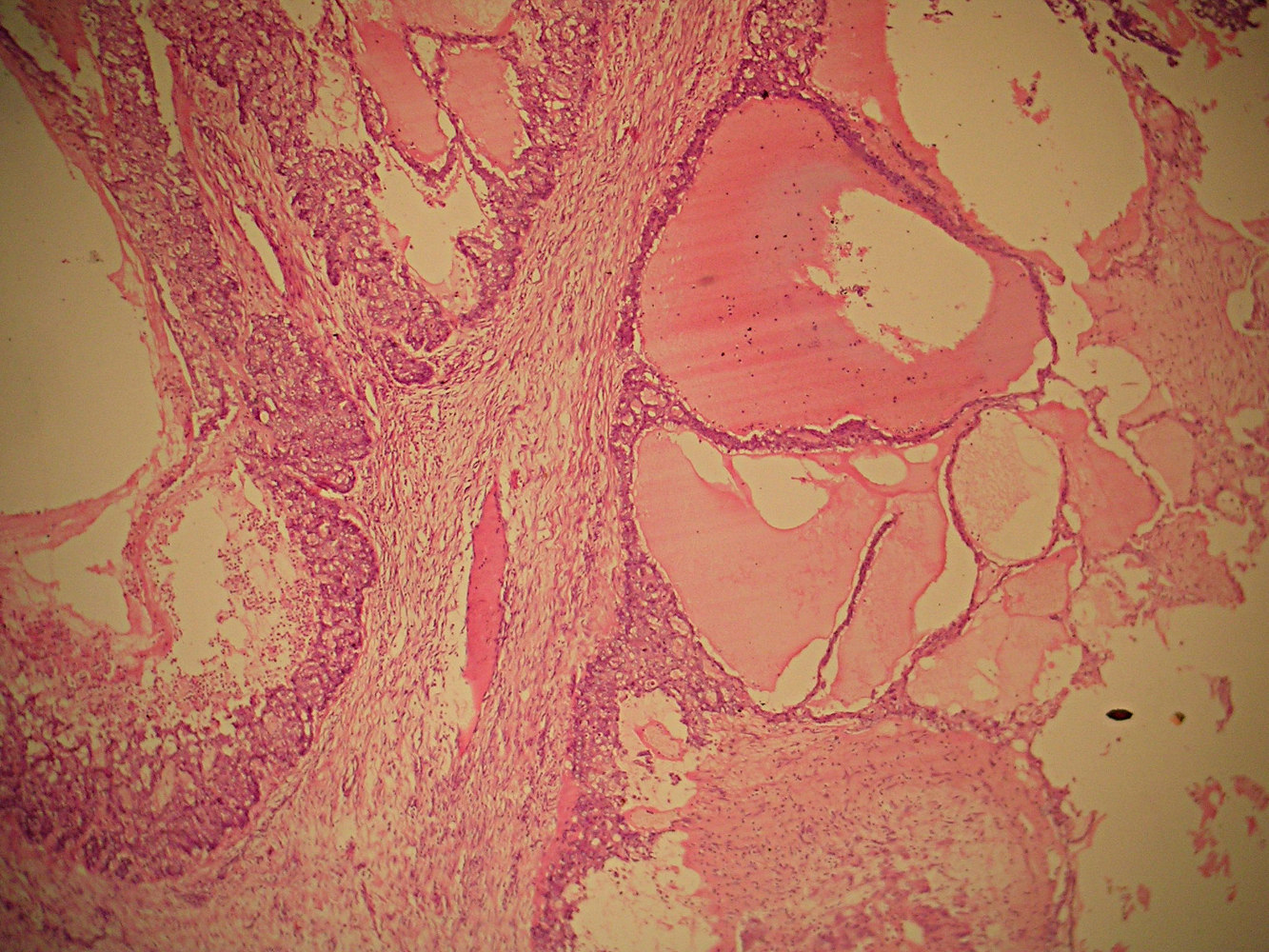
- Cystic dilation of ducts containing colloid-like eosinophilic material that often retracts from epithelium
- Epithelium focally has micropapillary DCIS
- Also invasion of surrounding stroma by nests of carcinoma, which may be high grade, usually without hypersecretory characteristics
- Extravasation of cyst material into stroma is not invasion
Microscopic (histologic) images
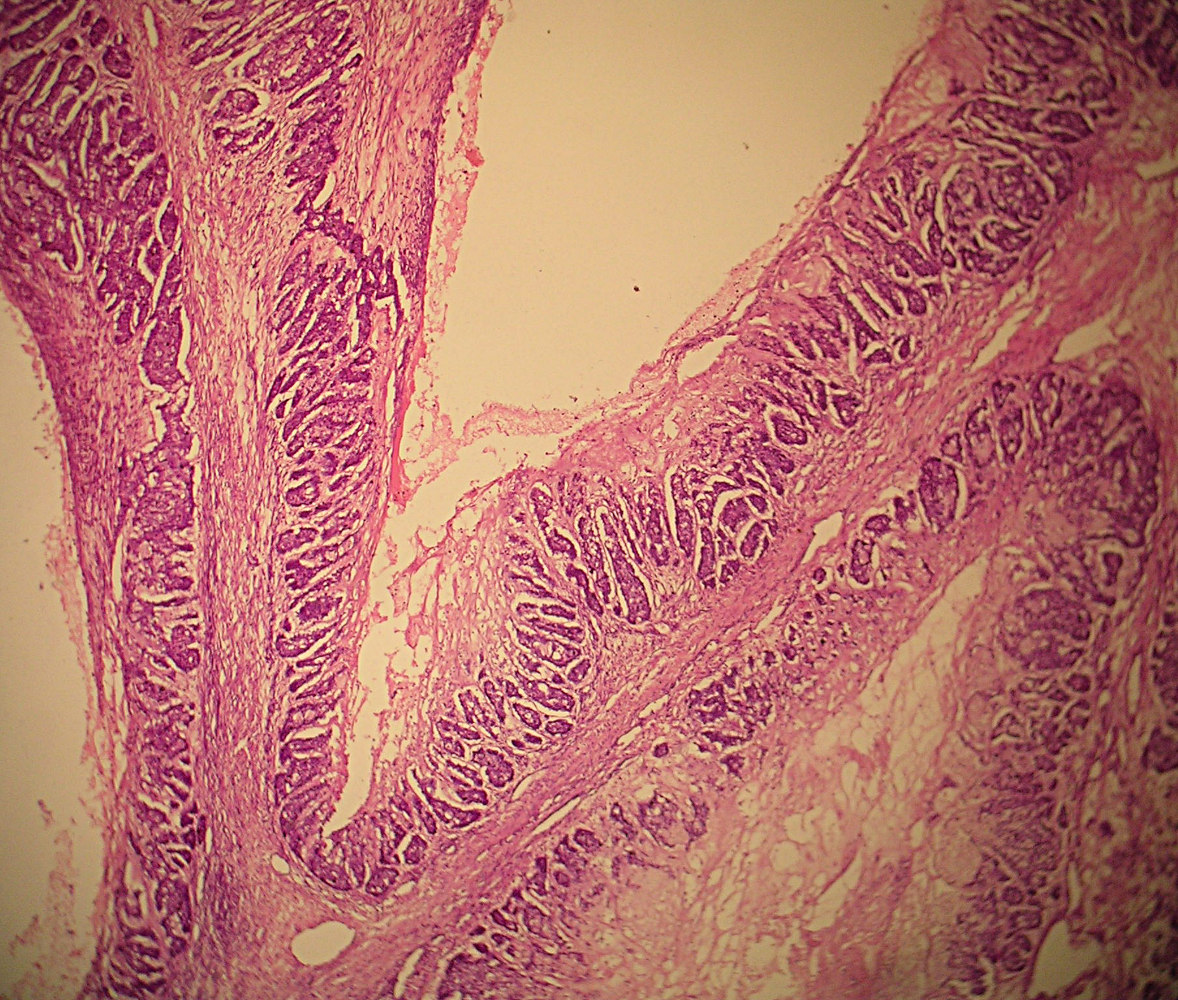
AFIP images

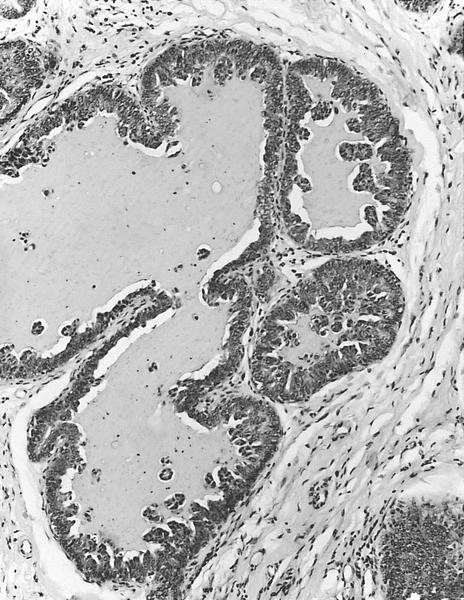
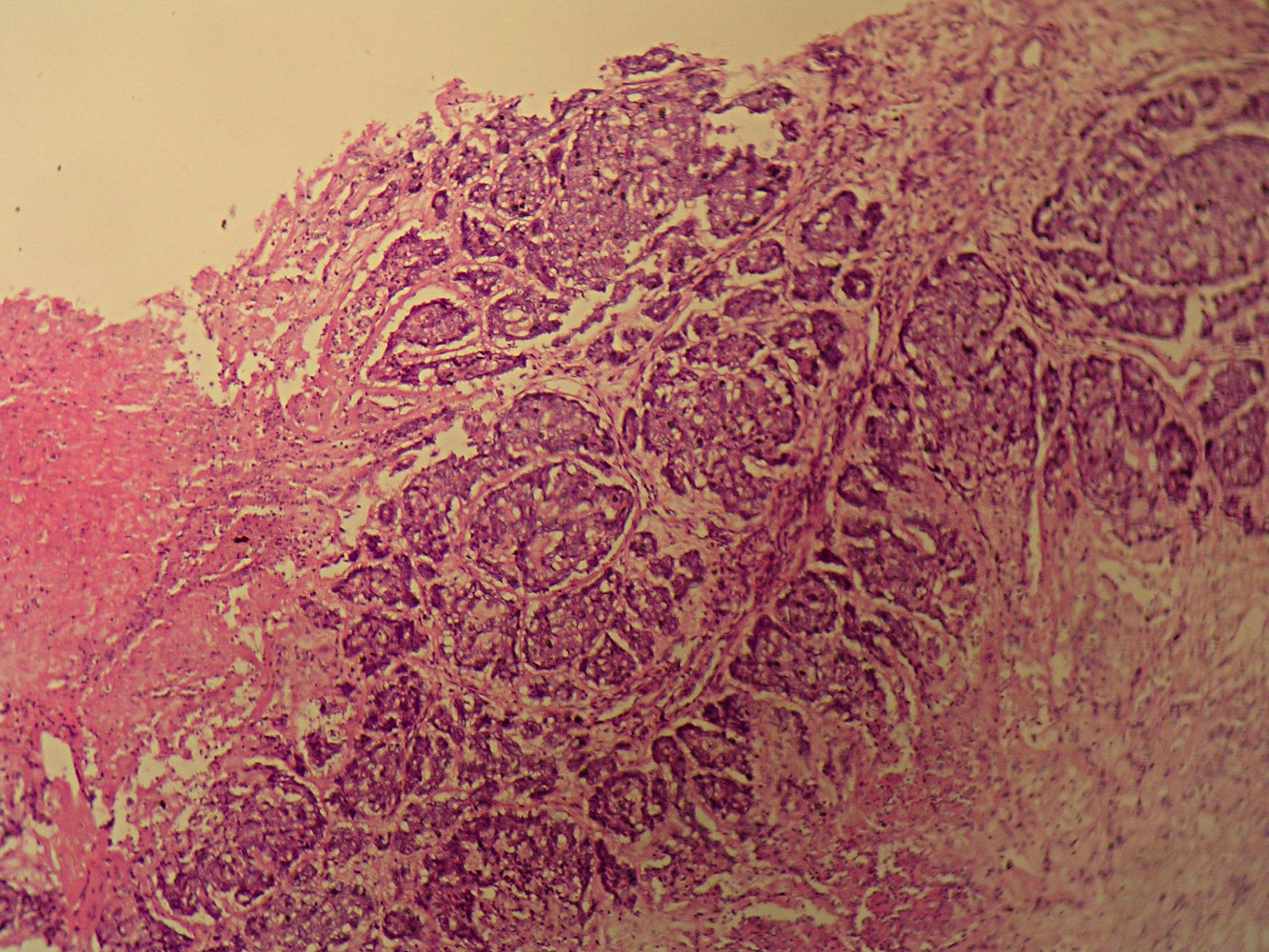
Associated micropapillary DCIS with no
evident secretion in tumor cells, which have
a hobnail appearance, nuclei are relatively
clear with small, discrete nucleoli
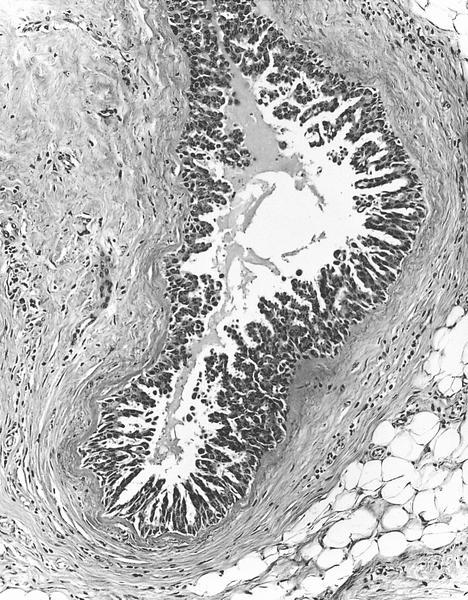
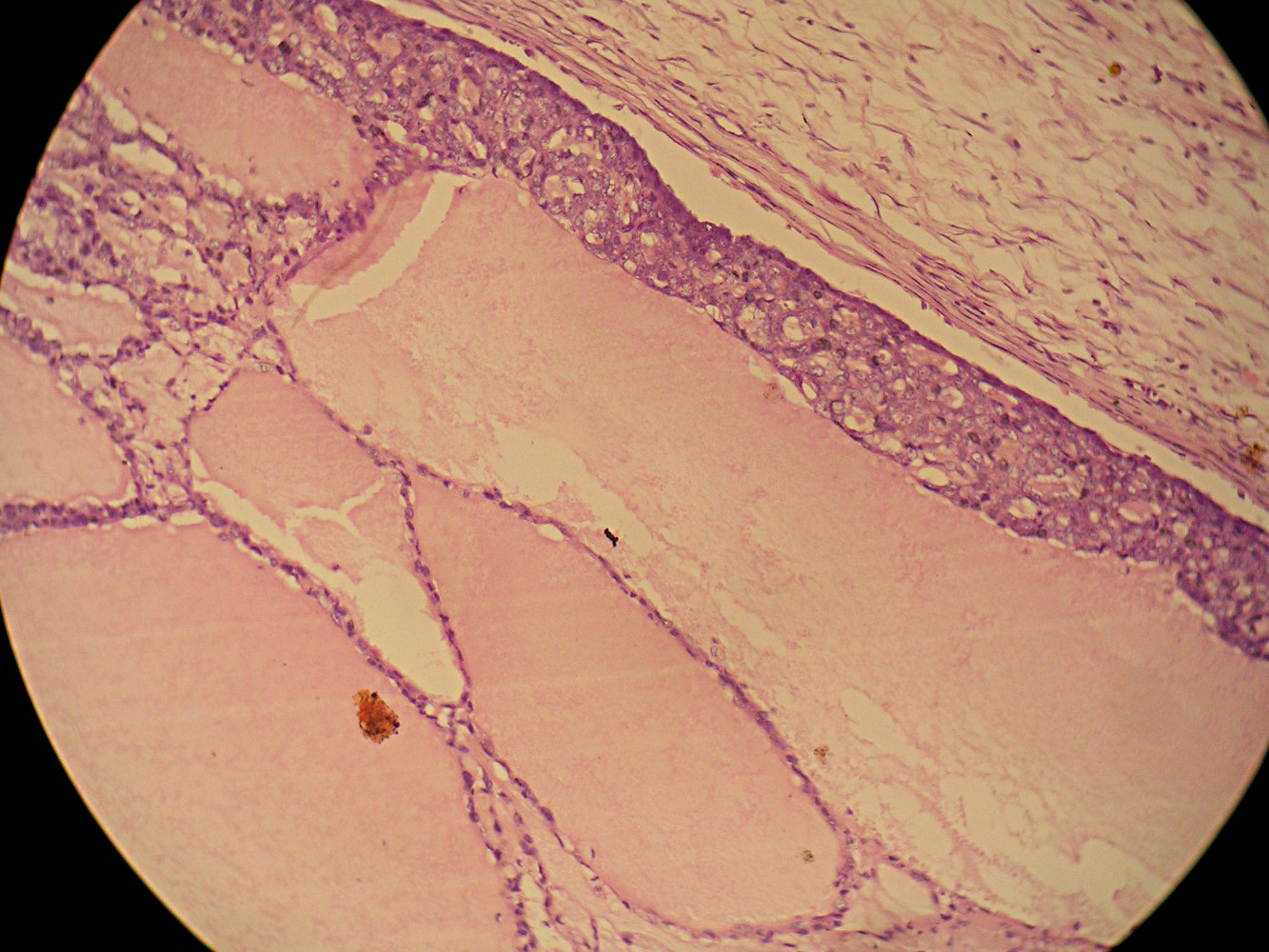
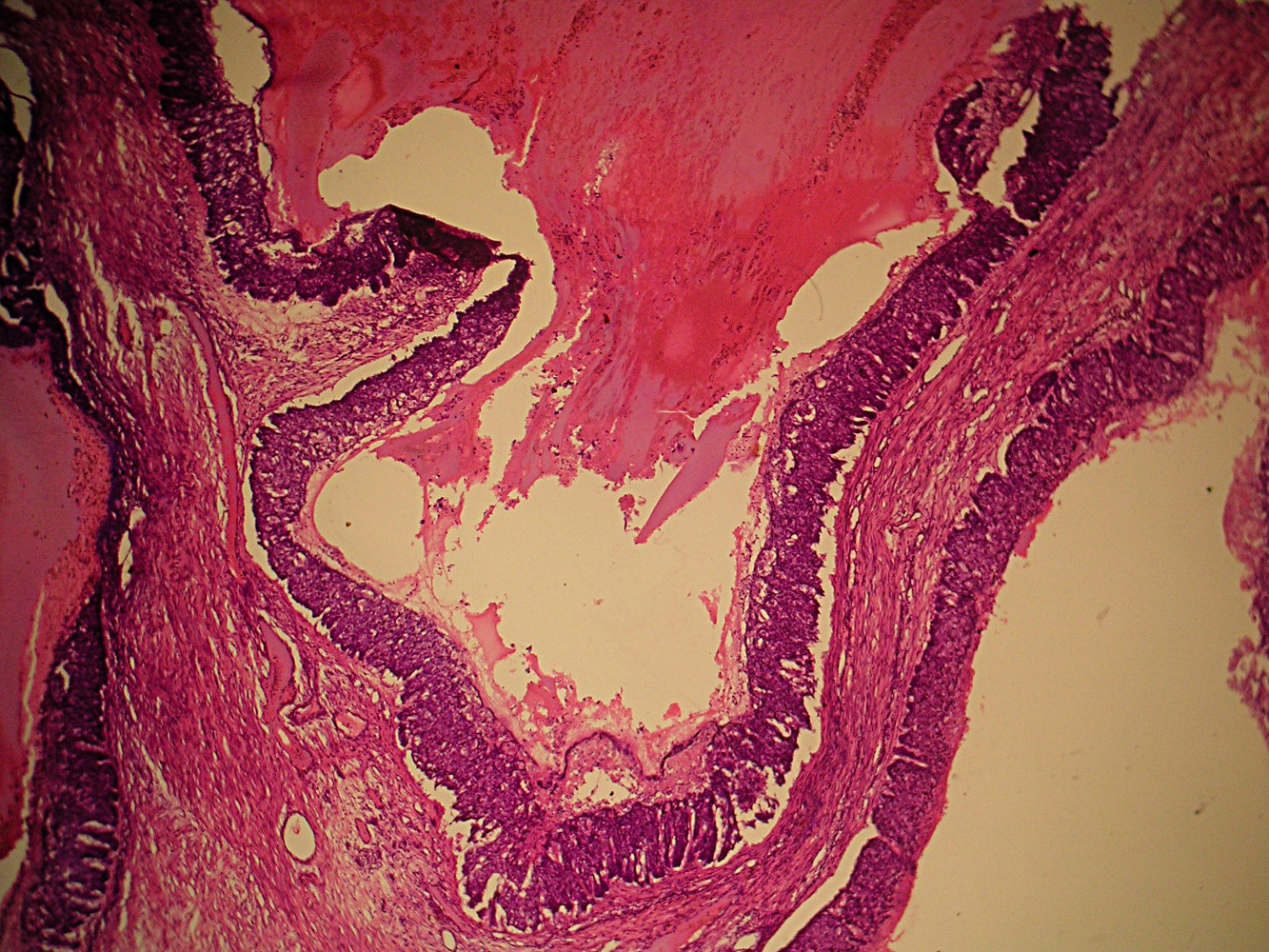
Cysts lined by flat cuboidal epithelium contain
homogeneous secretions, these cysts are
nonspecific - they can be found in cystic
hypersecretory hyperplasia or carcinoma

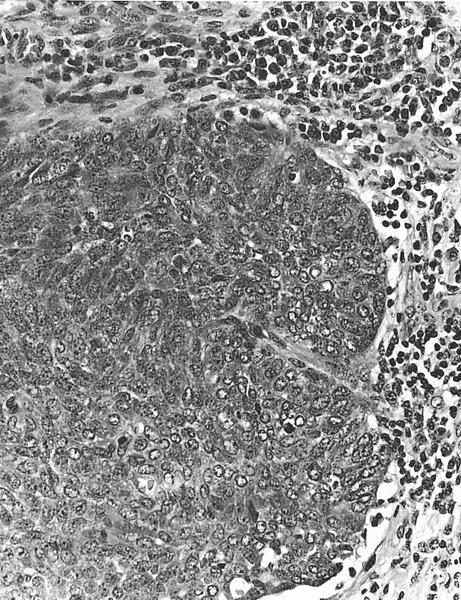
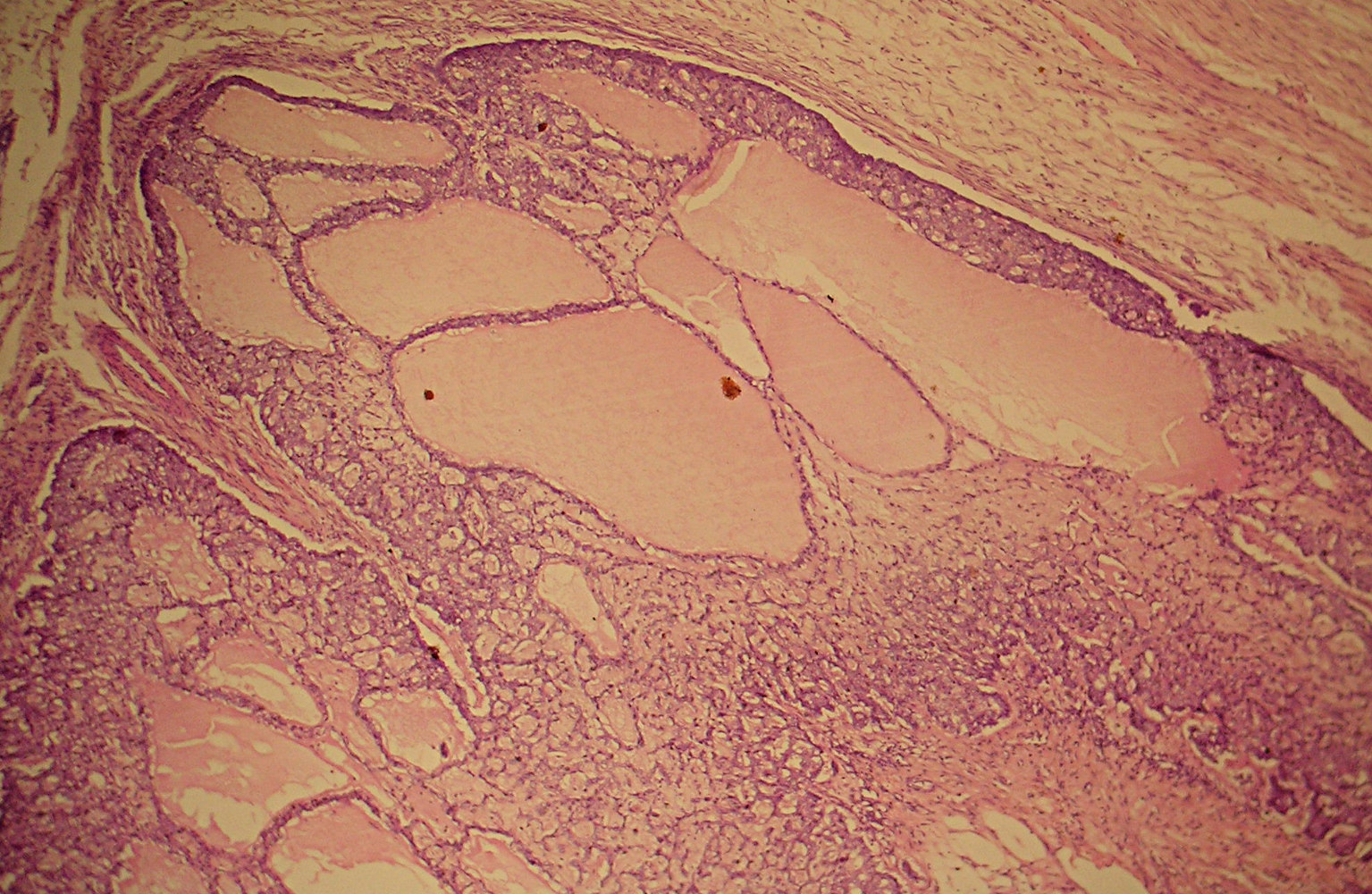
Note transition in cyst epithelium with plaque of tumor cells
in bottom half, micropapillary pattern is obscured where carcinoma
nearly fills ducts, but traces of retracted secretion remain
(arrows), clear nuclei are also evident, even at this magnification
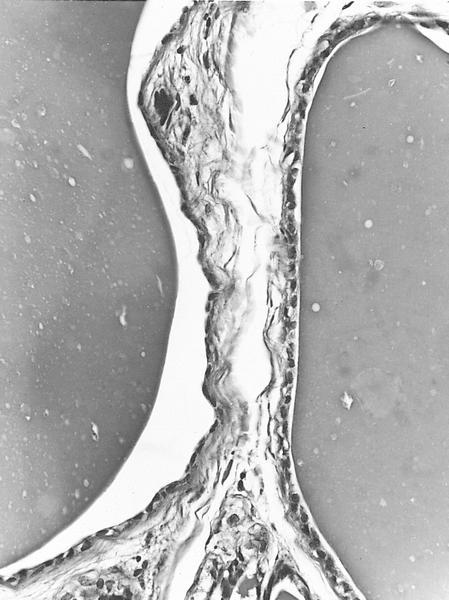
Contributed by Dr. Okechukwu C. Okafor
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
- Orange to grayish green colloid-like background with cracking artifact (Pap stain), clusters of malignant cells
- Also histiocytes and apocrine cells (Acta Cytol 1999;43:273, Acta Cytol 1997;41:892)
Positive stains
- Androgen receptors, HER2 (Ceska Gynekol 2005;70:73)
- Variable p53, ER and PR (Histopathology 2005;46:43)
Differential diagnosis
- Secretory carcinoma: predominantly microcysts, t(12;15)(p13;q25) in most cases
- Mucinous / colloid carcinoma: extracellular mucin, not intracystic secretions
- Cystic hypersecretory hyperplasia: no invasion present (Cancer 1988;61:1611)