Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Podoll MB, Reisenbichler ES. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantlobularpleomorphic.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Cytologic variant of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)
Essential features
- Aggressive variant which accounts for approximately 10% of ILC
- May show focal areas of classical ILC
Terminology
- Predominant cytologic features determine the histologic type of ILC
Epidemiology
- ILC are more common in older women (mean age 57, range 24 - 92) and very rare in men
- When they do occur in men, it is often in BRCA2 carriers
Etiology
- CDH1 germline mutation is seen in many ILC tumors, resulting in the loss of E-cadherin gene expression in approximately 85% of ILC
Clinical features
- Most tumors form mass-like lesions or result in architectural distortion
- Presents at more advanced stage than classic lobular carcinoma (J Surg Oncol 2008;98:314)
- Traditionally considered to have aggressive clinical course (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1650) but see Ann Diagn Pathol 2012;16:185
- Poorer clinical outcome: older patients, negative hormonal receptor status
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is often made on core needle biopsy
- Histologic tumor grade is assigned following the Nottingham grading system
- Reporting according to College of American Pathologists (CAP) invasive breast cancer protocol
Radiology description
- Tumors are most commonly detected as spiculated mass lesions on mammography
- Use of magnetic resonance imaging can aid in the detection of multicentric and contralateral lesions
Prognostic factors
- Factors which result in worse prognosis include high histologic grade (particularly high mitotic scores) and negative hormone receptor status
- Although the prognosis is typically worse for this variant versus the classic type ILC, it is thought to be more related to tumor grade versus variant type
Case reports
- 48 year old with pancreatic metastasis (Diagn Pathol 2017;12:52)
- 49 year old woman with vertebral metastasis (Spine J 2016;16:e303)
- 89 year old woman (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:434)
- Periocular breast carcinoma metastasis (Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2017;33:361)
Treatment
- Similar to that of invasive ductal carcinoma and depends on the tumor pathologic stage and hormone receptor status
Gross description
- Spiculated mass with ill defined margins; often no mass because of diffuse growth pattern
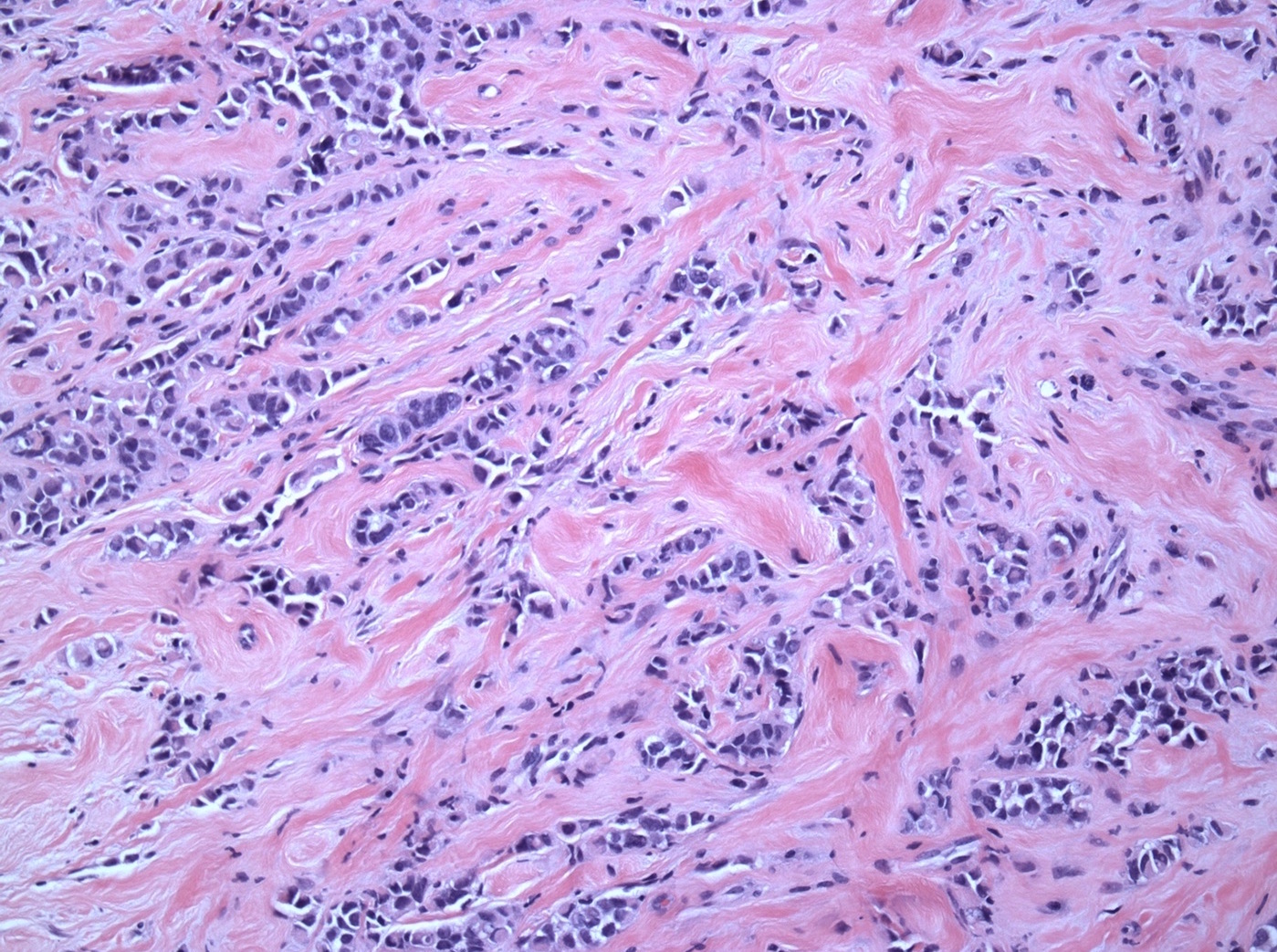
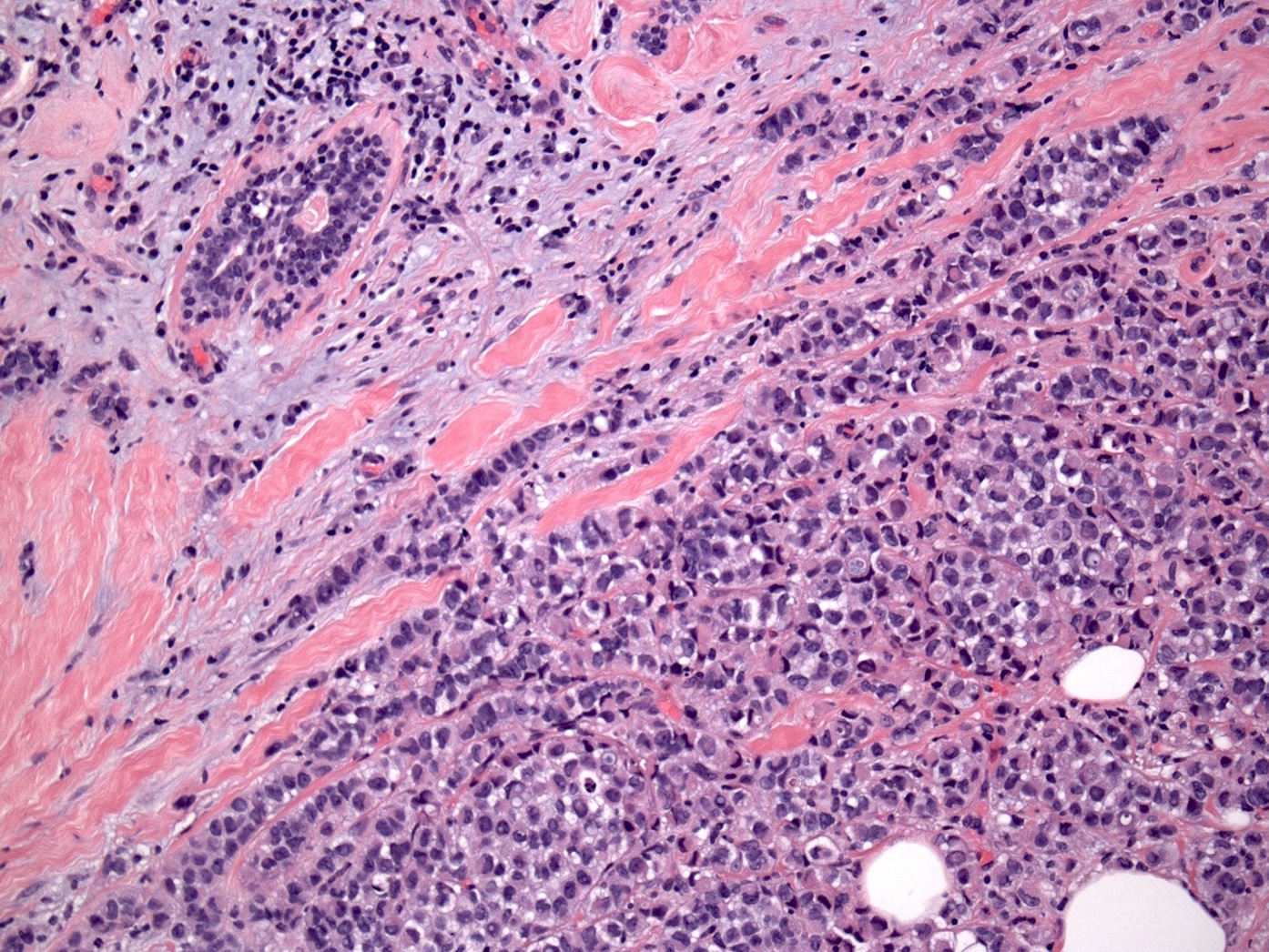
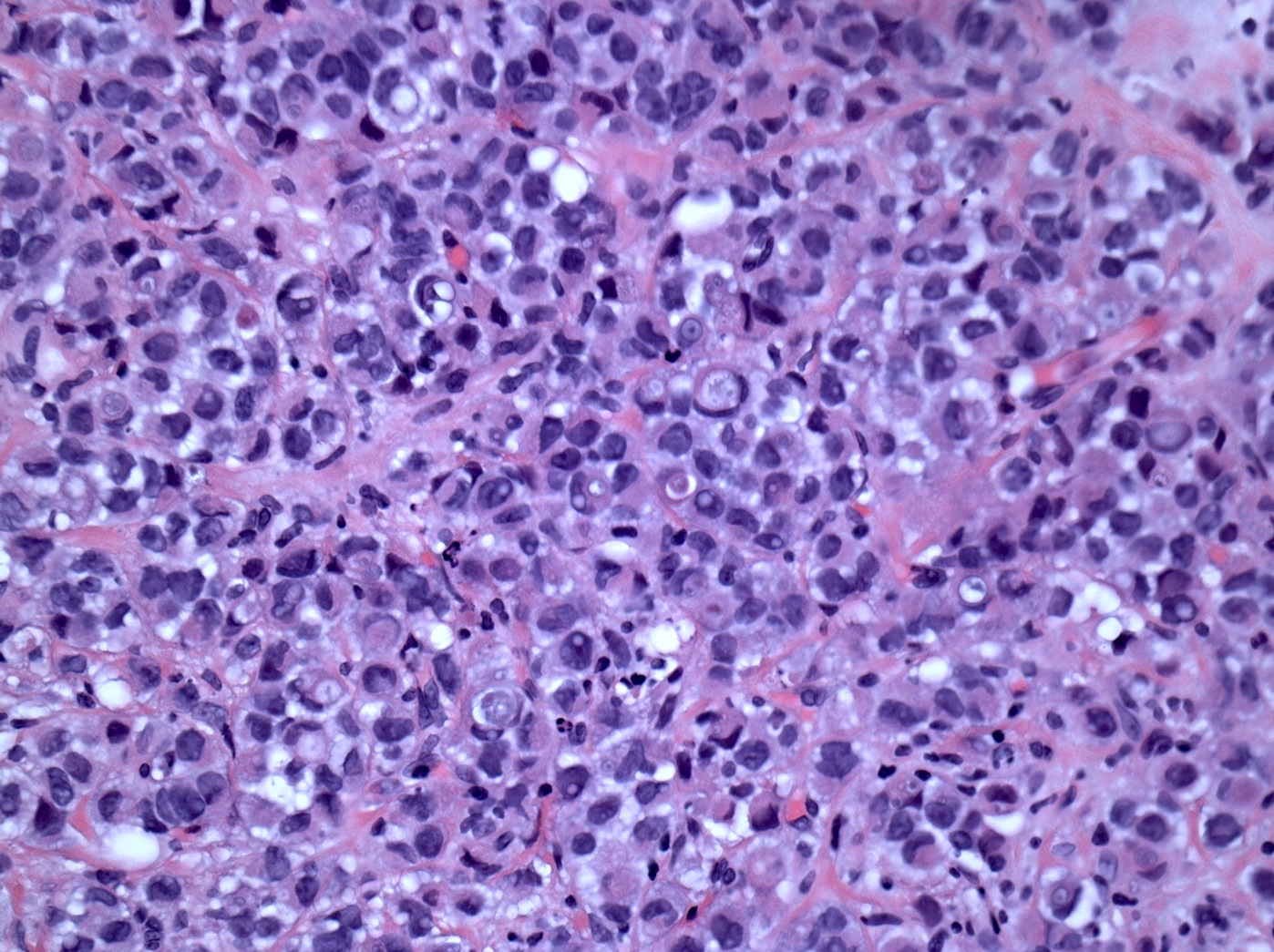
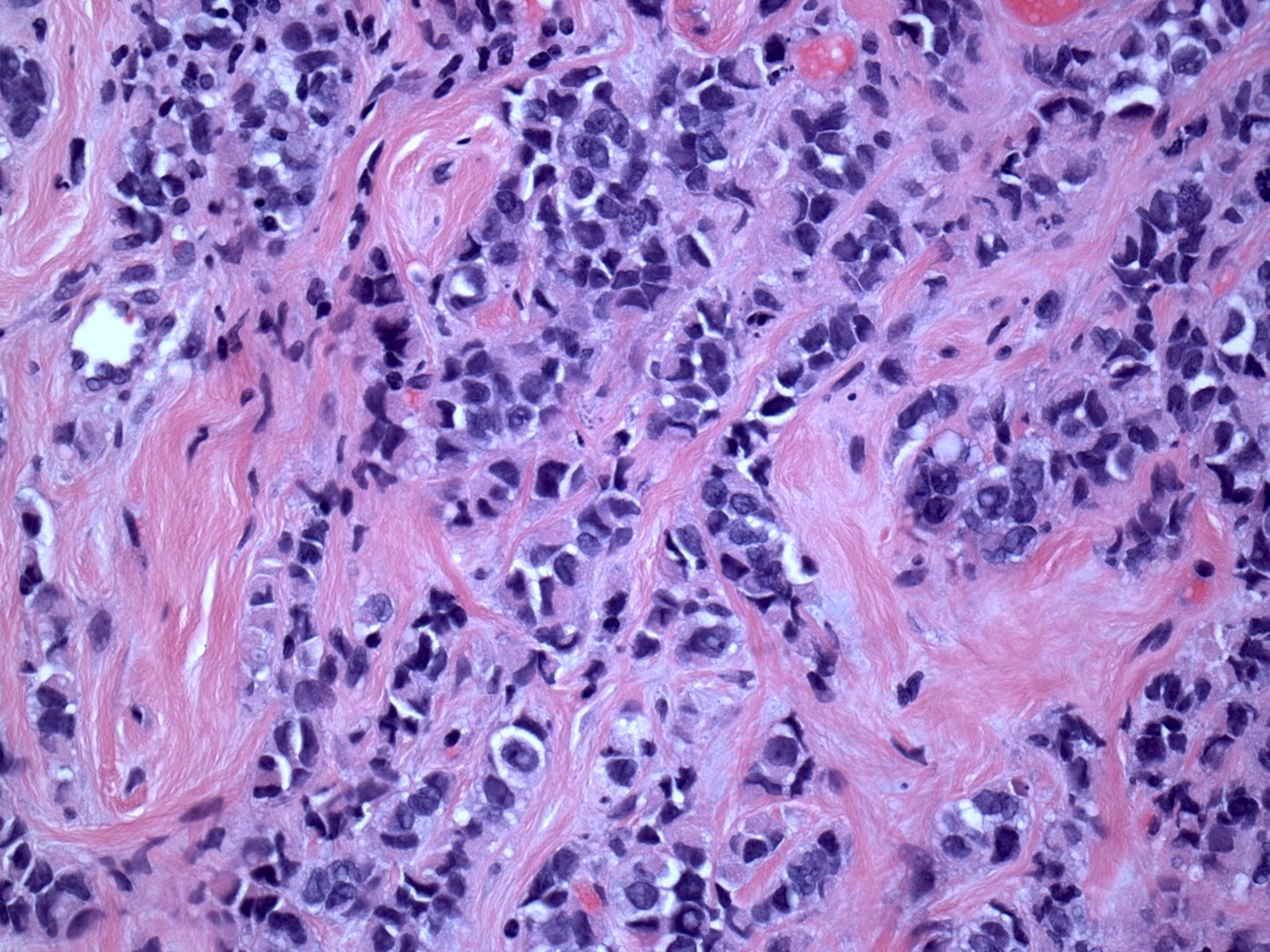
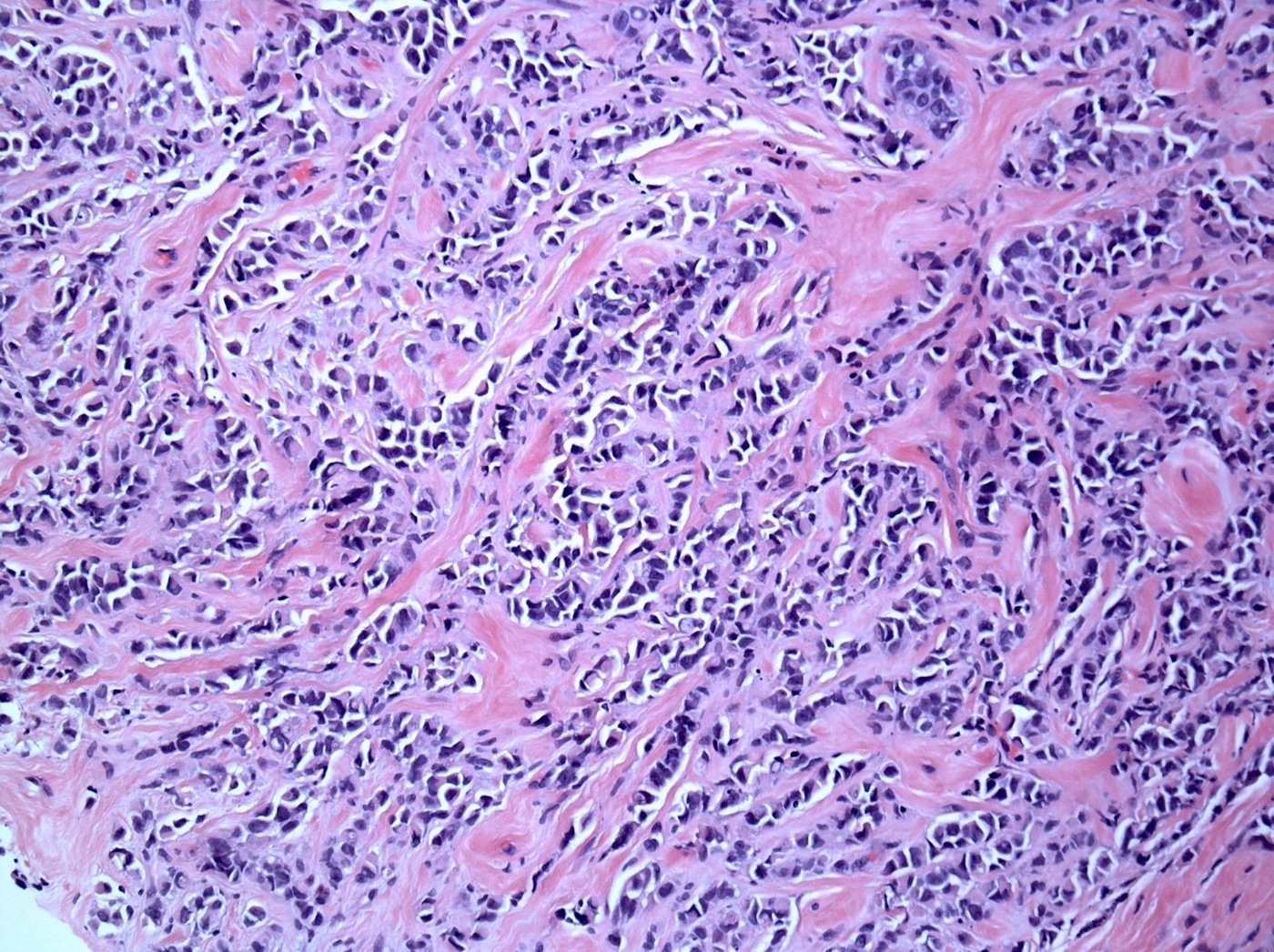
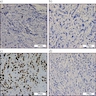
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Moderately to poorly differentiated carcinomas
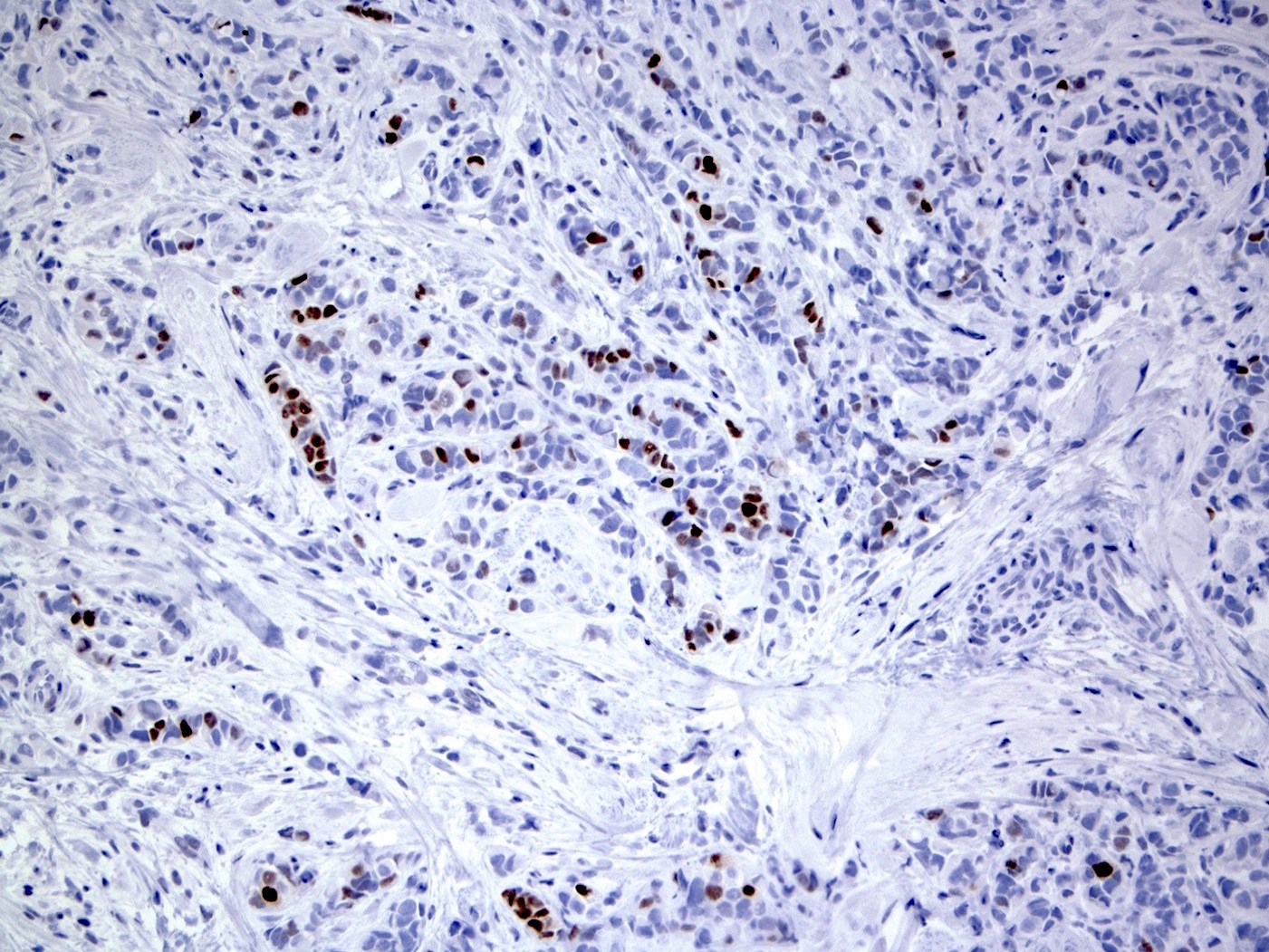
- Multifocal nodular aggregates of pleomorphic, high grade tumor cells with grade 2 - 3 nuclei which may contain prominent nucleoli
- Typical single file pattern or targetoid growth in a background of dense fibrotic breast parenchyma
- Distinctive cytologic cellular features with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (may look apocrine), signet ring and plasmacytoid cells
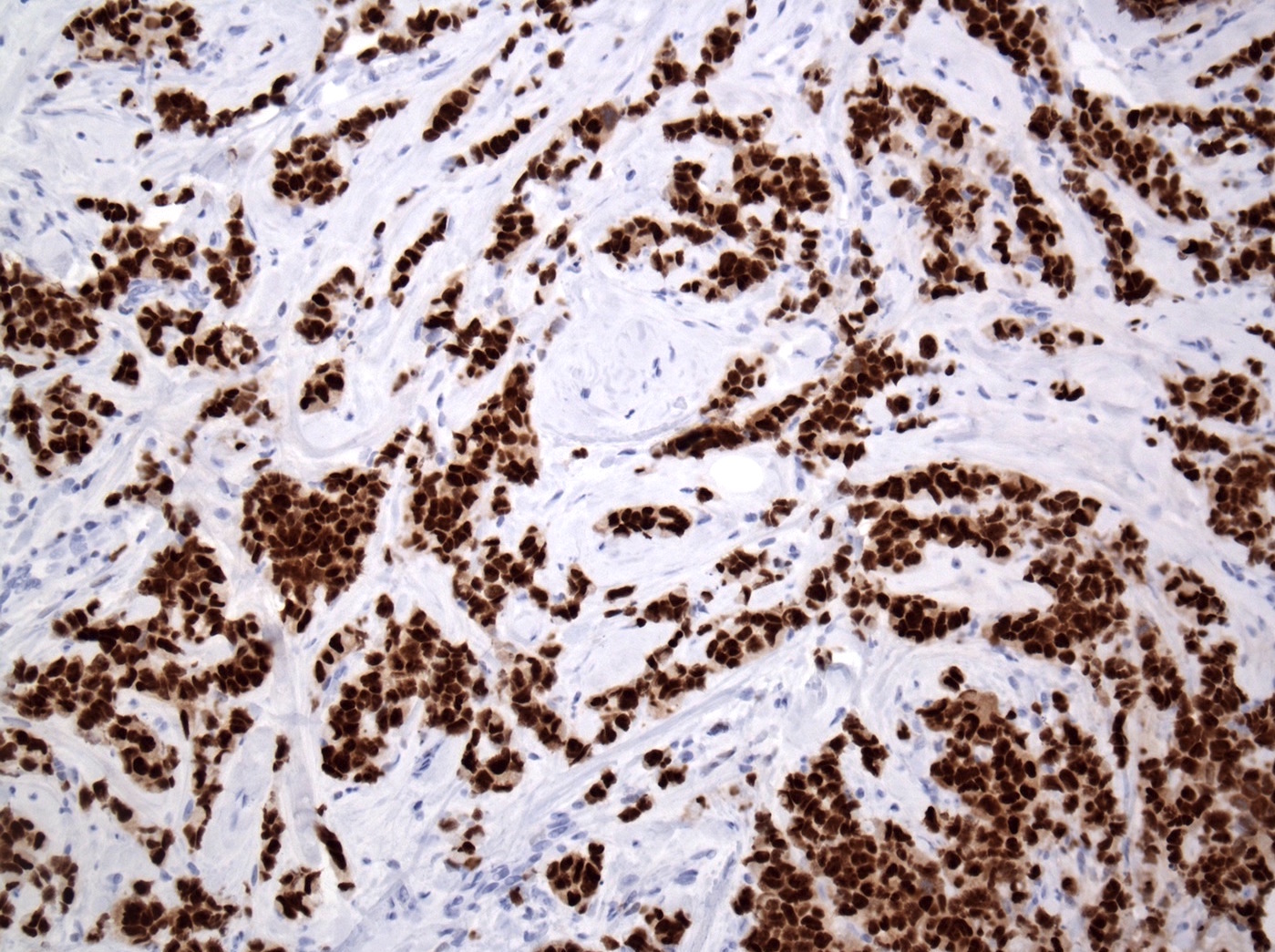
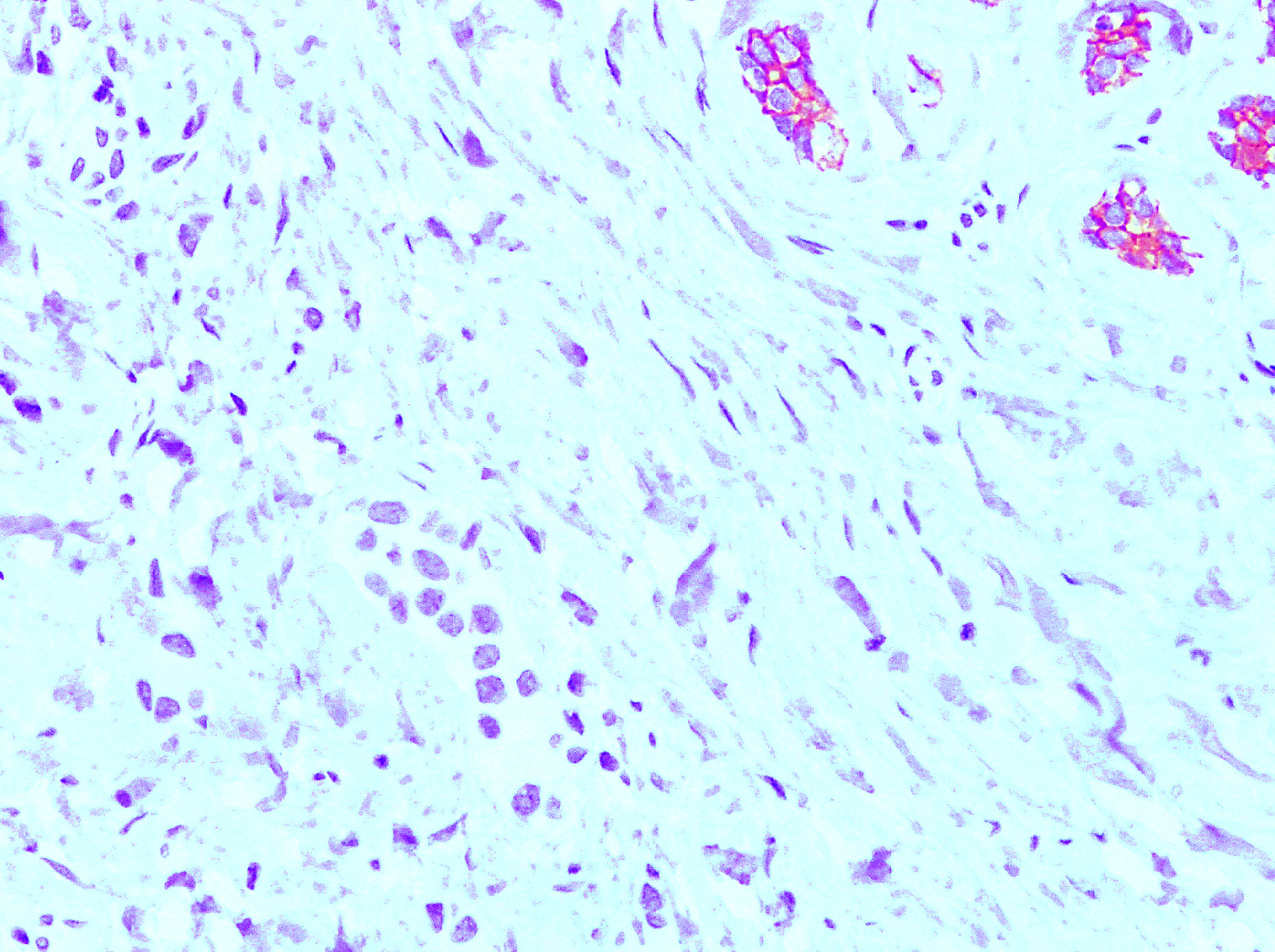
- Commonly positive for apocrine marker GCDFP-15
- Prognosis is related to the high tumor grade
Microscopic (histologic) images
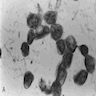
Cytology description
- More cellular than classic lobular, large tumor cells with single filing, tumor cells have cytoplasmic vacuoles and pleomorphic nuclei (Cancer 1997;81:29)
- May have apocrine features and resemble atypical mesothelial cells (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:657)
- Ductal lavage: similar features, although less striking, including epithelial cells in small clusters, single-file or isolated; also nuclear atypia, cytoplasmic vacuoles and signet ring features (Acta Cytol 2008;52:207)
Positive stains
Negative stains
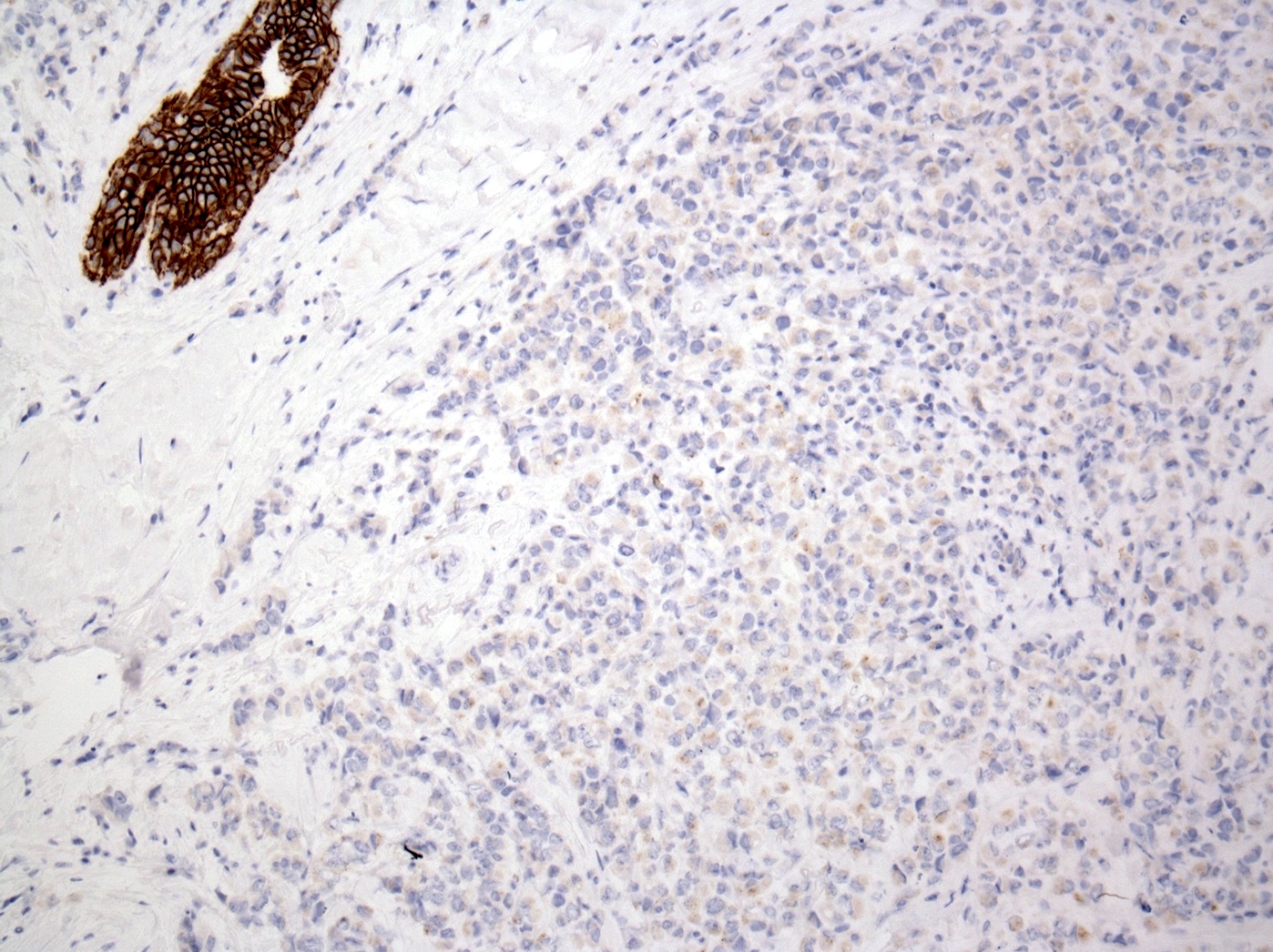
- E-cadherin (Mod Pathol 2003;16:674), beta-catenin (membrane staining is absent, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2007;15:260)
- 13% are triple negative (Histopathology 2012;61:365)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Resembles infiltrating lobular carcinoma more than infiltrative ductal carcinoma (J Pathol 2008;215:231)
- Frequent gains on 1q and 16p, losses on 11q and 16q and genomic amplifications of 8q24, 11q13, 12q13, 17q12 and 20q13 (Future Oncol 2009;5:233)
- More frequent p53 mutations than classic lobular (Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2012;35:111)
Differential diagnosis
- Invasive ductal carcinoma single cell pattern of infiltration in ILC; can be difficult to recognize particularly at metastatic sites
- Lymphoma: may involve breast as primary site but is not seen associated with LCIS Immunohistochemical studies for cytokeratin and lymphoid markers can aid in the diagnosis
- Metastatic melanoma: one of the most common metastasis to the breast; immunohistochemical studies for cytokeratin and melanoma markers can aid in the diagnosis
- Chemotherapy or radiation treatment effect
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following is true of pleomorphic variant of invasive lobular carcinoma?
- Are usually hormone receptor negative
- Do not show HER2 overexpression
- Frequency of p53 expression is similar to that of classic ILC
- The aggressive nature of these tumors is reflected by the pleomorphic variant designation
- The high histologic grade contributes to the poor patient outcomes
Board review style answer #1
E. The aggressive nature of the pleomorphic variant of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and poorer outcomes are related to the high histologic grade of this variant, rather than the pleomorphic designation itself. While these tumors may be ER and PR negative in approximately 5 - 10% of cases, the majority are hormone receptor positive. HER2 expression can be seen in approximately 20% of cases. In addition, the pleomorphic variant of ILC more commonly shows p53 expression when compared to the classic type ILC.
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma