Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Negative stains | Additional referencesCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Microinvasive. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantmicroinvasion.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Dominant lesion is not invasive, but there are 1+ separate small, microscopic foci of infiltration, each 1 mm or less in size
Terminology
- “Minimal breast carcinoma” includes microinvasive carcinoma and DCIS
- Can confirm using myoepithelial stains (myoepithelial layer is not intact) and keratin (to observe infiltrative growth)
- Diagnosis requires certainty of invasion; if doubt remains after recuts and immunostains, call DCIS or suspicious
Epidemiology
- Mean age 61 years
Clinical features
- Less than 1% of all breast cancers
- Usually detected by mammography due to abnormal calcifications in associated DCIS
- 72% associated with comedo DCIS, 89% with high nuclear grade and 89% with necrosis
- Sentinel lymph node dissection may be appropriate, although axillary nodal metastases occur in less than 10% (Breast J 2008;14:335, Breast 2008;17:395); controversial whether to perform complete axillary dissection if positive sentinel node (yes - Breast 2007;16:146, no - Am J Surg 2007;194:845)
- Commonly misdiagnosed, as true diagnosis is usually DCIS or T1a carcinoma (Cancer 2000;88:1403)
- In breast core needle biopsies, invasive carcinomas 1 mm or less are rare, are associated with DCIS and ADH, and often with large invasive foci at excision (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:996)
- Report number of foci of invasion, size of largest focus
Treatment
- Cure rate is close to 100% with surgical excision (Ann Oncol 2004;15:1633)
- Prognosis may depend on features of DCIS (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:422)
- Natural history closely resembles that of DCIS; thus, microinvasion alone should not be the sole criterion for more aggressive treatment (Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012;82:7)
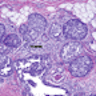
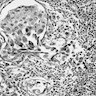
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Usually ductal, rarely tubular or lobular morphology
- Nodules of invading neoplastic cells in periductal or perilobular stroma, none exceeding 1.0 mm
- Usually arises in background of high grade DCIS; stromal microinvasion typically associated with fibroblast proliferation, collagenization and focal inflammation
- False positives: lobular cancerization, radial scar, sclerosing adenosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001;125:1259)
- False negatives: masking of invasion by inflammatory cells or histiocytes; use cytokeratin to highlight tumor cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
- Myoepithelial layer is not intact in invasive component (detected with smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, smooth muscle actin, calponin, p63)
Additional references